5 STEPS TO A 5: 500 AP Chemistry Questions to Know by Test Day! (2012)
Chapter 4. Solutions (Questions 151–180)
151. A solution is prepared by dissolving a nonvolatile solute in a pure solvent. Compared to the pure solvent, the solution
(A) has a higher normal boiling point.
(B) has a higher freezing point.
(C) has a higher vapor pressure.
(D) has less osmotic pressure.
(E) has the same vapor pressure, boiling point, and freezing point because the solute is nonvolatile.
152. A solution of NaCl is heated from 25°C to 75°C. True statements regarding this solution include which of the following?
I. The molality of the solution did not change.
II. The molarity of the solution did not change.
III. The density of the solution did not change.
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and II only
(E) II and III only
153. Approximately what mass of CuSO4·5H2O (250 g mol−1) is needed to prepare 125 mL of a 0.20-M copper (II) sulfate solution?
(A) 2.0 g
(B) 2.5 g
(C) 6.2 g
(D) 12.5 g
(E) 25.0 g
154. What volume of distilled water should be added to 20 mL of 5 M HCl(aq) to prepare a 0.8-M solution?
(A) 100 mL
(B) 105 mL
(C) 125 mL
(D) 140 mL
(E) 200 mL
155. What is the final concentration of Pb2+ ions when a 100 mL 0.20 M Pb(NO3)2 solution is mixed with a 100 mL 0.30 M NaCl solution?
(A) 0.005 M
(B) 0.010 M
(C) 0.015 M
(D) 0.020 M
(E) 0.025 M
156. A 0.2-M solution of K2CO3 is a better conductor of electricity than a 0.2-M solution of KBr. Which of the following best explains this observation?
(A) K2CO3 is more soluble than KBr.
(B) K2CO3 has more atoms than KBr.
(C) K2CO3 contains the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion.
(D) KBr has a higher molar mass than K2CO3.
(E) KBr dissociates into fewer ions than K2CO3.
157. An aqueous solution that is 66 percent C2H4O (44 g mol−1) by mass has a mole fraction of ethanol closest to:
(A) 0.29
(B) 0.44
(C) 0.50
(D) 0.66
(E) 1
158. A solution contains 144 g H2O and 92 g of ethanol (CH3CH2OH, molar mass 46 g mol−1). The mole fraction of ethanol is closest to:
(A) 20 percent
(B) 25 percent
(C) 40 percent
(D) 64 percent
(E) 80 percent
159. What is the molality of a solution that has 29 g NaCl dissolved in 200 g of water?
(A) 0.0025 m
(B) 0.025 m
(C) 0.15 m
(D) 2.5 m
(E) 2.9 m
160. Salts containing which of the following ions are insoluble in cold water?
(A) Nitrate
(B) Ammonium
(C) Sodium
(D) Phosphate
(E) Acetate
161. BaF2 is sparingly soluble in water. The addition of dilute HF to a saturated BaF2 solution at equilibrium is expected to
(A) raise the pH.
(B) react with BaF2 to produce H2 gas.
(C) increase the solubility of BaF2.
(D) precipitate out more BaF2.
(E) produce no change in the solution.
Questions 162–165 refer to the following solution.
Ethanol, CH3CH2OH(l), and water, H2O(l), are mixed in equal volumes at 25°C and 1 atm.
162. Which of the following include endothermic processes regarding the preparation of the solution?
I. Ethanol molecules move away from other ethanol molecules as they move into solution.
II. Water molecules move away from other water molecules as they move into solution.
III. Ethanol molecules form hydrogen bonds with water molecules as they move into solution.
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and II only
(E) I, II, and III
163. What is the mole fraction of ethanol in the solution? (The density of ethanol and water at 25°C are 0.79 g mL−1 and 1.0 g mL−1, respectively.)
(A) 0.24
(B) 0.33
(C) 0.40
(D) 0.50
(E) 0.72
164. Mixing different proportions of ethanol and water produce different enthalpy values. At low concentrations of water or ethanol, solvation is exothermic, but for mixing equal amounts, it is endothermic. Which of the following is a logical interpretation of this observation?
(A) The ratio of hydrogen bond breakages (between molecules of the pure liquids), and the formation of hydrogen bonds (between the two different molecules when combined in solution) varies with the ratios in which the two liquids are combined.
(B) At low concentrations of ethanol or water, fewer hydrogen bonds are formed than when mixing them in equal amounts.
(C) Mixing liquids that form the same type of intermolecular forces undergo no enthalpy changes when combined in equimolar amounts.
(D) Ethanol is capable of forming more hydrogen bonds than water.
(E) Water is capable of forming more hydrogen bonds than ethanol.
165. The intermolecular forces between ethanol and water include:
I. Hydrogen bonding
II. Dipole–dipole attraction
III. London dispersion forces
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and III only
(E) I, II, and III
166. A 1.0-L solution contains 0.1 mol KCl, 0.1 mol CaCl2, and 0.1 mol AlCl3. What is the minimum number of moles of Pb(NO3)2 that must be added to precipitate all of the Cl− ions as PbCl2?
(A) 0.1 mol
(B) 0.2 mol
(C) 0.3 mol
(D) 0.4 mol
(E) 0.6 mol
167. Under which of the following sets of conditions would the most N2(g) be dissolved in H2O(l)?

168. Sodium chloride is least soluble in which of the following liquids?
(A) CH3COOH
(B) CH3OH
(C) CCl4
(D) H2O
(E) HBr
169. The largest percentage of which of the following compounds can be collected by cooling a saturated solution of that compound from 90°C to 20°C?
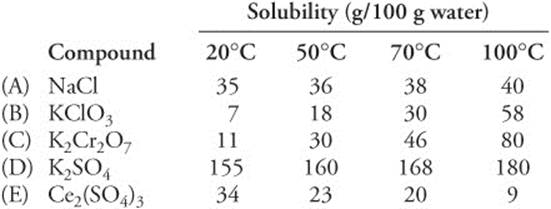
Questions 170 and 171 refer to the following data. Solutions of the five compounds in the table were mixed with equimolar solutions of one of two compounds, X or Y, also in the list. Compounds of the same identity were not combined. Assume all concentrations are 1.0 M.

170. The identity of substance X
171. The identity of substance Y
172. A sample of 60 mL of 0.4 M NaOH is added to 40 mL of 0.6 M Ba(OH)2. What is the hydroxide concentration [OH–] of the final solution?
(A) 0.24 M
(B) 0.40 M
(C) 0.48 M
(D) 0.50 M
(E) 0.72 M
173. A student mixes equal volumes of 1.0-M solutions of copper (II) chloride and magnesium sulfate, and no precipitate is observed. When the student mixes equal volumes of 1.0-M solutions of aluminum sulfate and copper (II) fluoride, a precipitate is observed. Which of the following is the formula of the precipitate?
(A) CuF2
(B) CuSO4
(C) AlF3
(D) AlCl3
(E) AlSO4
174. Which of the following pairs of liquids forms the most ideal solution when mixed in equal volumes at 25°C?
(A) HCl and H2O
(B) CH3CH2OH and H2O
(C) CH3CH2OH and C6H14
(D) C6H14 and C8H18
(E) C8H18 and H2O
175. Suppose a sample of a homogenous solution contains 10 percent hexane (molar mass 86 g mol−1) by mass. Which of the following statements is true regarding the minimum information needed to calculate the molarity of hexane in this solution?
(A) The temperature of the solution
(B) The total mass of the solution from which the sample is taken
(C) The mass and volume of a sample of the solution
(D) The volume of the sample
(E) The mass of the sample
176. A 360-mg sample of glucose, C6H12O6 (molar mass 180 g mol−1), is dissolved in enough water to produce a 200-mL solution. What is the molarity of a 10-mL sample of this solution?
(A) 0.01 M
(B) 0.10 M
(C) 1.0 M
(D) 2.0 M
(E) 10.0 M
177. Which of the following aqueous solutions has the highest boiling point at 1.0 atm?
(A) 0.2 m NaCl
(B) 0.3 m CaCl2
(C) 0.4 m K3PO4
(D) 0.5 m NaNO3
(E) 0.6 m C12H22O11
178. What is the vapor pressure of a solution in which 2.00-mol propylene glycol, a nonvolatile compound, is mixed with 8.00-mol water? Assume the solution behaves ideally and is at the temperature where the vapor pressure of water is 20.0 mmHg.
(A) 4.00 mmHg
(B) 15.00 mmHg
(C) 16.00 mmHg
(D) 18.00 mmHg
(E) 20.00 mmHg
179. A dilute hydrochloric acid solution was added to a sample of an unknown solution in a lab. A white precipitate was formed, filtered from the solution, washed with hot water, and then dissolved in a solution of NH3. A few drops of K2SO4 were added to the filtrate and another white precipitate formed. What two ions were precipitated out of solution?
(A) Mg2+ and Pb2+
(B) Mg2+ and Ag+
(C) Ag+ and Ba2+
(D) Ag+ and Pb2+
(E) NH4+ and Pb2+
180. Which of the following compounds is the least soluble in water?
(A) (NH4)2CO3
(B) BaCO3
(C) Fe(NO3)3
(D) Na3(PO4)
(E) LiO