University Mathematics Handbook (2015)
X. Algebra
Chapter 6. Determinants
6.1 Second-Order and Third-Order Determinants
a. ![]() is called second-order determinant of matrix
is called second-order determinant of matrix ![]() and is denoted
and is denoted
![]()
b. The third order determinant of the matrix is the number:
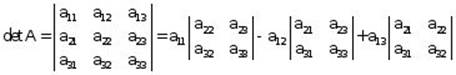
6.2 Permutations and ![]() -th Order Determinant
-th Order Determinant
a. The arrangement ![]() of
of ![]() integers
integers ![]() is called permutation.
is called permutation.
b. All ![]() permutations of
permutations of ![]() is denoted
is denoted ![]() .
.
c. Let ![]() be a permutation in
be a permutation in ![]() . A disorder in
. A disorder in ![]() is a pair of integers
is a pair of integers ![]()
![]() , when
, when ![]() , but
, but ![]() precedes
precedes ![]() in
in ![]() .
.
d. ![]() is an even permutation, if the number of disorders is even. On the other hand, it is an odd permutation if the number of disorders is odd. The sign of
is an even permutation, if the number of disorders is even. On the other hand, it is an odd permutation if the number of disorders is odd. The sign of ![]() is denoted by
is denoted by ![]() .
.
![]()
e. Switching the places of two elements in a permutation changes the evenness (or oddness).
f. For every square matrix ![]() the determinant is:
the determinant is:
![]()
when the sum includes all ![]() permutations
permutations ![]() of numbers
of numbers ![]() .
.
In other words: The determinant of matrix ![]() is the sum of
is the sum of ![]() elements in the form of
elements in the form of ![]() every one of which has a single representative of each row and each column with the corresponding sign.
every one of which has a single representative of each row and each column with the corresponding sign.
g. Scalar ![]() , called the cofactor
, called the cofactor ![]() of matrix
of matrix ![]() is an
is an ![]() -th order determinant of a matrix resulted from eliminating row
-th order determinant of a matrix resulted from eliminating row ![]() and column
and column ![]() of matrix
of matrix ![]() .
.
h. Expansion by row ![]() : The determinant of
: The determinant of ![]() -th order square matrix
-th order square matrix ![]() equals to
equals to ![]() .
.
6.3 Properties of Determinants
a. A determinant of upper or lower triangular or diagonal matrix equals to the product of diagonal elements.
b. If all elements in a row (column) of a matrix are zeroes, then its determinant equals zero.
c. If ![]() -th order matrices
-th order matrices ![]() are only different by the elements of row
are only different by the elements of row ![]() , that is,
, that is, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() , then
, then ![]() .
.
d. If matrix ![]() is obtained from matrix
is obtained from matrix ![]() , by multiplying all the elements of just one row by an
, by multiplying all the elements of just one row by an ![]() , then
, then ![]() .
.
e. The determinant of a matrix which has two equal rows, equals zero.
f. If two rows in a matrix are proportionate, then its determinant equals zero.
g. A determinant does not change if all the elements of one row are added corresponding elements of another row multiplied by a non-zero constant.
h. A determinant of a multiplication of matrices is equal to the multiplication of their determinants:
![]()
i. ![]() .
.
j. If ![]() , then
, then ![]() .
.
6.4 Inversion of Matrices and Determinants
a. Matrix ![]() s invertible, if and only if
s invertible, if and only if ![]() .
.
b. If ![]() is invertible, then
is invertible, then ![]() .
.
c. If matrix ![]() is invertible, then
is invertible, then

when ![]() is the algebraic cofactor of element
is the algebraic cofactor of element ![]() and
and ![]() is a cofactor corresponding to
is a cofactor corresponding to ![]() (see 6.2.g).
(see 6.2.g).