The Handy Chemistry Answer Book (2014)
THE WORLD AROUND US
CHEMICALS IN THE NATURAL WORLD
How do ants know how to organize their colonies so efficiently?
Ants use a set of pheromones to communicate information between individual members of the colony. There are different chemical markers that indicate trails to food, alarm pheromones that are released when an ant is killed, and a number are used in the reproductive process. Some ant colonies even use pheromones to trick enemy colonies into attacking themselves or to convince the opposition into becoming worker ants for their own benefit.
If chlorophyll gives plants its green color, then what cells give me my skin color?
Melanin is the molecule that is responsible for skin color in humans. It’s also what gives your eyes and hair their color. There isn’t one single structure of melanin, rather it refers to a whole class of highly colored molecules that are all derived from the amino acid tyrosine.
Why do polar bears have black skin and clear fur?
There is some debate on the subject, but the combination of black skin and clear fur is probably the best for keeping the polar bear warm while not giving away its position when hunting. The black color of the skin is the best for absorbing energy from the Sun—objects that appear black don’t reflect any wavelengths of light. The clear fur allows that light to get to the skin, but still looks white so the bear can blend in with the surrounding ice and snow.

Polar bears look white, but they actually have clear fur and black skin.
A few years ago, or maybe you heard this recently because it has achieved urban legend status, a rumor you may have heard is that polar bear fur is actually like a fiber optic network for harnessing or focusing sunlight toward the bear’s skin. While this would have been cool, it’s unfortunately completely bogus.
If polar bears have black skin and clear fur, why do they look white?
Polar bears appear white for the same reason that a pile of snow looks white—reflection. If there are a lot of surfaces that reflect light (either in the polar bear’s fur or a snowdrift), then any light that hits the object will be bounced around many times before coming back toward your eye. Most wavelengths of light are scattered equally well, so you end up with the object looking white (in other words, no wavelengths are absorbed, which would give rise to a color).
Why are snowflakes unique?
Excellent question! All snowflakes are made up of frozen water (ice), so why don’t they look exactly the same? Their unique shape comes from the unique conditions under which each snowflake is made. As a tiny ice crystal is blown into and out of a cloud, or rises or falls in a jet of slightly warmer or colder air, the shape of the growing snowflake can change. In a sense, their shape describes a story of how they were made.
What is a flame, really?
From a chemical perspective, a flame is the visible light product of an exothermic oxidation reaction. This reaction takes C–H bonds and oxygen (O2) in the atmosphere and starts a radical chain reaction that keeps going as long as there is still fuel and oxygen around. Actually, bonds other than just C–H bonds can give rise to burning; that’s just what’s happening during the burning of objects you’re most familiar with (like candles and wood fires).
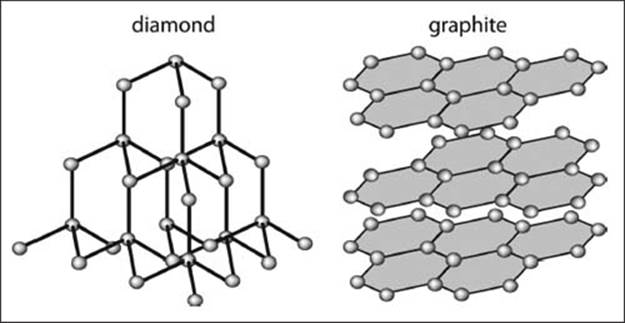
In a diamond crystal, carbon atoms are arranged in a rigid structure, while in graphite the carbon is arranged in layers, making a substance that can easily slough off its layers.
Where does all that wax go when I burn a candle?
Why, it burns! The long hydrocarbon chains that make up candle wax are transformed into carbon dioxide and water. Candle wax is the fuel for the flame; the wick just helps draw it up to the flame by capillary action.
Why is diamond so hard?
Pure diamond is a crystalline form of only carbon atoms. The crystal lattice is three-dimensional, and all carbon atoms are attached to four other carbon atoms in a perfect tetrahedral geometry. Because the lattice repeats in all three dimensions, there is no easy way to distort the structure, making it a very hard material. The structure of graphite, for comparison, is many stacked-up layers of carbon atoms. These two-dimensional sheets can “slide” relative to one another, making graphite relatively soft in comparison to diamond.
What about the fake diamonds at jewelry stores? What are those?
Diamonds themselves cannot be made in a laboratory very well, but crystals with similar properties and appearances can be made. One popular type of “simulated diamond” is a cubic zirconia crystal, which is a crystal with the chemical formula ZrO2. Cubic zirconia are more dense than diamonds, or, in other words, a cubic zirconia is heavier than a diamond of the same size. They are also a fairly hard material as minerals go, but they are not as hard as diamonds and can be scratched by diamonds. Cubic zirconia are usually colorless, which isn’t the case for diamonds. Most diamonds contain some amount of noncarbon impurity that makes them appear colored, and only very pure diamonds appear colorless.
What is snake venom?
Most venoms are mixtures of dozens of compounds, and the active toxic ingredients are proteins that wreak havoc on the recipient in a variety of ways. While the exact enzymes vary from species to species, and even geographically within a species, many snake venoms contain some sort of neurotoxins which block signals sent through your nervous system, leading to numbness or even paralysis.

An expert extracts venom from a snake, which will later be used to create antivenom for snake bite victims. Snakes can have different types of venom: neurotoxins or cytotoxins. Neurotoxins work by blocking nerve function, while cytotoxins destroy cells directly.