Barron's AP Psychology, 7th Edition (2016)
Diagnostic Test
This diagnostic test is designed to provide you a realistic experience of what taking the multiple-choice section of the AP Psychology Exam will be like. These items were written to accurately reflect the content represented on the AP Psychology Exam, and the items are written at a difficulty level similar to items on the actual exam. In addition, you can analyze your correct and incorrect responses in order to decide how to allocate your studying time. After you take this exam and score your responses, you can use the “Multiple-Choice Error Analysis Sheet” to figure out what AP exam score your performance might correspond with, and which units of study you should focus on. Answer the following 100 multiple-choice items (remember to time yourself to make sure you stay within the 70-minute time limit!) and then use the scoring key.
PART I—100 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
TIME—1 HOUR AND 10 MINUTES
Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best in each case.
1.Rocco is a fun-loving, easygoing fellow. He rarely gets angry or upset and never seems to be in a rush. Rocco would best be described as having
(A)an internal locus of control.
(B)a Type B personality.
(C)an Oedipus complex.
(D)an introverted temperament.
(E)self-actualized.
2.Tamil wants to see whether listening to Mozart will improve students’ performance on geometry exams. It is most important that her experimental group consist of
(A)students who already listen to Mozart.
(B)students randomly assigned to listen to Mozart.
(C)students randomly assigned not to listen to Mozart.
(D)students who have already completed geometry.
(E)students who have never studied geometry.
3.The space between the dendrites of one neuron and the terminal buttons of another is the
(A)node of Ranvier.
(B)axon.
(C)medulla.
(D)synapse.
(E)myelin sheath.
4.Which of the following factors helps most to explain the increasing rate of obesity in the United States over the last 100 years?
(A)the changing gene pool
(B)the sedentary nature of modern jobs
(C)the growth in popularity of the cities
(D)the increase in the length of the workday
(E)the lack of opportunities to exercise
5.Learned taste aversions generally result from
(A)negative reinforcement.
(B)shaping.
(C)insight learning.
(D)classical conditioning.
(E)operant conditioning.
6.Creativity is most closely associated with
(A)using algorithms.
(B)divergent thinking.
(C)functional fixedness.
(D)excellent recall ability.
(E)telegraphic speech.
7.Which theory of motivation best explains why some people enjoy dangerous hobbies such as skydiving and bungee jumping?
(A)drive reduction theory
(B)incentive theory
(C)arousal theory
(D)sociobiology
(E)Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
8.After finishing work on a big English project, Leo’s room is a mess. His parents are furious and, without letting him explain, prohibit him from using his car or his cell phone for a month. Using this information, which parenting style are Leo’s parents most likely using?
(A)authoritative
(B)indulgent
(C)neglectful
(D)authoritarian
(E)democratic
9.Calinda is usually a hardworking, frugal, single mother of two. Sometimes, however, she says her name is Meelo, a pop star, and instead of working she goes on spending sprees at local boutiques. On other occasions, she has been known to say that she is an eight-year-old boy named Curtis. Calinda’s symptoms are most typical of
(A)conversion disorder.
(B)dissociative identity disorder.
(C)schizophrenia.
(D)post-traumatic stress disorder.
(E)bipolar disorder.
10.Dr. Li thinks that Tony’s anxiety is due primarily to unresolved issues with his mother from his youth. Dr. Li would best be labeled a
(A)psychoanalyst.
(B)biomedical psychologist.
(C)behaviorist.
(D)cognitive psychologist.
(E)humanistic psychologist.
11.Which of the following types of approaches is used by the greatest number of clinical psychologists in the United States?
(A)eclectic
(B)psychodynamic
(C)humanistic
(D)client-centered
(E)systematic desensitization
12.If Marie Curie, James Madison, and Mahatma Gandhi had all taken an intelligence test and scored poorly, most people would doubt that the test was
(A)projective.
(B)standardized.
(C)valid.
(D)normed.
(E)reliable.
13.The easiest and most common technique used to gather information about people’s personalities is by
(A)administering projective tests.
(B)observing people’s behavior.
(C)using brain scans.
(D)asking people to fill out self-report inventories.
(E)using free association and dream analysis.
14.Saluja decides she wants to try hanging out with a new group of friends. She used to be on the debate team but now tries out for the spring musical. Which of Erikson’s stages is she most likely to be in?
(A)generativity versus stagnation
(B)intimacy versus isolation
(C)autonomy versus shame and doubt
(D)initiative versus guilt
(E)identity versus role confusion
15.Daniel is learning that five pennies spread out on his desk are the same number of coins as five pennies in a pile. According to Piaget, how old is Daniel likely to be?
(A)1 year
(B)2 years
(C)4 years
(D)8 years
(E)13 years
16.Which part of the nervous system is most active in the exhaustion stage of Seyle’s GAS?
(A)somatic
(B)peripheral
(C)central
(D)parasympathetic
(E)sympathetic
17.Your knowledge of skills such as how to tie your shoes or ride a bicycle is thought to be stored in which part of the brain?
(A)hippocampus
(B)cerebral cortex
(C)medulla
(D)amygdala
(E)cerebellum
18.Zach is leaving for college and wants to teach his parents how to program their DVR before he goes. What reinforcement schedule would be more effective to teach them this new skill?
(A)continuous reinforcement
(B)fixed ratio
(C)fixed interval
(D)variable ratio
(E)variable interval
19.Which of the following is an opiate?
(A)cocaine
(B)amphetamines
(C)heroin
(D)nicotine
(E)caffeine
20.Which structure is found in the middle ear?
(A)stirrup
(B)auditory nerve
(C)cochlea
(D)organ of Corti
(E)pinna
21.Mr. Kan is making soup. After tasting it, he decides it needs more salt and slowly adds some until he can first detect that the soup is saltier than it was before. The amount of salt Mr. Kan needs to add depends on his
(A)absolute threshold.
(B)perceptual set.
(C)difference threshold.
(D)olfactory sensitivity.
(E)gate-control theory.
22.Which type of scan uses X-ray technology to examine the structure of the brain?
(A)PET
(B)MRI
(C)CAT
(D)EEG
(E)fMRI
23.To safeguard participants’ rights, prior to collecting any data, researchers are supposed to seek approval from
(A)the American Psychological Association.
(B)at least two licensed psychiatrists.
(C)an Institutional Review Board.
(D)at least one psychiatrist and one psychologist.
(E)everyone on the research team.
24.Which of the following is the best example of basic research?
(A)a first-grade teacher tests two different methods of teaching reading
(B)a psychologist investigates how effective a new therapeutic approach is for treating phobias
(C)a campaign manager commissions a poll to see how popular her candidate’s stand on various issues is
(D)a developmental psychologist explores how children’s use of language changes as they age
(E)a social psychologist studies how charities can convince people to donate more generously
25.An extra chromosome on the twenty-first pair is associated with
(A)Alzheimer’s disease.
(B)Down syndrome.
(C)Tay-Sachs disease.
(D)Klinefelter’s syndrome.
(E)fetal alcohol syndrome.
26.Three-year-old Emma went to see a New York Yankees game in Yankee Stadium. From her seat in the bleachers, the players looked like tiny men, but as she walked toward the field, the players seemed to grow in size, as if by magic. Emma’s belief that the men grew larger is best explained by
(A)damage to her fovea.
(B)place theory.
(C)incomprehension about how to use the Gestalt principles of perception.
(D)her inability to use binocular cues.
(E)the fact that she is still developing size constancy.
27.Infants teach their parents to hold them a lot by crying whenever they are put down. When they are picked up, the babies stop crying. The parents are learning to pick up their babies via
(A)insight learning.
(B)positive reinforcement.
(C)negative reinforcement.
(D)latent learning.
(E)punishment.
28.Which of the following sentences illustrates overgeneralization?
(A)Toby is the fastest boy in the world.
(B)Homey don’t play that game.
(C)Dani goed to the store.
(D)Only human beings have the ability to used language.
(E)All dogs have fur.
29.What theory suggests that using the term “girls” to refer to women might affect the way those people think about women?
(A)the linguistic relativity hypothesis
(B)social learning theory
(C)the nativist theory of language
(D)signal detection theory
(E)arousal theory
30.Jenna invited Mari to a Ben Folds concert. Mari loves Ben Folds but loathes Jenna. What type of conflict is Mari experiencing?
(A)approach-approach
(B)avoidance-avoidance
(C)approach-avoidance
(D)multiple approach-avoidance
(E)None, she should just go to the concert.
31.Wilhelm Wundt’s early work led to the theory of
(A)functionalism.
(B)Gestalt psychology.
(C)trephination.
(D)repression.
(E)structuralism.
32.Which type of personality theorist would most likely be criticized for underestimating the impact of the environment?
(A)trait
(B)behaviorist
(C)cognitive
(D)psychodynamic
(E)social-cognitive
33.Which of the following seems to be least heritable?
(A)hair color
(B)heart disease
(C)religious beliefs
(D)conscientiousness
(E)extraversion
34.Mohammed is trying to develop a test that will predict how great someone’s potential is to be a prizefighter. This type of test would be best described as a(n)
(A)power test
(B)speed test
(C)achievement test
(D)aptitude test
(E)individual test
35.Before you see a question on the AP Psychology exam, it is usually pretested on a group of college students taking an introductory course in psychology. This group of people are referred to as the
(A)standardization sample.
(B)validity testers.
(C)test population.
(D)basis for comparison.
(E)trial group.
36.Which of the following is a somatoform disorder?
(A)narcissistic personality disorder
(B)masochism
(C)generalized anxiety disorder
(D)psychogenic amnesia
(E)conversion disorder
37.Dr. Hernandez believes that poverty lies at the root of most of her inner-city clients’ mental illnesses. This perspective is best labeled
(A)humanistic.
(B)sociocultural.
(C)biomedical.
(D)cognitive.
(E)behavioral.
38.A man calls Janie soliciting money for a charity that fights AIDS. He asks if they can count on Janie to contribute $100. Having never contributed to this charity before, Janie is taken aback by the amount and refuses. The representative of the charity then asks if Janie would be willing to make a $25 donation. What technique is the man representing the charity using?
(A)door-in-the-face
(B)lowballing
(C)norms of reciprocity
(D)self-fulfilling prophecy
(E)foot-in-the-door
39.Elsa hates her boss, but, in order to be successful at work, she goes out of her way to be nice to him. According to cognitive dissonance theory, Elsa’s behavior is likely to
(A)make her resent her boss.
(B)lead her to displace her hostility onto others.
(C)cause her to work below her potential.
(D)result in more positive feelings about her boss.
(E)produce psychological problems in other aspects of her life.
40.ECT is most likely to be used to treat
(A)schizophrenia.
(B)phobias.
(C)depression.
(D)antisocial personality disorder.
(E)ECT is no longer an accepted medical treatment.
41.Which of the following types of therapies would be classified as insight therapy?
(A)psychopharmacology
(B)psychosurgery
(C)flooding
(D)token economy
(E)client-centered therapy
42.Keela’s car breaks down. A woman driving by would be most likely to help her
(A)if the weather is bad.
(B)if they are on a highly trafficked road.
(C)if the driver is a highly religious woman.
(D)if they are on a desolate country road.
(E)if the driver is in a bad mood and can therefore sympathize with Keela.
43.Which of the following is a common symptom of depression?
(A)eating more than usual
(B)working harder than usual
(C)abandoning old hobbies and picking up new ones
(D)making a new group of friends
(E)feeling closer to one’s family
44.Kevin is hoping to find a mate who will love and support him despite all his faults. Carl Rogers might say that Kevin recognizes the importance of
(A)narcissism.
(B)reciprocal determinism.
(C)thematic apperception.
(D)self-actualization.
(E)unconditional positive regard.
45.One drawback of cross-sectional research is that
(A)differences between groups can be due to age or to cohort effects.
(B)it takes a long time to complete this type of research.
(C)participants are particularly likely to drop out during the study.
(D)it is more expensive than most other kinds of research.
(E)it is only effective with participants in certain socioeconomic strata.
46.Which of the following people demonstrates the most achievement motivation?
(A)Joey is a carpenter who is anxious to find a life partner with whom to settle down.
(B)Paula wants to make enough money as a doctor that she can work part-time and still support herself comfortably.
(C)Nino works in an office-supply store. He frequently volunteers to come in early or stay late and prides himself on being a good worker.
(D)Luther is in high school. He studies constantly because his parents give him $10 for every A he brings home, and Luther is saving up to buy a car.
(E)Rula works 80 hours a week at a corporate law firm she hates because she needs to support her extravagant lifestyle.
47.Research has shown that gay and heterosexual men differ in that
(A)homosexual men do not make good parents.
(B)some of their brain structures differ in size.
(C)heterosexual men are less likely to have suffered traumatic experiences as children.
(D)the mothers of gay men are unusually domineering.
(E)heterosexual men have more conflict with their parents.
48.In the past when Nuara’s computer wouldn’t print, she remedied the situation by restarting the computer. One day Nuara’s printer came unplugged, but instead of checking the connections, she repeatedly restarted the computer. Nuara’s behavior can best be explained by
(A)proactive interference.
(B)functional fixedness.
(C)belief bias.
(D)framing.
(E)mental set.
49.According to the partial reinforcement effect,
(A)highly desirable rewards are more effective than partial ones.
(B)it is essentially impossible to find a reinforcer that influences everyone.
(C)behaviors will be more resistant to extinction if they were reinforced intermittently.
(D)punishment is most effective when it is divorced entirely from any signs of reinforcers.
(E)people prefer certain types of reinforcement.
50.During a typical night of sleep, the average adult spends the most time in
(A)stage 1.
(B)stage 2.
(C)stage 3.
(D)stage 4.
(E)REM.
51.Paul stared out the window as the train he was on raced through the countryside. He noticed that the telephone poles near the tracks seemed to fly by while the houses in the distance seemed to move slowly. This apparent difference in speed of movement is known as
(A)texture gradient.
(B)motion parallax.
(C)stroboscopic motion.
(D)the phi phenomenon.
(E)relative speed.
52.In vision, the goal of accommodation is
(A)to focus the image on the retina.
(B)to maximize the amount of light that gets through the pupil.
(C)to decrease the size of the blind spot.
(D)to protect the lens.
(E)to help the eyes rotate.
53.Farnaz randomly selected 50 new mothers to interview out of the 362 new mothers who gave birth in Random City’s Central Hospital during the summer of 2011. What is Farnaz’s population?
(A)new mothers in Random City hospitals
(B)new mothers in urban areas in the United States
(C)new mothers throughout the world
(D)the 50 new mothers with whom Farnaz speaks
(E)the 362 new mothers at Central Hospital that summer
54.Sabrina finds a strong, negative correlation between hours spent meditating and reported stress levels. Her findings indicate that
(A)if a person meditates daily, she or he will not experience any stress.
(B)people who meditate a lot tend to have higher stress levels.
(C)meditation lowers stress levels in humans.
(D)people with low stress levels meditate more than people with high stress levels.
(E)the failure to meditate is a major cause of stress in humans.
55.In the early twentieth century in the United States which of the following perspectives was most prominent?
(A)biological
(B)behaviorist
(C)psychoanalytic
(D)gestalt
(E)cognitive
56.In which of the following groups would you expect to find the greatest standard deviation in IQ scores?
(A)the graduating class of Princeton University
(B)a special program for children who suffer from severe mental retardation
(C)elementary school students in a large, public school system
(D)the entering class of an elite preparatory school in India
(E)girls who attend a small, single-sex, private high school
57.Which of the following is a hormone?
(A)dopamine
(B)endorphins
(C)insulin
(D)GABA
(E)acetylcholine
58.Gonzo raised his hand to answer his teacher’s question. Which part of his nervous system most directly allowed him to perform this behavior?
(A)parasympathetic
(B)somatic
(C)autonomic
(D)sympathetic
(E)central
59.Which part of the brain is most important in regulating an animal’s sex drive?
(A)amygdala
(B)hypothalamus
(C)pituitary gland
(D)medulla
(E)hippocampus
60.Five-year-old Olivia has never been outside of her neighborhood in New York City. Walking home from school one day, Olivia saw a cow standing in the middle of a cement ball field. To recognize the cow, Olivia most likely had to rely on
(A)signal detection theory.
(B)perceptual set.
(C)bottom-up processing.
(D)difference threshold.
(E)brightness constancy.
61.After staring at a painting of a red and yellow parrot in a birdcage for a full minute, Saju turns his gaze to an empty birdcage painted on a white wall. What will he see in the empty cage?
(A)the red and yellow parrot
(B)a red and green parrot
(C)a green and blue parrot
(D)a blue and yellow parrot
(E)nothing, just an empty cage
62.In Tolman’s experiment on latent learning, latent learning was shown by
(A)the rats whose performance declined steadily throughout the trials.
(B)the rats whose progress improved steadily throughout the trials.
(C)the rats whose progress improved markedly once a reward was introduced.
(D)the rats whose progress declined markedly once a reward was introduced.
(E)the rats whose progress never improved significantly.
63.According to the contingency theory of classical conditioning,
(A)stronger URs result in better learning.
(B)the more pleasant the CR, the more likely it will be learned.
(C)the more times you pair a CS and US, the stronger the conditioning that will result.
(D)people learn best when the US precedes the CS.
(E)strength of conditioning depends on the extent to which the CS reliably predicts the US.
64.Which statement about memory is true?
(A)People can correctly gauge the accuracy of their memories.
(B)Children initially have accurate memories of their first few years of life but forget them as they age.
(C)Older people are worse at all types of memory tasks than are younger people.
(D)Memories are like stored video images.
(E)There is no one place in the brain where memories are stored.
65.Kelsey is an attractive twenty-something with many friends. She is struggling to make a name for herself in Hollywood as an actress. Although she gets enough work to support herself, she does mostly commercials and small roles in minor films. Abraham Maslow would say that Kelsey is still striving to meet her need
(A)to self-actualize.
(B)for safety.
(C)for esteem.
(D)to belong.
(E)for power.
66.When a newborn baby is sleeping, which reflex will be elicited by a sudden noise or touch?
(A)Babinski
(B)plantar
(C)rooting
(D)Moro
(E)grasping
67.Kate, a newborn baby, probably most likes to look at
(A)her cousin’s toy robot.
(B)pastel colored blocks.
(C)her stuffed sheep.
(D)cartoons on television.
(E)her own face.
68.Roscoe works for a nasty and abusive boss but tells everyone what a wonderful woman she is. Psychoanalysts would say that Roscoe is using which of the following defense mechanisms?
(A)displacement
(B)reaction formation
(C)projection
(D)sublimation
(E)intellectualization
69.In a normal distribution, approximately what percentage of people’s scores fall between the z scores of –2 and +2?
(A)25
(B)50
(C)75
(D)82
(E)95
70.The typical age of onset for schizophrenia is
(A)at birth.
(B)during childhood.
(C)during young adulthood.
(D)during middle age.
(E)after age 70.
71.Research suggests that genetic and other biological factors play the greatest role in causing
(A)simple phobias.
(B)agoraphobia.
(C)dissociative identity disorder.
(D)bipolar disorder.
(E)conversion disorder.
72.Armand is the president of his local chapter of the National Rifle Association (NRA). He incorrectly believes that only a tiny, fringe element of Americans favor stronger gun control laws. Armand’s mistake is best explained by
(A)deindividuation.
(B)the just-world bias.
(C)norms of reciprocity.
(D)the false consensus effect.
(E)outgroup bias.
73.Dr. Lupin challenges her depressed clients’ beliefs that their lives are hopeless and without purpose and gives them homework assignments in which the clients are required to engage in the activities that used to bring them joy. What type of therapy is Dr. Lupin using?
(A)existential
(B)rational emotive behavior therapy
(C)Gestalt
(D)psychoanalytic
(E)modeling
74.Milgram’s obedience studies showed that
(A)members of minority groups were better able to stand up to authority figures than Caucasians.
(B)absolute obedience was best achieved under hypnosis.
(C)most people would obey an authority figure’s order to harm a stranger.
(D)people would follow orders up to a point but almost all refused to do something illegal or immoral.
(E)women are far more obedient than men are.
75.If Artie always seems to act competitively, even in situations where others do not, people are likely to make what kind of attribution about the cause of Artie’s competitiveness?
(A)fundamental
(B)situation-stable
(C)situation-unstable
(D)person-stable
(E)person-unstable
76.Which of the following is one of the main advantages of group therapy?
(A)The client develops lasting friendships with all the other members of the group.
(B)The success rate of group therapy is higher.
(C)It reduces the financial burden of therapy.
(D)Group therapists generally have more years of training than individual therapists.
(E)The therapy usually takes less time.
77.Tom is a Type A individual who is seeking short-term, focused psychotherapy to help him make his lifestyle healthier. With what kind of therapist do you think Tom would be happiest?
(A)behaviorist
(B)psychodynamic
(C)sociocultural
(D)humanistic
(E)somatic
78.Which of the following is an example of hostile aggression?
(A)Billy shoots a deer in order to feed his family supper.
(B)Joe beats up a man at an ATM because he wants to steal his money.
(C)Lula screams at her cat to scare him off the kitchen table.
(D)Tutti hits her younger brother because she’s angry at her mother.
(E)Mike pushes another man out of the way to grab the shirt he wants off the sale rack.
79.According to Howard Gardner, which of the following is a type of intelligence?
(A)naturalist
(B)practical
(C)experiential
(D)fluid
(E)general
80.Dr. Kraysin rejects the Big Five model of personality because she believes that people are so different it is impossible to describe them all with a common set of traits. What kind of trait theory would Dr. Kraysin favor?
(A)cognitive
(B)psychodynamic
(C)idiographic
(D)sociocultural
(E)individual
81.Drinking alcohol while pregnant increases the chance that the child
(A)will be born with an addiction to alcohol.
(B)will have a low birth weight.
(C)will suffer from mental retardation.
(D)will grow up to be a drug dealer.
(E)will have heart disease.
82.Supporters of attachment parenting argue that babies like to be held all the time and that parents should seek to maximize the amount of physical contact they have with their babies. Such research is most in line with the findings of
(A)Gilligan.
(B)Piaget.
(C)Harlow.
(D)Freud.
(E)Kohlberg.
83.Isabella fondly remembers the first time she went skydiving. This information is an example of
(A)declarative memory.
(B)semantic memory.
(C)implicit memory.
(D)eidetic memory.
(E)procedural memory.
84.According to the James-Lange theory of emotion
(A)a specific physiological reaction to an event triggers the recognition of a specific emotion.
(B)the thalamus is the key part of the brain involved in emotion.
(C)an initial emotion leads to the expression of the antagonistic emotion and that second emotion grows stronger with repetition.
(D)emotions are expressed the same way across different cultures.
(E)different emotions result from different interpretations of similar physiological responses.
85.Which of the following is an example of observational learning?
(A)a girl learns to howl by watching wolves on a television show
(B)a parrot learns to say “mama” by listening to its owner
(C)a student learns to type through the process of trial and error
(D)a kitten learns to chase birds by copying its mother
(E)a boy learns to make his bed after his parents reward him with money
86.Which of the following is an example of discrimination?
(A)Jessica continues to talk during class even after being publicly reprimanded by the teacher.
(B)Melissa has learned to dig for earthworms only after it rains.
(C)Franz always bounces the basketball three times before shooting a free throw.
(D)After his father yells at and punishes him, Helmut winces when he hears a man yell on television.
(E)Mr. Black wants his students to call him by his first name and not to raise their hands. Weeks into the semester after having given up these habits, some of Mr. Black’s students still occasionally raise their hands.
87.In a normal distribution,
(A)95 percent of the scores fall within one standard deviation of the mean.
(B)everyone scores within three standard deviations of the mean.
(C)the mean is always greater than the median.
(D)the mean, median, and mode are all equal.
(E)the standard deviation is always less than 1.0.
88.When a neuron initially depolarizes
(A)sodium ions flow into the cell.
(B)chloride ions flow into the cell.
(C)magnesium ions flow into the cell.
(D)potassium ions flow out of the cell.
(E)strontium ions flow out of the cell.
89.The part of the brain most responsible for making decisions is the
(A)thalamus.
(B)amygdala.
(C)hippocampus.
(D)prefrontal cortex.
(E)corpus callosum.
90.Which of the following cognitive tendencies is most closely related to the problem of experimenter bias?
(A)the availability heuristic
(B)functional fixedness
(C)the representative heuristic
(D)confirmation bias
(E)overconfidence
91.As Mobu walked to homeroom, he passed dozens of his classmates in the hallway. What they were wearing that day was briefly in Mobu’s
(A)short-term memory.
(B)iconic memory.
(C)long-term memory.
(D)echoic memory.
(E)working memory.
92.Tiger lillies appear orange because they
(A)reflect orange light.
(B)absorb orange light.
(C)transduce orange light.
(D)reflect red light and absorb yellow light.
(E)reflect yellow light and absorb red light.
93.Your knowledge of who the first president of the United States was is usually found in which level of your consciousness?
(A)conscious
(B)nonconscious
(C)preconscious
(D)subconscious
(E)unconscious
94.Karl is so consumed by his fears of sexual inadequacy that he has not been on a date in over two years. To which of the following would a psychoanalyst be most likely to attribute Karl’s problem?
(A)an overly strong libido
(B)the reality principle
(C)the preconscious
(D)an anal expulsive personality
(E)a phallic fixation
95.Banu scored 130 on the WISC. What is his z score and approximately what percentile is he in?
(A)–2, 2nd
(B)–2, 16th
(C)0, 50th
(D)2, 90th
(E)2, 98th
96.Which of the following is a positive symptom of schizophrenia?
(A)flat affect
(B)greater sensitivity toward others
(C)catatonia
(D)reduced depression
(E)hallucinations
97.Broca’s area is usually located in which part of the cortex?
(A)left frontal lobe
(B)right frontal lobe
(C)left temporal lobe
(D)right temporal lobe
(E)right parietal lobe
98.Dr. Soo is a psychiatrist who wants to prescribe a drug for one of her patients who is suffering from GAD. Which of the following drugs is she most likely to prescribe?
(A)tricyclic antidepressants
(B)Thorazine
(C)Haldol
(D)lithium
(E)Valium
99.One possible explanation for group polarization is
(A)out-group bias.
(B)self-fulfilling prophecy.
(C)self-serving bias.
(D)the fundamental attribution error.
(E)diffusion of responsibility.
100.Which is typical of a positively skewed distribution?
(A)The mean is higher than the median.
(B)The mean is lower than the median.
(C)There are more high scores than low scores.
(D)The mode is higher than the median but lower than the mean.
(E)The mode is lower than the median but higher than the mean.
PART II—TWO FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS
TIME: 50 MINUTES
Directions: You have 50 minutes to answer the TWO questions that follow. Your answer should present an argument rather than a list of facts. Make sure to incorporate psychological terminology into your answers whenever possible.
1.Professor Willborn recently completed a naturalistic observation study on people who play violent video games. She submitted her work for publication and one of the reviewers suggested that she further investigate the relationship between violent video games and attitudes toward real-world violence using a different research method. Professor Willborn is considering using the experimental method or the correlational method for the follow-up study. Answer the following questions about both research methods:
■What variables would Professor Willborn examine in her experimental study? What variables would Professor Willborn examine in her correlational study? (Use specific terminology associated with the variables if appropriate.)
■How could Professor Willborn operationally define at least one of the variables in her experimental study? How could Professor Willborn operationally define at least one of the variables in her correlational study? (Do not define the same variable for both methods.)
■How could Professor Willborn organize her participants to gather data in her experimental study? How could Professor Willborn organize her participants to gather data in her correlational study?
■What kind of conclusion would Professor Willborn be able to form based on the results of her experimental study? What kind of conclusion would Professor Willborn be able to form based on the results of her correlational study?
2.One of the important contributions of psychology has been to identify aspects of thinking and experiences outside of conscious awareness. Define each of the terms below and provide an example showing how each concept describes an influence on behavior that people are not consciously aware of.
■Selective attention
■Cognitive dissonance
■Fundamental attribution error
■Perceptual set
■Sensory memory
MULTIPLE-CHOICE ERROR ANALYSIS SHEET
After checking your answers on the practice test, use the tables below to analyze your results.
The first table below indicates what overall AP exam score is mostly likely for different ranges of scores on the multiple-choice section of the test. Performance on the free-response questions will influence the overall score, but performance on the multiple-choice section is a good predictor of the overall exam score. Note that this exam is different than many exams you are used to: getting 75% correct on an exam in your AP psychology class would probably worry you and your teacher, but getting 70 out of the 100 multiple-choice items correct on the AP Psychology Exam is likely to earn you an overall score of a 4! (Note: This table changes for each test each year, so the table below is an approximation based on recently released exams).
|
Number of Multiple-Choice Items Correct |
Overall Exam Score You Would Most Likely Receive |
|
88–100 |
5 |
|
74–87 |
4 or a 5 |
|
60–73 |
3 or a 4 |
|
45–59 |
2 or a 3 |
|
30–44 |
1 |
|
0–29 |
1 |
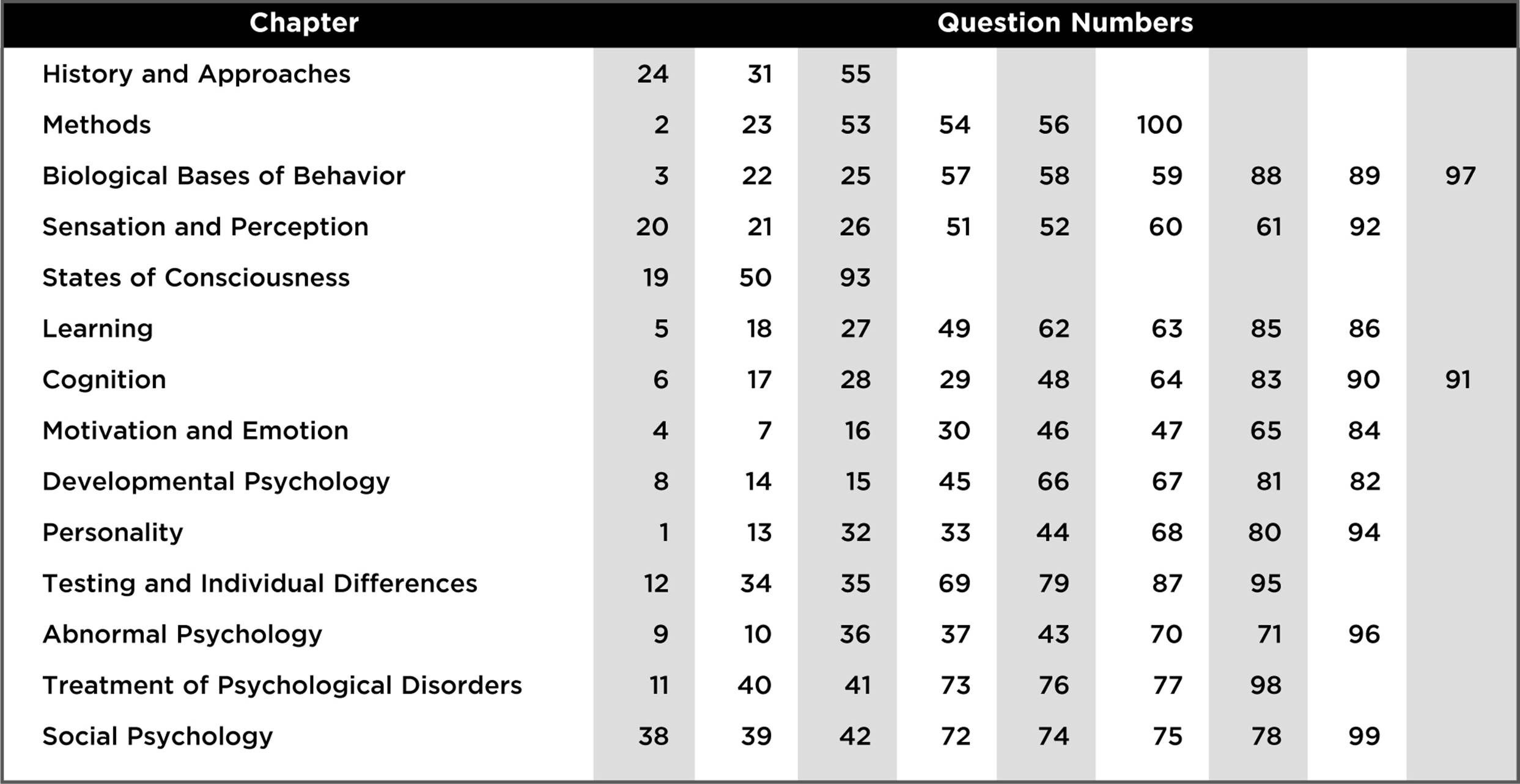
Use the table below to “diagnose” your performance on the practice test: You can classify your errors by topic area, which will give you an idea about what your “stronger” and “weaker” chapters might be. By circling the numbers of the questions you answered incorrectly in the table below, you can get a picture of which chapters you might need to focus your study on.
PART II
QUESTION 1 SCORING RUBRIC
Directions: This is an 8-point question. Each bullet represents two possible points. You earn 1 point for answering the question about the experimental method and one point for answering the question about the correlational method.
You would need to describe the follow-up studies and address the questions somewhere in your descriptions.
You do NOT need to define terms in your answer, and definitions alone will not score. The question asks you to answer questions about how Professor Willborn could use the experimental and correlational method to study the relationship between violent video games and attitudes toward real-world violence.
POINT 1
What variables would Professor Willborn examine in her experimental study?
Awarded if you identified playing violent video games as the independent variable in the experiment and attitude toward real-world violence as the dependent variable. The reviewer suggested that the follow-up study investigate the relationship between playing violent video games and attitudes toward real-world violence, so playing violent video games is the only valid independent variable and attitude toward real-world violence is the only valid dependent variable for an experimental study on this research question.
POINT 2
What variables would Professor Willborn examine in her correlational study?
Awarded if you identified playing violent video games and attitudes toward real-world violence as the two variables to be correlated. The terms independent variable and dependent variable are not usually associated with correlational studies.
POINT 3
How could Professor Willborn operationally define at least one of the variables in her experimental study?
Awarded if you explained a possible operational definition for either playing violent video games or attitude toward real-world violence. There are multiple ways to operationally define these variables, and the point will be awarded if you describe any of the ways to measure this behavior (e.g., self-reports of video game playing, observations of video game playing) or this attitude (e.g., a survey, interview, physiological measure while watching a media portrayal of real-world violence, etc.).
POINT 4
How could Professor Willborn operationally define at least one of the variables in her correlational study?
Awarded if you explained a possible operational definition for either playing violent video games or attitude toward real-world violence. There are multiple ways to operationally define these variables, and the point will be awarded if you describe any of the ways to measure this behavior (e.g., self-reports of video game playing, observations of video game playing) or this attitude (e.g., a survey, interview, physiological measure while watching a media portrayal of real-world violence, etc.). Note: You cannot earn point 4 if you operationally define the same variable as the variable defined for point 3.
POINT 5
How could Professor Willborn organize her participants to gather data in her experimental study?
You must explain that participants are organized into at least two separate groups differing by the independent variable (playing violent video games). You may use the term “control group” and “experimental group” but need to clearly show that the groups are different based on the independent variable.
POINT 6
How could Professor Willborn organize her participants to gather data in her correlational study?
Awarded if you explained how two pieces of data (the two variables: playing violent video games and attitude toward real-world violence) are gathered from each participant in the correlational study. You will NOT be awarded the point if you implied that participants are divided into separate groups based on the independent variable.
POINT 7
What kind of conclusion would Professor Willborn be able to form based on the results of her experimental study?
Awarded if you explained that the experimental study could lead to a causal inference about the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable. You can explain this conceptually or through an example of a causal conclusion based on this study.
POINT 8
What kind of conclusion would Professor Willborn be able to form based on the results of her correlational study?
Awarded if you explained that the correlational study could lead to predictions about the relationship between the variables. You will NOT be awarded the point if you implied that correlational studies can lead to causal inferences about the relationship between the variables. You can describe how the study might indicate that one variable increases as the other variable increases (positive correlation), one variable decreases as the other variable increases (negative correlation), or that the study might establish no statistical relationship between the variables (no or zero correlation). You can also use correlation coefficients (r values) correctly to gain the point.
Sample Essay
Professor Willborn should redesign her study as an experiment or a correlation. These methods are considered to get better data than naturalistic observation studies.
When she redesigns her study as an experiment, Professor Willborn would have to assign the variables correctly. In every experiment, there is an independent variable and a dependent variable. In this study, the independent variable is video games and the dependent variable is how violent the video games are and what that does to the players attitude toward violence. So what she could do is find a sample of people willing to do her experiment, get them all to play violent video games in her lab under controlled conditions, and then observe them to figure out whether they enjoyed the violence in the video games or not. In this way the dependent variable is operationally defined by getting everyone to play violent video games in a controlled way that she can measure. She could organize her participants to gather her data by making sure they are all present and ready for the testing, and again by measuring them carefully. Also, she should probably set up this experiment in a double-blind way. Since the people playing the games don’t know what she’s testing, they wouldn’t be biased and change their natural reactions. In the end, after doing all this, Professor Willborn should be able to conclude whether playing violent video games causes people to change their attitudes about real-world violence. It might turn out that playing violent video games causes people to not care as much about violence they see in their lives.
When she redesigns her study as a correlational study, Professor Willborn should try to correlate the important variables to figure out whether they correlate or not. In her study, just like in the experimental study, she would choose the variables “playing violent video games” and “attitude toward real-world violence” as the variables she will correlate. She could operationally define these variables by being careful how she observes them. If she observes them in a controlled way in her lab, then they will be operationally defined. What she would have to do is, again, have people play violent video games in her lab in a controlled way. But in the correlational study, she would organize her people to get her data by interviewing them after she times how long they play the games to see if their attitude toward real-world violence has changed. She would use these interviews to figure out if their attitude toward real-world violence changed after playing the video games. Then she could look at how long they played the games and how much their attitude changed. After she got all her data, she should be able to figure out if there is a correlation between playing video games and attitude change. She might find a positive correlation, which means that the people who played violent video games the most also changed their attitudes the most. Correlation does not imply causation, but she might find this correlation relationship between these variables in this study.
This might be a lot of work for Professor Willborn, but if she really wants to figure out what playing violent video games does to people, she’s going to have to do something like this. Psychological studies are often complicated and take a lot of time.
Sample Essay Scoring
Notice that the first paragraph of this (fictional) student’s essay does not score any points. This student introduces the topic with a short paragraph, which is fine but does not answer any part of the essay question directly. It’s not necessary to provide an introduction paragraph in your AP Psychology essay—just dive into answering the question in order. This student chooses to answer all of the questions about the experimental design in one paragraph and all of the questions about the correlational method in a separate paragraph. This organization works well. The student could have also chosen to answer the questions in paragraphs grouped by the pairs of questions listed within the question.
The points this fictional student essay scores and doesn’t score are:
POINT 1
What variables would Professor Willborn examine in her experimental study?
Does NOT score, because the student incorrectly identifies the independent variable as video games. The rubric requires that students identify the independent variable as playing violent video games. Defining the independent variable as video games is too vague to score.
POINT 2
What variables would Professor Willborn examine in her correlational study?
Scores in the second sentence of the third paragraph when the student identifies the two variables to be correlated correctly: “the variables playing violent video games and attitude toward real-world violence as the variables she will correlate.”
POINT 3
How could Professor Willborn operationally define at least one of the variables in her experimental study?
Does NOT score. The student does not explain specific operational definitions of either variable. Stating that “being careful how she observes them . . . in a controlled way in her lab” is not specific enough to earn the point for operational definitions. The student does not provide possible operational definitions of both variables, so the point is not awarded.
POINT 4
How could Professor Willborn operationally define at least one of the variables in her correlational study?
Does NOT score. The student says “She could operationally define these variables by being careful how she observes them. If she observes them in a controlled way in her lab, then they will be operationally defined.” This statement is too vague to score, because it does not meet the rubric requirement to provide a possible operational definition for either variable in the study.
POINT 5
How could Professor Willborn organize her participants to gather data in her experimental study?
Does NOT score. The student never mentions organizing participants into groups based on the independent variable. What the student says about organizing participants is too vague and not relevant to creating control and experimental groups in the study.
POINT 6
How could Professor Willborn organize her participants to gather data in her correlational study?
Scores when the student says “organize her people to get her data by interviewing them after she times how long they play the games to see if their attitude toward real-world violence has changed.” The student meets the rubric requirement by describing how data on the two variables could be gathered from each participant.
POINT 7
What kind of conclusion would Professor Willborn be able to form based on the results of her experimental study?
Scores when the student says “playing violent video games causes people to change their attitudes about real-world violence.” This statement states a causal conclusion about the variables clearly, which meets the requirement of the rubric.
POINT 8
What kind of conclusion would Professor Willborn be able to form based on the results of her correlational study?
Scores when the student says “She might find a positive correlation which means that the people who played violent video games the most also changed their attitudes the most.” The student states and explains the positive correlation that might be found between the variables. The student goes on to clearly demonstrate knowledge about the difference between causal and correlational influences, but the point was already scored when the student explained the potential positive correlation conclusion.
Overall, this essay scores 5 of the 8 possible points.
QUESTION 2 SCORING RUBRIC
Directions: This is a 10-point question. Each definition of the 5 terms counts for 1 point, and each description of how the concept demonstrates a nonconscious influence is 1 point.
You do not need to use the exact words used to define the terms, but must communicate the meaning of the definition provided in the rubric.
You should use examples for the description points that describe an influence on behavior out of our conscious awareness. Examples alone will NOT score the definition points, but will score on the description points.
POINT 1
Definition, Selective Attention
Awarded if you defined selective attention as the process of focusing on something in the environment, and as a consequence that information is encoded into memory. You may be more specific about the process, stating that selective attention determines what information from sensory memory is encoded into short-term memory, but that level of detail is not needed to score the point.
POINT 2
Description, Selective Attention
Awarded if you provided an example that explains how selective attention is often not deliberate. Some aspect of our consciousness that we are not aware of often determines what we pay attention to, and consequently what information is encoded into memory through selective attention.
POINT 3
Definition, Cognitive Dissonance
Awarded if you defined cognitive dissonance as the tension that exists when our attitudes do not match our behaviors.
POINT 4
Description, Cognitive Dissonance
Awarded if you provided an example that describes how we are not aware of cognitive dissonance and its subsequent effects on our attitudes and behaviors. The example must clearly show that we are not consciously aware of either the tension created by cognitive dissonance or how we change our attitudes or behavior to relieve the dissonance.
POINT 5
Definition, Fundamental Attribution Error
Awarded if you defined the fundamental attribution error as the tendency to overestimate the importance of dispositional (such as personality) factors and underestimate the role of situational factors when we judge the behaviors of others. Both dispositional and situational factors need to be referred to in the definition.
POINT 6
Description, Fundamental Attribution Error
Awarded if you provided an example that shows we are not consciously aware of attributing behavior to being caused by inner dispositions rather than being caused by the situation. The example must clearly show how this error is not purposeful or a matter of choice. The error occurs and we are not consciously aware of having committed it.
POINT 7
Definition, Perceptual set
Awarded if you defined perceptual set as a predisposition to perceiving sensations in a certain way. Valid definitions must include the words or appropriate synonyms for perception and sensation.
POINT 8
Description, Perceptual set
Awarded if you provided an example that shows how perceptual sets determine how we perceive sensations without our choice or conscious awareness of their effects. The example must clearly show how perceptual sets create perceptions out of sensations instead of a conscious choice about how to perceive sensations.
POINT 9
Definition, Sensory Memory
Awarded if you defined sensory memory as the split-second holding area for incoming sensory information. Scorable definitions must include the concept that sensory memory lasts a very short period of time and all sensory information flows into sensory memory.
POINT 10
Description, Sensory Memory
Awarded if you provided an example that shows how sensory events are automatically encoded into sensory memory for a split second without our choice or awareness. The example must include the idea that we are not aware of encoding these sensory events and we do not choose which sensory events are encoded in sensory memory.
Sample Essay
Psychology is a very important subject that has discovered many important things. We all need to pay attention to psychology and psychology theories because they matter to us and to our loved ones.
One of the most important contributions of psychology has been to identify aspects of thinking and experiences outside of conscious awareness. What this means is that psychology helps us figure out what we think even if we don’t really know why we think it.
Perceptual sets are things that determine what we perceive. They are like rules that help our brains figure out what to do with what we see, hear, etc. How this applies to this question is that we don’t really know what these rules are, and these perceptual set rules determine how we see the world around us even though we aren’t aware of them.
Cognitive dissonance are things that really bother us about what we think. If we think something bad about a friend then it’s going to bother us even if we aren’t aware of why it’s bothering us.
Selective attention is when you pay attention to something so you remember it better later. We all choose to pay attention to certain things and then those things get encoded into memory a lot better. Sometimes you don’t even know why you pay attention to something (like a loud bang or someone saying your name), but because of selective attention you are going to remember those things better even though you didn’t know or choose what to pay attention to.
Sensory memory is our memory for sensory things. It applies to this question because we don’t choose what senses to pay attention to. Everything that happens around us ends up in sensory memory at least for a little while, so that happens outside our conscious awareness.
The fundamental attribution error is when you attribute something to someone without being consciously aware of it. You might think they are mean or nice or rich or poor but you don’t really choose to think that way about them. It’s just automatic, like stereotyping.
All of these concepts and theories are very important to psychology and to figuring out why we do what we do, even if we aren’t aware of doing them.
Sample Essay Scoring
Notice that the first two paragraphs of this (fictional) student’s essay do not score any points. This is a good example of a student who tries to introduce the topic and provide a transition into answering the question. These writing techniques are useful in most other contexts, but remember that answering the AP Psychology essay question is a unique experience unlike a lot of other writing you do. Don’t worry about writing an introductory paragraph, or easing the reader into the topic. Just dive in and answer the question.
Also, notice that this (fictional) student answers the points out of order. This way of organizing is not necessarily a problem because readers are trained to look for scorable points wherever they occur in a student essay. But you aren’t doing yourself or the AP reader any favors by going out of order. The readers are using a scoring rubric that is written in the order provided by the question, and you make their lives easier by going in order, and there is a slight chance they may miss a scorable part of your essay by going out of order.
The points this (fictional) student essay scores and doesn’t score are:
POINT 1
Definition of Selective Attention
Scores when student says in the fifth paragraph: “Selective attention is when you pay attention to something so you remember it better later.” This definition matches the rubric definition. Notice that the student gives what might be incorrect information in the next sentence: “We all choose to pay attention to certain things and then those things get encoded into memory a lot better.” The point is already awarded, so the reader doesn’t worry about whether this next sentence indicates that the student thinks that selective attention is always under our control.
POINT 2
Description, Selective Attention
Scores in the fifth paragraph when the students says: “Sometimes you don’t even know why you pay attention to something (like a loud bang or someone saying your name), but because of selective attention you are going to remember those things better.” This statement and example indicates that the student understands that selective attention is not always under our conscious control, and meets the rubric requirement.
POINT 3
Definition, Cognitive Dissonance
Does NOT score. The student tries to define cognitive dissonance in the fourth paragraph, but the definition “Cognitive dissonance are things that really bother us about what we think” does not meet the rubric requirement that it must be a dissonance between our attitudes and behaviors.
POINT 4
Description, Cognitive Dissonance
Does NOT score. The example provided about stereotyping is not specific enough to cognitive dissonance to match the rubric or score the point.
POINT 5
Definition, Fundamental Attribution Error
Does NOT score. The student defines fundamental attribution error in paragraph seven as “when you attribute something to someone without being consciously aware of it.” This definition is not specific enough to score the point. The rubric requires that a definition of this concept address situational factors and dispositional factors in some way, and the definition the student provided does not address these factors.
POINT 6
Description, Fundamental Attribution Error
Does NOT score. The student may be trying to address this point with the example in paragraph seven, but the example just describes an automatic thought about another person, not an example of the fundamental attribution error being committed. The student establishes clearly that the thought is “automatic” and nonconscious, but the example is not specific enough to the fundamental attribution error to match the rubric.
POINT 7
Definition, Perceptual set
Scores in the third paragraph when the student says: “They are like rules that help our brains figure out what to do with what we see, hear, etc.” This definition matches the rubric requirement for the definition, since it implies that perceptual sets are predispositions to perceiving sensations in certain ways. Notice that the first sentence comes close to a valid definition, but the student uses the word “things,” which is too vague because it does not establish that these “things” are cognitive rules, predispositions, and so on.
POINT 8
Description, Perceptual set
Scores in the third paragraph when the student says: “we don’t really know what these rules are, and these perceptual set rules determine how we see the world around us even though we aren’t aware of them.” This example matches the rubric requirement that students need to describe how perceptual sets determine perceptions without our conscious choice or awareness.
POINT 9
Definition, Sensory Memory
Does NOT score. The student defines sensory memory in a very vague way in paragraph six, and the definition does not match the rubric requirement. The student does not say that sensory memory is a split-second holding area, and “sensory things” is too vague to imply sensory information.
POINT 10
Description, Sensory Memory
Scores in the sixth paragraph when the student says: “Everything that happens around us ends up in sensory memory at least for a little while, so that happens outside our conscious awareness.” This is a good example of how a student may not be able to define a concept well, but does understand the concept well enough to apply it to lack of conscious awareness. The student describes how all sensory events are encoded into sensory memory for a short time without our conscious awareness. This matches the rubric requirement well and scores the point.
Overall, this essay scores 5 points out of 10.