March's Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure, 7th Edition (2013)
Part I. Introduction
Chapter 4. Stereochemistry and Conformation
4.M. Stereospecific and Stereoselective Syntheses
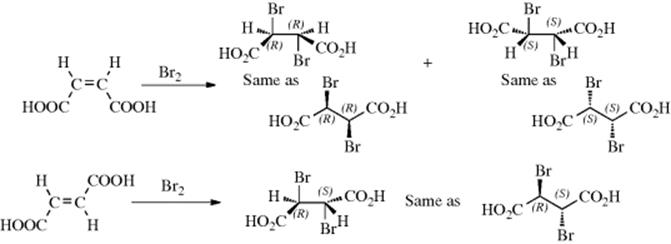
Any reaction in which only one of a set of stereoisomers is formed predominantly is called a stereoselective synthesis.268 The same term is used when a mixture of two or more stereoisomers is exclusively or predominantly formed at the expense of other stereoisomers. In a stereospecific reaction, a given isomer leads to one product while another stereoisomer leads to the opposite product. All stereospecific reactions are necessarily stereoselective, but the converse is not true. These terms are best illustrated by examples. Thus, if maleic acid treated with bromine gives the dl pair of 2,3-dibromosuccinic acid while fumaric acid gives the meso isomer (this is the case), the reaction is stereospecific as well as stereoselective because two opposite isomers give two opposite isomers, However, if both maleic and fumaric acid gave the dl pair or a mixture in which the dl pair predominated, the reaction would be stereoselective, but not stereospecific. If more or less equal amounts of dl and meso forms were produced in each case, the reaction would be nonstereoselective. A consequence of these definitions is that if a reaction is carried out on a compound that has no stereoisomers, it cannot be stereospecific, but at most stereoselective. For example, addition of bromine to methylacetylene could (and does) result in preferential formation of trans-1,2-dibromopropene, but this can be only a stereoselective, not a stereospecific reaction.