5 Steps to a 5 AP Calculus AB & BC, 2012-2013 Edition (2011)
STEP 5. Build Your Test-Taking Confidence
AP Calculus BC Practice Exam 2
ANSWER SHEET FOR MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS

Section I—Part A

Directions:
Use the answer sheet provided in the previous page. All questions are given equal weight. There is no penalty for unanswered questions. Unless otherwise indicated, the domain of a function f is the set of all real numbers. The use of a calculator is not permitted in this part of the exam.
1. If f (3) = − 2 and f′(3) = 5, then the equation of the tangent to the curve y = f(x) at x = 3 is
(A) y = 5 x − 2
(B) y = 5 x − 17
(C) y = −2 x + 5
(D) y = −2 x − 17
(E) y = 5 x + 3
2. On the interval − 3 < x < − 1, the curve ![]() is
is
(A) increasing and concave up.
(B) increasing and concave down.
(C) decreasing and concave up.
(D) decreasing and concave down.
(E) horizontal.
3. The relative extremum of the function ![]() , a > 0 is
, a > 0 is
(A) relative maximum at (− 2a, 2a⅔).
(B) relative maximum at (− 2a, 0).
(C) relative minimum at (− 2a, 2a⅔).
(D) relative minimum at (0, − 2a).
(E) no relative extrema.
4. A function is defined for all real numbers and has the property f(x + h) − f(x) = 4x2h + 2xh − 6x3h2. Find f′(3).
(A) − 18
(B) − 3
(C) 0
(D) 3
(E) 42
5. For what positive value of k is the line y = −9x + k tangent to the curve y = x3 − 6x2?
(A) − 27
(B) 0
(C) 3
(D) 5
(E) 4
6. The tangent to the parabola y = ax2 at x = p intersects the y-axis at
(A) (− ap2, 0)
(B) (− 2a, 0)
(C) (0, − ap2)
(D) (0, ap2)
(E) (0, − ap)
7. If h(x) = f(x)g(x), then h′(1) =
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
8. If h(x) = f(g(x)), then h′(2) =
(A) − 2
(B) − 1
(C) 0
(D) 1
(E) 2
9. If f(x) is a continuous function and f(5) = 2 and f′(5) = 3, then f (5.01) is approximately
(A) 0.02
(B) 0.03
(C) 2.01
(D) 2.03
(E) 3.02
The table show some of the values of differentiable functions f and g and their derivatives. Use this information for questions 10 and 11.
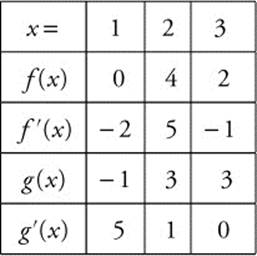
10. Evaluate 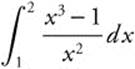
(A) ln 2
(B) − ln 2
(C) 0
(D) 1
(E) Does not exist
11. A cube is expanding so that its surface area is increasing at a constant rate of 4 square inches per second. How fast is the volume increasing at the instant when the surface area is 24 square inches?
(A) 2 cubic inches per second
(B) 4 cubic inches per second
(C) 8 cubic inches per second
(D) 16 cubic inches per second
(E) 24 cubic inches per second
12. If 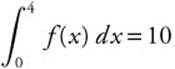 ,
, 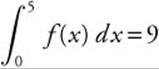 and
and 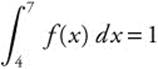 , then
, then 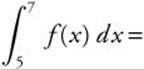
(A) 2
(B) 8
(C) 9
(D) 10
(E) 11
13. An antiderivative for ![]() is
is
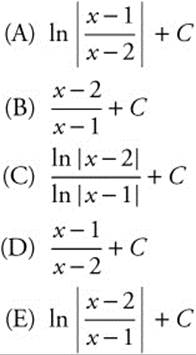
14. ![]() is
is
(A) Indeterminate
(B) 1
(C) 0
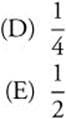
15. 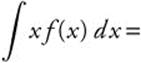
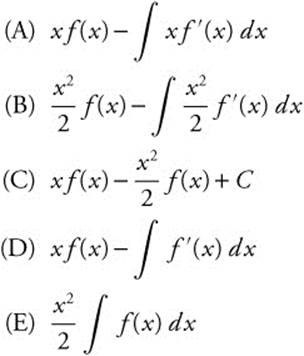
16. If x3 + 3xy + 2y3 = 17, then in terms of x and y, ![]()
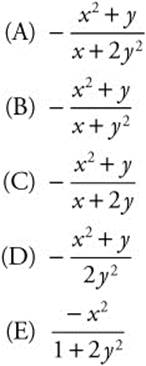
17. If f(x) = 3tan5(2x), then f′(x) is:
(A) 3 sec10(2x)
(B) 30 sec10(2x)
(C) 15 tan4(2x)
(D) 30 tan4(2x)
(E) 30 tan4(2x) sec2(2x)
18. If f′(x) = cos x sin2 x and f (0) = 2, then 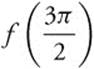 is
is
(A) 0
(B) −1
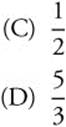
(E) 2
19. The particular solution for the differential equation ![]() satisfying the initial condition y (0) = 1 is
satisfying the initial condition y (0) = 1 is
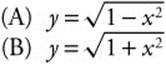
(C) y = 1 + x2
(D) y = 1 − x2
(E) y = 1 + x
20. Let f(x) be a differentiable function on the closed interval [1, 3]. The average value of f′(x) on [1, 3] is
(A) f(3) − f(1)
(B) 2f(3) − f(1))
![]()
(D) f(3) − f(1)
![]()
21. Which of the following improper integrals converge?
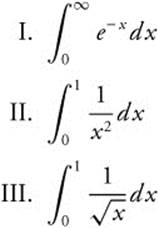
(A) I only
(B) III only
(C) I and II
(D) II and III
(E) I and III
22. A particle moves in the xy-plane so that its coordinates at time t are given by x = t2 and y = 4 − t3. At t = 1, its acceleration vector is
(A) ⟨2, − 3⟩
(B) ⟨2, − 6⟩
(C) ⟨1, − 6⟩
(D) ⟨2, 6⟩
(E) ⟨1, − 2⟩
23. If 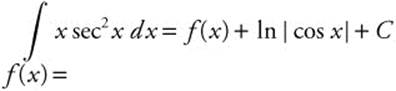 , then
, then
(A) tan x
![]()
(C) x tan x
(D) x2 tan x
(E) tan2 x
24. 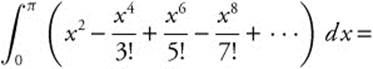
(A) −π
(B) π
(C) π2
![]()
(E) π + 1
25. Which of the following equations has a graph that is a circle with radius 2 and center at the origin?
![]()
II. x = cos t, y = sin t; 0 ≤ t ≤ 2π
III. r = 4 cos θ; 0 ≤ θ ≤ π
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) All of these
(E) None of these
26. If r = f(θ) is continuous and non-negative for α ≤ x ≤ β, then the area enclosed by the polar curve r = f(θ) and the lines θ = α and θ = β is given by
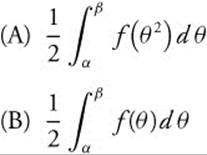
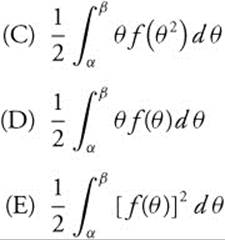
27. The first five nonzero terms in the series expansion of e−4x about x = 0 are
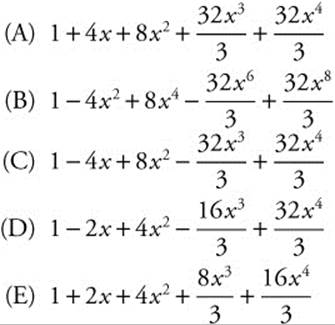
28. The general solution of 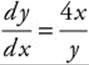 is a family of
is a family of
(A) Lines
(B) Circles
(C) Ellipses
(D) Hyperbolas
(E) Parabolas
Section I—Part B

Directions:
Use the same answer sheet for Part A. Please note that the questions begin with number 76. This is not an error. It is done to be consistent with the numbering system of the actual AP Calculus BC Exam. All questions are given equal weight. There is no penalty for unanswered questions. Unless otherwise indicated, the domain of a function f is the set of all real numbers. If the exact numerical value does not appear among the given choices, select the best approximate value. The use of a calculator is permitted in this part of the exam.
76. If y = 5(7−2x2), then ![]() at x = 1 is approximately
at x = 1 is approximately
(A) 5
(B) 25
(C) 3125
(D) 5029.494
(E) −20117.974
77. Given f(x) = 2x and 23.03 ≈ 8.168, using differentials, determine which of the following is closest to f′(3)?
(A) 3.2
(B) 4.6
(C) 5.6
(D) 8.2
(E) 9.1
78. The rate of growth of a population is proportional to the population. If the population in 2000 was 3 million and in 2010, the population was 3.21 million, what is the predicted population for the year 2020?
(A) 3.315 million
(B) 3.435 million
(C) 6.420 million
(D) 7.913 million
(E) 11.609 million
79. The function f(x) = 5x3 − 7x2 − 5 has which of these relative extrema?
(A) Relative maximum at (0.933, − 7.033)
(B) Relative maximum at (− 5, 0)
(C) Relative minimum at (0, − 5)
(D) Relative minimum at (0.933, − 7.033)
(E) No relative maxima or minima
80. The slope of the tangent line to the curve r = 4 − 3 cos θ at ![]() is approximately
is approximately
(A) 3.284
(B) 0.524
(C) 1.001
(D) 0.027
(E) − 4.837
81. A particle moves in the xy-plane in such a way that its path is defined by x = et cos t and y = et sin 2t. Find the speed of the particle when ![]() .
.
(A) 10.757
(B) − 4.810
(C) − 9.621
(D) 14.431
(E) 4.810
82. At what value of x does the graph of ![]() have a point of inflection?
have a point of inflection?
(A) x = 1
(B) x = 2
(C) x = 3
(D) x = 4
(E) x = 5
83. 
(A) e
(B) 1 + e
(C) 2 + e
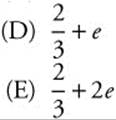
84. The base of a solid is the region enclosed by the ellipse 4x2 + y2 = 1. If all plane cross sections perpendicular to the x-axis are semicircles, then its volume is
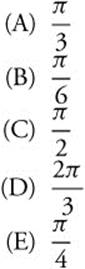
85. The area under the curve ![]() bounded by the line x = 0 and x = 3 is approximately
bounded by the line x = 0 and x = 3 is approximately
(A) 0.633
(B) 1.937
(C) 3.874
(D) 4.667
(E) 5.333
86. Which of the following is the interval of convergence for the power series given by 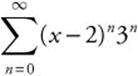
(A) (− 2, 2)
(B) (− 1, 5)
(C) (− 1, 1)
(D) (− 4, 0)
(E) (− ∞, ∞)
87. Find the coordinates of the point where the line tangent to y = 4 − 3x − x2 at x = 1 intersects the axis of symmetry of the parabola.
(A) (5, 0)
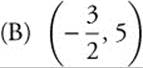
(C) (0, 5)
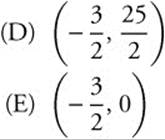
88. A rectangular field is fenced off along the bank of a river, and no fence is required along the river. If the material for the fence costs $5.00 per foot for the two ends and $7.50 per foot for the side parallel to the river, find the largest possible area that can be enclosed with $9,000 worth of fence.
(A) 270,000 square feet
(B) 27,000 square feet
(C) 600 square feet
(D) 450 square feet
(E) 270 square feet
89. Let R be the region in the first quadrant enclosed by the graph of ![]() , the line x = 7, the x-axis and the y-axis. The volume of the solid generated when R is revolved about the x-axis is
, the line x = 7, the x-axis and the y-axis. The volume of the solid generated when R is revolved about the x-axis is
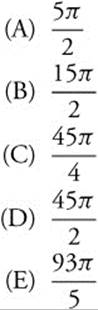
90. If ![]() and y = −1 when x = 1, then when x = 2, y =
and y = −1 when x = 1, then when x = 2, y =
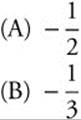
(C) 0
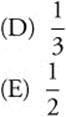
91. For all x, if 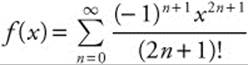 , then f′(x) =
, then f′(x) =
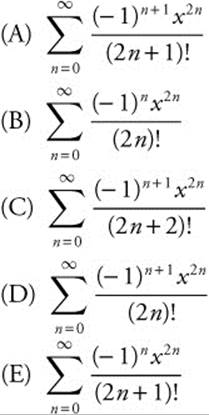
92. Find the equation of the tangent line to y = x3 + 2x at its point of inflection.
(A) y = 2x
(B) y = 3x + 2
(C) y = 6x
(D) y = 2x − 3
(E) y = −2x + 5
STOP. AP Calculus BC Practice Exam 2 Section I—Part B
Section II—Part A

Directions:
Show all work. You may not receive any credit for correct answers without supporting work. You may use an approved calculator to help solve a problem. However, you must clearly indicate the setup of your solution using mathematical notations and not calculator syntax. Calculators may be used to find the derivative of a function at a point, compute the numerical value of a definite integral, or solve an equation. Unless otherwise indicated, you may assume the following: (a) the numeric or algebraic answers need not be simplified; (b) your answer, if expressed in approximation, should be correct to 3 places after the decimal point; and (c) the domain of a function f is the set of all real numbers.
1. Let R represent the region in the first quadrant bounded by the graphs of y = cos x, y = 1 − cos x, and the y-axis.
(A) Find the area of region R.
(B) Find the volume of the solid created when region R is revolved about the x-axis.
(C) Find the volume of the solid that has R as its base if each of the cross sections is an isosceles triangle of height x.
2. A drum containing 100 gallons of oil is punctured by a nail and begins to leak at the rate of 10 sin ![]() gallons/minute where t is measured in minutes and 0 ≤ t ≤ 10.
gallons/minute where t is measured in minutes and 0 ≤ t ≤ 10.
(A) How much oil to the nearest gallon leaked out after t = 6 minutes?
(B) What is the average amount of oil leaked out per minute from t = 0 to t = 6tothe nearest gallon?
(C) Write an expression for f(t) to represent the total amount of oil in the drum at time t, where 0 ≤ t ≤ 10.
(D) At what value of t to the nearest minute will there be 40 gallons of oil remaining in the drum?
STOP. AP Calculus BC Practice Exam 2 Section II—Part A
Section II—Part B

Directions:
The use of a calculator is not permitted in this part of the test. When you have finished this part of the test, you may return to the problems in Part A of Section II and continue to work on them. However, you may not use a calculator. You should show all work. You may not receive any credit for correct answers without supporting work. Unless otherwise indicated, the numeric or algebraic answers need not be simplified, and the domain of a function fis the set of all real numbers.
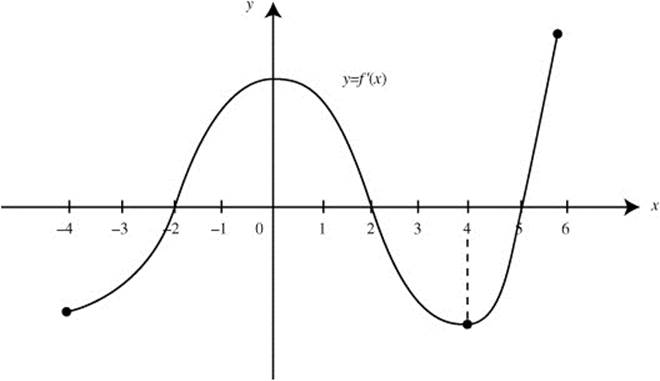
Figure D-11
3. A population is modeled by a function P that satisfies the logistic differential equation
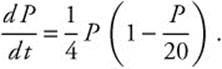 .
.
(A) If P(0) = 4, what is ![]() , what is
, what is ![]()
(B) If P (0) = 4, for what value of P is the population growing fastest?
(C) A different population is modeled by a function Q that satisfies the separable differential equation ![]() . Find Q(t) if Q(0) = 3.
. Find Q(t) if Q(0) = 3.
(D) For the function found in part (C), what is ![]()
4. The graph of f′, the derivative of the function f, for − 4 ≤ x ≤ 6 is shown above. (See Figure D-11.)
(A) At what value(s) of x does f have a relative maximum value? Justify your answer.
(B) At what value(s) of x does f have a relative minimum value? Justify your answer.
(C) At what value(s) of x is f′(x) > 0? Justify your answer.
(D) At what value(s) of x, if any, does the graph of f″ have a point of inflection? Justify your answer.
(E) Draw a possible sketch of f (x), if f (− 2) = 3.
5. The MacLaurin series for the function f is given by
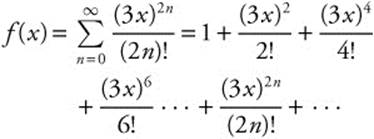
on its interval of convergence.
(A) Find the interval of convergence.
(B) Find the first four terms and the general term for the MacLaurin series for 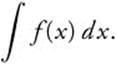
(C) Find the first four terms of f′(x) and approximate 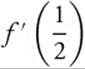 .
.
6. Given the equation x2y2 = 4:
(A) Find ![]() .
.
(B) Write an equation of the line tangent to the graph of the equation at the point (1, − 2).
(C) Write an equation of the line normal to the curve at point (1, − 2).
(D) The line ![]() is tangent to the curve P. Find the coordinates of point P.
is tangent to the curve P. Find the coordinates of point P.
STOP. AP Calculus BC Practice Exam 2 Section II—Part B
Answers to BC Practice Exam 2—Section I
Part A
1. B
2. D
3. C
4. E
5. E
6. C
7. B
8. B
9. D
10. D
11. A
12. A
13. E
14. D
15. B
16. A
17. E
18. D
19. A
20. E
21. E
22. B
23. C
24. B
25. E
26. E
27. C
28. D
Part B
76. E
77. C
78. B
79. D
80. A
81. A
82. B
83. B
84. A
85. D
86. B
87. D
88. A
89. E
90. B
91. D
92. A
Answers to BC Practice Exam 2—Section II
Part A
1. (A) 0.685
(B) 2.152
(C) 0.133
2. (A) 38 gallons
(B) 6 gallons
![]()
(D) 8 minutes
Part B
3. (A) 20; 20
(B) when P = 10
![]()
(D) 0
4. (A) x = 2
(B) x = 5 and x = −2
(C) (− 4, 0) and (4, 6)
(D) x = 0 and x = 4
(E) See solution.
5. (A) (− ∞, ∞)
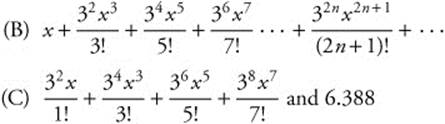
6. ![]()
![]()
(D) (− 2, 1)
Solutions to BC Practice Exam 2—Section I
Section I Part A
1. The correct answer is (B).
At the point (3, − 2), m = f′(3) = 5, so the equation of the tangent line is y + 2 = 5(x − 3) or y = 5x − 17.
2. The correct answer is (D).
If ![]() , then y′ =
, then y′ =
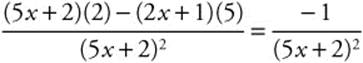
Since the numerator is always negative and the denominator is always positive, y′ is always negative and so the function is monotonically decreasing.
![]()
On the interval − 3 < x < − 1, − 13 ≤ 5x + 2 ≤ − 3 ⇒ (5x + 2)3 < 0 ⇒ y″ < 0. Therefore, the function is concave down on the given interval.
3. The correct answer is (C).
If ![]() ,
, ![]() . Set the derivative equal to zero.
. Set the derivative equal to zero.
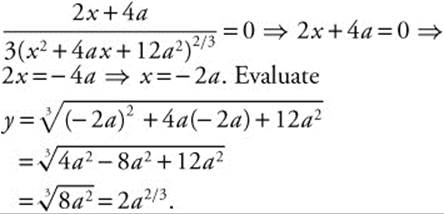
The second derivative,
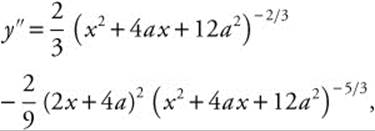
evaluated at ⇒ x = −2a, is
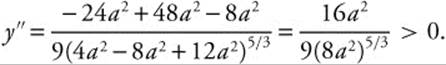
Therefore, the point (−2a, 2a⅔) is a relative minimum.
4. The correct answer is (E).
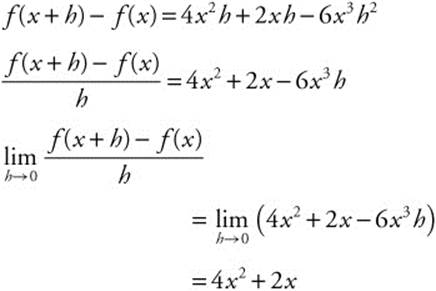
Find f′(3) = 4(3)2 + 2(3) = 42.
5. The correct answer is (E).
y = x3 − 6x2 ⇒ y′ = 3x2 − 12x. Slope of the tangent line is − 9, so 3x2 − 12x = −9, and solving gives x = 3 or x = 1. For each value, determine the equation of the tangent line. For x = 3, y = 27 − 54 = −27 and y + 27 = −9(x − 3) which gives k = 0. Reject this possibility since k must be positive. For x = 1, y = 1 − 6 = −5 and the tangent is y + 5 = −9(x − 1), which implies k = 4.
6. The correct answer is (C).
y = ax2 ⇒ y′ = 2ax. Evaluate when x = p to find the slope of the tangent line is m = 2ap. The point of tangency is (p, ap2), so the equation of the tangent line is y − ap2 = 2ap(x − p) or y = 2apx − ap2. This tangent intersects the y-axis at (0, − ap2).
7. The correct answer is (B).
If h(x) = f(x)g(x), then
h′(x) = f(x)g′(x) + g(x) f′(x) and
h′(1) = f (1)g′(1) + g (1) f′(1)
= (0)(5) + (− 1)(− 2) = 2.
8. The correct answer is (B).
If h(x) = f(g(x)), then
h′(x) = f′(g(x))g′(x) and
h′(2) = f′(g (2))g′(2)
⇒ h′(2) = f′(3)g′(2)
⇒ h′(2) = (− 1)(1) = − 1.
9. The correct answer is (D).
If f(x) is a continuous function and
f(5) = 2 and f′(5) = 3, then
f (5.01) = f(5) + 0.01 f′(5)
= 2 + 0.01(3) = 2.03.
10. The correct answer is (D).
Simplify the expression ![]() as
as 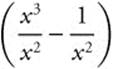 ,
,
which is equivalent to 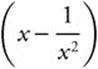 .
.
Thus,
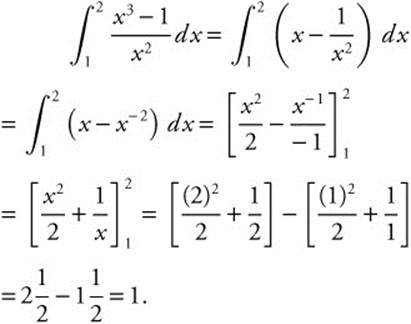
11. The correct answer is (A).
At the moment the surface area is 24 square inches, A = 6x2 = 24 ⇒ x2 = 4 ⇒ x = 2, so the edge of the cube is 2 inches. The surface area is changing so
![]()
and when the edge is 2 inches, 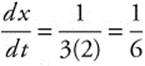 .
.
The volume V = s3 is changing at the rate
![]() . When the surface area is
. When the surface area is
24 square inches and the edge is 2 inches,
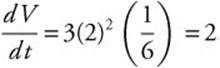 . The volume increasing
. The volume increasing
at 2 cubic inches per second.
12. The correct answer is (A).
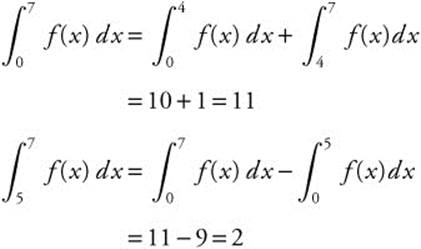
13. The correct answer is (E).
Integrate 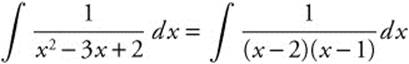 by partial fractions.
by partial fractions.
A(x − 1) + B(x − 2) = 1 ⇒ Ax + Bx = 0
⇒ A = − B. Substituting, − A − 2B = 1
⇒ − A + 2A = 1 and so A = 1, B = − 1. Then the integral becomes
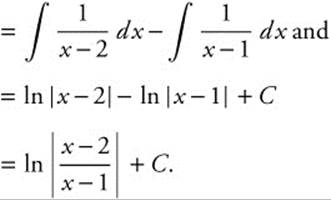
14. The correct answer is (D).
Since θ → 0 ⇒ 1 − cos θ → 0
and θ → 0 ⇒ 2 sin2 θ → 0,
![]() and is indeterminate.
and is indeterminate.
Differentiate ![]()
and ![]() .
.
Then, by L’Hôpital’s Rule,
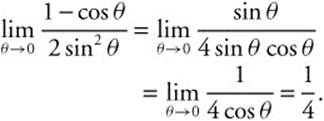
15. The correct answer is (B).
∫ xf(x) dx requires integration by parts. Let
u = f(x), du = f′(x) dx, dv = x dx, and
![]() . Then
. Then 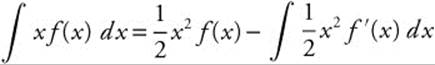 .
.
16. The correct answer is (A).
Differentiate x3 + 3xy + 2y3 = 17 implicitly.
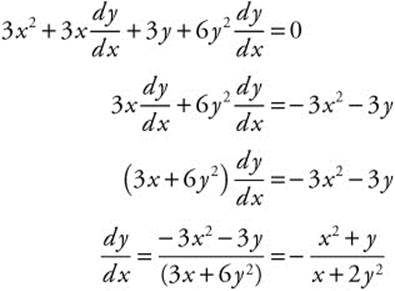
17. The correct answer is (E).
Rewrite 3 tan5(2x) as 3 [tan(2x)]5.
Thus, f′(x) = 15 [tan(2x)]4 [sec2(2x)](2)
= 30 [tan(2x)]4 [sec2(2x)].
18. The correct answer is (D).
Letting u = sin x gives us du = cos x dx
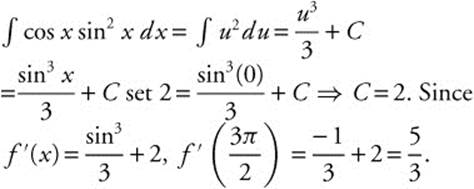
19. The correct answer is (A).
Separate ![]() as
as
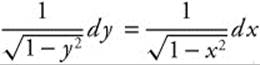 .
.
Integrate to produce sin−1(y)
= sin−1(x) + C. With the initial condition
y(0)= 1, sin−1(1) = sin−1(0) + C, ![]() .
.
So ![]()
![]() . Thus
. Thus ![]() .
.
20. The correct answer is (E).
The average value of f′(x) on [1, 3] is
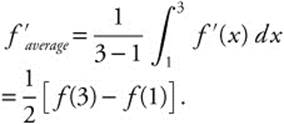 .
.
21. The correct answer is (E).
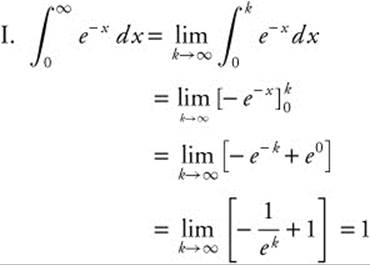
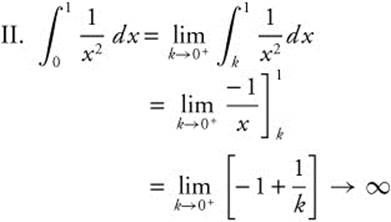
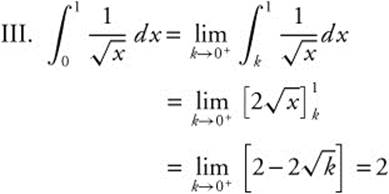
22. The correct answer is (B).
![]() and
and ![]() .
.
At t = 1, the acceleration vector is ⟨2, −6t⟩|t=1 = ⟨2, −6⟩.
23. The correct answer is (C).
Integrate 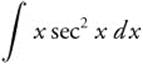 by parts. Let u = x,
by parts. Let u = x,
du = dx, dv = sec2 x dx, and v = tan x.
Then 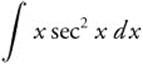 = x tan x − ∫ tan x dx = x tan x + ln |cos x| + C.
= x tan x − ∫ tan x dx = x tan x + ln |cos x| + C.
Comparing to the given information, 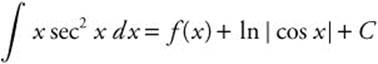 tells us that f(x) = x tan x.
tells us that f(x) = x tan x.
24. The correct answer is (B).
The integrand of
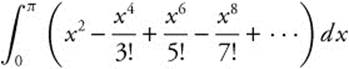 can be factored as
can be factored as
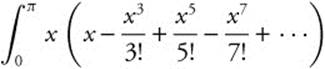
dx, which can be recognized as 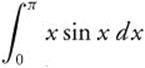 .
.
Integrate by parts with u = x, du = dx,
dv = sin x dx, and v = − cos x. Then
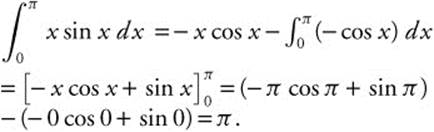
25. The correct answer is (E).
Consider each curve.
(I) ![]() ; − 2 ≤ x ≤ 2 defines a semicircle, not a circle. (II) x = cos t, y = sin t; 0 ≤ t ≤ 2π is a circle, but its radius is 1. (III) r = 4 cos θ;0 ≤ θ ≤ π is a circle of radius 2, but its center is at (2, 0). Therefore, none of these equations defines a circle of radius 2 with center at the origin.
; − 2 ≤ x ≤ 2 defines a semicircle, not a circle. (II) x = cos t, y = sin t; 0 ≤ t ≤ 2π is a circle, but its radius is 1. (III) r = 4 cos θ;0 ≤ θ ≤ π is a circle of radius 2, but its center is at (2, 0). Therefore, none of these equations defines a circle of radius 2 with center at the origin.
26. The correct answer is (E).
The area enclosed by a polar curve is
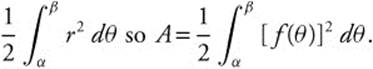
27. The correct answer is (C).
Begin with the known MacLaurin series
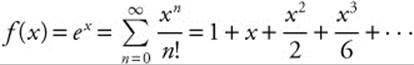 and substitute −4x for x.
and substitute −4x for x.
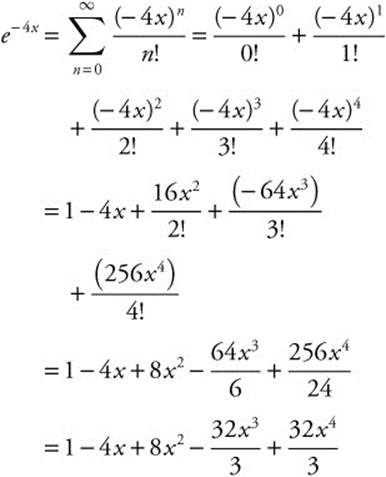
28. The correct answer is (D).
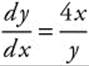 separates to y dy = 4x dx, which
separates to y dy = 4x dx, which
integrates to ![]()
⇒ 4x2 − y2 = − 2C. This form is the family of hyperbolas.
Section I—Part B
76. The correct answer is (E).
If ![]() , then ln y = (7 − 2x2) ln 5.
, then ln y = (7 − 2x2) ln 5.
Differentiating implicitly, 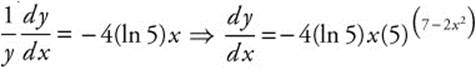 .
.
Evaluating at x = 1 produces ![]() .
.
77. The correct answer is (C).
If f(x) = 2x, f(3) = 8 and f′(x) = 2x ln 2, so
f′(3) = 8 ln 2. We could estimate f (3.03)
≈ f (3) + 0.03 f′(3), and since we know
23.03 ≈ 8.168, 8.168 ≈ 8 + 0.03 f′(3). Solve
![]()
78. The answer is (B).
Separate ![]() as
as ![]() . Integrate
. Integrate
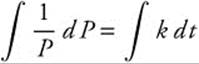 to produce
to produce
ln |P| = kt + c1. The initial condition tells us
P = c2ekt ⇒ 3 = c2e0 ⇒ c2 = 3 so P = 3ekt. In
2010, the population was 3.21 million. Thus
3.21 = 3e10k ⇒ 1.07 = e10k
⇒ ln 1.07 = 10k ⇒ 0.00677 = k. Therefore,
P = 3e0.00677t and P = 3e0.00677(20) = 3.435.
79. The correct answer is (D).
The function f(x) = 5x3 − 7x2 − 5
⇒ f′(x) = 15x2 − 14x. Set the first derivative equal to zero. 15x2 − 14x = 0
⇒ x (15x − 14) = 0 ⇒ x = 0 or ![]() .
.
Evaluate the second derivative
f″(x) = 30x − 14 at each of the critical points.
f′(0) = − 14
⇒ max ⇒
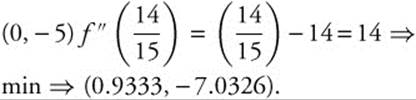
80. The correct answer is (A).
![]() . Since
. Since
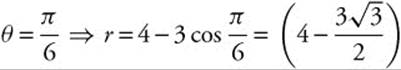 and
and
![]() ,
,
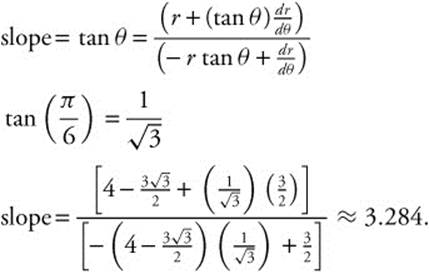
81. The correct answer is (A).
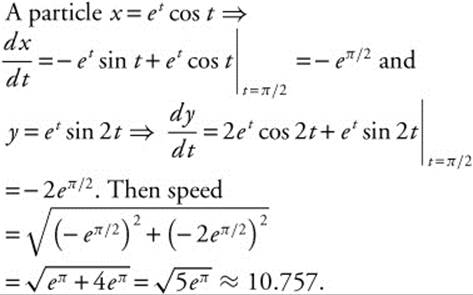
82. The correct answer is (B).
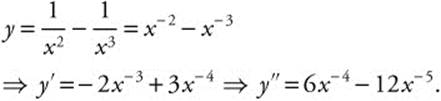
Set the second derivative equal to zero and
solve. ![]()
⇒ 6x − 12 = 0 ⇒ x = 2. Also y″ < 0
for x < 2 and y″ > 0 for x > 2.
83. The correct answer is (B).
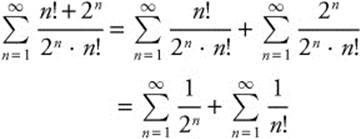
The series ![]() is a geometric series, so
is a geometric series, so
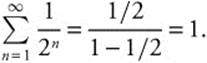
Compare the series ![]() to the known
to the known
MacLaurin series ![]() , and
, and
![]()
Therefore, ![]() .
.
84. The correct answer is (A).
The ellipse 4x2 + y2 = 1 has x −intercepts
![]() . The semicircles will have radius
. The semicircles will have radius
of ![]() and area of
and area of
![]() .
.
Then the volume is
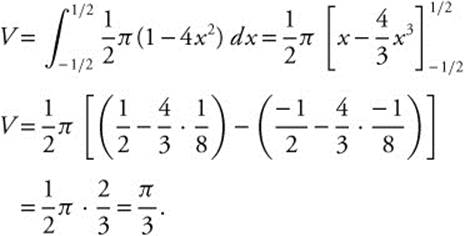
85. The correct answer is (D).
86. The correct answer is (B).
The series 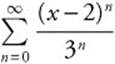 will converge when
will converge when
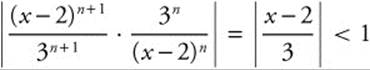 . This
. This
means ![]()
⇒ − 3 < x − 2 < 3 ⇒ − 1 < x < 5. When
x = − 1, the series becomes
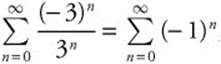 , which diverges. When
, which diverges. When
x = 5, the series becomes
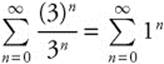 , which diverges. Therefore,
, which diverges. Therefore,
the interval of convergence is (− 1, 5).
87. The correct answer is (D).
If y = 4 − 3x − x2, ⇒ y′ = − 3 − 2x. The slope
of the tangent line is y′(1) = − 3 − 2(1) = − 5, and the point is (1, 0), since
y (1) = 4 − 3(1) − (1)2 = 0. The equation of the
tangent line is y − 0 = − 5(x − 1) or
y = − 5x + 5. The axis of symmetry of the
parabola is 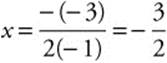 . Evaluating the
. Evaluating the
tangent equation when ![]() gives
gives
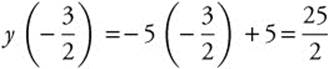 . The line
. The line
y= − 5x + 5 intersects the axis of symmetry at
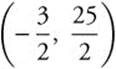 .
.
88. The correct answer is (A).
Let l be the length of the section of fence
parallel to the river and w be the length of the
two remaining sides. The cost of the fence is
C = 5(2w) + 7.50(l) = 9000. Set cost equal to
9000 and solve for l. 5(2w) + 7.50(l) = 9000
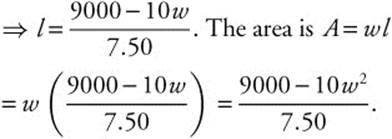
Differentiate ![]() and set the
and set the
derivative equal to zero.![]()
⇒ 9000 − 20w = 0 ⇒ w = 450. If the width is
450, the length ![]() ,
,
dA″ < 0; so the maximum area is
450 · 600 = 270,000.
89. The correct answer is (E).
![]()
Using your calculator you obtain 93π/5.
90. The correct answer is (B).
Separate ![]() into
into 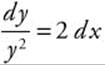 , and
, and
integrate 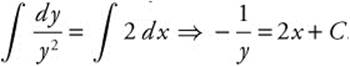
If y = − 1 when x = 1,
![]()
Thus 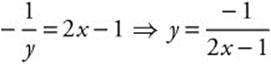 . If x = 2,
. If x = 2,
![]()
91. The correct answer is (D).
If 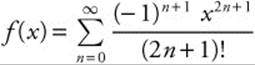 , then
, then
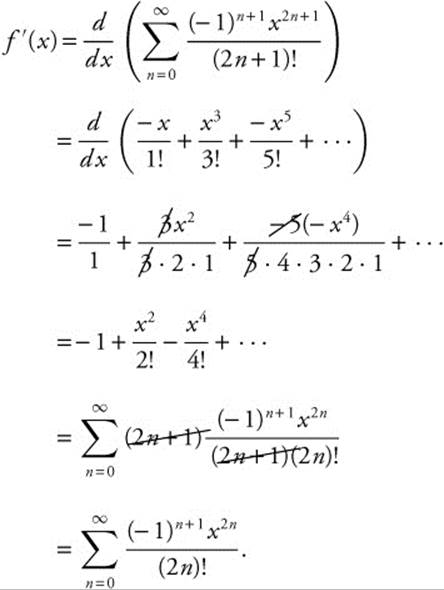
92. The correct answer is (A).
y = x3 + 2x ⇒ y′ = 3x2 + 2 ⇒ y″ = 6x. Set the second derivative equal to zero. y″ = 6x = 0 ⇒ x = 0. When x < 0, y″ < 0, and when x > 0, y″ > 0. The point of inflection is (0, 0) and the slope at that point is ![]() . The equation of the tangent line to the curve at its point of inflection is y − 0 = 2(x − 0) ⇒ y = 2x.
. The equation of the tangent line to the curve at its point of inflection is y − 0 = 2(x − 0) ⇒ y = 2x.
Solutions to BC Practice Exam 2—Section II
Section II—Part A
1. (A) Determine the point of intersection of the two curves, either by calculator, or algebraically. cos x = 1 − cos x ![]() , so
, so ![]() is the x −coordinate of the point of intersection. The area of region R is
is the x −coordinate of the point of intersection. The area of region R is
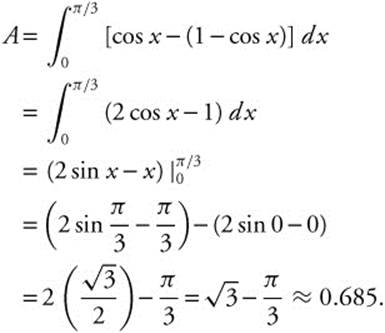
(B) The volume of the solid created when the region R is revolved about the x −axis can be found by the method of washers.
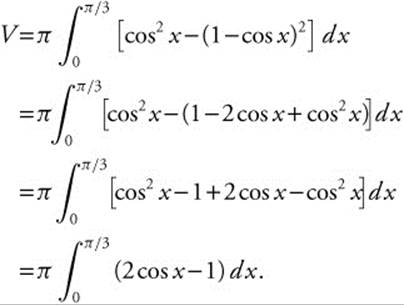
Integrate and evaluate.
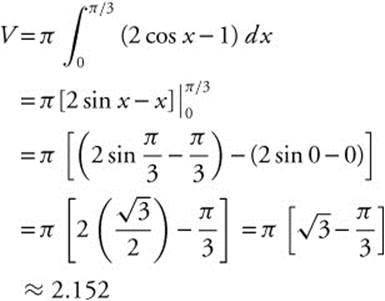
(C) To find the volume of the solid that has R as its base, and cross sections that are isosceles triangles of height x, recognize that the area of each cross section is ![]() , so the volume is
, so the volume is 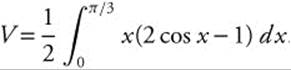 . Integrate by parts, with u = x, du = dx, dv = (2 cos x − 1)dx, and v = 2 sin x − x.
. Integrate by parts, with u = x, du = dx, dv = (2 cos x − 1)dx, and v = 2 sin x − x.
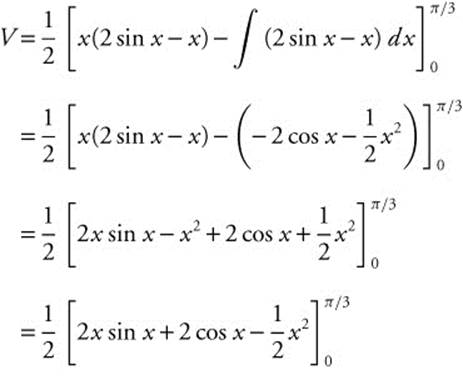
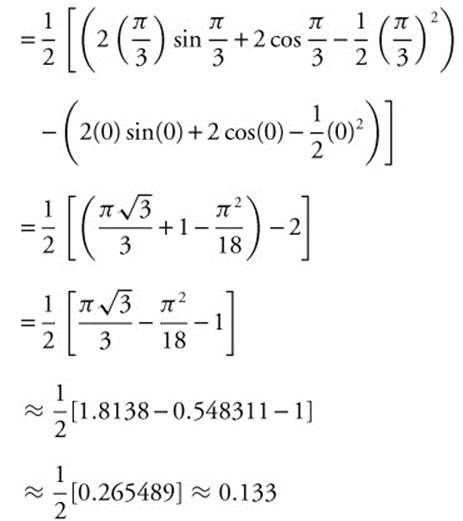
Or simply use your calculator and obtain the same results.
2. (A) The amount of oil leaked out after 6 minutes
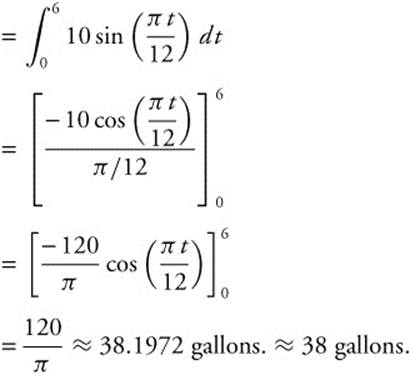
(B) Average amount of oil leaked out per minute from t = 0to t = 6:
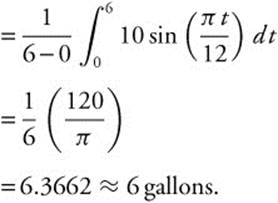
(C) The amount of oil in the drum at t:
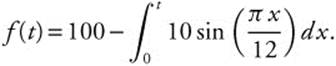
(D) Let a be the value of t:
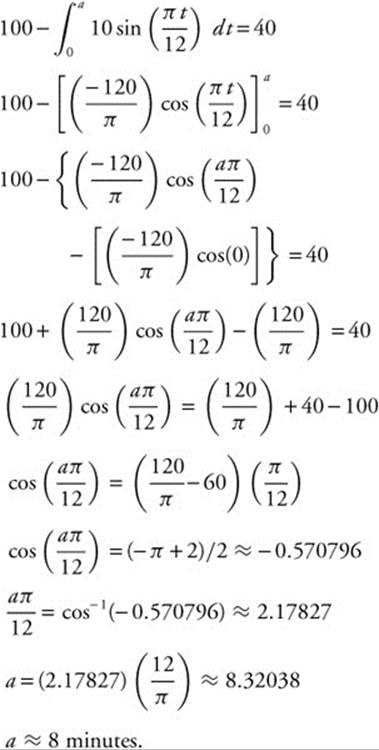
Section II—Part B
3. If
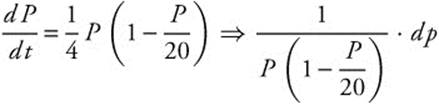
![]() Integrate
Integrate
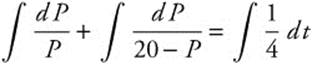
![]()
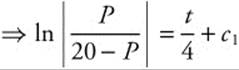 . Exponentiate for
. Exponentiate for
![]() and isolate P. Thus,
and isolate P. Thus,
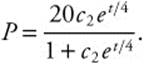
(A) If P(0) = 4, ![]()
![]() , so
, so ![]() and
and
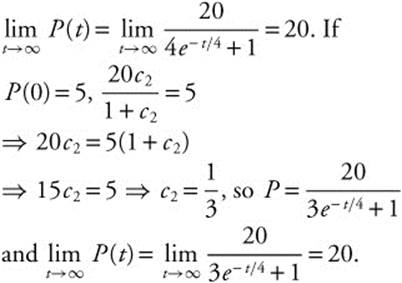
(B) The rate of growth is given by
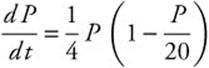 . To find the maximum value of the growth function, take the derivative of the function.
. To find the maximum value of the growth function, take the derivative of the function.
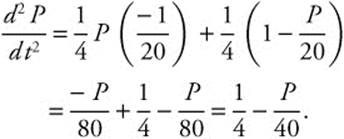
Set ![]()
When P = 10, 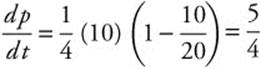 .
.
The population is growing fastest, at a rate of 125%, when the population is 10.
(C) Separate ![]() to
to
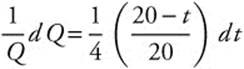 and integrate.
and integrate.
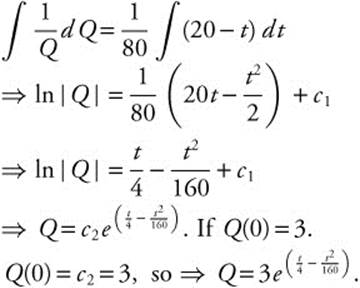
(D) For the function found in part (C), as t
increases, ![]() so
so
![]() ; therefore,
; therefore,
![]()
4. (A) (See Figure DS-15.) Since f increases on (− 2, 2) and decreases on (2, 5), f has a relative maximum at x = 2.
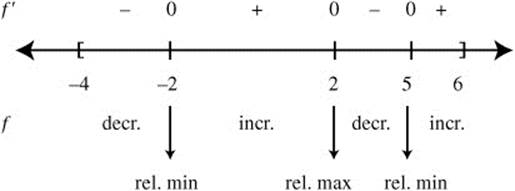
Figure DS-15
(B) Since f decreases on (− 4, − 2) and increases on (− 2, 2), f has a relative minimum at x = − 2. Since f decreases on (2, 5) and increases on (5, 6), f has a relative minimum at x = 5.
(C) (See Figure DS-16.)
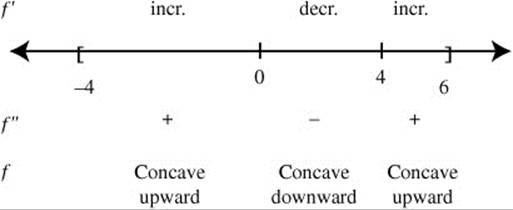
Figure DS-16
Since f′ is increasing on the intervals (− 4, 0) and (4, 6), f″ > 0 on (− 4, 0) and (4, 6).
(D) A change of concavity occurs at x = 0 and at x = 4. (See Figure DS-16). Thus, f has a point of inflection at x = 0 and at x = 4.
(E) (See Figure DS-17.)
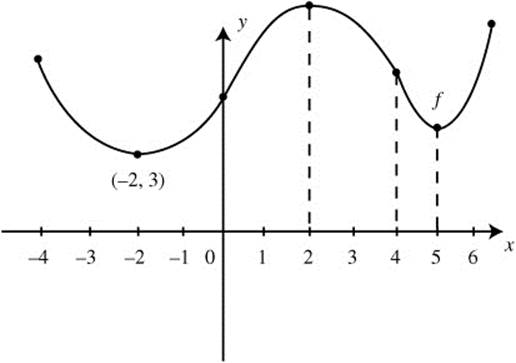
Figure DS-17
5.
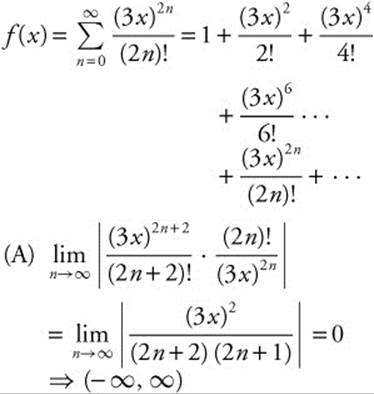
(B) The first terms and the general term for the MacLaurin series for
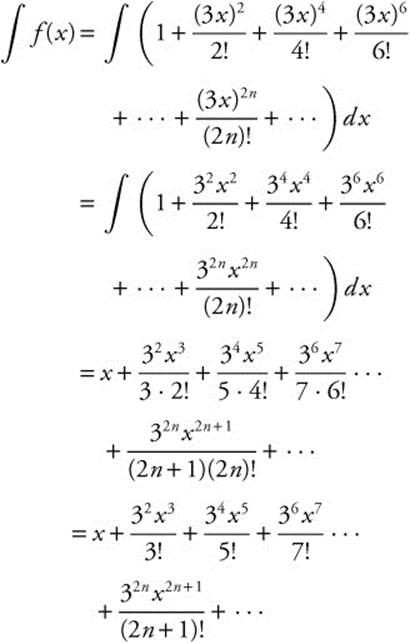
(C) The first four terms of f′(x):
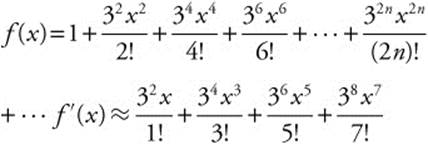
The approximate value of
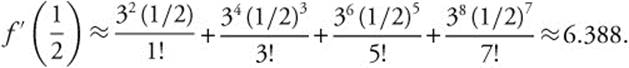
6. (A) x2y2 = 4. Differentiating using product and chain rules:
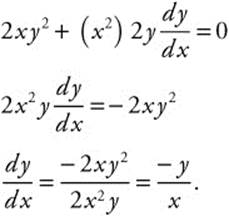
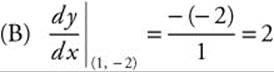
Equation of tangent: y − (2) = 2(x − 1)
⇒ y + 2 = 2x − 2
or y = 2x − 4.
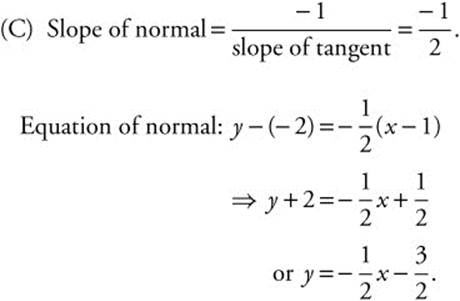
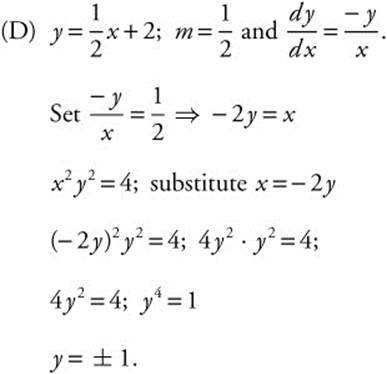
If y = 1, x2y2 = 4 ⇒ x2(1)2 = 4
⇒ x2 = 4 ⇒ x = ± 2.
If y = − 1, x2y2 = 4 ⇒ x2(− 1)2 = 4
⇒ x2 = 4 ⇒ x = ± 2.
Possible points for P are: (2, 1), (2, − 1), (− 2, 1), and (− 2, − 1).
The only point on the tangent line is (− 2, 1).
Scoring Sheet for BC Practice Exam 2