5 Steps to a 5 500 AP Physics Questions to Know by Test Day (2012)
Chapter 7. Gravitation and Circular Motion
181. A car moves in a horizontal circle with a radius of 10 m. The tangential velocity of the car is 30 m/s. What is the car’s acceleration?
(A) 3 m/s2 toward the center
(B) 3 m/s2 away from the center
(C) 90 m/s2 toward the center
(D) 90 m/s2 away from the center
(E) 270 m/s2 toward the center
182. If the car in Question 181 has a mass of 1,000 kg, then what is the force of friction acting on the car?
(A) 3,000 N toward the center
(B) 3,000 N away from the center
(C) 90,000 N away from the center
(D) 90,000 N toward the center
(E) 90,000 N vertically
183. A satellite orbits the Earth at a distance of 100 km. The mass of the satellite is 100 kg, while the mass of the Earth is approximately 6.0 × 1024 kg. The radius of the Earth is approximately 6.4 × 106 m. What is the approximate force of gravity acting on the satellite?
(A) 4 × 104 N
(B) 6.2 × 106 N
(C) 4 × 108 N
(D) 6.2 × 109 N
(E) 4 × 1014 N
184. Two satellites of equal mass orbit a planet. Satellite B orbits at twice the orbital radius of Satellite A. Which of the following statements is true?
(A) The gravitational force on Satellite A is four times less than that on Satellite B.
(B) The gravitational force on Satellite A is two times less than that on Satellite B.
(C) The gravitational force on the satellites is equal.
(D) The gravitational force on Satellite A is two times greater than that on Satellite B.
(E) The gravitational force on Satellite A is four times greater than that on Satellite B.
185. A 70-kg astronaut floats at a distance of 10 m from a 50,000-kg spacecraft. What is the force of attraction between the astronaut and spacecraft?
(A) 2.4 × 10−6 N
(B) 2.4 × 10−5 N
(C) Zero; there is no gravity in space
(D) 2.4 × 105 N
(E) 2.4 × 106 N
186. The centripetal acceleration on a 1,000-kg car in a turn is 1 × 105 m/s2. The radius of the turn is 10 m. What is the car’s velocity?
(A) 1 × 101 m/s
(B) 1 × 102 m/s
(C) 1 × 103 m/s
(D) 1 × 104 m/s
(E) 1 × 105 m/s
187. An ice skater skates around a circular rink with a diameter of 20 m. If it takes her 62.8 s to go around the rink once, what is the coefficient of friction of the ice?
(A) 0.01
(B) 0.10
(C) 0.20
(D) 0.30
(E) 0.50
188. A proposed “space elevator” can lift a 1,000-kg payload to an orbit of 150 km above the Earth’s surface. The radius of the Earth is 6.4 × 106 m and the Earth’s mass is 6 × 1024 kg. What is the gravitational potential energy of the payload when it reaches orbit?
(A) 1.0 × 103 J
(B) 2.7 × 106 J
(C) 6.1 × 1010 J
(D) 2.7 × 1012 J
(E) 1.0 × 1015 J
189. A warrior spins a slingshot in a horizontal circle above his head at a constant velocity. The sling is 1.5 m long and the stone has a mass of 50 g. The tension in the string is 3.3 N. When he releases the sling, what will the stone’s velocity be?
(A) 5 m/s
(B) 10 m/s
(C) 25 m/s
(D) 30 m/s
(E) 50 m/s
Questions 190 and 191 are based on the following graph:
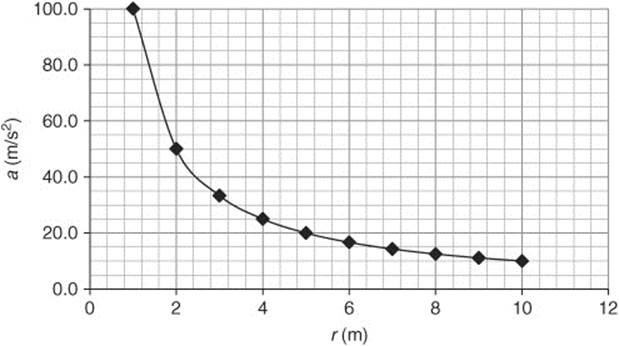
190. Engineers have designed a centrifuge for studying the effects of high gravity environments on plants and animals. This graph shows the results of the relationship between the radius and the centripetal acceleration. If the scientists want to simulate a “3-G environment,” then what should the radius of the centrifuge be?
(A) 1 m
(B) 2 m
(C) 3 m
(D) 5 m
(E) 10 m
191. If an astronaut with a mass of 70 kg was placed in that centrifuge with a radius of 5 m, what would be the centripetal force acting on him?
(A) 30 N
(B) 70 N
(C) 140 N
(D) 210 N
(E) 240 N
192. [For Physics C Students Only] The Earth is at an average distance of 1 AU from the Sun and has an orbital period of 1 year. Jupiter orbits the Sun at approximately 5 AU. About how long is the orbital period of Jupiter?
(A) 1 year
(B) 2 years
(C) 5 years
(D) 11 years
(E) 125 years
193. A satellite orbits the Earth at a distance of 200 km. If the mass of the Earth is 6 × 1024 kg and the Earth’s radius is 6.4 × 106 m, what is the satellite’s velocity?
(A) 1 × 103 m/s
(B) 3.5 × 103 m/s
(C) 7.8 × 103 m/s
(D) 5 × 106 m/s
(E) 6.1 × 107 m/s
194. A block with a mass of 30 kg is hanging still from a string. If you place another block with a mass of 10 kg at a distance of 2 m away, what is the gravitational attraction between the two blocks?
(A) 1 × 10−11 N
(B) 5 × 10−10 N
(C) 1 × 10−10 N
(D) 5 × 10−9 N
(E) 1 × 10−9 N
195. A 1,000-kg car experiences a centripetal force of 1.8 × 105 N while making a turn. The car is moving at a constant speed of 30 m/s. What is the radius of the turn?
(A) 0.2 m
(B) 1 m
(C) 2 m
(D) 4 m
(E) 5 m
196. A skater holds out her arms level to the ground as she spins. In one hand she holds a tennis ball. Each of her arms is 1 m long. If the tennis ball travels at 5 m/s, what is its centripetal acceleration?
(A) 5 m/s2
(B) 10 m/s2
(C) 15 m/s2
(D) 20 m/s2
(E) 25 m/s2
197. Mars orbits the Sun at a distance of 2.3 × 1011 m. The mass of the Sun is 2 × 1030 kg, and the mass of Mars is 6.4 × 1023 kg. Approximately what is the gravitational force that the Sun exerts on Mars?
(A) 1.6 × 1020 N
(B) 1.6 × 1021 N
(C) 3.7 × 1021 N
(D) 3.7 × 1032 N
(E) 3.7 × 1042 N
198. A record player has four coins at different distances from the center of rotation. Coin A is 1 cm away, Coin B is 2 cm away, Coin C is 4 cm away, and Coin D is 8 cm away. If the player is spinning 45 rotations/min, what coin has the greatest velocity?
(A) Coin A
(B) Coin B
(C) Coin C
(D) Coin D
(E) All the coins have equal velocities
199. A space shuttle is in orbit around the Earth. It travels at an unknown speed (v) at an orbital radius (r). The commander fires the engine and the speed doubles to 3v. What happens to the orbit if the centripetal acceleration stays the same?
(A) The orbital radius decreases by one-third.
(B) The orbital radius decreases by a factor of nine.
(C) The orbital radius remains the same.
(D) The orbital radius triples.
(E) The orbital radius increases by a factor of nine.
200. This graph depicts the tangential velocities of several circular space stations with different radii. All the stations are spinning. Which of the following statements is true?
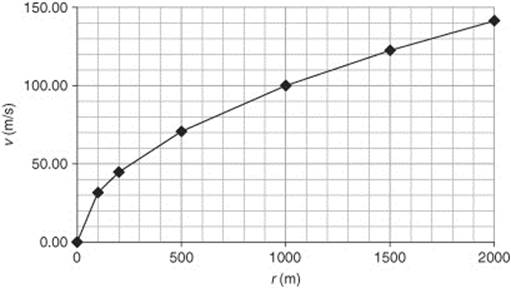
(A) The centripetal accelerations of the short radii space stations are greater than 10 m/s2; those of the larger ones are less than 10 m/s2.
(B) The centripetal accelerations of the short radii space stations are greater than 5 m/s2; those of the larger ones are less than 5 m/s2.
(C) The centripetal accelerations of all the stations are the same at 5 m/s2.
(D) The centripetal accelerations of all the stations are the same at 10 m/s2.
(E) The centripetal accelerations of the short radii space stations are less than 10 m/s2; those of the larger ones are greater than 10 m/s2.
201. The Moon has a mass of 7.4 × 1022 kg and a radius of 1.7 × 106 m. What is the force of gravity experienced by a 70-kg astronaut standing on the lunar surface?
(A) 10 N
(B) 50 N
(C) 100 N
(D) 120 N
(E) 150 N
202. A bicycle wheel has a radius of 0.5 m. When it spins, it completes one full turn in 1.6 s. A pebble wedged in the tread has a mass of 10 g. What is the centripetal force on the pebble?
(A) 0.01 N
(B) 0.08 N
(C) 0.1 N
(D) 0.8 N
(E) 1 N
203. The Moon has a mass of 7.4 × 1022 kg and a distance from the Earth of 3.8 × 108 m. The Earth’s mass is 6 × 1024 kg. What is the gravitational potential energy of the Moon?
(A) 2.0 × 1020 J
(B) 7.8 × 1028 J
(C) 2.0 × 1030 J
(D) 7.8 × 1030 J
(E) 2.0 × 1040 J
204. [For Physics C Students Only] Saturn has an orbital period of 29 Earth years. What is its approximate orbital distance?
(A) 1 AU
(B) 2 AU
(C) 5 AU
(D) 10 AU
(E) 15 AU
205. The coefficient of friction between the rubber tires of a car and dry concrete is μ = 0.64. If a car enters a horizontal turn with a radius of 10.0 m, what is the maximum velocity that the car can have and still hold the road?
(A) 4 m/s
(B) 8 m/s
(C) 32 m/s
(D) 64 m/s
(E) 144 m/s
206. A spinning top has a radius of 2 cm. If the top takes 0.06 s to complete one rotation, what is the centripetal acceleration at the edge of the top?
(A) 10 m/s2
(B) 22 m/s2
(C) 100 m/s2
(D) 220 m/s2
(E) 1,000 m/s2
207. You swing a 100-g object attached to a 2-m string in a circle above your head. The velocity of the object is 12 m/s. What is the centripetal force on its mass?
(A) 0.72 N
(B) 7.2 N
(C) 72 N
(D) 720 N
(E) 7,200 N
208. Four planets, A through D, orbit the same star. The relative masses and distances from the star for each planet are shown in the table. Which planet has the highest gravitational attraction to the star?
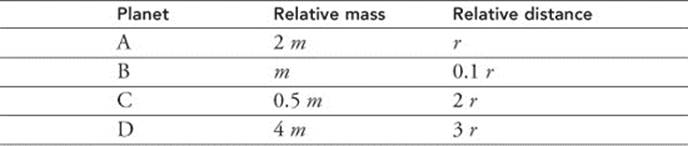
(A) Planet A
(B) Planet B
(C) Planet C
(D) Planet D
(E) All have the same gravitational attraction to the star
209. A 1,000-kg satellite orbits the Earth in a circular orbit at an altitude of 1,000 km. The Earth’s mass is 6.0 × 1024 kg and its radius is 6.4 × 106 m.
(a) How does the force of gravity on the satellite compare with the centripetal force on the satellite? What is the magnitude of the force of gravity acting on the satellite?
(b) What is the magnitude of the satellite’s tangential velocity?
(c) What is the gravitational potential energy of the satellite?
(d) What is the value of the acceleration due to gravity at this altitude?
210. A 1,000-kg car makes a turn on a banked curve. The radius of the turn is 300 m and the turn is inclined at an angle (θ = 30°). Assume that the turn is frictionless.
(a) Draw a free-body diagram of this situation and label all the forces on the car.
(b) Calculate the car’s maximum velocity.
(c) Calculate the centripetal force on the car.