The Handy Chemistry Answer Book (2014)
BIOCHEMISTRY
BRAINS!
What are neurons?
Neurons are cells responsible for transmitting information between different locations in the body. Their functions are diverse and include telling muscles to move, passing information from your sensory organs to your brain, making you experience pleasure, and processing information in your brain.
What is neuroscience?
Neuroscience refers to science that studies the way the brain and nervous system works.
What are the different parts of the brain?
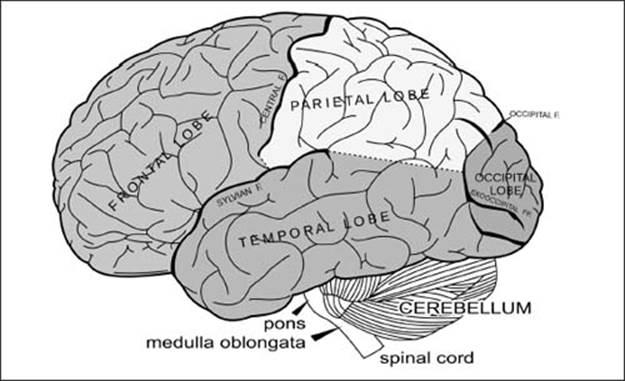
The brain is divided into several areas that specialize in different functions. Some of the major sections of the brain are the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the temporal lobe, the pons, the medulla oblongata, the occipital lobe, and the cerebellum. The spinal cord connects the brain to the body via millions of nerves that transmit information between the brain and the rest of the body.
What is the cerebrum?
The cerebrum is the top part of the brain, and it contains your memories, knowledge, and languages, and it manages your senses as well. The cerebrum is the part of your brain that controls your movements and emotions and it’s where your thoughts take place.
The major parts of the human brain.
What happens in the frontal lobe?
The frontal lobe is responsible for decision-making processes and problem-solving as well as managing your active memory.
What is the parietal lobe for?
Your parietal lobe controls your speech, visual perception, pain and touch perception, spatial orientation (like knowing what direction is up), and other cognitive processes. As you can probably tell by now, there is some degree of overlap between the broad types of functions carried out by different parts of the brain.
And the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobe is involved in hearing, memory, and language skills.
What about the occipital lobe?
The occipital lobe is in charge of visual perception; it’s responsible for processing the information received by our eyes.
What happens in the cerebellum?
The cerebellum is important for controlling your sense of balance, motion, and your motor skills in general.
A part of my brain is called the pons?
Yes. The pons is located in the brainstem, and its function is to move information between the cerebellum and the cerebrum.
Medulla oblongata? Now you’re just making words up.
Nope. The medulla oblongata is a bunch of neurons packed together in the back of the brain. These neurons control bodily functions such as your heartbeat, breathing patterns, the constriction or dilation of blood vessels, sneezing, and swallowing.

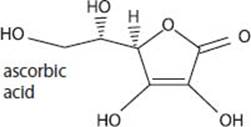
Many fruits contain ascorbic acid (vitamin C), which is important to our health. It aids in preventing inflammations, boosts our immune systems, and helps us in the digestion of foods, among other benefits.
What is a prion disease?
Prions are misfolded forms of proteins that behave in an infectious manner. They do so by causing other proteins they encounter to misfold as well. A prion disease is a disease that results from this misfolding. Some examples of prion diseases include Mad Cow Disease, Scrapie, and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. In mammals, all known prion diseases are actually caused by the same prion protein, known as PrP; the abbreviation actually stands for “prion protein.”
What are some examples of naturally occurring molecules that affect our biochemistry?
Ascorbic acid, also known as vitamin C, plays an important role in keeping us healthy. It was isolated for the first time in 1932 from citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, limes, grapefruits), and can be synthesized naturally from D-glucose via two distinct biological pathways. The hydroxyl groups allow it to be soluble in water (i.e., in biologically relevant environments), and it is used as a coenzyme in the synthesis of collagen.
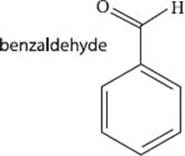
Benzaldehyde is found in almonds, cherries, apricots, and peach pits. It is often used as an artificial oil of almond (perhaps not surprisingly) in making perfumes, dyes, and food flavorings. Researchers are also continuing to look into its utility as a pesticide and anticancer agent. Benzaldehyde can be readily synthesized in the laboratory using toluene as a precursor.
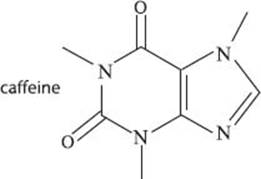
We all know about caffeine. For coffee drinkers, this is probably one of our favorite chemicals! In its pure form, caffeine is just another white crystalline powder, though most people have probably never seen it that way. It’s more commonly found in the cocoa plant, coffee beans, and tea leaves, where people have been consuming it for thousands of years. Historically people have consumed caffeine to increase their heart rate, body temperature, mental alertness, and attention span. Today, people still use caffeine for most of the same reasons. Caffeine can be extracted using chemical solvents from sources like tea leaves and coffee beans to be used in other caffeinated products like soft drinks. Not to scare you, but it’s worth mentioning that caffeine is a potentially addictive substance that stimulates the central nervous system, and if you consume too much at a given time, you may suffer from headaches, irritation, and insomnia.
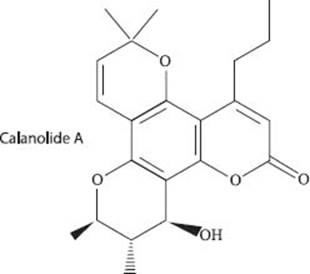
Calanolide A comes from a tree found in the rainforests of Malaysia. It was originally tested as an anticancer agent, but was found to be unsuccessful in this regard. However, Calanolide A has been found to be very effective in fighting the HIV-1 virus (which causes AIDS). Due to the rarity of this chemical, a synthesis was designed soon after its utility was realized. This drug acts by preventing the transcription of the viral RNA into DNA in a cell, which serves to prevent the HIV virus from replicating. Fortunately, it does this with relatively mild, and temporary, side effects.
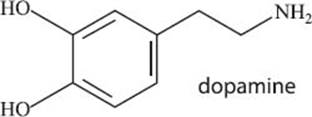
Dopamine is synthesized in our bodies from an amino acid precursor. It is an important neurotransmitter that balances our feelings of happiness. Imbalances or deficiencies in dopamine production or its regulation have been linked to a number of diseases, including Parkinson’s disease, schizophrenia, and Tourette’s syndrome. While dopamine was recognized for its role as a neurotransmitter in the 1950s, it took decades of research before its role was more completely understood. The work that led to its connection to the disorders we mentioned, and to an understanding of its exact function, was awarded a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in the year 2000. An understanding of the role of dopamine in physiology has been extremely important in understanding several neurological diseases.
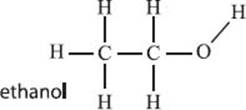
Ethanol is a molecule you are probably familiar with: it’s the alcohol found in alcoholic beverages that makes you feel intoxicated, and humans have consumed it for hundreds of years. Additionally, it is useful as a solvent, an antiseptic, a sedative, and a component in perfumes, lacquers, cosmetics, aerosols, antifreeze, and mouthwash. Ethanol can be produced from a raw feedstock, like corn or grain, by fermenting it in the presence of microbes, which can readily digest sugars and produce ethanol as a byproduct.
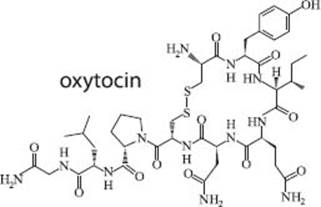
Oxytocin is a hormone produced naturally in females’ posterior pituitary glands, which are located at the back of the brain. It is responsible for causing lactation and uterine contractions in pregnant women. Oxytocin is also used to induce labor when a pregnancy does not begin on time naturally.
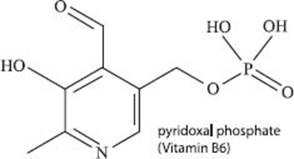
Pyridoxal phosphate is more commonly known as vitamin B6. It helps your nerves and brain to function properly and to maintain the right chemical balances in your body. It is also necessary for the enzymatic reaction that frees up glucose (the sugar monomer) from glycogen (the sugar storage polymer). Vitamin B6 can be obtained from many types of foods including meats, grains, nuts, vegetables, and bananas.
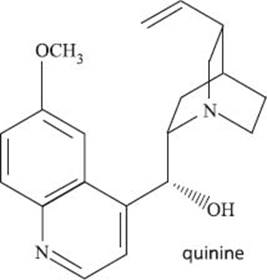
Quinine is a molecule that has been used to treat malaria and nighttime leg cramps as well. It was first discovered in South America, in the bark of a type of tree called the Cinchona tree, by Spanish explorers, who used it as a medicine. The high demand for quinine eventually led to Cinchona trees becoming very hard to find, but thankfully a synthetic method for its production was eventually developed.
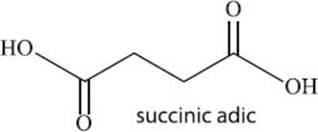
Succinic acid plays an important role in the Krebs cycle and can deliver electrons to the electron transport chain. Succinic acid has been found in a very wide range of plant and animal tissues, though its purification challenged chemists for a long time before it was finally successfully purified from tissues. Today succinic acid can be produced readily in the laboratory, and one method even can use corn as a feedstock. In addition to its role in the Krebs cycle, succinic acid has been used as an intermediate in dyes, perfumes, paints, inks, and fibers.