High School Geometry Unlocked (2016)
Chapter 1. Translation, Reflection, Rotation
GOALS
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
•Perform translations, reflections, and rotations of figures
•Describe translations, reflections, and rotations of figures
•Write algebraic expressions for translations, reflections, and rotations of figures
•Perform and describe translations and reflections of functions
•Identify congruent and similar figures
•Classify figures as having reflectional symmetry and/or rotational symmetry
Lesson 1.1. Transformations
In everyday language, transformation means change. In geometry, transformation refers to changing a figure. You can transform a figure by moving, flipping, turning, or resizing it.
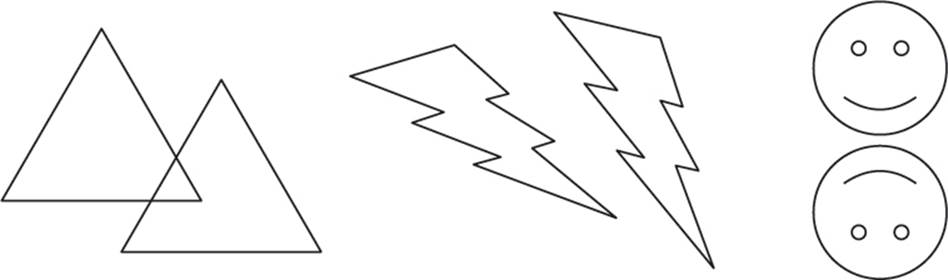
Examples of Transformations
Two figures are congruent if they have the same shape and size. If a figure is moved, flipped, or turned, the original and resulting figures are still congruent. These types of transformations are called rigid motions—the location or position of the figure may change, but its shape and size are the same. In other words, lengths and angles of the figure remain the same. (Note that resizing is NOT a type of rigid motion.)
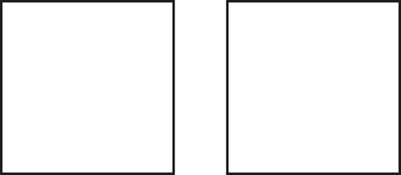
Example of Congruent Figures
When discussing transformations, we refer to the original figure as the pre-image, and the new, transformed figure as the image. In the figure above, the image and pre-image are congruent.

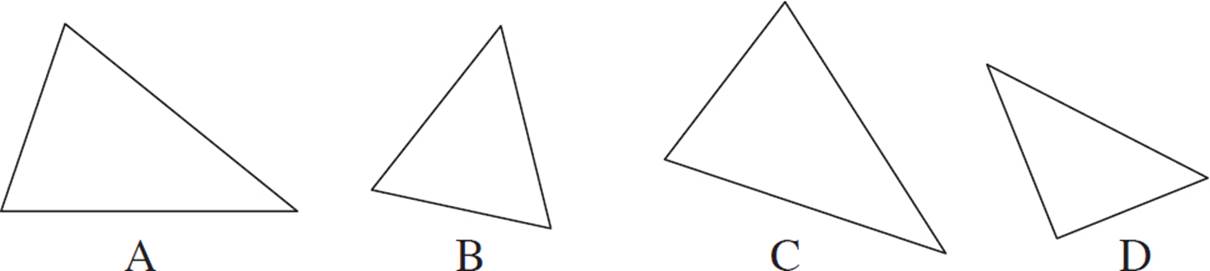
Which of the triangles is congruent to triangle A?
(B) (C) (D)
Note that for this question, we’re just basing our answer on the way the triangles look. If there were additional information given, such as angle measures and/or side lengths, that would have provided additional support for our answer.
Triangle C is congruent to triangle A. The two triangles have the same shape and size, even though triangle C is rotated slightly.
Triangle B is not congruent to triangle A. Triangle B appears to be the same shape, but it is noticeably smaller than triangle A.
Triangle D is not congruent to triangle A. The two triangles have noticeably different shapes.

Two figures are similar if they have the same shape, but they may have different sizes. If a figure is proportionally resized, the original and resulting figures are similar, but not congruent.
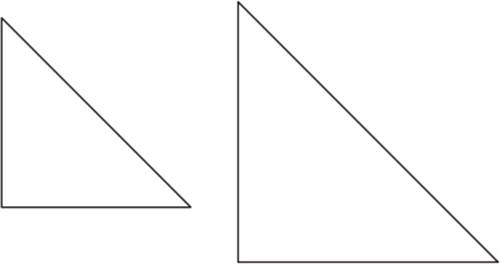
Example of Similar Figures

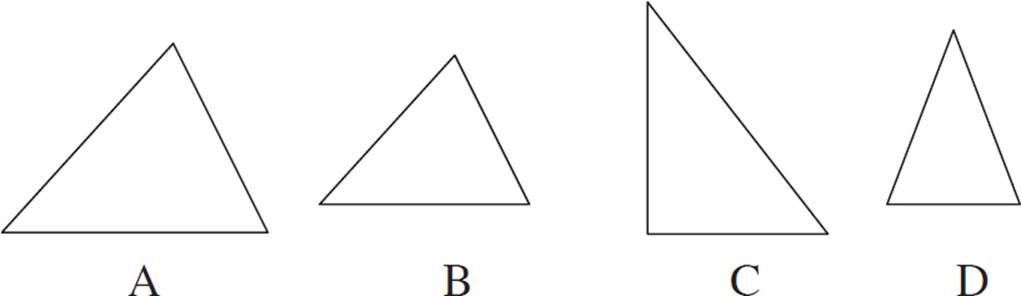
Which of the triangles is similar to triangle A?
(B) (C) (D)
Note that for this question, we’re just basing our answer on the way the triangles look. If there were additional information given, such as angle measures and/or side lengths, that would have provided additional support for our answer.
Triangle B is similar to triangle A. The two triangles have the same shape, but different sizes.
Triangle C is not similar to triangle A. The two triangles have noticeably different shapes.
Triangle D is not similar to triangle A. The two triangles have noticeably different shapes.