Organic Chemistry: Concepts and Applications - Headley Allan D. 2020
Synthetic Polymers and Biopolymers
20.20 Properties and Reactions of Triglycerides
Triglycerides gained their name from glycerol, also known as glycerin, the basic structure from which they were derived.
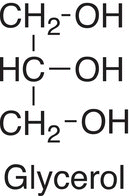
Triglycerides are triesters of glycerol and examples are shown below.
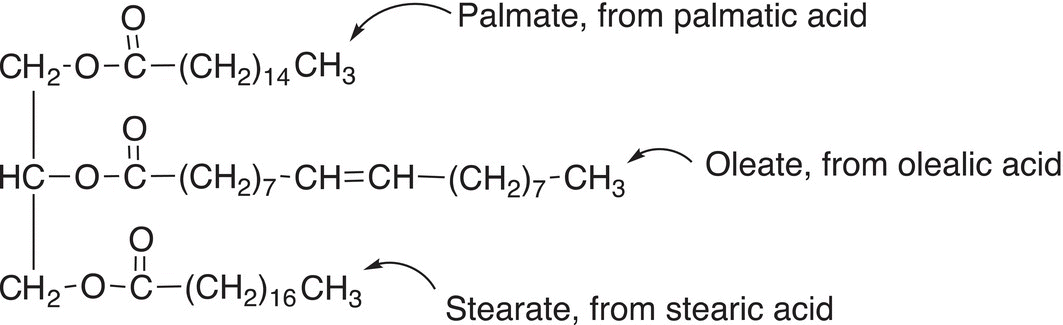
Animal fats are typically solids at room temperature, and plant oils are typically liquids at room temperature; they are forms of triglycerides. One explanation for this difference in states between animal fats and plant oils at room temperature is that animal fats are typically saturated esters and hence more structured in their molecular orientation resulting in a higher melting point and therefore often solids at room temperature. On the other hand, plant oils contain unsaturated portions and hence cannot attain a structured arrangement so the result is lower melting points and are therefore liquids at room temperature.
20.20.1 Saponification (Hydrolysis) of Triglycerides
Since triglycerides are also esters, they will undergo hydrolysis, similar to those that we have seen earlier for esters. Shown in Reaction (20-76) is the basic hydrolysis of a triglyceraldehyde.
(20-76)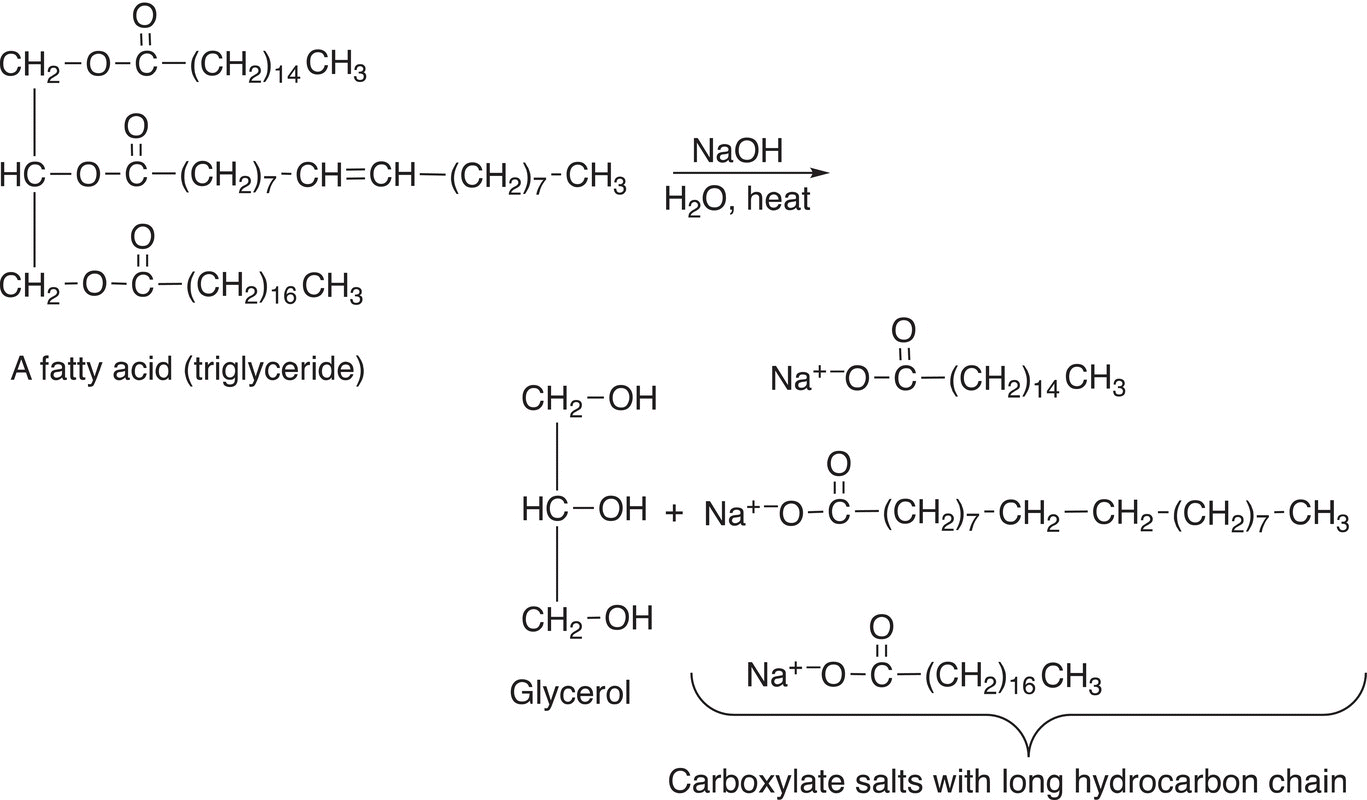
The hydrolysis of animal fats under basic conditions is sometimes described as saponification since one of the products of the reaction is soap. As shown in the reaction above, the products are salts of carboxylic acids that have a long hydrocarbon tail, sometimes referred to as hydrophobic since not soluble in water. The carboxylate salt end is polar and hence hydrophilic, since water soluble. Carboxylate salts with long hydrocarbon tails are used as soaps since they have hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties and as shown in Figure 20.4 and can surround grease particles and extract them during the washing process.
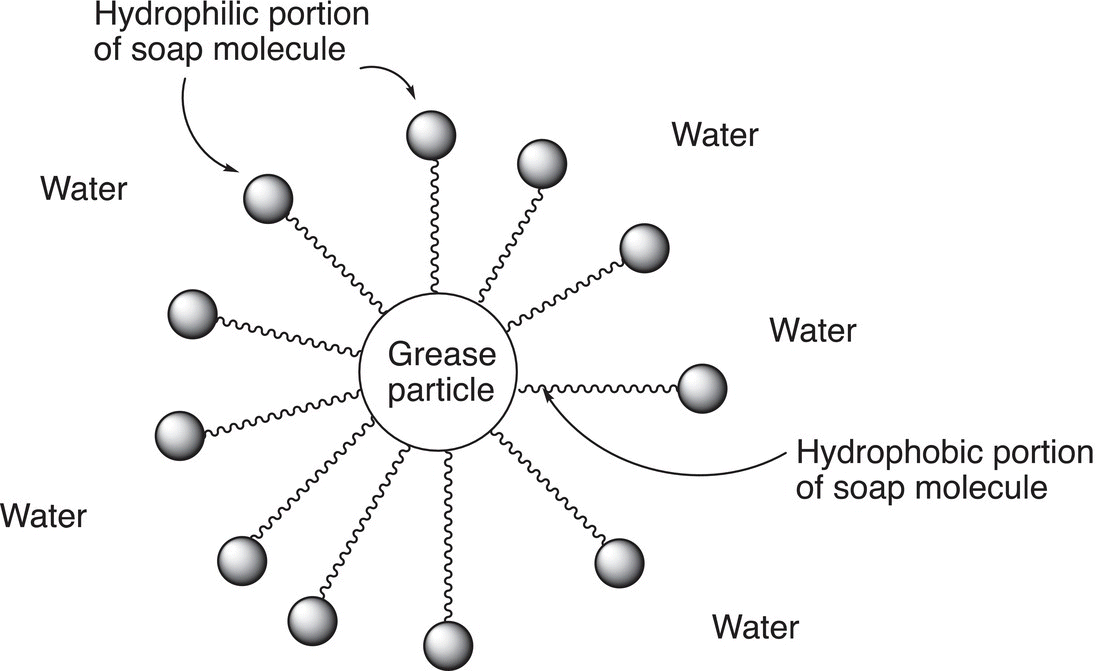
Figure 20.4 Representation of soap molecules in water surrounding grease particles.
20.20.2 Reduction of Triglycerides
Reactions of these molecules are the same as that of compounds that we have seen before. Shown below is the reduction (hydrogenation) of the alkene functionality of the triglyceride shown in Reaction (20-77).
(20-77)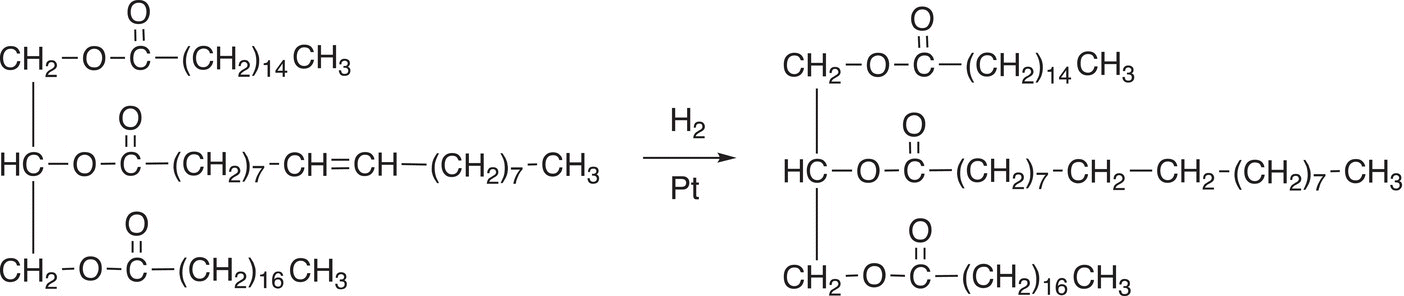
These reductions are frequently carried out in industry, and the products are sold under different names, such as shortenings, Crisco, and margarine. Some are partially hydrogenated oils. For trans-fatty acids, the process of hydrogenation of plant oil results in saturated fatty acids.
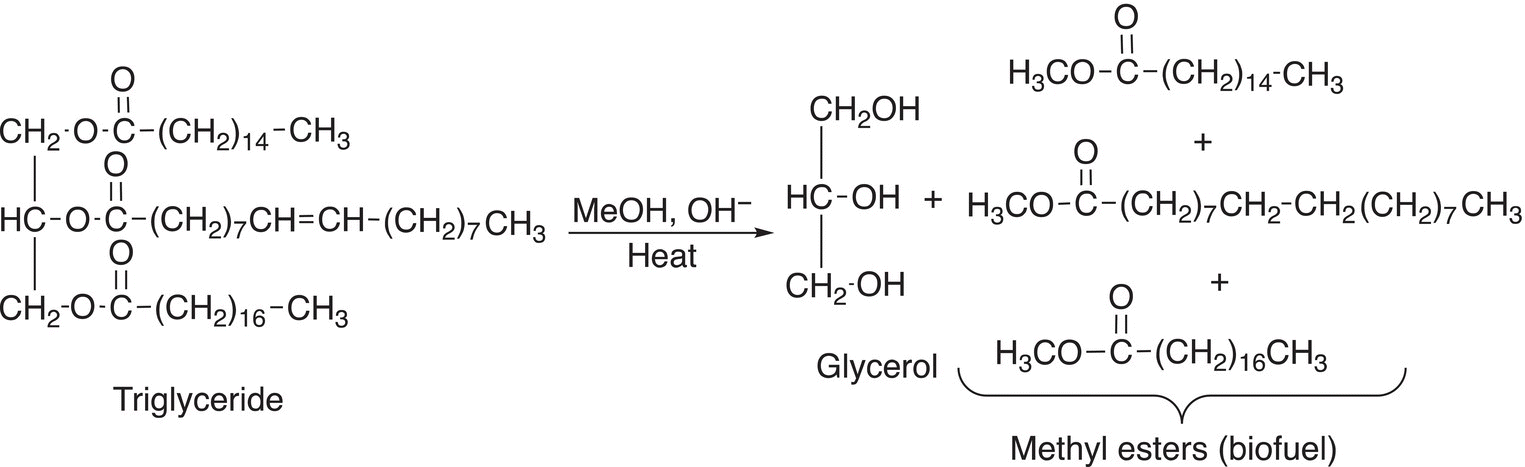
20.20.3 Transesterification of Triglycerides
Biodiesel is made by the process of transesterification of triglycerides or fatty acids as shown in the reaction below in Reaction (20-78).
(20-78)