AP Physics B Exam
19 AP Physics B Practice Exam 1
AP® Physics B Exam
![]()
DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO.

Instructions
Section I of this examination contains 70 multiple-choice questions. Fill in only the ovals for numbers 1 through 70 on your answer sheet.
CALCULATORS MAY NOT BE USED IN THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION.
Indicate all of your answers to the multiple-choice questions on the answer sheet. No credit will be given for anything written in this exam booklet, but you may use the booklet for notes or scratch work. After you have decided which of the suggested answers is best, completely fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. Give only one answer to each question. If you change an answer, be sure that the previous mark is erased completely. Here is a sample question and answer.
Sample Question
Chicago is a
(A) state
(B) city
(C) country
(D) continent
(E) village
Sample Answer
![]()
Use your time effectively, working as quickly as you can without losing accuracy. Do not spend too much time on any one question. Go on to other questions and come back to the ones you have not answered if you have time. It is not expected that everyone will know the answers to all the multiple-choice questions.
About Guessing
Many candidates wonder whether or not to guess the answers to questions about which they are not certain. Multiple choice scores are based on the number of questions answered correctly. Points are not deducted for incorrect answers, and no points are awarded for unanswered questions. Because points are not deducted for incorrect answers, you are encouraged to answer all multiple-choice questions. On any questions you do not know the answer to, you should eliminate as many choices as you can, and then select the best answer among the remaining choices.
Advanced Placement Examination
PHYSICS B
SECTION I

Click here to see a larger image
PHYSICS B
SECTION I
Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best in each case and mark it on your sheet.
1. If the acceleration of an object is not zero, then all of the following could be constant EXCEPT the object”s
I. speed
II. linear momentum
III. kinetic energy
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) II only
(E) II and III only
2. What happens to the force of gravitational attraction between two small objects if the mass of each object is doubled and the distance between their centers is doubled?
(A) It is doubled.
(B) It is quadrupled.
(C) It is halved.
(D) It is reduced fourfold.
(E) It remains the same.
3. A particle travels in a circular path of radius 0.2 m with a constant kinetic energy of 4 J. What is the net force on the particle?
(A) 4 N
(B) 16 N
(C) 20 N
(D) 40 N
(E) Cannot be determined from the information given
4. Which of the following is NOT a vector quantity?
(A) Displacement
(B) Velocity
(C) Acceleration
(D) Linear momentum
(E) Potential energy
Questions 5–7 refer to the following figure:
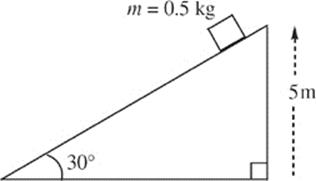
5. If the surface of the incline is frictionless, how long will it take the block to reach the bottom if it was released from rest at the top?
(A) 0.5 s
(B) 1.0 s
(C) 1.4 s
(D) 2.0 s
(E) 2.8 s
6. If the surface of the incline is frictionless, with what speed will the block reach the bottom if it was released from rest at the top?
(A) 8 m/s
(B) 10 m/s
(C) 14 m/s
(D) 18 m/s
(E) 20 m/s
7. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the incline is 0.4, how much work is done by the normal force on the block as it slides down the full length of the incline?
(A) 0 J
(B) 2.0 J
(C) 4.0 J
(D) 4.9 J
(E) 10 J
8. Two satellites are in circular orbit around the earth. The distance from Satellite 1 to the earth”s center is r1, and the distance from Satellite 2 to the earth”s center is r2. If the speed of Satellite 1 is v1, what is the speed of Satellite 2?
(A) v1![]()
(B) v1![]()
(C) v1(r2/r1)
(D) v1(r2/r1)2
(E) v1(r1/r2)2
9. Which of the following would increase the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor?
(A) Using smaller plates
(B) Replacing the dielectric material between the plates with one that had a smaller dielectric constant
(C) Moving the plates closer together
(D) Increasing the voltage between the plates
(E) Decreasing the voltage between the plates
10. A simple harmonic oscillator has a frequency of 2.5 Hz and an amplitude of 0.05 m. What is the period of the oscillations?
(A) 0.4 s
(B) 0.2 s
(C) 8 s
(D) 20 s
(E) 50 s
11. What happens to the image formed by a concave mirror as the object is moved from far away toward the focal point?
(A) The image moves away from the mirror and gets shorter.
(B) The image moves away from the mirror and gets taller.
(C) The image moves toward the mirror and gets shorter.
(D) The image moves toward the mirror and gets taller.
(E) None of the above
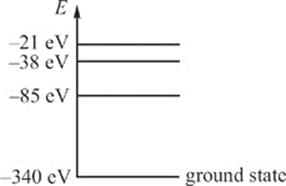
12. The diagram above (not drawn to scale) gives the first few electron energy levels within a single-electron atom. Which of the following gives the energy of a photon that could NOT be emitted by this atom during an electron transition?
(A) 17 eV
(B) 42 eV
(C) 64 eV
(D) 255 eV
(E) 302 eV
13. During an isothermal expansion, a confined ideal gas does –150 J of work against its surroundings. Which of the following describes the heat transfer during this process?
(A) 150 J of heat was added to the gas.
(B) 150 J of heat was removed from the gas.
(C) 300 J of heat was added to the gas.
(D) 300 J of heat was removed from the gas.
(E) No heat was transferred because the process was isothermal.
14. Sound waves travel at 350 m/s through warm air and at 3500 m/s through brass. What happens to the wavelength of a 700 Hz acoustic wave as it enters brass from warm air?
(A) It decreases by a factor of 20.
(B) It decreases by a factor of 10.
(C) It increases by a factor of 10.
(D) It increases by a factor of 20.
(E) The wavelength remains unchanged.
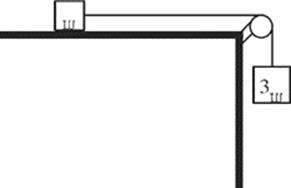
15. In the figure above, the coefficient of sliding friction between the small block and the tabletop is 0.2. If the pulley is frictionless and massless, what will be the acceleration of the blocks once they are released from rest?
(A) (0.5)g
(B) (0.6)g
(C) (0.7)g
(D) (0.8)g
(E) (0.9)g
16. Two people, one of mass 100 kg and the other of mass 50 kg, stand facing each other on an ice-covered (essentially frictionless) pond. If the heavier person pushes on the lighter one with a force F, then
(A) the force felt by the heavier person is ![]() F
F
(B) the force felt by the heavier person is –2F
(C) the magnitude of the acceleration of the lighter person will be ![]() of the magnitude of the acceleration of the heavier person
of the magnitude of the acceleration of the heavier person
(D) the magnitude of the acceleration of the lighter person will be twice the magnitude of the acceleration of the heavier person
(E) None of the above
17. An object of volume 2 × 10–3 m3 and weight 6 N is placed into a tank of water, where it floats. What percentage of the object”s volume is above the surface of the water?
(A) 3%
(B) 12%
(C) 30%
(D) 60%
(E) 70%
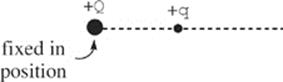
18. The figure above shows two positively charged particles. The +Q charge is fixed in position, and the +q charge is brought close to +Q and released from rest. Which of the following graphs best depicts the acceleration of the +q charge as a function of its distance r from +Q?
(A) 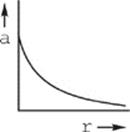
(B) 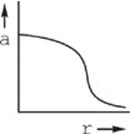
(C) 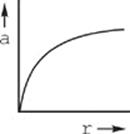
(D) 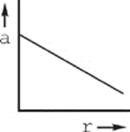
(E) 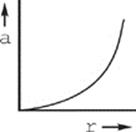
19. A spring of force constant 800 N/m is hung from a ceiling. A block of mass 4.0 kg is hung from its lower end and allowed to come to rest. How far will the block stretch the spring?
(A) 0.50 cm
(B) 1.0 cm
(C) 3.2 cm
(D) 5.0 cm
(E) 10.0 cm
20. A crane lifts a shipping crate that weighs 5000 N at a constant speed of 4 m/s. At what rate is this crane doing work on the crate?
(A) 1250 W
(B) 2000 W
(C) 4000 W
(D) 10,000 W
(E) 20,000 W
21. Each of the following particles is projected with the same speed into a uniform magnetic field B such that the particle”s initial velocity is perpendicular to B. Which one would move in a circular path with the largest radius?
(A) Proton
(B) Beta particle
(C) Alpha particle
(D) Electron
(E) Positron
22. An astronaut lands on a planet whose mass and radius are each twice that of Earth. If the astronaut weighs 800 N on Earth, how much will he weigh on this planet?
(A) 200 N
(B) 400 N
(C) 800 N
(D) 1600 N
(E) 3200 N
23. An object of mass 5 kg is acted upon by exactly four forces, each of magnitude 10 N. Which of the following could NOT be the resulting acceleration of the object?
(A) 0 m/s2
(B) 2 m/s2
(C) 4 m/s2
(D) 8 m/s2
(E) 10 m/s2
24. What is the maximum efficiency of an engine operating between a heat source at 127°C and a heat reservoir (sink) at 27°C?
(A) 25%
(B) 33%
(C) 50%
(D) 67%
(E) 79%
25. A rope stretched between two fixed points can support transverse standing waves. What is the ratio of the sixth harmonic frequency to the third harmonic frequency?
(A) 1/2
(B) 1/![]()
(C) 2
(D) 2![]()
(E) 4
26. How much current does a 60 W light bulb draw if it operates at a voltage of 120 V?
(A) 0.25 A
(B) 0.5 A
(C) 2 A
(D) 4 A
(E) 30 A
Questions 27–28 refer to the following plane diagram. The figure shows four point charges arranged at the corners of a square with point B as its center.
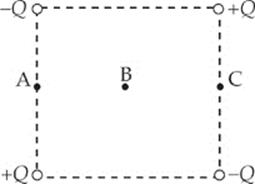
27. A positive charge would experience no net force if it were placed at which of the three points shown in the figure?
(A) A only
(B) B only
(C) C only
(D) A or B only
(E) A, B, or C
28. At which points is the electric potential equal to zero?
(A) A only
(B) B only
(C) C only
(D) A or B only
(E) A, B, or C
29. A spherical balloon filled with helium is floating in air. If the balloon is inflated until its radius is doubled, how will the buoyant force on the balloon be affected?
(A) It will decrease by a factor of 4.
(B) It will increase by a factor of 2.
(C) It will increase by a factor of 4.
(D) It will increase by a factor of 8.
(E) It will not be affected.
30. A beam of monochromatic light entering a glass window pane from the air will experience a change in
(A) frequency and wavelength
(B) frequency and speed
(C) speed and wavelength
(D) speed only
(E) wavelength only
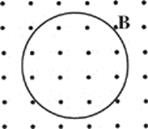
31. A metal loop of wire shown above is situated in a magnetic field B pointing out of the plane of the page. If B decreases uniformly in strength, the induced electric current within the loop is
(A) clockwise and decreasing
(B) clockwise and increasing
(C) counterclockwise and decreasing
(D) counterclockwise and constant
(E) counterclockwise and increasing
32. How does λe, the de Broglie wavelength of an electron (mass = me), compare with λp, the de Broglie wavelength of a proton (mass = mp) moving with the same kinetic energy as the electron?
(A) λe = λP![]()
(B) λe = λP![]()
(C) λe = λP(mP/me)2
(D) λe = λP(me/mP)2
(E) λe = λP, because the electron and proton have the same magnitude of charge
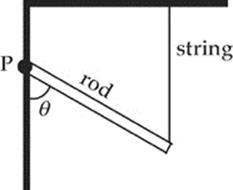
33. If the rod in the figure above is uniform and has mass m, what is the tension in the supporting string? The rod is free to rotate about point P.
(A) ![]() mg sin θ
mg sin θ
(B) mg sin θ
(C) ![]() mg cos θ
mg cos θ
(D) ![]() mg
mg
(E) mg
34. Which of the following statements is true concerning phase changes?
(A) When a liquid freezes, it releases thermal energy into its immediate environment.
(B) When a solid melts, it releases thermal energy into its immediate environment.
(C) For most substances, the latent heat of fusion is greater than the latent heat of vaporization.
(D) As a solid melts, its temperature increases.
(E) As a liquid freezes, its temperature decreases.
35. Which of the following changes to a double-slit interference experiment would increase the widths of the fringes in the interference pattern that appears on the screen?
(A) Use light of a shorter wavelength.
(B) Move the screen closer to the slits.
(C) Move the slits closer together.
(D) Use light with a lower wave speed.
(E) Increase the intensity of the light.
![]()
36. Identify the missing particle in the nuclear reaction given above.
(A) Electron
(B) Proton
(C) Deuteron
(D) Positron
(E) Gamma-ray photon
Questions 37–38 refer to the circuit shown below:
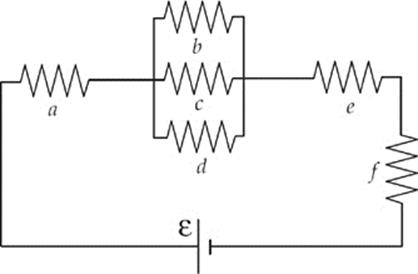
37. If each of the resistors in the circuit has a resistance of 3Ω, what must be the emf of the battery if the circuit draws a total current of 3 A?
(A) ![]() V
V
(B) ![]() V
V
(C) 10 V
(D) 30 V
(E) 54 V
38. Which of the following relates Pb, the rate at which energy is dissipated by Resistor b, and Pe, the rate at which energy is dissipated by Resistor e?
(A) Pb = 3Pe
(B) Pb = 9Pe
(C) Pb = Pe
(D) Pe = 3Pb
(E) Pe = 9Pb
39. In which of the following situations involving a source of sound and a detector of the sound is it possible that there is NO perceived Doppler shift?
(A) The source travels toward the stationary detector.
(B) The detector travels toward the stationary source.
(C) Both the source and detector travel in the same direction.
(D) Both the source and detector travel in opposite directions, with the source and detector moving away from each other.
(E) Both the source and detector travel in opposite directions, with the source and detector moving toward each other.
40. If L, M, and T denote the dimensions of length, mass, and time, respectively, what are the dimensions of power?
(A) ML/T2
(B) L2M/T2
(C) M2L/T2
(D) L2M/T3
(E) M2L/T3
41. Consider two adjacent transparent media. The speed of light in Medium 1 is v1, and the speed of light in Medium 2 is v2. If v1 < v2, then total internal reflection will occur at the interface between these media if a beam of light is
(A) incident in Medium 1 and strikes the interface at an angle of incidence greater than sin–1(v1/v2)
(B) incident in Medium 1 and strikes the interface at an angle of incidence greater than sin–1(v2/v1)
(C) incident in Medium 2 and strikes the interface at an angle of incidence greater than sin–1(v1/v2)
(D) incident in Medium 2 and strikes the interface at an angle of incidence greater than sin–1(v2/v1)
(E) Total internal reflection is impossible in the situation described.
42. An object (mass = m) above the surface of the Moon (mass = M) is dropped from an altitude h equal to the Moon”s radius (R). What is the object”s impact speed?
(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
(E) ![]()
43. Traveling at an initial speed of 1.5 × 106 m/s, a proton enters a region of constant magnetic field of magnitude 1.5 T. If the proton”s initial velocity vector makes an angle of 30° with the magnetic field, compute the proton”s speed 4 s after entering the magnetic field.
(A) 5.0 × 105 m/s
(B) 7.5 × 105 m/s
(C) 1.5 × 106 m/s
(D) 3.0 × 106 m/s
(E) 6.0 × 106 m/s
44. At a distance of 20 m from a source of sound, the sound level is 40 dB. If the observer backs up to a distance of 40 m from the source, what will the sound level be? (Assume no absorption nor reflection of sound.)
(A) 10 dB
(B) 14 dB
(C) 20 dB
(D) 28 dB
(E) 34 dB
45. An electric dipole consists of a pair of equal but opposite point charges of magnitude 4.0 nC separated by a distance of 2.0 cm. What is the electric field strength at the point midway between the charges?
(A) 0
(B) 9.0 × 104 N/C
(C) 1.8 × 105 N/C
(D) 3.6 × 105 N/C
(E) 7.2 × 105 N/C
46. A lightweight toy car crashes head-on into a heavier toy truck. Which of the following statements is true as a result of the collision?
I. The car will experience a greater impulse than the truck.
II. The car will experience a greater change in momentum than the truck.
III. The magnitude of the acceleration experienced by the car will be greater than that experienced by the truck.
(A) I and II only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) II and III only
(E) I, II, and III
47. A projectile is launched with an initial velocity of magnitude a at an angle β to the horizontal. Find its maximum vertical displacement, ignoring effects due to the air.
(A) (a2 sin 2β)/(2g)
(B) (a2 sin2β)/(2g)
(C) (a2 sin 2β)/g
(D) (a2 sin2β)/g
(E) (a sin β cos β)/g
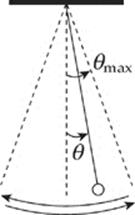
48. A simple pendulum executes simple harmonic motion as it swings through small angles of oscillation. If θmax denotes the amplitude of the oscillations, which of the following statements is true?
(A) When θ = 0, the tangential acceleration is 0.
(B) When θ = θmax, the tangential acceleration is 0.
(C) When θ = 0, the speed is 0.
(D) When θ = 0, the restoring force is maximized.
(E) When θ = θmax, the speed is maximized.
49. Assume that the Moon (mass = m) orbits Earth (mass = M) in a circular path of radius R. What is the Moon”s orbital angular momentum with respect to Earth”s center?
(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
(E) ![]()
50. In an experiment designed to study the photoelectric effect, it is observed that low-intensity visible light of wavelength 550 nm produced no photoelectrons. Which of the following best describes what would occur if the intensity of this light were increased dramatically?
(A) Almost immediately, photoelectrons would be produced with a kinetic energy equal to the energy of the incident photons.
(B) Almost immediately, photoelectrons would be produced with a kinetic energy equal to the energy of the incident photons minus the work function of the metal.
(C) After several seconds, necessary for the electrons to absorb sufficient energy from the incident light, photoelectrons would be produced with a kinetic energy equal to the energy of the incident photons.
(D) After several seconds, necessary for the electrons to absorb sufficient energy from the incident light, photoelectrons would be produced with a kinetic energy equal to the energy of the incident photons minus the work function of the metal.
(E) Nothing would happen.

51. Electric current is established in each of two long parallel wires, as shown in the figure above. Describe the force per unit length on each wire.
(A) attractive, strength = (μ0/2π)I2/a2
(B) repulsive, strength = (μ0/2π)I2/a2
(C) attractive, strength = (μ0/2π)I2/a
(D) repulsive, strength = (μ0/2π)I2/a
(E) attractive, strength = (μ0/2π)I2/(![]() a)2
a)2
52. An object is placed 100 cm from a plane mirror. How far is the image from the object?
(A) 50 cm
(B) 100 cm
(C) 150 cm
(D) 200 cm
(E) 300 cm
53. What happens to the pressure, P, of an ideal gas if the temperature is increased by a factor of 2 and the volume is increased by a factor of 8?
(A) P decreases by a factor of 16.
(B) P decreases by a factor of 4.
(C) P decreases by a factor of 2.
(D) P increases by a factor of 4.
(E) P increases by a factor of 16.
54. Two nuclides that have the same excess number of neutrons over protons are called isodiapheres. Which of the following is an isodiaphere of ![]() ?
?
(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
(E) ![]()
55. The plates of a capacitor are charged to a potential difference of 5 V. If the capacitance is 2 mF, what is the charge on the positive plate?
(A) 0.005 C
(B) 0.01 C
(C) 0.02 C
(D) 0.5 C
(E) 0.1 C
56. An object of mass 2 kg increases in speed from 2 m/s to 4 m/s in 3 s. Calculate the total work performed on the object during this time interval.
(A) 4 J
(B) 6 J
(C) 12 J
(D) 36 J
(E) Cannot be determined from the information given
57. A confined ideal gas undergoes a cyclical process in three steps—an isobaric step, followed by an isochoric step, followed by an isothermal step. Which of the following must be true?
(A) The change in internal energy of the gas is equal to the work done during the isobaric step.
(B) The change in internal energy of the gas is equal to the work done during the isobaric step minus the work done during the isothermal step.
(C) The work done during the isothermal step is equal but opposite to the work done during the isochoric step.
(D) The total work done during the cycle is positive.
(E) The total work done during the cycle is equal but opposite to the net amount of heat transferred.
58. How much force is required to lift a 50-newton object with an acceleration of 10 m/s2?
(A) 10 N
(B) 50 N
(C) 100 N
(D) 150 N
(E) 200 N
59. Why do baseball catchers wear a mitt rather than just using their bare hands to catch a pitched baseball?
(A) The impulse delivered to the catcher”s hand is reduced due to the presence of the mitt.
(B) The force on the catcher”s hand is reduced because of the increased area provided by the mitt.
(C) The baseball”s change in momentum is reduced due to the presence of the mitt.
(D) The force on the catcher”s hand is reduced because the mitt increases the time of impact.
(E) The force on the catcher”s hand is reduced because the mitt decreases the time of impact.
60. A liquid flows at a constant flow rate through a pipe with circular cross-sections of varying diameters. At one point in the pipe, the diameter is 2 cm and the flow speed is 18 m/s. What is the flow speed at another point in this pipe, where the diameter is 3 cm?
(A) 4 m/s
(B) 6 m/s
(C) 8 m/s
(D) 12 m/s
(E) 27 m/s
61. A bi-convex lens has a radius of curvature of magnitude 20 cm. Which of the following best describes the image formed of an object of height 2 cm placed 30 cm from the lens?
(A) real, inverted, height = 1 cm
(B) virtual, upright, height = 0.25 cm
(C) real, upright, height = 1 cm
(D) virtual, inverted, height = 0.25 cm
(E) real, inverted, height = 4 cm
62. Lenz”s law concerning induced emf can be viewed most directly as a result of which of the following principles?
(A) Gauss”s law
(B) Ampere”s law
(C) Biot-Savart law
(D) Conservation of charge
(E) Conservation of energy
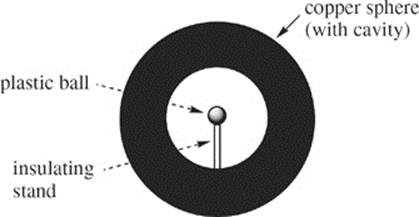
63. The figure above shows a solid copper sphere carrying a charge of +1 mC that contains a hollow cavity. Which of the following best describes what will occur when a plastic ball carrying a charge of +1 mC is placed inside the cavity?
(A) A charge of +1 mC will appear on the wall of the cavity, leaving zero net charge on the outer surface of the sphere.
(B) A charge of +1 mC will appear on the wall of the cavity, leaving a charge of –2 mC on the outer surface of the sphere.
(C) A charge of –1 mC will appear on the wall of the cavity, leaving a charge of –2 mC on the outer surface of the sphere.
(D) A charge of –1 mC will appear on the wall of the cavity, leaving a charge of +2 mC on the outer surface of the sphere.
(E) Nothing will happen.
64. Wire Y is made of the same material but has twice the diameter and half the length of Wire X. If Wire X has a resistance of R then Wire Y would have a resistance of
(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) R
(D) 2R
(E) 8R
65. How much work is required to charge a 10 µF capacitor to a potential difference of 100 V?
(A) 0.005 J
(B) 0.01 J
(C) 0.05 J
(D) 0.1 J
(E) 0.5 J
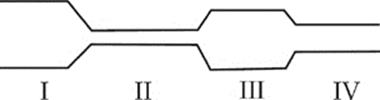
66. A fluid flows through a pipe of changing cross-section as shown. In which section would the pressure of the fluid be greatest?
(A) Section I
(B) Section II
(C) Section III
(D) Section IV
(E) All sections have the same pressure.
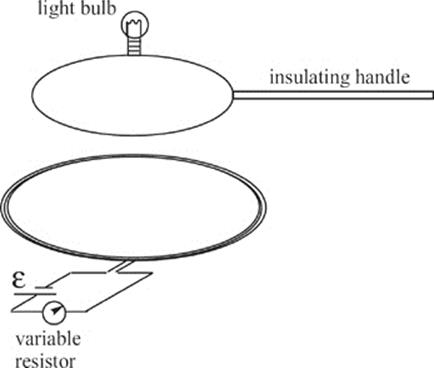
67. In the figure shown above, a loop of metal wire containing a tiny light bulb is attached to an insulating handle and placed over a coil of wire in which a current can be established by a source of emf and controlled by a variable resistor. The plane of the top loop is parallel to the plane of the bottom coil. Which of the following could NOT cause the bulb to light?
(A) Rotating the handle 90° while keeping the plane of the top loop parallel to the plane of the bottom coil
(B) Raising the handle up and away from the coil
(C) Lowering the handle down toward the coil
(D) Decreasing the resistance of the coil
(E) Increasing the resistance of the coil
68. Which of the following types of electromagnetic radiation has the longest wavelength?
(A) Gamma rays
(B) Ultraviolet
(C) Blue light
(D) X-rays
(E) Orange light
69. Two traveling waves of equal frequency, one of amplitude 4 cm and the other of amplitude 6 cm, superimpose in a single medium. Which of the following best describes the displacement, D, of the resultant wave?
(A) 2 cm ≤ D ≤ 10 cm
(B) D = 5 cm
(C) D = 10 cm
(D) 10 cm ≤ D ≤ 12 cm
(E) 12 cm ≤ D ≤ 24 cm
70. A uniform bar is lying on a flat table. Besides the gravitational and normal forces (which cancel), the bar is acted upon by exactly two other forces, F1 and F2, which are parallel to the surface of the table. If the net force on the rod is zero, then which one of the following is true?
(A) The net torque on the bar must also be zero.
(B) The bar can accelerate translationally if F1 and F2 are not applied at the same point.
(C) The net torque will be zero if F1 and F2 are applied at the same point.
(D) The bar cannot accelerate translationally or rotationally.
(E) None of the above
END OF SECTION I
PHYSICS B
SECTION II
Free-Response Questions
Time—90 minutes
6 required questions. Questions 1–4 are worth 15 points each. Questions 5–6 are worth 10 points each.
Percent of total grade—50
General Instructions
Use a separate piece of paper to answer these questions.
Show your work. Be sure to write CLEARLY and LEGIBLY. If you make an error, you may save time by crossing it out rather than trying to erase it.

Click here to see a larger image

Click here to see a larger image
PHYSICS B
SECTION II
Time—90 minutes
6 Questions
Directions: Answer all six questions. The suggested time is 17 minutes for answering each of questions 1–4, and about 11 minutes for answering each of questions 5–6. The parts within a question may not have equal weight.
1. (15 points)
A light spring of natural length 10 cm with force constant k = 500 N/m is embedded vertically in the ground. A ball of mass m = 0.15 kg is placed on top of the spring, which is compressed 8.0 cm; when released, the spring pushes the ball. When the ball reaches ground level, it leaves its light supporting platform and continues vertically upward. When it reaches the top of its path, a batter strikes the ball at an angle θ0 to the horizontal. Ignore air resistance.
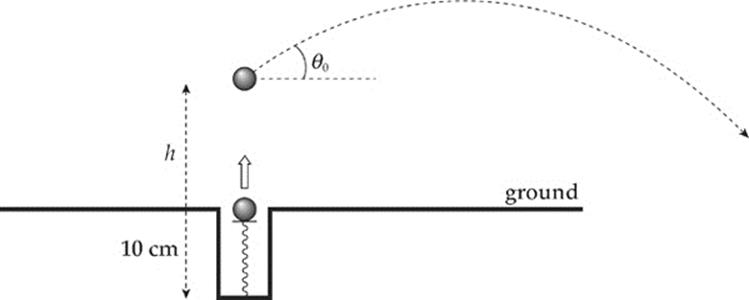
(a) Find the height h at which the batter strikes the ball.
(b) If the batter gives the ball an initial velocity of 30 m/s with θ0 = 0 by striking the ball with an impact time of 4 ms, determine:
(i) the average force exerted on the ball by the bat;
(ii) how long the ball is in flight after it”s been hit;
(iii) how far the ball travels horizontally.
(c) If the ball failed to release from the platform, with what frequency would it oscillate?
2. (15 points)
The figure below shows an electric circuit containing a source of emf, ε, a variable resistor (r) and a resistor of fixed resistance R. The resistor R is immersed in a sealed beaker containing a mass m of water, currently at temperature Ti. When the switch S is closed, current through the circuit causes the resistor in the water to dissipate heat, which is absorbed by the water. A stirrer at the bottom of the beaker simply ensures that the temperature is uniform throughout the water at any given moment. The apparatus is well-insulated (insulation not shown), and it may be assumed that no heat is lost to the walls or lid of the beaker or to the stirrer.
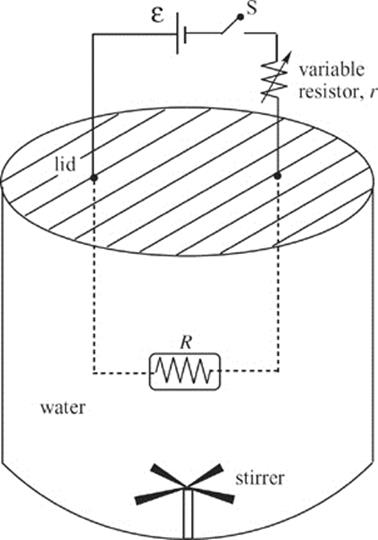
(a) Determine the current in the circuit once S is closed. Write your answer in terms of ε, r, and R.
(b) How much heat is dissipated by the resistor R in time t?
(c) (i) Give an equation that expresses T, the temperature of the water as a function of time t since turning on the circuit. Write your answer in terms of ε, r, R, Ti, m, and c (the specific heat of water).
(ii) On the axes below, provide a sketch of T vs. t. Be sure to mark T = Ti at t = 0.

(d) Explain briefly how the temperature of the water can be increased more rapidly by adjusting the rotation rate of the stirrer.
3. (15 points)
A cyclotron is a device used to accelerate charged particles to high speeds. It consists of two hollow containers—called dees because of their shape—facing each other and separated by a small gap. They are immersed in a uniform magnetic field, B, and are attached to a source of alternating voltage. A charged particle is projected from the center of the cyclotron into Dee #1, and the magnetic force causes it to turn in a circle. When it completes its semicircular path within one dee, the polarity of the voltage is reversed, and the particle is accelerated across the gap into the adjacent dee. This process continues, and the particle spirals outward at faster and faster speeds, until it emerges from Dee #2. Notice that the voltage must be alternated twice during each revolution of the particle. The figure below shows a view—looking down from above—of a cyclotron.
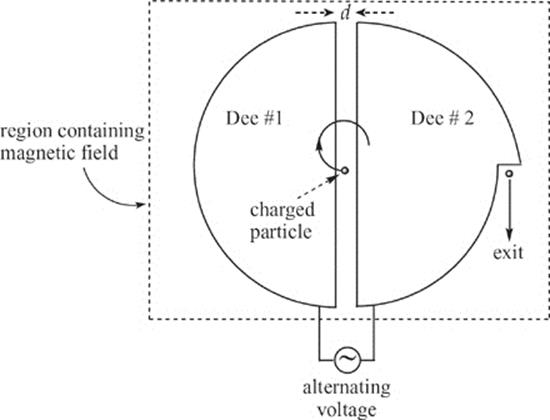
(a) Explain why the electric field in the gap must be used to increase the speed of the particle.
Assume that the charged particle to be accelerated by the cyclotron is a proton.
(b) Should the magnetic field point into the plane of the page or out of the plane of the page in order to cause the particle to rotate clockwise as shown in the figure?
For each of the following, write your answer in terms of the magnetic field strength B, the proton”s charge (+e) and mass (m), and fundamental constants.
(c) Show that the time to complete one revolution does not depend on the speed of the proton, and determine this orbital period.
(d) How many revolutions does the proton make per second?
(e) What must be the frequency (in Hz) of the alternating voltage?
(f) If the maximum radius of the proton”s orbit is R, what is its maximum kinetic energy upon exiting? (Your answer should also include R.)
4. (15 points)
The figure below shows two boxes attached by a light cord that runs over a frictionless peg. The mass of the block on the 60° incline is M = 8 kg, and the mass of the block on the 45° incline is m = 2 kg.
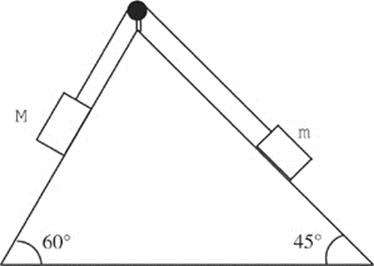
Assume that both inclined surfaces are frictionless for parts (a), (b), and (c).
(a) Find the acceleration of the blocks once they are released from rest.
(b) What is the total force exerted by the cord on the peg?
(c) If block M is released from rest at a height of H = 1.5 m above the bottom of the triangle, find its speed when it reaches the bottom.
(d) Answer the question posed in part (a) assuming that the coefficient of sliding friction between the blocks and the inclined surfaces is 0.2.
5. (10 points)
The figure below is a view from above of two clay balls moving toward each other on a frictionless surface. They collide completely inelastically at the indicated point and are observed to then move in the direction indicated by the post-collision velocity vector, v′. The masses are m1 = 200 g and m2 = 100 g, and the speed of m1 just before impact is v1 = 6.0 m/s.
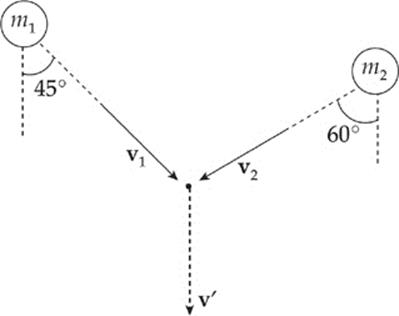
(a) What is v2?
(b) What is v′, the common speed of the clay balls immediately after the collision?
6. (10 points)
A cylindrical tank 50 m high and 60 m in diameter resting on level ground is completely filled with water which is open to the air. A worker accidentally pokes a small hole in the side of the tank, 35 m above the base. The water then flows out through the hole at a rate of 3 × 10–4 m3/min. The tank is shown in the figure below.
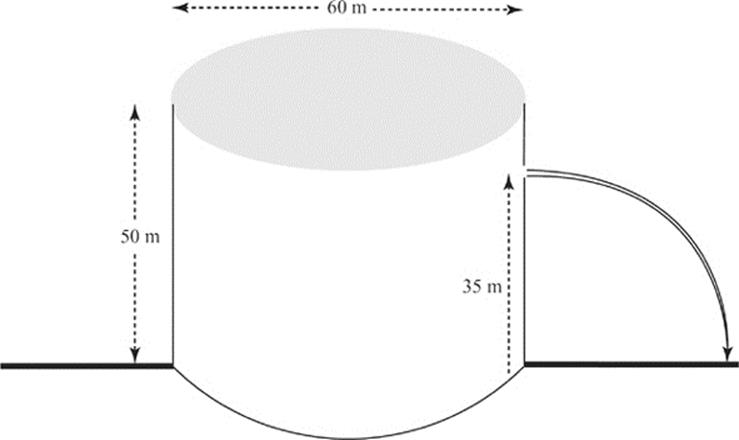
(a) Determine the speed with which the water exits the hole.
(b) What is the diameter of the hole?
(c) How far from the base of the tank does the stream of water initially hit the ground?
STOP
END OF EXAM