5 Steps to a 5 500 AP Physics Questions to Know by Test Day (2012)
Chapter 13. Circuits
361. A positive charge of 240 C passes a point in a circuit in 10 s. What is the magnitude of the current?
(A) 0.004 A
(B) 0.04 A
(C) 24 A
(D) 240 A
(E) 2,400 A
362. A 9.0-V battery drives a circuit containing a 10-Ω resistor. What is the current that flows through this circuit?
(A) 0.9 A
(B) 1.1 A
(C) 9.0 A
(D) 11 A
(E) 90 A
363. A 9-V battery drives 3 A of electrical current through a resistor. What is the power dissipated by the resistor?
(A) 0.3 J
(B) 3 J
(C) 6 J
(D) 12 J
(E) 27 J
364. Three resistors (20Ω, 150Ω, 500Ω) are linked in series. What is the equivalent resistance?
(A) 0.001 Ω
(B) 0.06 Ω
(C) 670 Ω
(D) 1.5 kΩ
(E) 1.5 MΩ
Questions 365–368 use the following figure:
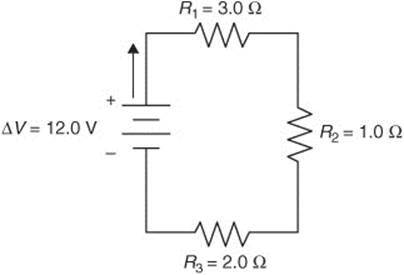
365. What is the current flowing through the circuit shown in the diagram?
(A) 1 A
(B) 2 A
(C) 4 A
(D) 6 A
(E) 12 A
366. Which of the following statements is true about the circuit shown in the diagram?
(A) The voltage drop is greatest across R1, but R1 has the least amount of current flowing through it.
(B) The voltage drop is greatest across R2, but R2 has the least amount of current flowing through it.
(C) The voltage drop is greatest across R3, but R3 has the least amount of current flowing through it.
(D) The voltage drops and current are equal across all resistors.
(E) The voltage drop is greatest across R1, but the current is equal at all points in the circuit.
367. In this diagram, what is the power dissipated by all of the resistors in the circuit?
(A) 2 W
(B) 6 W
(C) 12 W
(D) 24 W
(E) 48 W
368. In this diagram, what is the voltage drop across the third resistor (R3)?
(A) 2 V
(B) 3 V
(C) 4 V
(D) 6 V
(E) 12 V
369. Which of the following statements best summarizes a series circuit with three different resistances?
(A) In all parts of the circuit, the resistances are different, the voltage drops are the same, and the current is different.
(B) In all parts of the circuit, the resistances are the same, the voltage drops are the same, and the current is different.
(C) In all parts of the circuit, the resistances are different, the voltage drops are different, and the current is the same.
(D) In all parts of the circuit, the resistances are different, the voltage drops are the same, and the current is the same.
(E) In all parts of the circuit, the resistances are the same, the voltage drops are the same, and the current is the same.
370. When one light in a string of holiday lights goes out, all of the lights go out. Which statement best describes this situation?
(A) All of the lights are wired in parallel.
(B) The lights are wired in a series and in parallel.
(C) Only the parallel portions of the lights went out.
(D) All of the lights are wired in a series.
(E) You cannot tell how the lights are wired.
Questions 371–374 use the following figure:
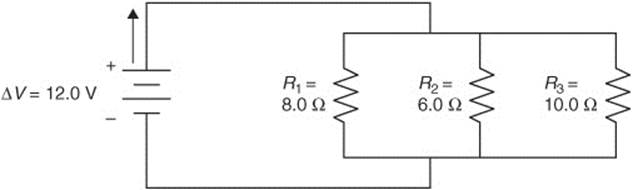
371. For the circuit in the diagram, which of the following expressions will describe the amount of current flowing through the resistors?
(A) R1 = R2 = R3
(B) R3 > R2 > R1
(C) R1 > R2 < R3
(D) R2 > R1 > R3
(E) R1 < R2 < R3
372. For the circuit in the diagram, what is the equivalent resistance?
(A) 0.04 Ω
(B) 0.4 Ω
(C) 1.0 Ω
(D) 2.6 Ω
(E) 24 Ω
373. For the circuit in the diagram, what is the total current?
(A) 0.5 A
(B) 4.6 A
(C) 12 A
(D) 30 A
(E) 300 A
374. For the circuit in the diagram, how much power is dissipated by the third resistor (R3)?
(A) 12 W
(B) 14 W
(C) 46 W
(D) 212 W
(E) 300 W
375. [For Physics C Students Only] A 100-kΩ resistor is wired in series with a 200-μF capacitor. How long will it take to charge the capacitor to 126 μF?
(A) 1 s
(B) 2 s
(C) 20 s
(D) 1 hr
(E) 5 hr
376. Three capacitors (5 μF, 4 μF, 2 μF) are wired in series with a 9-V battery. What is the equivalent capacitance?
(A) 0.09 μF
(B) 0.95 μF
(C) 1.05 μF
(D) 3.7 μF
(E) 11 μF
377. Three capacitors (5 μF, 4 μF, 2 μF) are wired in parallel with a 9-V battery. What is the equivalent capacitance?
(A) 0.09 μF
(B) 0.95 μF
(C) 1.05 μF
(D) 3.7 μF
(E) 11 μF
378. A 9.0-V battery is hooked up to a 10-μF capacitor. What is the charge on the capacitor?
(A) 9.0 × 10−5 C
(B) 9.0 × 10−4 C
(C) 9.0 × 10−3 C
(D) 9.0 × 100 C
(E) 9.0 × 101 C
379. In a circuit, 40 C of charge passes through a 10-Ω resistor in 80 s. What is the voltage that drives the current?
(A) 0.5 V
(B) 1.0 V
(C) 5.0 V
(D) 10 V
(E) 20 V
380. A 100-V power supply is hooked to a resistor. The current flowing through the circuit is 2.0 A. What is the resistance of the circuit?
(A) 0.05 Ω
(B) 0.5 Ω
(C) 2.0 Ω
(D) 5.0 Ω
(E) 50 Ω
381. 100 kW of power is dissipated by a resistor with a 5-A current passing through it. What is the value of the resistance?
(A) 1 kΩ
(B) 2 kΩ
(C) 4 kΩ
(D) 5 kΩ
(E) 201 kΩ
382. A 9.0-V battery is wired in series with three resistors (20Ω, 30Ω, 15Ω). What is the sum of the voltages through the circuit?
(A) 0 V
(B) 2.1 V
(C) 2.7 V
(D) 4.2 V
(E) 9.0 V
383. [For Physics C Students Only] A 10.0-μF capacitor is in series with a resistor. When the capacitor discharges to 37 percent of the charge remaining, it takes 50.0 s. What is the value of the resistor?
(A) 5 Ω
(B) 50 Ω
(C) 5 kΩ
(D) 5 MΩ
(E) 50 MΩ
Questions 384–386 use the following figure:
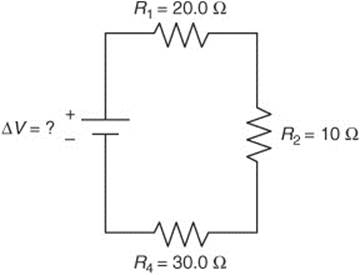
384. For the circuit shown in the figure, what is the voltage of the battery if the current is 2.0 A?
(A) 20 V
(B) 40 V
(C) 50 V
(D) 60 V
(E) 120 V
385. For the circuit shown in the figure, what is the voltage drop across the third resistor if the current is 5.0 A?
(A) 0 V
(B) 50 V
(C) 100 V
(D) 150 V
(E) 300 V
386. For the circuit shown in the figure, what must be the sum of the voltages around the circuit if the current is 10 A?
(A) 0 V
(B) 200 V
(C) 100 V
(D) 300 V
(E) 600 V
Questions 387 and 388 use the following figure:
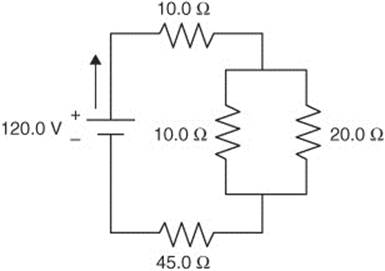
387. For the circuit shown in the diagram, what is the equivalent resistance of the circuit?
(A) 6.7 Ω
(B) 61.7 Ω
(C) 65 Ω
(D) 70 Ω
(E) 85 Ω
388. For the circuit shown in the figure, what is the value of the current leaving the parallel branch of the circuit?
(A) 1.0 A
(B) 1.9 A
(C) 5 A
(D) 10 A
(E) 12 A
389. For the circuit depicted in this figure, find the following:
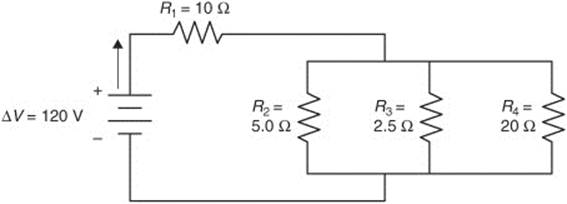
(A) What is the equivalent resistance of the circuit?
(B) What is the current flowing through the circuit?
(C) What is the voltage drop across each resistor?
(D) How much current flows through each resistor?
390. You have a 12-V battery and four 1-Ω resistors. You conduct the following experiments.
Experiment 1
(a) You wire the battery to a resistor, calculate the equivalent resistance, measure the total current, and calculate the power dissipated by the resistor in the circuit.
(b) You add another resistor in series and repeat the measurements and calculations.
(c) You add each resistor in series and repeat the measurements and calculations.
(d) The graphs of each measurement and calculation as a function of the number of resistors in series are shown in the figure.
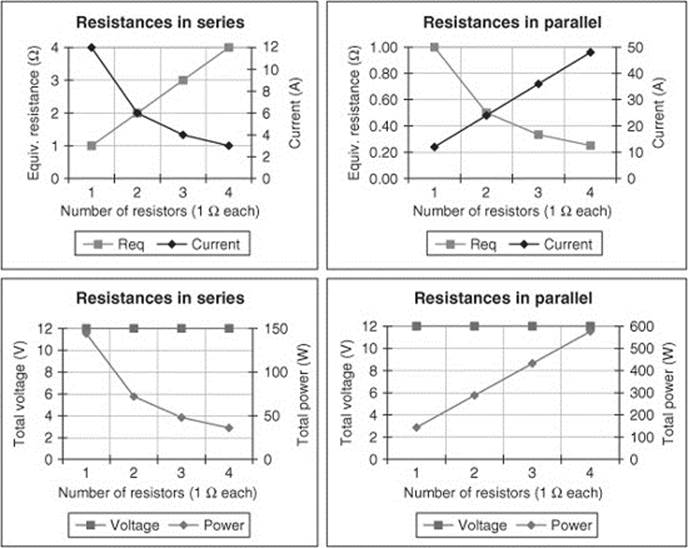
Experiment 2
You follow the procedure for Experiment 1, but you wire the resistors in parallel for this second experiment.
Using the graphs, answer the following questions:
(a) Describe the behavior of the equivalent resistance as you add resistors in series versus parallel.
(b) Describe the behavior of the current as you add resistors in series versus parallel.
(c) Describe the behavior of the total voltage as you add resistors in series versus parallel.
(d) Describe the behavior of the power as you add resistors in series versus parallel.
(e) If the resistors were light bulbs in strings of holiday lights, one wired in series and one in parallel, what can you say about the brightness of the bulbs as you increase the number? Why?