SAT SUBJECT TEST MATH LEVEL 1
PLANE GEOMETRY
![]()
CHAPTER 9 Triangles
![]()
PERIMETER AND AREA
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of the three sides.
EXAMPLE 6: To find the perimeter of an equilateral triangle whose height is 12, note that the height divides the triangle into two 30-60-90 right triangles. In the figure below, by KEY FACT H8,
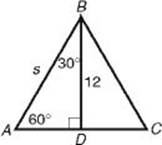
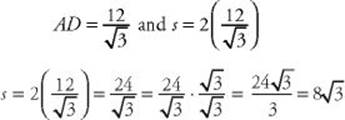
So the perimeter is 3s =24 ![]() .
.
Key Fact H9
TRIANGLE INEQUALITY
• The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side.
• The difference of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is less than the length of the third side.
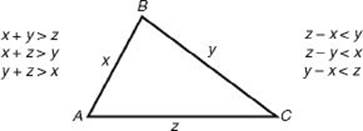
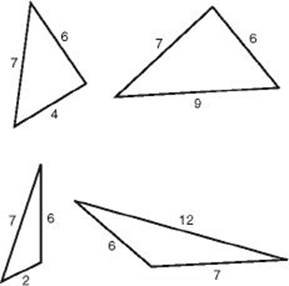
EXAMPLE 7: A teacher asked her class to draw triangles in which the lengths of two of the sides were 6 inches and 7 inches and the length of the third side was also a whole number of inches. To determine how many different triangles the class could draw, note that if x represents the length of the third side, then by KEY FACT H9, 6 + 7 > x, so x < 13. Also, 7 – 6 < x, so x > 1. So x could have 11 different values: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12. The perimeters of the triangles are the integers from 15 to 25. The following diagram illustrates four of the triangles the class could have drawn.
Frequently, questions on the Math 1 test require you to calculate the area of a triangle.
Key Fact H10
The area of a triangle is given by ![]() bh, where b and h are the lengths of the base and height, respectively.
bh, where b and h are the lengths of the base and height, respectively.
(1) Any side of the triangle can be taken as the base.
(2) The height (which is also called an altitude) is a line segment drawn perpendicular to the base from the opposite vertex.
(3) In a right triangle, either leg can be the base and the other the height.
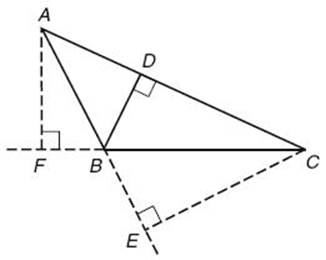
(4) If one endpoint of the base is the vertex of an obtuse angle, then the height will be outside the triangle.
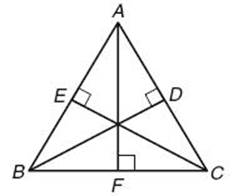
(5) In each figure at the top of this page
• If ![]() is the base,
is the base, ![]() is the height.
is the height.
• If ![]() is the base,
is the base, ![]() is the height.
is the height.
• If ![]() is the base,
is the base, ![]() is the height.
is the height.
TIP 
The height can be outside the triangle. See ![]() in the diagram shown below.
in the diagram shown below.
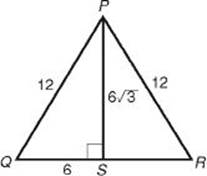
EXAMPLE 8: To find the area of equilateral triangle PQR, below, whose sides are 12, draw in altitude ![]() .
. ![]() PQS is a 30-60-90 right triangle, and so by KEY FACT H8, QS = 6 and PS =6
PQS is a 30-60-90 right triangle, and so by KEY FACT H8, QS = 6 and PS =6![]() . Finally, the area of
. Finally, the area of
![]()
Replacing 12 by s in Example 8 yields a useful formula.
Key Fact H11
if A represents the area of an equilateral triangle with side s, then ![]() .
.
Smart Strategy
Learning this formula for the area of an equilateral triangle can save you time.