5 Steps to a 5 AP Calculus AB & BC, 2012-2013 Edition (2011)
STEP 5. Build Your Test-Taking Confidence
AP Calculus BC Practice Exam 1
ANSWER SHEET FOR MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS

Section I—Part A

Directions:
Use the answer sheet provided on the previous page. All questions are given equal weight. There is no penalty for unanswered questions. Unless otherwise indicated, the domain of a function f is the set of all real numbers. The use of a calculator is not permitted in this part of the exam
1. 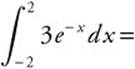
(A) − 3e−2
(B) − 3e2
(C) 6 (1 − e−2
(D) 3 (e2 − e−2)
(E) 3 (e−2 − e2)
2. If f(x) = x3 + 3x2 + cx + 4 has a horizontal tangent and a point of inflection at the same value of x, what is the value of c?
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) −1
(D) −3
(E) 3
3. Find ![]() if tan y = (x − y)2
if tan y = (x − y)2
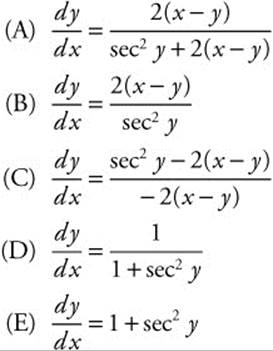
4. Find ![]() if y = 3(4 − x2).
if y = 3(4 − x2).
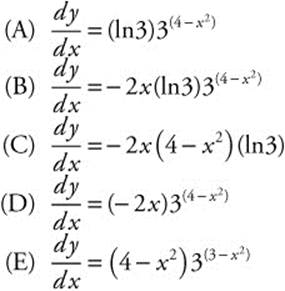
5. If x = cos t and y = sin2 t, then ![]() at
at ![]() is
is
![]()
(B) − 2
(C) 1
(D) 0
(D) − 1
6. If g(x) is continuous for all real values of x, then 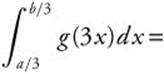
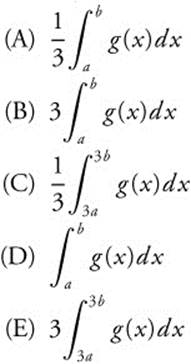
7. The area enclosed by the parabola y = x − x2, the line x = 1, and the x-axis is revolved about the x-axis. The volume of the resulting solid is
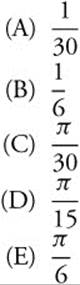
8. ![]()
![]()
(B) 1
(C) 0
(D) 4
![]()
9. The function f(x) is defined on the interval (− 2, 2) such that for all x, − 2 < x < 2, f′(x) > 0 and f″ (x) > 0. Which of the following could be the graph of f(x) on (−2, 2)?
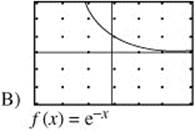
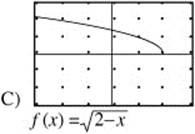
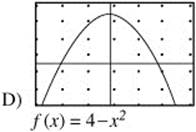
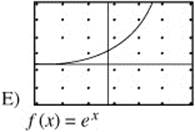
10. Which of the following series are convergent?
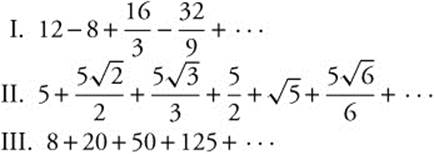
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and II
(E) II and III
11. Find the values of a and b that assure that
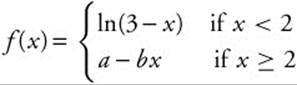
is differentiable at x = 2.
(A) a = 3, b = 1
(B) a = 1, b = 2
(C) a = 2, b = 1
(D) a = − 2, b = − 1
(E) a = 1, b = 3
12. A particle moves in the xy-plane so that its velocity vector at time t is v(t) = ⟨2 − 3t2, π sin (π t)⟩ and the particle’s position vector at time t = 2 is ⟨4, 3⟩. What is the position vector of the particle when t = 3?
(A) ⟨− 25, 0⟩
(B) ⟨− 21, 1⟩
(C) ⟨− 10, 0⟩
(D) ⟨− 13, 5⟩
(E) ⟨4, 3⟩
13. The ![]() is
is
(A) ln(x + 3)
(B) ln(x + 3)
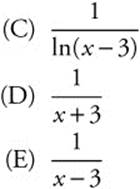
14. The area of the region enclosed by the polar curve r = 3 − sinθ is
(A) 19π
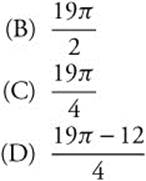
(E) 6π
15. The slope of the normal line to the graph of r = 5 + 5 sinθ at ![]() is
is
(A) 1
(B) −1
(C) 5
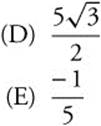
16. Use the trapezoidal method with 4 divisions to approximate the area of the region bounded by the graph of ![]() , the lines x = 1 and x = 3, and the x-axis.
, the lines x = 1 and x = 3, and the x-axis.
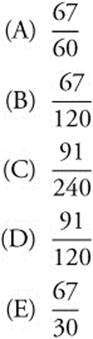
17. The shortest distance from the origin to the graph of ![]() is
is
(A) 2
(B) −2
![]()
(E) 4
18. 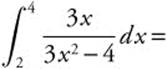
![]()
(B) [ln 18]
(C) [ln 22 − ln 4]
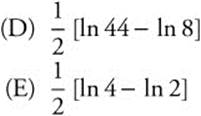
19. The graph of y = esin x has a relative minimum at
![]()
(B) x = π
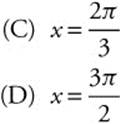
(E) x = 2π
20. Which of the following is an equation of the line tangent to the curve with parametric equations x = 3t2 − 2, y = 2t3 + 2 at the point when t = 1?
(A) y = 3x2 + 7x
(B) y = 9
(C) y = 6x − 2
(D) y = x
(E) y = x + 3
21. The series expansion for 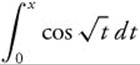 is
is
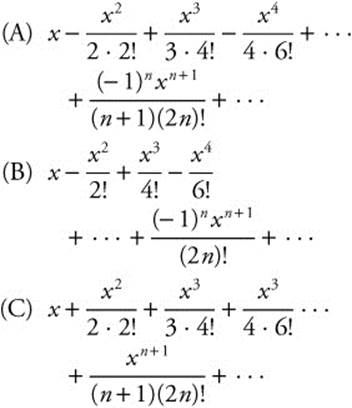
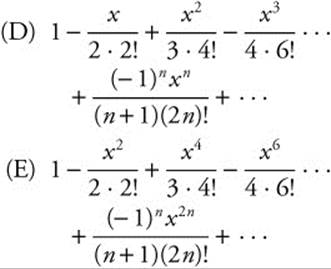
22. 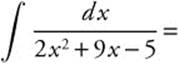
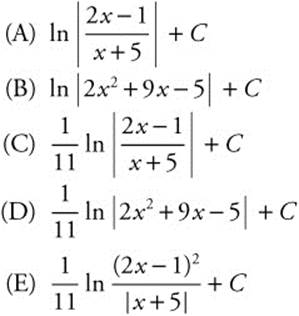
23. A solid has a circular base of radius 4. If every plane cross section perpendicular to the x-axis is a square, then the volume of the solid is
24. If a particle moves in the xy-plane on a path defined by x = sin2 t and y = cos(2t) for ![]() , then the length of the arc the particle traces out is
, then the length of the arc the particle traces out is
![]()
(B) 2
![]()
(D) 5
![]()
25. Find the interval of convergence for ![]()
(A) (0, 1)
(B) (− 1, 1)
(C) [− e, e)
(D) (− e, e)
(E) (− e, e ]
26. If n is a positive integer, then
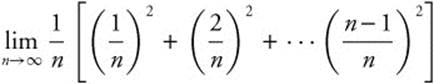
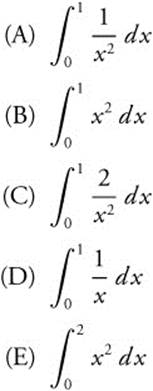
27. 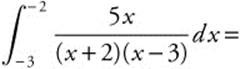
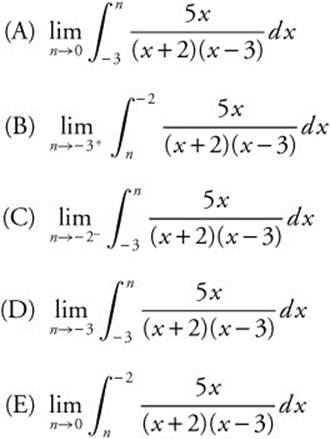
28. 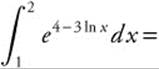
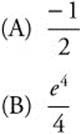
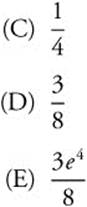
STOP. AP Calculus BC Practice Exam 1 Section I—Part A
Section I—Part B

Directions:
Use the same answer sheet from Part A. Please note that the questions begin with number 76. This is not an error. It is done to be consistent with the numbering system of the actual AP Calculus BC Exam. All questions are given equal weight. There is no penalty for unanswered questions. Unless otherwise indicated, the domain of a function f is the set of all real numbers. If the exact numerical value does not appear among the given choices, select the best approximate value. The use of a calculator is permitted in this part of the exam.
76. If ![]() then f′(2) is approximately
then f′(2) is approximately
(A) 1.110
(B) 2.245
(C) 0.101
(D) 12.107
(E) 18.161
77. 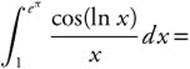
(A) −0.913
(B) −0.043
(C) −1.754
(D) 0
(E) 72.699
78. A rumor spreads through a community of 200 people at a rate modeled by ![]() . If the rumor began with two people, find the number of people who have heard the rumor after thirty days.
. If the rumor began with two people, find the number of people who have heard the rumor after thirty days.
(A) 5
(B) 32
(C) 161
(D) 199
(E) 200
79. Which best approximates ![]()
(A) −0.757
(B) 0.757
(C) −0.654
(D) 0.654
(E) 1.514
80. The area under the curve y = 3x2 − kx + 1 bounded by the lines x = 1 and x = 2 is approximately − 5.5. Find the value of k.
(A) 9
(B) 11
(C) 5.5
(D) 16.5
(E) 1
81. The rate of growth of a population is proportional to the population and increases by 23% at the end of the first 12 years. What is the constant of proportionality, correct to three decimal places?
(A) 0.230
(B) 0.023
(C) 0.017
(D) 0.019
(E) 2.760
82. 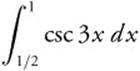
(A) − 0.285
(B) 0.04704
(C) 0.906
(D) 1.193
(E) ∞
83. Let 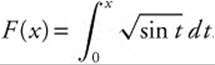 . Which of the following is the best approximation for F′(0.2)?
. Which of the following is the best approximation for F′(0.2)?
(A) 0.040
(B) 0.060
(C) 0.137
(D) 0.446
(E) 2.199
84. The velocity of a particle moving on a number line is given by v(t)= sin(t2+1), t ≥ 0. At t = 1, the position of the particle is 5. When the velocity of the particle is equal to 0 for the first time, what is the position of the particle?
(A) 5.250
(B) 4.750
(C) 3.537
(D) 1.463
(E) − 5.250
85. If y = sec2(3x), then ![]() at
at ![]() is
is

86. Find the approximate value of y when x = 3.1 if ![]() and y = 4.5 when x = 3.
and y = 4.5 when x = 3.
(A) 1.290
(B) − 9.104
![]()
![]()
(E) 4.525
87. The slope of the normal line to y = e−2x when x = 1.158 is approximately
(A) 5.068
(B) 0.864
(C) − 0.197
(D) 0.099
(E) 10.135
88. The volume of the solid generated by revolving the region bounded by y = sin x + cos x and the x-axis between x = 0 and ![]() about the x-axis is approximately
about the x-axis is approximately
(A) 1
(B) 1.071
(C) 2.071
(D) 8.076
(E) 16.153
89. The absolute minimum of f(x) = ln(3x) + cos x on the interval ![]() is approximately
is approximately
(A) 1.186 when x = 2.773.
(B) 2.773 when x = 1.186.
![]() .
.
(D) 1.243 when x = π.
(E) −1.186 when x = 2.773.
90. A particle moves along the y-axis so that its position at time t is y(t) = 5t3 − 9t2 + 2t − 1. At the moment when the particle first changes direction, the (x, y) coordinates of its position are
(A) (0, 0.124)
(B) (0.124, − 0.881)
(C) (0.124, 0)
(D) (0, − 0.881)
(E) (− 0.881, 0)
91. The area of the region enclosed by the graphs of y = cos x + 1 and y = 2 + 2x − x2 is approximately
(A) 3.002
(B) 2.424
(C) 2.705
(D) 0.094
(E) 0.009
92. The interval of convergence of the series ![]() is
is
(A) (−4, 4)
(B) (2, 4)
(C) (2, 4]
(D) [2, 4)
(E) [2, 4]
STOP. AP Calculus BC Practice Exam 1 Section I—Part B
Section II—Part A

Directions:
Show all work. You may not receive any credit for correct answers without supporting work. You may use an approved calculator to help solve a problem. However, you must clearly indicate the setup of your solution using mathematical notations and not calculator syntax. Calculators may be used to find the derivative of a function at a point, compute the numerical value of a definite integral, or solve an equation. Unless otherwise indicated, you may assume the following: (a) the numeric or algebraic answers need not be simplified; (b) your answer, if expressed in approximation, should be correct to 3 places after the decimal point; and (c) the domain of a function f is the set of all real numbers.
1. The slope of a function f at any point (x, y) is 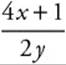 . The point (2, 4) is on the graph of f.
. The point (2, 4) is on the graph of f.
(A) Write an equation of the line tangent to the graph of f at x = 2.
(B) Use the tangent line in part (A) to approximate f (2.1).
(C) Solve the differential equation 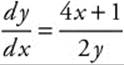 with the initial condition f(2) = 4.
with the initial condition f(2) = 4.
(D) Use the solution in part (C) and find f (2.1).
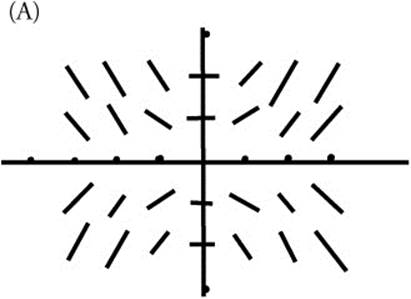
2. Consider the differential equation given by ![]() .
.
(A) On the axes provided, sketch a slope field for the given differential equation at the points indicated.
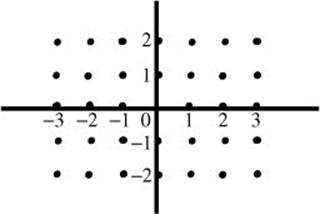
(B) Let y = f(x) be the particular solution to the given differential equation with the initial condition f(0) = 2. Use Euler’s method, starting at x = 0, with a step size of 0.1, to approximate f(0.3). Show the work that leads to your answer.
(C) Find the particular solution y = f(x) to the given differential equation with the initial condition f(0) = 2. Use your solution to find f(0.3).
STOP. AP Calculus BC Practice Exam 1 Section II—Part A
Section II—Part B

Directions:
The use of a calculator is not permitted in this part of the exam. When you have finished this part of the test, you may return to the problems in Part A of Section II and continue to work on them. However, you may not use a calculator. You should show all work. You may not receive any credit for correct answers without supporting work. Unless otherwise indicated, the numeric or algebraic answers need not be simplified, and the domain of a function fis the set of all real numbers.
3. Let f be a function that has derivatives of all orders for all real numbers. Assume f(0) = 1, f′(0) = 6, f″(0) = − 4, and f‴(0) = 30.
(A) Write the third-degree Taylor polynomial for f about x = 0 and use it to approximate f(0.1).
(B) Write the sixth-degree Taylor polynomial for g, where g(x) = f(x2), about x = 0.
(C) Write the seventh-degree Taylor polynomial for h, where 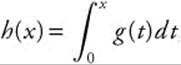 , about
, about
x = 0
4. Given the parametric equations x = 2(θ− sinθ) and y = 2(1 − cos θ),
(A) find ![]() in terms of θ.
in terms of θ.
(B) find an equation of the line tangent to the graph at θ = π.
(C) find an equation of the line tangent to the graph at θ = 2π.
(D) set up but do not evaluate an integral representing the length of the curve over the interval 0 ≤ θ ≤ 2π.
5. Let R be the region enclosed by the graph of y = x3, the x-axis, and the line x = 2.
(A) Find the area of region R.
(B) Find the volume of the solid obtained by revolving region R about the x-axis.
(C) The line x = a divides region R into two regions such that when the regions are revolved about the x-axis, the resulting solids have equal volume. Find a.
(D) If region R is the base of a solid whose cross sections perpendicular to the x-axis are squares, find the volume of the solid.
6. Given the function f(x) = xe2x,
(A) at what value(s) of x, if any, is f′(x) = 0?
(B) at what value(s) of x, if any, is f″(x) = 0?
(C) find ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
(D) find the absolute extrema of f and justify your answer.
(E) show that if f(x) = xeax where a > 0, the absolute minimum value of f is ![]()
STOP. AP Calculus BC Practice Exam 1 Section II−Part B
Answers to BC Practice Exam 1—Section I
Part A
1. D
2. E
3. A
4. B
5. B
6. A
7. C
8. A
9. E
10. A
11. C
12. D
13. E
14. B
15. A
16. B
17. C
18. D
19. D
20. E
21. A
22. C
23. E
24. C
25. D
26. B
27. C
28. E
Part B
76. A
77. D
78. C
79. E
80. A
81. C
82. C
83. D
84. A
85. D
86. C
87. A
88. D
89. A
90. D
91. A
92. E
Answers to BC Practice Exam 1—Section II
Part A
1. ![]()
(B) 4.113
![]()
(D) 4.113
2.
(B) 2.03984
![]()
Part B
3. (A) f(x) = 1 + 6x − 2x2 + 5x3; f(0.1) ≈ 1.585
(B) g(x) = 1 + 6x2 − 2x4 + 5x6
![]()
4. ![]()
(B) y = 4
(C) x = 4π
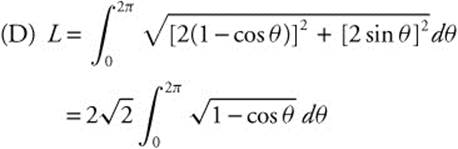
5. (A) 4
![]()
(C) 26/7
![]()
6. (A) f′(x) = e2x (1 + 2x), x = − 0.5
(B) x = − 1
![]()
![]()
(E) See solution.
Solutions to BC Practice Exam 1—Section I
Section I—Part A
1. The correct answer is (D).
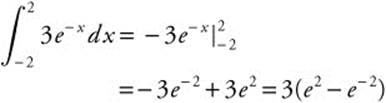
2. The correct answer is (E).
f(x) = x3 + 3x2 + cx + 4 ⇒ f′(x) = 3x2 + 6x + c ⇒ f″(x) = 6x + 6. Set 6x + 6 = 0 so x = − 1. f″ > 0 if x > − 1 and f″ < 0 if x < − 1. f′(− 1) = 3(− 1)2 + 6(− 1) + c = 0 ⇒ 3 − 6 + c = 0 ⇒ − 3 + c = 0 ⇒ c = 3.
3. The correct answer is (A).
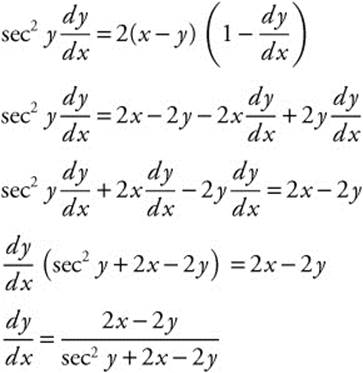
4. The correct answer is (B).
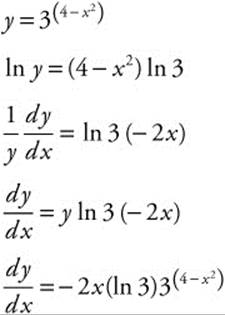
5. The correct answer is (B).
![]() and
and ![]()
Then, ![]()
Then, 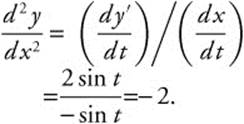
Evaluate at ![]() for
for 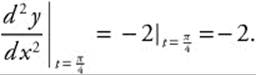
6. The correct answer is (A).
Let u = 3x, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . Then
. Then
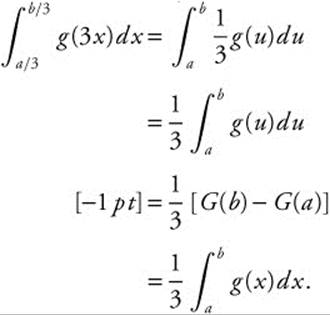
7. The correct answer is (C).
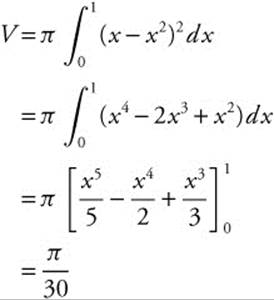
8. The correct answer is (A).
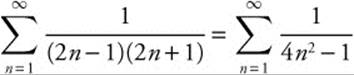
The sequence of partial sums 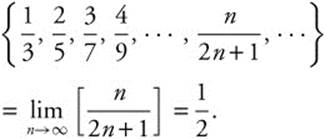 and
and
9. The correct answer is (E)
The graph must be increasing and concave up. f(x) = e−x and ![]() are decreasing. f(x) = 4 − x2 is increasing on (− 2, 0) but decreasing on (0, 2).
are decreasing. f(x) = 4 − x2 is increasing on (− 2, 0) but decreasing on (0, 2). ![]() is increasing, but concave down. Only f(x) = ex is increasing and concave up.
is increasing, but concave down. Only f(x) = ex is increasing and concave up.
10. The correct answer is (A).
Which of the following series are convergent?
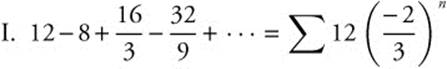 is a geometric series with
is a geometric series with ![]() . Since |r| < 1, the series converges.
. Since |r| < 1, the series converges.
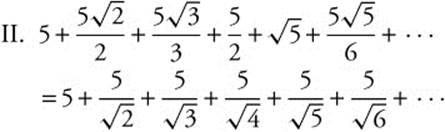
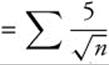 is a p-series, with
is a p-series, with ![]() . Since p < 1, the series diverges.
. Since p < 1, the series diverges.
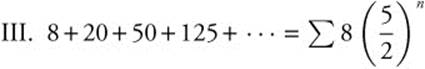 is also a geometric series, but since
is also a geometric series, but since ![]() , the series diverges. Therefore, only series I converges.
, the series diverges. Therefore, only series I converges.
11. The correct answer is (C).
To assure that 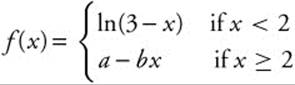 is differentiable at x = 2, we must first be certain that the function is continuous. As x → 2,
is differentiable at x = 2, we must first be certain that the function is continuous. As x → 2,
ln(3 − x) → 0, so we want a − 2b = 0 ⇒ a = 2b. Continuity does not guarantee differentiability, however; we must assure that ![]() exists. We must be certain that
exists. We must be certain that ![]() is equal to
is equal to ![]() .
.
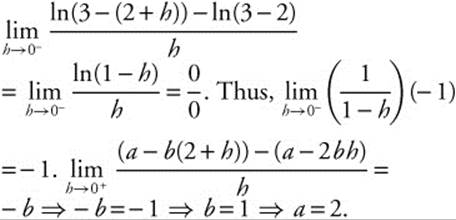
12. The correct answer is (D).
The velocity vector v(t) = ⟨2 − 3t2, π sin(π t)⟩ = (2 − 3t2)i + (π sin(πt)) j. Integrate to find the position. ![]() = 4i + 3 j. Evaluate at t = 2 to find the constant. s(2) = (4 − 8)i + (− 1 cos(2π)) j + C = 4i + 3 j
= 4i + 3 j. Evaluate at t = 2 to find the constant. s(2) = (4 − 8)i + (− 1 cos(2π)) j + C = 4i + 3 j
s(2) = (− 4)i − j + C = 4i + 3 j C = 8i + 4 j
Therefore s(t) = 8 + 2t − t3 i + (4 − cos(π t)) j = ⟨8 + 2t − t3, 4 − cos(π t)⟩. Evaluate at t = 3. s(3) = (8 + 6 − 27)i + (4 − cos(3π)) j s(3) = − 13i + 5 j
The position vector is ⟨− 13, 5⟩.
13. The correct answer is (E).
The ![]() is the definition of the derivative for the function y = ln(x − 3), therefore the limit is equal to
is the definition of the derivative for the function y = ln(x − 3), therefore the limit is equal to ![]() .
.
14. The correct answer is (B).
To enclose the area, θ must sweep through the interval from 0 to 2π. The area of the region enclosed by r = 3 − sinθ is
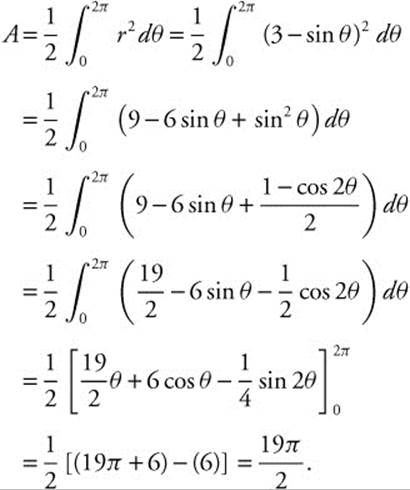
15. The correct answer is (A).
Differentiate r = 5 + 5 sinθ to get ![]() . Use a parametric representation of the curve.
. Use a parametric representation of the curve. 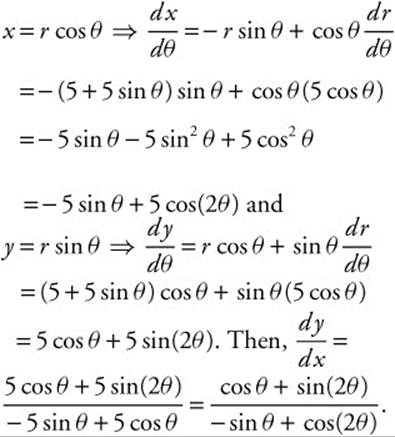
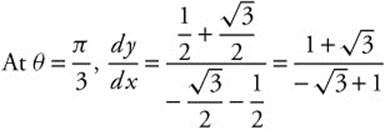
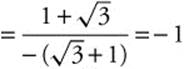 . The slope of the tangent line is equal to 1, so the slope of the normal line is the negative reciprocal; thus, the slope of the normal line is 1.
. The slope of the tangent line is equal to 1, so the slope of the normal line is the negative reciprocal; thus, the slope of the normal line is 1.
16. The correct answer is (B).
Use the trapezoidal method with 4 divisions: x = 1. ![]() , x = 1.5,
, x = 1.5, ![]() , x = 2,
, x = 2, ![]() , x = 2.5,
, x = 2.5, ![]() , and x = 3,
, and x = 3, ![]() . The area is approximated by the sum of the areas of the four trapezoids.
. The area is approximated by the sum of the areas of the four trapezoids.
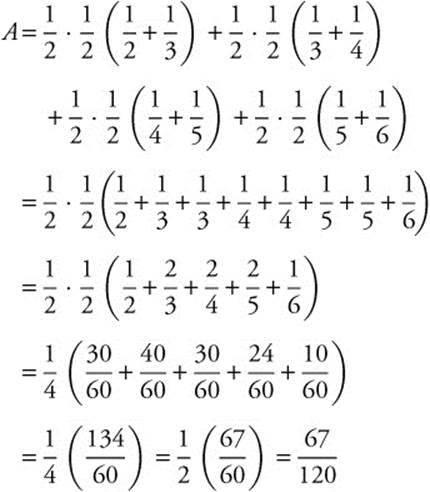
17. The correct answer is (C).
Let 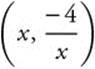 be a point on
be a point on ![]() . Then the distance from the origin to the point
. Then the distance from the origin to the point 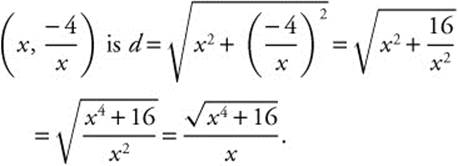 To find the minimum distance, differentiate
To find the minimum distance, differentiate 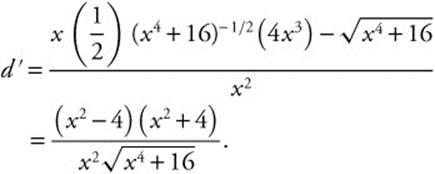
Set the derivative equal to zero and solve for x. 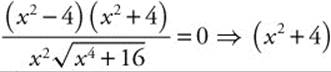 (x2 − 4) = 0. The first factor gives x2 = − 4 which has no real solution. The second gives x2 = 4 ⇒ x = ± 2. There are two points at minimum distance from the origin. x = 2 ⇒ y = − 2 ⇒ (2, − 2) and x = − 2, y = 2 ⇒ (− 2, 2). Calculate the distance from the origin to one of those points.
(x2 − 4) = 0. The first factor gives x2 = − 4 which has no real solution. The second gives x2 = 4 ⇒ x = ± 2. There are two points at minimum distance from the origin. x = 2 ⇒ y = − 2 ⇒ (2, − 2) and x = − 2, y = 2 ⇒ (− 2, 2). Calculate the distance from the origin to one of those points. ![]()
18. The correct answer is (D).
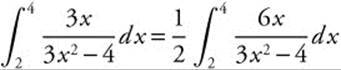
Let u = 3x2 − 4, du = 6x dx, x = 2 ⇒ u = 8, and x = 4 ⇒u = 44. Then the integral 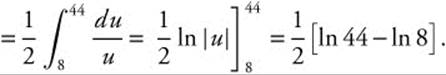
19. The correct answer is (D).
The graph of y = esin x has a relative extremum when ![]() or cos x = 0. Since we know esin x > 0, it must be the case that cos x = 0 ⇒
or cos x = 0. Since we know esin x > 0, it must be the case that cos x = 0 ⇒ ![]() ,
, ![]() . The graph of y = esin x has a relative extremum at
. The graph of y = esin x has a relative extremum at ![]() and
and ![]() . Find the second derivative
. Find the second derivative ![]() and evaluate at each critical number.
and evaluate at each critical number.
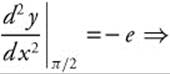 max but
max but
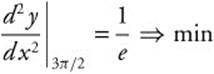 . Therefore, the graph of y = esin x has a relative minimum when
. Therefore, the graph of y = esin x has a relative minimum when ![]() .
.
20. The correct answer is (E).
![]() and
and ![]() , so
, so 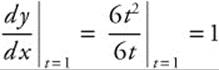 is the slope of the tangent line. At t = 1, x = 1, y = 4, so the point of tangency is (1, 4). Equation of tangent: y − 4 = 1(x − 1) ⇒ y= x + 3.
is the slope of the tangent line. At t = 1, x = 1, y = 4, so the point of tangency is (1, 4). Equation of tangent: y − 4 = 1(x − 1) ⇒ y= x + 3.
21. The correct answer is (A).
We know
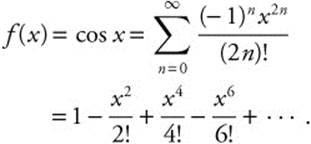
Substitute ![]() for x, and
for x, and ![]()
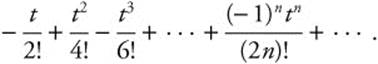 The required integral,
The required integral, 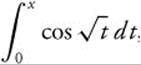 , will be equal to
, will be equal to 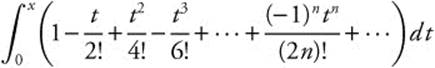 which, when integrated term by term, is
which, when integrated term by term, is
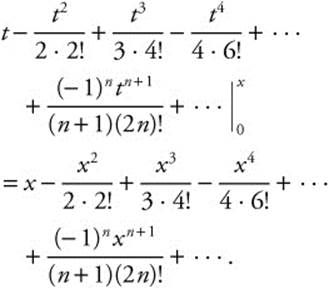
The series expansion for 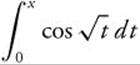 is
is 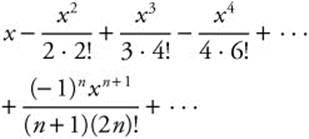
22. The correct answer is (C).
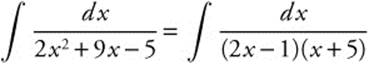 . Use a partial fractions decomposition with
. Use a partial fractions decomposition with 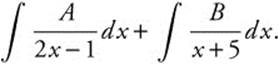 Then A(x + 5) + B(2x − 1) = 1 ⇒ Ax + 2Bx = 0 ⇒ A = −2B. Substituting and solving, 5A − B = 1 ⇒ 5(− 2B) − B = 1, so
Then A(x + 5) + B(2x − 1) = 1 ⇒ Ax + 2Bx = 0 ⇒ A = −2B. Substituting and solving, 5A − B = 1 ⇒ 5(− 2B) − B = 1, so ![]() and
and ![]() . Then
. Then 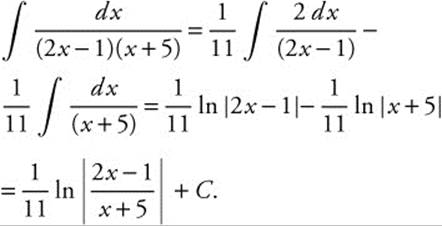
23. The correct answer is (E).
Assume that the base of the solid is the circle ![]() Then the area of each cross section is
Then the area of each cross section is ![]() . Then the volume is
. Then the volume is
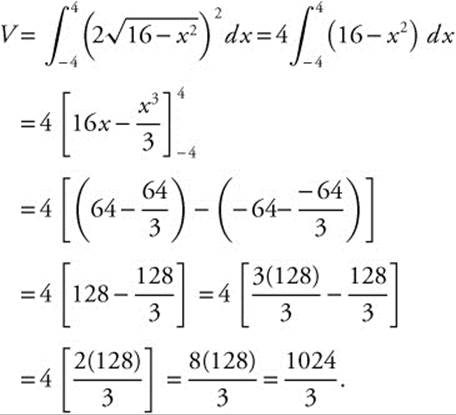
24. The correct answer is (C).
![]() and
and ![]() . Then
. Then 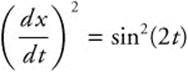 and
and 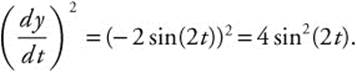 For
For ![]() , the length of the arc the particle traces out is
, the length of the arc the particle traces out is
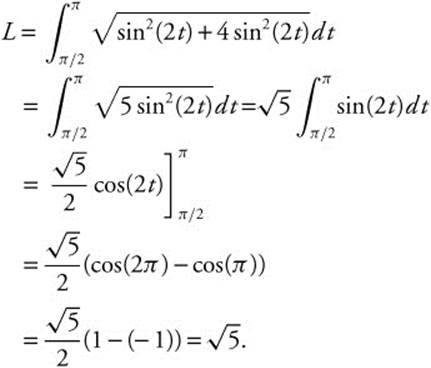
25. The correct answer is (C).
The series ![]() will converge when the ratio
will converge when the ratio 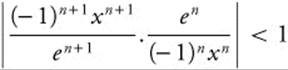 . Simplify, and the series converges when
. Simplify, and the series converges when 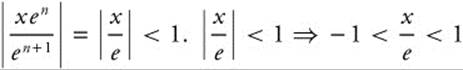 ⇒ − e < x < − e. When x = e, the series becomes Σ(− 1)n, which diverges. When x = − e, the series becomes Σ(− 1)2n = Σ 1n, which diverges. So the interval of convergence is (− e, e).
⇒ − e < x < − e. When x = e, the series becomes Σ(− 1)n, which diverges. When x = − e, the series becomes Σ(− 1)2n = Σ 1n, which diverges. So the interval of convergence is (− e, e).
26. The correct answer is (B).
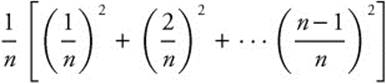 represents the sum of the areas of n rectangles each of width
represents the sum of the areas of n rectangles each of width ![]() . The heights of the rectangles are the squares of the division points,
. The heights of the rectangles are the squares of the division points, ![]() , all of which are between 0 and 1. Thus,
, all of which are between 0 and 1. Thus, 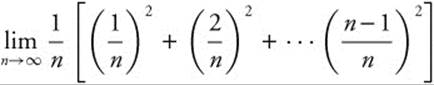 represents the area under the y = x2 from 0 to 1, or
represents the area under the y = x2 from 0 to 1, or 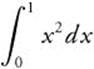 .
.
27. The correct answer is (C).
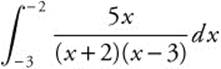 is an improper integral since
is an improper integral since ![]() has an infinite discontinuity at x = −2, one of the limits of integration. Therefore
has an infinite discontinuity at x = −2, one of the limits of integration. Therefore 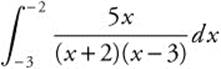 is equal to
is equal to 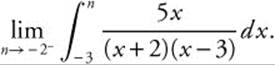 .
.
28. The correct answer is (E).
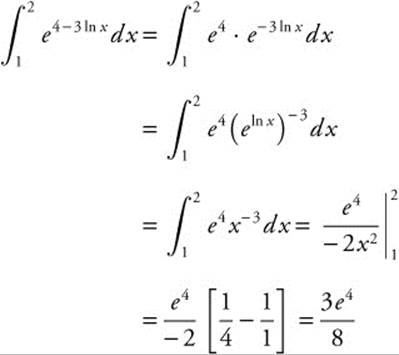
Section I—Part B
76. The correct answer is (A).
If ![]() , then
, then ![]() Evaluating at x = 2,
Evaluating at x = 2, 
77. The correct answer is (D).
Let u = ln x, ![]() , x = 1 ⇒ u = 0, and x = eπ ⇒ u = π. Then
, x = 1 ⇒ u = 0, and x = eπ ⇒ u = π. Then 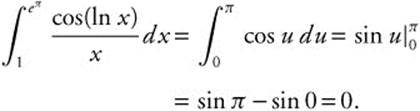
78. The correct answer is (C).
![]() is separable and can be integrated by partial fractions.
is separable and can be integrated by partial fractions. 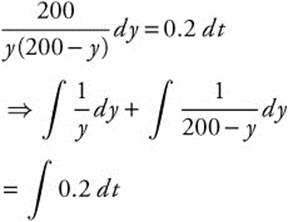
ln |y| − ln |200 − y|
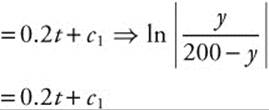
Exponentiate and solve for y:
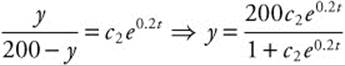 or
or ![]() .
.
Since the rumor begins with two people, ![]() so
so ![]() . Evaluate at t = 30,
. Evaluate at t = 30, ![]()
The total number of people who have heard the rumor after thirty days is about 161.
79. The correct answer is (E).
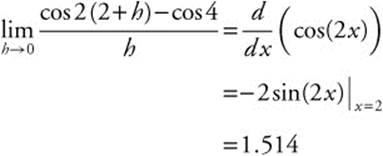
80. The correct answer is (A).
The area under the curve y = 3x2 − kx + 1 bounded by the lines x = 1 and x = 2 is
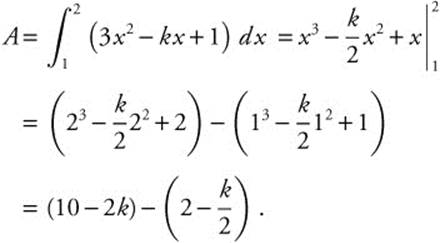
Since the area is known to be − 5.5, set ![]() and solve:
and solve:
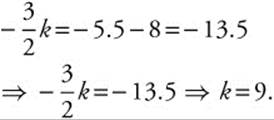
81. The correct answer is (C).
![]() is separable, so
is separable, so ![]() can be integrated to ln |P| = kt + C. Exponentiate for P = cekt. Since the population increases 23% in 12 years, 1.23 = 1ek(12)
can be integrated to ln |P| = kt + C. Exponentiate for P = cekt. Since the population increases 23% in 12 years, 1.23 = 1ek(12)
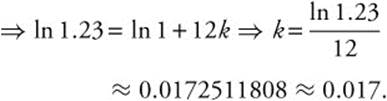
82. The correct answer is (C).
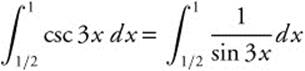
Use the [Integral] function on your calculator to find that the integral is ≈ 0.90571039.
83. The correct answer is (D).
If 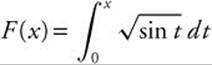 . Then
. Then ![]() , so
, so ![]() .
.
84. The correct answer is (A)
Step 1. Begin by finding the first non-negative value of t such that v(t) = 0. To accomplish this, use your graphing calculator, set y1 = sin(x2 + 1) and graph.
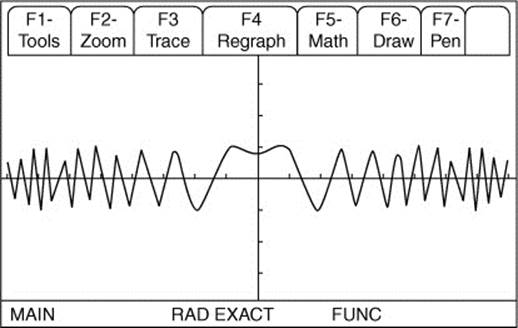
Use the [Zero] function and find the first non-negative value of x such that y1 = 0. Note that x = 1.46342.
Step 2. The position function of the particle is 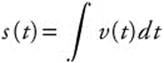 . Since s(1) = 5, we have
. Since s(1) = 5, we have 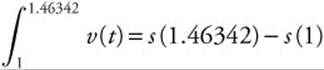 . Using your calculator, evaluate
. Using your calculator, evaluate 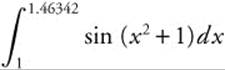 and obtain 0.250325. Therefore, .250325
and obtain 0.250325. Therefore, .250325
= s (1.46342) − s(1) or .250325
= s (1.46342) − 5. Thus, s (1.46342)
= 5.250325 ≈ 5.250.
85. The correct answer is (D).
Rewrite: y = sec2(3x) as y = [sec(3x)]2
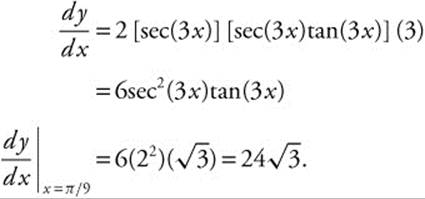
86. The correct answer is (C).
If ![]() Integrate
Integrate ![]() to get y = 4 ln |x| + C. Since y = 4.5 when x = 3, 4.5 = 4 ln 3+ C ⇒ 0.106 = C. Thus, y = 4 ln|x| + 0.106. At x = 3.1, y = 4.632.
to get y = 4 ln |x| + C. Since y = 4.5 when x = 3, 4.5 = 4 ln 3+ C ⇒ 0.106 = C. Thus, y = 4 ln|x| + 0.106. At x = 3.1, y = 4.632.
87. The correct answer is (A).
The slope of the tangent line to y = e−2x is ![]() . The slope of the normal is the negative reciprocal,
. The slope of the normal is the negative reciprocal, ![]() . When x = 1.158,
. When x = 1.158, ![]() The slope of the normal line is approximately 5.068.
The slope of the normal line is approximately 5.068.
88. The correct answer is (D).
The volume of the solid generated by revolving about the x-axis is
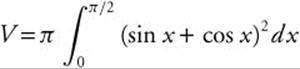 .
.
Since (sin x + cos x)2 = sin2 x + 2 sin x cos x + cos2 x = 1 + 2 sin x cos x
= 1 + sin 2x,
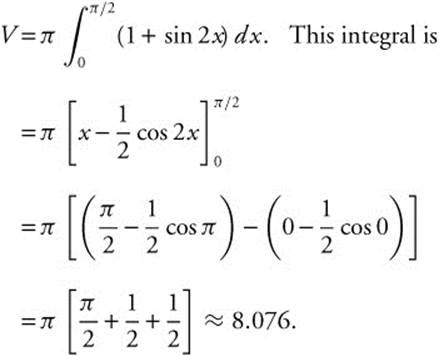
89. The correct answer is (A).
The absolute minimum of f(x) = ln(3x) + cos x on the closed interval ![]() . First find the relative extrema of f(x) = ln(3x) + cos x on
. First find the relative extrema of f(x) = ln(3x) + cos x on ![]() .
.
Set the derivative ![]() and
and ![]() (not in the interval) or x = 2.7726047.
(not in the interval) or x = 2.7726047.
![]() is positive at x = 2.7726047, indicating a relative minimum. f(2.7726047) = 1.1857067, so the relative minimum is approximately (2.773, 1.186). Checking the endpoints of the interval,
is positive at x = 2.7726047, indicating a relative minimum. f(2.7726047) = 1.1857067, so the relative minimum is approximately (2.773, 1.186). Checking the endpoints of the interval, ![]() and f(π) = 1.243. Therefore, the absolute minimum is (2.773, 1.186).
and f(π) = 1.243. Therefore, the absolute minimum is (2.773, 1.186).
90. The correct answer is (D).
The position of the particle is y(t) = 5t3 − 9t2 + 2t − 1, and the velocity is v(t) = y′(t) = 15t2 − 18t + 2. At the moment the particle changed direction, its velocity was zero, so 15t2 − 18t + 2 = 0. Solving tells us that the particle changes direction twice, first at t ≈ 0.124 and later at t = 1.076. Taking the first of these, and evaluating the position function, y ≈ − 0.881. At the moment when the particle first changes direction, its position is (0, − 0.881).
91. The correct answer is (A).
Use the intersect function to find that the points of intersection of y = cos x + 1 and y = 2 + 2x − x2 are (0, 2) and (2.705, 0.094). The area enclosed by the curves is
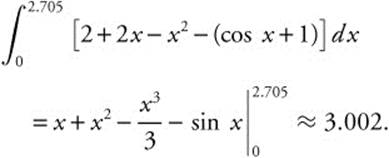
92. The correct answer is (E).
Use the ratio test for absolute convergence.
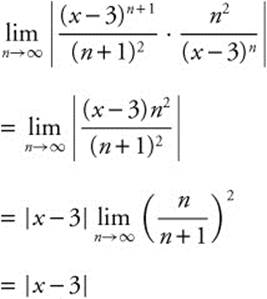
Set |x − 3| < 1 ⇒ − 1 < (x − 3) < 1 ⇒ 2 < x < 4. At x = 4, the series becomes ![]() which is a p-series with p = 2. The series converges. At x = 2, the series becomes
which is a p-series with p = 2. The series converges. At x = 2, the series becomes ![]() which converges absolutely. Thus, the interval of convergence is [2,4].
which converges absolutely. Thus, the interval of convergence is [2,4].
Solutions to BC Practice Exam 1—Section II
Section II—Part A
1.
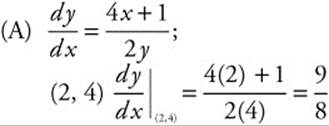
Equation of tangent line: ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
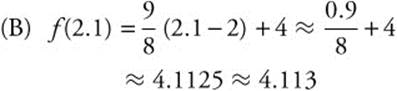
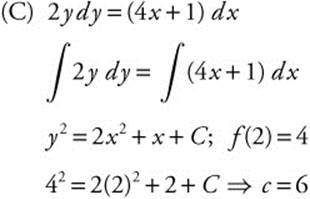
Thus, y2 = 2x2 + x + 6 or ![]() . Since the point (2, 4) is on the graph of f,
. Since the point (2, 4) is on the graph of f, ![]()
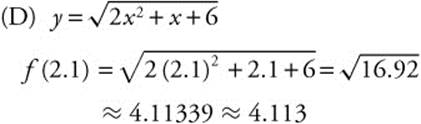
2. Given the differential equation ![]() :
:
(A) Calculate slopes.
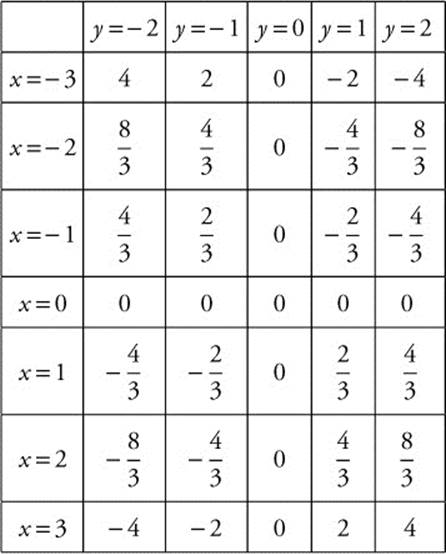
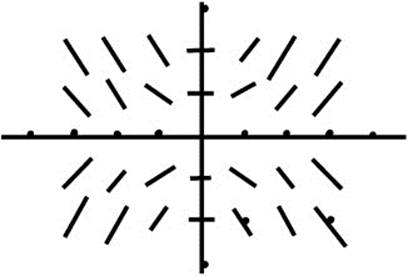
Sketch the slope field.
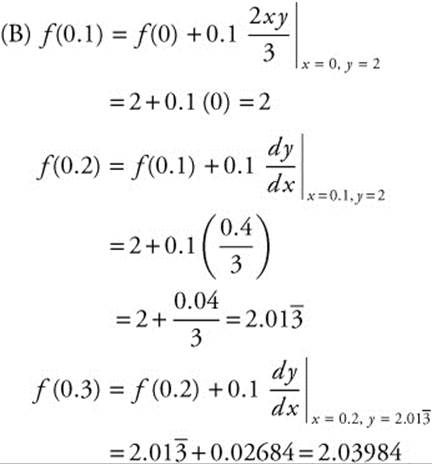
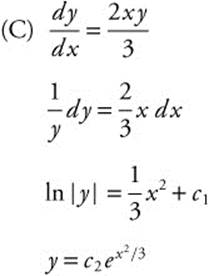
According to the initial condition, ![]() , so the particular solution is
, so the particular solution is ![]() . Evaluate at x = 0.3 and
. Evaluate at x = 0.3 and ![]()
Section II—Part B
3. Given f(0) = 1, f′(0) = 6, f″(0) = − 4, and f″′(0) = 30.
(A) The third-degree Taylor polynomial for f about x = 0 is
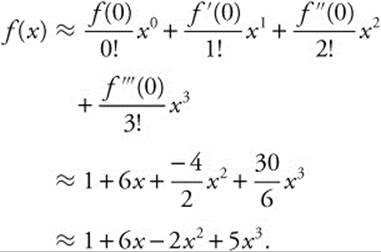
To approximate f(0.1):
f(0.1) ≈ 1 + 6(0.1) − 2(0.1)2 + 5(0.1)3
≈ 1 + 0.6 − 2(0.01) + 5(0.001)
≈ 1 + 0.6 − 0.02 + 0.005
≈ 1.585.
(B) The sixth degree Taylor polynomial for g(x) = f(x2), about x = 0, is
g(x) = f(x2)
= 1 + 6(x2) − 2(x2)2 + 5(x2)3
g(x) = 1 + 6x2 − 2x4 + 5x6.
(C) The seventh degree Taylor polynomial for
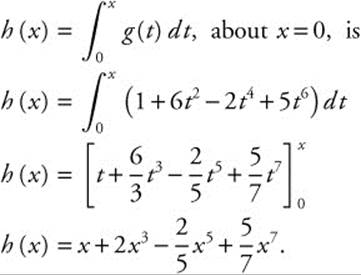
4. Given x = 2(θ − sinθ) and y = 2(1 − cos θ):
(A) ![]() and
and ![]() . Divide to find
. Divide to find
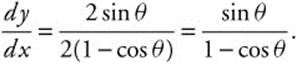
(B) At θ = π, x = 2(π − sin π) = 2π, y = 2(1 − cos π) = 4, and 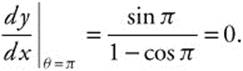
The tangent line at (2π, 4) is horizontal, so the equation of the tangent is y = 4.
(C) At θ = 2π, x = 2(2π − sin 2π) = 4π, y = 2(1 − cos 2π) = 0, and 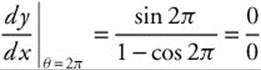 . Since the derivative is undefined, the tangent line at (4π, 0) is vertical, so the equation of the tangent is x = 4π.
. Since the derivative is undefined, the tangent line at (4π, 0) is vertical, so the equation of the tangent is x = 4π.
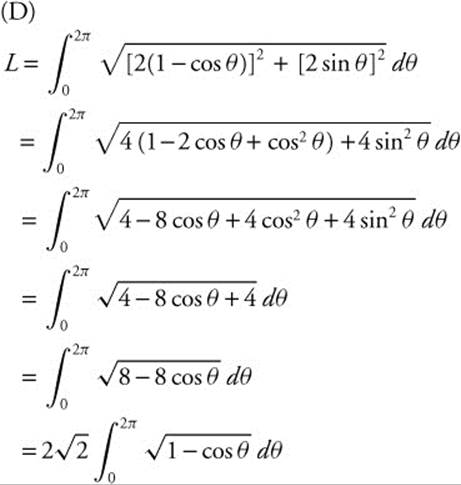
5. (See Figure DS-18.)
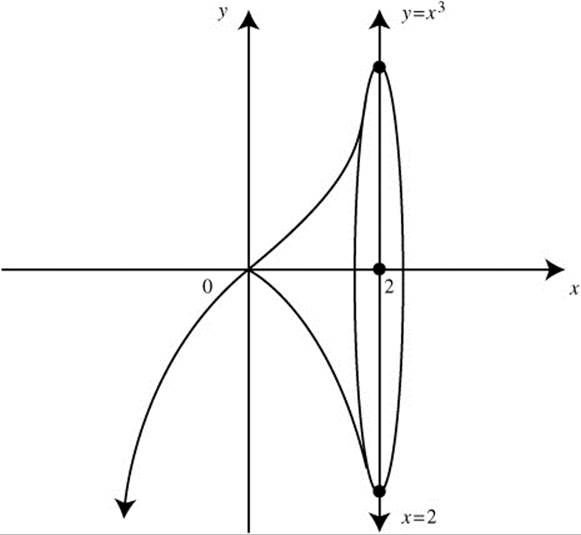
Figure DS.18
(A) Area of 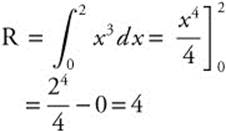
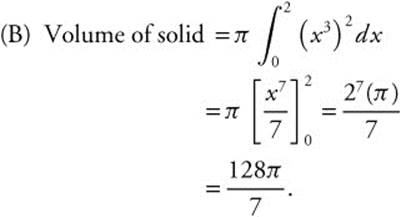
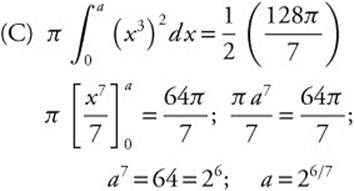
(D) Area of cross section = (x3)2 = x6. Volume of solid 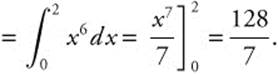
6. (A) f(x) = xe2x
f′(x) = e2x + x(e2x)(2) = e2x + 2xe2x = e2x (1 + 2x)
Set f″(x) = 0 ⇒ e2x (1 + 2x) = 0. Since e2x > 0, 1 + 2x = 0 ⇒ x = −0.5.
(B) f′(x) = e2x + 2xe2x
f″(x) = e2x (2) + 2e2x + 2xe2x(2)
= 2e2x + 2e2x + 4xe2x
= 4e2x + 4xe2x
= 4e2x (1 + x)
Set f″(x) = 0 ⇒ 4e2x (1 + x) = 0. Since e2x > 0, thus 1 + x = 0 or x = −1.
(C) ![]() , since xe2x increases without bound as x approaches + ∞.
, since xe2x increases without bound as x approaches + ∞. ![]() . As x → − ∞. the numerator → − ∞. As x → − ∞, the denominator e−2x → ∞. However, the denominator increases at a much greater rate, and thus
. As x → − ∞. the numerator → − ∞. As x → − ∞, the denominator e−2x → ∞. However, the denominator increases at a much greater rate, and thus ![]() .
.
(D) Since as x ⇒∞, xe2x increases without bound, f has no absolute maximum value. From part (A), f(x) has one critical point at x = − 0.5. Since f′(x) = e2x (1 + 2x), f′(x) < 0 for x < − 0.5 and f′(x) > 0 for x > − 0.5, thus f has a relative minimum at x = − 0.5, and it is the absolute minimum because x = − 0.5 is the only critical point on an open interval. The absolute minimum value is ![]() .
.
(E) f(x) = xeax, a > 0
f′(x) = eax + x (eax)(a) = eax + axeax
= eax (1 + ax)
Set f′(x) = 0 ∞ eax (1 + ax) = 0 or 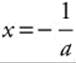 . If
. If ![]() , f′(x) < 0, and if
, f′(x) < 0, and if ![]() , f′(x) > 0. Thus,
, f′(x) > 0. Thus, ![]() is the only critical point, and f has an absolute minimum at
is the only critical point, and f has an absolute minimum at ![]() .
. 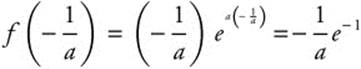
![]() . The absolute minimum value of f is
. The absolute minimum value of f is ![]() for all a > 0.
for all a > 0.
Scoring Sheet for BC Practice Exam 1