Barron's SAT Subject Test Math Level 2, 10th Edition (2012)
Part 3. MODEL TESTS
Answer Sheet
MODEL TEST 6

Model Test 6
![]()
|
The following directions are for the print book only. Since this is an e-Book, record all answers and self-evaluations separately. |
Tear out the preceding answer sheet. Decide which is the best choice by rounding your answer when appropriate. Blacken the corresponding space on the answer sheet. When finished, check your answers with those at the end of the test. For questions that you got wrong, note the sections containing the material that you must review. Also, if you do not fully understand how you arrived at some of the correct answers, you should review the appropriate sections. Finally, fill out the self-evaluation chart in order to pinpoint the topics that give you the most difficulty.
|
50 questions: 1 hour Directions: Decide which answer choice is best. If the exact numerical value is not one of the answer choices, select the closest approximation. Fill in the oval on the answer sheet that corresponds to your choice. Notes: (1) You will need to use a scientific or graphing calculator to answer some of the questions. (2) You will have to decide whether to put your calculator in degree or radian mode for some problems. (3) All figures that accompany problems are plane figures unless otherwise stated. Figures are drawn as accurately as possible to provide useful information for solving the problem, except when it is stated in a particular problem that the figure is not drawn to scale. (4) Unless otherwise indicated, the domain of a function is the set of all real numbers for which the functional value is also a real number. |
|
Reference Information. The following formulas are provided for your information. Volume of a right circular cone with radius r and height h: Lateral area of a right circular cone if the base has circumference C and slant height is l: Volume of a sphere of radius r: Surface area of a sphere of radius r: S = 4πr2 Volume of a pyramid of base area B and height h: |
1. If 10y – 6 = 3k(5y – 3) for all y, then k =
(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
(E) 2
2. For what values of x and y is |x – y| ![]() |y – x|?
|y – x|?
(A) x < y
(B) y < x
(C) x > 0 and y < 0
(D) for no value of x and y
(E) for all values of x and y
3. If (a,b) is a solution of the system of equations 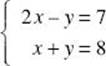 , then the difference, a – b, equals
, then the difference, a – b, equals
(A) –12
(B) –10
(C) 0
(D) 2
(E) 4
4. If f(x) = x – 1, g(x) = 3x, and h(x) = ![]() , then f –1(g(h(5))) =
, then f –1(g(h(5))) =
(A) 4
(B) 2
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
(E) ![]()
5. A sphere is inscribed in a cube. The ratio of the volume of the sphere to the volume of the cube is
(A) 0.79:1
(B) 1:2
(C) 0.52:1
(D) 1:3.1
(E) 0.24:1
6. Find y if the slope of the line containing the point (–1, 3) and (4, y) is 0.75.
(A) 0.75
(B) 1
(C) 6.75
(D) 8
(E) 9.67
7. The nature of the roots of the equation 3x4 + 4x3 + x – 1 = 0 is
(A) three positive real roots and one negative real root
(B) three negative real roots and one positive real root
(C) one negative real root and three complex roots
(D) one positive real root, one negative real root, and two complex roots
(E) two positive real roots, one negative real root, and one complex root
8. For what value(s) of k is x2 + 3x + k divisible by x + k?
(A) only 0
(B) only 0 or 2
(C) only 0 or –4
(D) no value of k
(E) any value of k
9. What number should be added to each of the three numbers 3, 11, and 27 so that the resulting numbers form a geometric sequence?
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5
(E) 6
10. What is the equation of the set of points that are 5 units from point (2,3,4)?
(A) 2x + 3y + 4z = 5
(B) x2 + y2 + z2 – 4x – 6y – 8z = 25
(C) (x – 2)2 + (y – 3)2 + (z – 4)2 = 25
(D) x2 + y2 + z2 = 5
(E) ![]()
11. If 3x3/2 = 4, then x =
(A) 1.1
(B) 1.2
(C) 1.3
(D) 1.4
(E) 1.5
12. If f(x) = x3 – 4, then the inverse of f =
(A) – x3+4
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
(E) ![]()
13. If f is an odd function and f(a) = b, which of the following must also be true?
I. f(a) = –b
II. f(–a) = b
III. f(–a) = –b
(A) only I
(B) only II
(C) only III
(D) only I and II
(E) only II and III
14. For all ![]() , tan
, tan![]() + cos
+ cos![]() + tan(–
+ tan(–![]() ) + cos(–
) + cos(–![]() ) =
) =
(A) 0
(B) 2tan![]()
(C) 2cos![]()
(D) 2(tan![]() + cos
+ cos![]() )
)
(E) 2
15. The period of the function f(x) = k cos kx is ![]() . The amplitude of f is
. The amplitude of f is
(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) 1
(D) 2
(E) 4
16. If ![]() , its graph will have
, its graph will have
(A) one horizontal and three vertical asymptotes
(B) one horizontal and two vertical asymptotes
(C) one horizontal and one vertical asymptote
(D) zero horizontal and one vertical asymptote
(E) zero horizontal and two vertical asymptotes
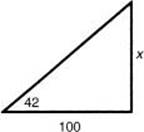
17. At a distance of 100 feet, the angle of elevation from the horizontal ground to the top of a building is 42°. The height of the building is
(A) 67 feet
(B) 74 feet
(C) 90 feet
(D) 110 feet
(E) 229 feet
18. A sphere has a surface area of 36π. Its volume is
(A) 84
(B) 113
(C) 201
(D) 339
(E) 905
19. A pair of dice is tossed 10 times. What is the probability that no 7s or 11s appear as the sum of the sides facing up?
(A) 0.08
(B) 0.09
(C) 0.11
(D) 0.16
(E) 0.24
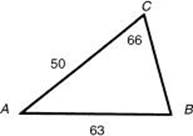
20. The lengths of two sides of a triangle are 50 inches and 63 inches. The angle opposite the 63-inch side is 66°. How many degrees are in the largest angle of the triangle?
(A) 66°
(B) 67°
(C) 68°
(D) 71°
(E) 72°
21. Which of the following is an equation of a line that is perpendicular to 5x + 2y = 8?
(A) 8x – 2y = 5
(B) 5x – 2y = 8
(C) 2x – 5y = 4
(D) 2x + 5y = 10
(E) ![]()
22. What is the period of the graph of the function ![]()
(A) 4π
(B) 2π
(C) π
(D) ![]()
(E) ![]()
23. For what values of k are the roots of the equation kx2 + 4x + k = 0 real and unequal?
(A) 0 < k < 2
(B) |k| < 2
(C) |k| > 2
(D) k > 2
(E) –2 < k < 0 or 0 < k < 2
24. A point moves in a plane so that its distance from the origin is always twice its distance from point (1,1). All such points form
(A) a line
(B) a circle
(C) a parabola
(D) an ellipse
(E) a hyperbola
25. If f(x) = 3x2 + 24x – 53, find the negative value of f –1(0).
(A) –58.8
(B) –9.8
(C) –8.2
(D) –1.8
(E) –0.2
26. The operation # is defined by the equation a # b = ![]() . What is the value of k if 3 # k = k # 2?
. What is the value of k if 3 # k = k # 2?
(A) ![]() 2.0
2.0
(B) ![]() 2.4
2.4
(C) ![]() 3.0
3.0
(D) ![]() 5.5
5.5
(E) ![]() 6.0
6.0
27. If 7x–1 = 6x, find x.
(A) –13.2
(B) 0.08
(C) 0.22
(D) 0.52
(E) 12.6
28. A red box contains eight items, of which three are defective, and a blue box contains five items, of which two are defective. An item is drawn at random from each box. What is the probability that one item is defective and one is not?
(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
(E) ![]()
29. If (log3 x)(log5 3) = 3, find x.
(A) 5
(B) 9
(C) 25
(D) 81
(E) 125
30.If ![]() and
and ![]() , then f(g(h(2))) =
, then f(g(h(2))) =
(A) 1.2
(B) 1.4
(C) 2.9
(D) 4.7
(E) 8.5
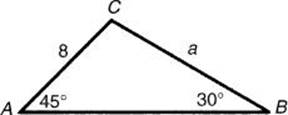
31. In ![]() ABC,
ABC, ![]() A = 45°,
A = 45°, ![]() B = 30°, and b = 8. Side a =
B = 30°, and b = 8. Side a =
(A) 6.5
(B) 11
(C) 12
(D) 14
(E) 16
32. The equations of the asymptotes of the graph of 4x2 – 9y2 = 36 are
(A) y = x and y = – x
(B) y = 0 and x = 0
(C) ![]() and
and ![]()
(D) ![]() and
and ![]()
(E) ![]() and
and ![]()
33. If g(x – 1) = x2 + 2, then g(x) =
(A) x2 – 2x + 3
(B) x2 + 2x + 3
(C) x2 – 3x + 2
(D) x2 + 2
(E) x2 – 2
34. If f(x) = 3x3 – 2x2 + x – 2, then f(i) =
(A) –2i – 4
(B) 4i – 4
(C) 4i
(D) –2i
(E) 0
35. If the hour hand of a clock moves k radians in 48 minutes, k =
(A) 0.3
(B) 0.4
(C) 0.5
(D) 2.4
(E) 5
36. If the longer diagonal of a rhombus is 10 and the large angle is 100°, what is the area of the rhombus?
(A) 37
(B) 40
(C) 42
(D) 45
(E) 50
37. Let ![]() and g(x) = 3x. The sum of all values of x for which f(x) = g(x) is
and g(x) = 3x. The sum of all values of x for which f(x) = g(x) is
(A) –8.5
(B) 0
(C) 8
(D) 9
(E) 9.4
38. How many subsets does a set with n elements have?
(A) n2
(B) 2n
(C) ![]()
(D) n
(E) n!
39. If f(x) = 23x – 5, find f –1(16).
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
40. For what positive value of n are the zeros of P(x) = 5x2 + nx + 12 in ratio 2:3?
(A) 0.42
(B) 1.32
(C) 4.56
(D) 15.8
(E) 25
41. If f(–x) = – f(x) for all x and if the point (–2, 3) is on the graph of f, which of the following points must also be on the graph of f ?
(A) (–3, 2)
(B) (2, –3)
(C) (–2, 3)
(D) (–2, –3)
(E) (3, –2)
42. A man piles 150 toothpicks in layers so that each layer has one less toothpick than the layer below. If the top layer has three toothpicks, how many layers are there?
(A) 15
(B) 17
(C) 20
(D) 148
(E) 11,322
43. If the circle x2 + y2 – 2x – 6y = r2 – 10 is tangent to the line 12y = 60, the value of r is
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
44. If a0 = 0.4 and an + 1 = 2|an| – 1, then a5 =
(A) –0.6
(B) –0.2
(C) 0.2
(D) 0.4
(E) 0.6
45. If 5.21p = 2.86q, what is the value of ![]() ?
?
(A) –0.60
(B) 0.55
(C) 0.60
(D) 0.64
(E) 1.57
46. As ![]() , find the limit of the product
, find the limit of the product ![]() .
.
(A) 1.9
(B) 2.0
(C) 2.1
(D) 2.2
(E) 2.3
47. There is a linear relationship between the number of chirps made by a cricket and the air temperature. A least-squares fit of data collected by a biologist yields the equation:
estimated temperature in °F = 22.8 + (3.4) (the number of chirps per minute)
What is the estimated increase in temperature that corresponds to an increase of 5 chirps per minute?
(A) 3.4°F
(B) 17.0°F
(C) 22.8°F
(D) 26.2°F
(E) 39.8°F
48. If the length of the diameter of a circle is equal to the length of the major axis of the ellipse whose equation is x2 + 4y2 – 4x + 8y – 28 = 0, to the nearest whole number, what is the area of the circle?
(A) 28
(B) 64
(C) 113
(D) 254
(E) 452
49. The force of the wind on a sail varies jointly as the area of the sail and the square of the wind velocity. On a sail of area 50 square yards, the force of a 15-mile-per-hour wind is 45 pounds. Find the force on the sail if the wind increases to 45 miles per hour.
(A) 135 pounds
(B) 225 pounds
(C) 405 pounds
(D) 450 pounds
(E) 675 pounds
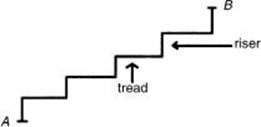
50. If the riser of each step in the drawing above is 6 inches and the tread is 8 inches, what is the value of |AB|?
(A) 40 inches
(B) 43.9 inches
(C) 46.6 inches
(D) 48.3 inches
(E) 50 inches

If there is still time remaining, you may review your answers.
Answer Key
MODEL TEST 6
|
|
|
|
ANSWERS EXPLAINED
The following explanations are keyed to the review portions of this book. The number in brackets after each explanation indicates the appropriate section in the Review of Major Topics (Part 2). If a problem can be solved using algebraic techniques alone, [algebra] appears after the explanation, and no reference is given for that problem in the Self-Evaluation Chart at the end of the test.
An asterisk appears next to those solutions in which a graphing calculator is necessary.
1. (B) Divide both sides by 5y – 3 to have the k-term on its own, ![]() = 3k. Factor out 2 from the numerator and then divide common terms,
= 3k. Factor out 2 from the numerator and then divide common terms, ![]() = 2 = 3k. Divide both sides by 3 to get k =
= 2 = 3k. Divide both sides by 3 to get k = ![]() . [algebra]
. [algebra]
2. (E) Since |x – y| and |y – x| both represent the distance between x and y, they must be equal, and they are equal for any values of x and y. [1.6]
3. (D) Adding the equations gives 3x = 15. x = 5 and y = 3. a – b = 2. [1.2]
4. (A) h(5) = 1. g (1) = 3. Interchange x and y to find that f –1(x) = x + 1, and so f –1(3) = 4. [1.1]
5. * (C) Diameter of sphere = side of cube.
Volume of sphere = ![]() .
.
Volume of cube = s3 = (2r)3 = 8r3. 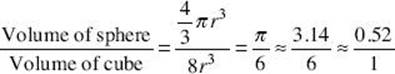 [2.2]
[2.2]
6. (C) The desired slope is ![]() . Cross-multiply and solve for y: 4y – 12 = 15, so y = 6.75. [algebra]
. Cross-multiply and solve for y: 4y – 12 = 15, so y = 6.75. [algebra]
7. * (D) Plot the graph of y = 3x4 + 4x3 + x – 1 in the standard window. Observe that the graph crosses the x-axis twice—once at a positive x value and once at a negative one. Since the function is a degree 4 polynomial, there are 4 roots, so the other two must be complex conjugates. [1.2]
8. (B) If x2 + 3x + k is divisible by x + k, then (–k)2 + 3(–k) + k = 0, or k2 – 2k = 0. Factoring and solving yields the correct answer choice. [1.2]
9. (D) If x is the number, then to have a geometric sequence, ![]() .
.
Cross-multiplying yields 121 + 22x + x2 = 81 + 30x + x2, and subtracting x2 and solving gives the desired solution.
An alternative solution is to backsolve. Determine which answer choice yields a sequence of 3 integers with a common ratio. [3.4]
10. (C) The set of points represents a sphere with equation (x – 2)2 + (y – 3)2 + (z – 4)2 = 52. [2.2]
11. * (B) Plot the graph of y = 3x3/2 – 4 in the standard window and use CALC/zero to find the correct answer choice.
An alternative solution is to divide the equation by 3 to get x3/2 = ![]() and then raise both sides to the
and then raise both sides to the ![]() power:
power: ![]() . [1.4]
. [1.4]
12. (B) Let y = f(x) = x3 – 4. To get the inverse, interchange x and y and solve for y. x =y3 – 4. y = ![]() . [1.1]
. [1.1]
13. (C) Use the definition of an odd function. If f(a) = b, then f(–a) = –b. Only III is true. [1.1]
14. (C) Tangent is an odd function, so tan(–![]() ) = –tan
) = –tan![]() , and cosine is an even function, so cos(–
, and cosine is an even function, so cos(–![]() ) = cos
) = cos![]() . Therefore, the sum in the problem is 2cos
. Therefore, the sum in the problem is 2cos![]() . [1.3]
. [1.3]
15. (E) Period = ![]() . k = 4. Amplitude = 4. [1.3]
. k = 4. Amplitude = 4. [1.3]
16. * (C) Plot the graph of ![]() in the standard window and observe one vertical asymptote (x = 2) and one horizontal asymptote (y = 0). [1.2]
in the standard window and observe one vertical asymptote (x = 2) and one horizontal asymptote (y = 0). [1.2]
17. * (C) Tan 42° = ![]() , so x = 100 tan 42
, so x = 100 tan 42 ![]() 90. [1.3]
90. [1.3]
18. * (B) 4πr2 = 36π. r2 = 9. r = 3. V= ![]() . [2.2]
. [2.2]
19. * (A) There are six ways to get a 7 and two ways to get an 11 on two dice, and so there are 36 – 8 = 28 ways to get anything else. Therefore, P(no 7 or 11) = P(always getting something else) = ![]() . [4.2]
. [4.2]
20. * (C) Use the law of sines: ![]() . B = sin–1(0.725)
. B = sin–1(0.725) ![]() 46° and
46° and ![]() A = 180 – 46 – 66 = 68°. [1.3]
A = 180 – 46 – 66 = 68°. [1.3]
21. (C) Solve the equation for y to find the slope of the line is – ![]() . The slope of a perpendicular line is
. The slope of a perpendicular line is ![]() . Inspection of the answer choices yields C as the correct answer. [1.2]
. Inspection of the answer choices yields C as the correct answer. [1.2]
22. * (B) With your calculator in radian mode, plot the graph of y = sin x/(1 + cos x) and observe that the period is 2π.
An alternative solution is to use the identity tan ![]() and the fact that the period of tan x is π to deduce the period of tan
and the fact that the period of tan x is π to deduce the period of tan ![]() as
as ![]() . [1.3]
. [1.3]
23. (E) b2 – 4ac > 0. b2 – 4ac = 16 – 4k2 > 0. 4 > k2. So –2 < k < 2. However, k ![]() 0 because if k = 0, there would no longer be a quadratic equation. [1.2]
0 because if k = 0, there would no longer be a quadratic equation. [1.2]
24. (B) If (x,y) represents any of the points, ![]() x2 + y2 = 4(x2 – 2x + y2 – 2y + 2), or 3x2 + 3y2 – 8x –8y + 8 = 0. Since the coefficients of x2 and y2 are equal, the points that satisfy this equation form a circle. [2.1]
x2 + y2 = 4(x2 – 2x + y2 – 2y + 2), or 3x2 + 3y2 – 8x –8y + 8 = 0. Since the coefficients of x2 and y2 are equal, the points that satisfy this equation form a circle. [2.1]
25. * (B) Find f –1(0) means to find a value of x that makes 3x2 + 24x – 53 = 0. Use the Quadratic Formula to evaluate the solutions and then use your calculator to find the decimal approximation to the negative solution. [1.2]
26. * (B) Plot the graphs of ![]() and
and ![]() in the standard window, and use CALC/intersect to find the points of intersection ±2.4.
in the standard window, and use CALC/intersect to find the points of intersection ±2.4.
An alternative solution is to evaluate ![]() and
and ![]() . Setting these two equal to each other and multiplying both sides by 6k yields 18 – 2k2 = 3k2 – 12, or k2 = 6. Therefore,
. Setting these two equal to each other and multiplying both sides by 6k yields 18 – 2k2 = 3k2 – 12, or k2 = 6. Therefore, ![]() . [1.1]
. [1.1]
27. * (E) Enter 7^(x – 1) – 6^x into Y1, and generate an Auto table with TblStart = –14 and ![]() tbl = 1. Scan through values of x and observe a change in the sign of Y1 between x = 12 and x = 13. Thus, E is the correct answer choice.
tbl = 1. Scan through values of x and observe a change in the sign of Y1 between x = 12 and x = 13. Thus, E is the correct answer choice.
An alternative solution is to take log7 of both sides to get x – 1 = log7 6x= x log7 6 = ![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore, ![]() , so
, so ![]() . [1.4]
. [1.4]
28. (D) Probability that an item from the red box is defective and an item from the blue box is good = ![]() . Probability that an item from the red box is good and that an item from the blue box is defective =
. Probability that an item from the red box is good and that an item from the blue box is defective = ![]() . Since these are mutually exclusive events, the answer is
. Since these are mutually exclusive events, the answer is ![]() . [4.2]
. [4.2]
29. * (E) By the change-of-base theorem, log3 x = ![]() . Therefore, log5 x = 3 and x = 53 = 125.
. Therefore, log5 x = 3 and x = 53 = 125.
30. * (A) Enter f into Y1; g into Y2; and h into Y3. Then return to the Home Screen and evaluate Y1(Y2(Y3(2))) to get the correct answer choice.
An alternative solution is to evaluate each function, starting with h in turn:![]() . [1.1]
. [1.1]
31. * (B) Use the law of sines: ![]() . Therefore
. Therefore ![]() . [1.3]
. [1.3]
32. (C) From this form of the equation of the hyperbola, ![]() , the equations of the asymptotes can be found from
, the equations of the asymptotes can be found from ![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]() . [2.1]
. [2.1]
33. (B) Since x = (x – 1 + 1), g(x) = g((x – 1) + 1) = (x + 1)2 + 2 = x2 + 2x + 3. [3.1]
34. * (D) Evaluate f(i) = 3i3 – 2i2 + i – 2 = –2i on your graphing calculator. [3.2]
35. * (B) In 1 hour, the hour hand moves ![]() of the way around the clock, or
of the way around the clock, or ![]() radians.
radians. ![]() . [1.3]
. [1.3]
36. * (C) Diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular; they bisect each other, and they bisect angles of the rhombus. From the figure below, tan 40° = ![]() .
.![]() [1.3]
[1.3]
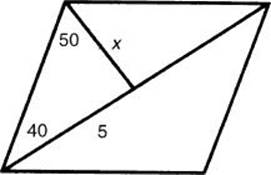
37. * (E) Plot the graphs of f and g in a [–10,15] by [–10, 50] window. One point of intersection is the origin. Find the other by using CALC/intersection to get the correct answer choice.
An alternative solution is to set ![]() , square both sides, and factor out x to get x(x2 – 9x – 4) = 0. Use the Quadratic Formula with the second factor to find the solutions x
, square both sides, and factor out x to get x(x2 – 9x – 4) = 0. Use the Quadratic Formula with the second factor to find the solutions x ![]() –0.4,9.4, and observe that the first does not satisfy the original equation. Thus, the two solutions are 0 and 9.4, resulting in the correct answer choice. [1.2]
–0.4,9.4, and observe that the first does not satisfy the original equation. Thus, the two solutions are 0 and 9.4, resulting in the correct answer choice. [1.2]
38. (B) Each element is either in a subset or not, so there are 2 choices for each of n elements. This yields 2 × 2 × · · · × 2 (n factors) = 2nsubsets. [3.1]
39. (C) This problem is most readily solved by substituting each answer choice into f to determine which produces the value 16. Since f(3) = 16, f –1(16) = 3. [1.4]
40. * (D) If the zeros of P(x) are in the ratio 2 : 3, they must take the form 2k and 3k for some value k, and (x – 2k)(x – 3k) = x2 – 5k + 6k2 = 0. Dividing P(x) by 5 and equating coefficients yields ![]() and
and ![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore, ![]() . Since the problem asks for a positive value of n, we use
. Since the problem asks for a positive value of n, we use ![]() , so n = –25k
, so n = –25k ![]() 15.8. [1.2]
15.8. [1.2]
41. (B) The function f is odd, so it is symmetrical about the origin. If (–2, 3) is on the graph of f, (2, –3) must also be on the graph.
An alternative solution is to conclude f(–2) = 3 since (–2, 3) is on the graph of f. Therefore, f(2) = –3, so the point (2, –3) is also on the graph. [1.1]
42. (A) This is an arithmetic series with t1 = 3, d = 1, and S = 150. ![]() . n = 15. [3.4]
. n = 15. [3.4]
43. * (B) Complete the square in the equation of the circle: (x – 1)2 + (y – 3)2 = r2. The center of the circle is at (1,3). If the circle is tangent to the line, then the distance between (1,3) and the line y = 5 is the radius of the circle, r. Therefore, r = 2. [2.1]
44. * (C) Enter 0.4 into your calculator, followed by 2|Ans| – 1 five times to get a5 = 0.2. An alternative solution is to evaluate each ai in turn: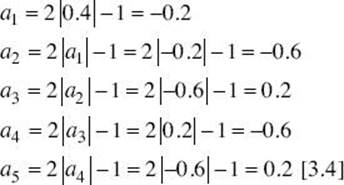
45. * (D) Take the logarithms (either base 10 or base e) to get p log 5.21 = q log 2.86. Divide both sides of this equation by q log 5.21 to get ![]() . [1.4]
. [1.4]
46. * (C) The infinite product can be approximated by using your calculator and a “large” value of n. The exponents ![]() form a geometric sequence with a first term of
form a geometric sequence with a first term of ![]() and constant ratio of
and constant ratio of ![]() . Enter prod
. Enter prod 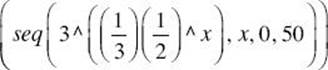 to approximate the product of the first 50 terms as 2.08. Evaluating the product of 75 terms yields the same approximation to 9 decimals, so choose C.
to approximate the product of the first 50 terms as 2.08. Evaluating the product of 75 terms yields the same approximation to 9 decimals, so choose C.
An alternative solution is to recognize that the desired product is equal to 31/3+1/6+1/12+..., so the exponent is the sum of an infinite geometric series with ![]() . Using the formula for the sum of such a series yields
. Using the formula for the sum of such a series yields ![]() so the desired product is 32/3
so the desired product is 32/3 ![]() 2.1. [3.4]
2.1. [3.4]
47. * (B) Temperature increases by 3.4°F for each additional chirp. Therefore, 5 additional chirps indicate an increase of 5(3.4) = 17.0°F. [1.2]
48. * (C) Complete the square on the ellipse formula, and put the equation in standard form: x2 – 4x + 4 + 4(y2 + 2y – 1) = 28 + 4 + 4. ![]() . This leads to the length of the major axis:
. This leads to the length of the major axis: ![]() = 12. Therefore, the radius of the circle is 6, and the area = 36π
= 12. Therefore, the radius of the circle is 6, and the area = 36π ![]() 113. [2.1]
113. [2.1]
49. (C) Since the velocity of a 45-mile-per-hour wind is 3 times that of a 15-mile-per-hour wind and the force on the sail is proportional to the square of the wind velocity, the force on the sail of a 45-mile-per-hour wind is 9 times that of a 15-mile-per-hour wind: 9 · 45 = 405. [algebra]
50. * (B) Total horizontal distance traveled = (4)(8) = 32. Total vertical distance traveled = (5)(6) = 30. If a coordinate system is superimposed on the diagram with A at (0,0), then B is at (32,30). Use the program on your calculator to find the distance between two points to compute the correct answer choice. [2.1]
Self-Evaluation Chart for Model Test 6
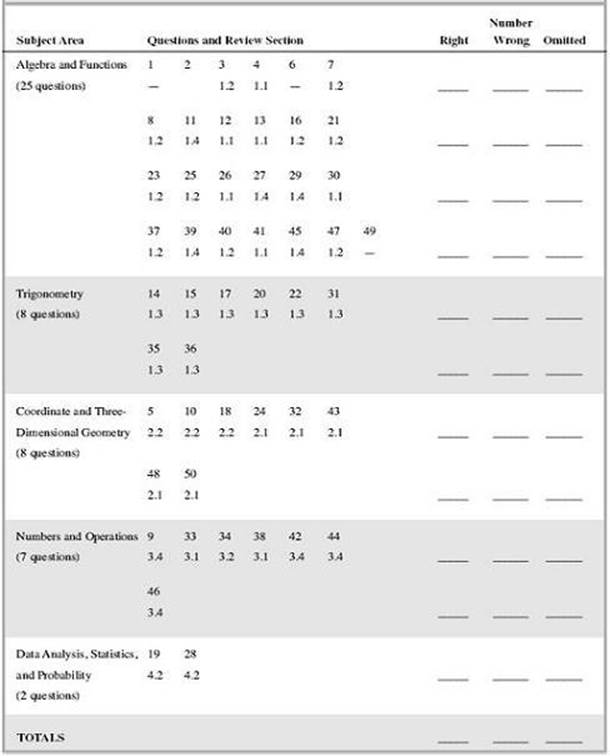
|
Evaluate Your Performance Model Test 6 |
|
|
Rating |
Number Right |
|
Excellent |
41–50 |
|
Very good |
33–40 |
|
Above average |
25–32 |
|
Average |
15–24 |
|
Below average |
Below 15 |
Calculating Your Score
Raw score R = number right – ![]() (number wrong), rounded = ______________
(number wrong), rounded = ______________
Approximate scaled score S = 800 – 10(44 – R) = ______________
If R ![]() 44, S = 800.
44, S = 800.