MCAT General Chemistry Review
Chapter 12: Electrochemistry
Practice Questions
1. Rusting occurs due to the oxidation–reduction reaction of iron with environmental oxygen:
4 Fe (s) + 3 O2 (g) → 2 Fe2O3 (s)
Some metals cannot react with oxygen in this fashion.
Which of the following best explains why iron can?
1. Iron has a more positive reduction potential than those metals, making it more likely to donate electrons to oxygen.
2. Iron has a more positive reduction potential than those metals, making it more likely to accept electrons from oxygen.
3. Iron has a less positive reduction potential than those metals, making it more likely to donate electrons to oxygen.
4. Iron has a less positive reduction potential than those metals, making it more likely to accept electrons from oxygen.
2. Given the following standard reduction potentials:
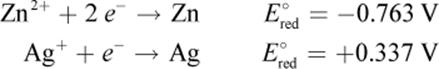
What is the standard electromotive force of the following reaction?
Zn2+ + 2 Ag → 2 Ag+ + Zn
1. –2.2 V
2. –1.1 V
3. +1.1 V
4. +2.2 V
3. Consider the following data:
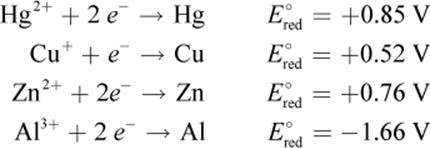
The anode of a certain galvanic cell is composed of copper. Which of the metals from the data table can be used at the cathode, assuming equal concentrations of the two electrolyte solutions?
1. Hg
2. Cu
3. Zn
4. Al
4. An electrolytic cell is filled with water. Which of the following will move toward the cathode of such a cell?
1. H+ ions
2. O2– ions
3. Electrons
1. I only
2. II only
3. I and III only
4. II and III only
5. If the value of E°cell is known, what other data is needed to calculate ΔG°?
1. Equilibrium constant
2. Reaction quotient
3. Temperature of the system
4. Half-reactions of the cells
6. Which of the following compounds is LEAST likely to be found in the salt bridge of a galvanic cell?
1. NaCl
2. SO3
3. MgSO3
4. NH4NO3
7. If the surface area of electrode material in an electrochemical cell is tripled, what else is necessarily tripled?
1. E°cell
2. Current
3. Keq
1. I only
2. II only
3. I and II only
4. II and III only
8. Which of the following can alter the emf of an electrochemical cell?
1. The mass of the electrodes
2. The length of the wire connecting the half-cells
3. The overall size of the battery
4. The temperature of the solutions in the half-cells
9. Which of the following statements could be true about a Na–Cd cell, based on the information below?
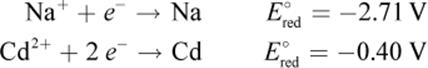
1. It is a galvanic cell, and sodium is the cathode.
2. It is an electrolytic cell, and cadmium is the anode.
3. It is a galvanic cell, with E°cell = 3.11 V.
4. It is an electrolytic cell, with E°cell = −3.11 V.
10.Which of the following expressions correctly describes the relationship between standard electromotive force and standard change in free energy?
1. ΔG° = −nF(E°red,anode − E°red,cathode)
2. ![]()
3. ![]()
4. ΔG° = nF(E°red,anode − E°red,cathode)
11.Which of the following choices is indicative of a spontaneous reaction, assuming standard condition?
1. E°cell is negative
2. Q = Keq
3. The cell is a concentration cell
4. Keq > 1
12.For a cell with the following half-reactions:
Anode: SO2 + 2 H2O → SO42− + 4 H+ + 2 e−
Cathode: Pd2+ + 2 e− → Pd
How would decreasing the pH of the solution inside the cell affect the electromotive force (emf)?
1. The emf would decrease.
2. The emf would remain the same.
3. The emf would increase.
4. The emf would become zero.
13.An electrolytic cell necessarily has:
1. ΔS° > 0
2. ΔG° < 0
3. Keq < 1
4. E°cell > 0
14.Which of the following is the best explanation for the fact that a larger mass of electrodes are required for lead–acid batteries, as compared to other batteries, to produce a certain current?
1. The lead–acid electrolyte, sulfuric acid, is diprotic and incompletely dissociates in solution.
2. The energy density of lead–acid electrodes is higher than that of other batteries.
3. The electrolytes in other batteries less readily dissociate than those of lead–acid batteries.
4. The energy density of lead–acid electrodes is lower than that of other batteries.
15.Which of the following best describes why over-charging a Ni–Cd battery is not detrimental?
1. The energy density of a Ni–Cd battery is high, so it can store more charge than other batteries per its mass.
2. The electrodes of a Ni–Cd battery can discharge through the circuit when they are fully charged.
3. The Ni–Cd battery will stop accepting electrons from an outside source when its electrodes are recharged.
4. Ni–Cd batteries have a high surge current and can dissipate the overcharge before damage can occur to electrodes.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS