Why Is Milk White?: & 200 Other Curious Chemistry Questions (2013)
4. Health and Safety
How can Zanfel soap get off poison oak?
Zanfel is a cream that contains several strong surfactants (detergents) and tiny polyethylene beads. The main detergent in Zanfel is sodium lauroyl sarcosinate.
This detergent has a capability we have not discussed in other detergents. It is a penetration enhancer. That means it helps other molecules penetrate deeper into the skin. It is an ionic surfactant (you can see the plus sign by the sodium ion and the minus sign by the oxygen). It is derived from coconut oil and cleans without completely stripping the skin of all oils.
The second detergent in Zanfel is nonoxynol-9.
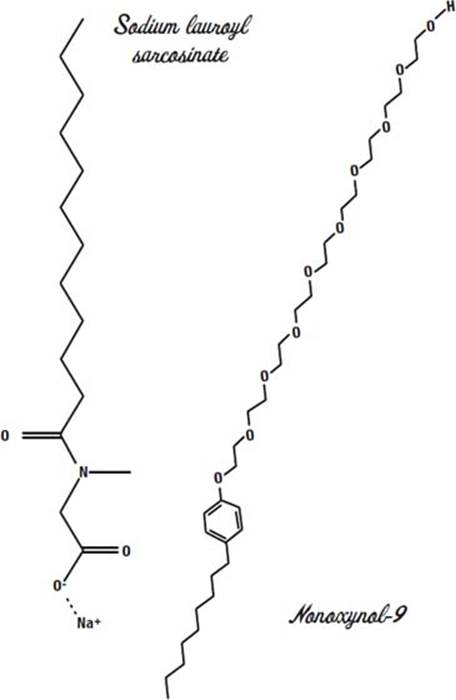
Nonoxynol-9 is a nonionic detergent. We saw these earlier when we discussed laureth-12 in Shout stain remover (page 75). The long chain of nine ethylene oxide groups is water-loving, and the long fatty acid chain at the bottom is oil-loving.
In the section on another surfactant, benzalkonium chloride, the antiseptic in Bactine (page 80), the discussion mentioned that some surfactants are good at breaking up cell walls and killing microbes. The same thing happens with nonoxynol-9: it is used in Zanfel to break up the poison urushiol that causes poison ivy and poison oak rashes.
Nonoxynol-9 is a polyethylene glycol. The long chain with all ethylene oxide units (two carbons and an oxygen) is the polyethylene part (poly means “many”). Another polyethylene glycol is C12- 15 Pareth-9, and it is the third detergent in Zanfel.
To make these detergents work better in hard water, sodium EDTA is added. It grabs onto magnesium and calcium ions in the water and keeps them from interfering with the detergents. To keep the detergents from spoiling, a bactericide (bacteria killer) called quaternium-15 is used. It releases formaldehyde to kill germs.
Another surfactant, triethanolamine (which is three ethylene molecules all attached to a central nitrogen atom) helps make the urushiol soluble in water. It also adjusts the acidity of the product and neutralizes fatty acids.