Organic Chemistry: Concepts and Applications - Headley Allan D. 2020
Heteroatomic Functional Groups and Organic Nomenclature
3.4 Structure and Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones
Aldehydes and ketones have the carbon—oxygen double bond, also known as the carbonyl group, as a common feature. The type of groups that are bonded to the carbon atom of the carbon—oxygen double bond determine whether these types of compounds are ketones or aldehydes. If two alkyl groups are bonded to the carbonyl carbon, as shown below, the functional group is a ketone. If there is one alkyl group, along with a hydrogen atom bonded to the carbonyl group, the functional group is an aldehyde.
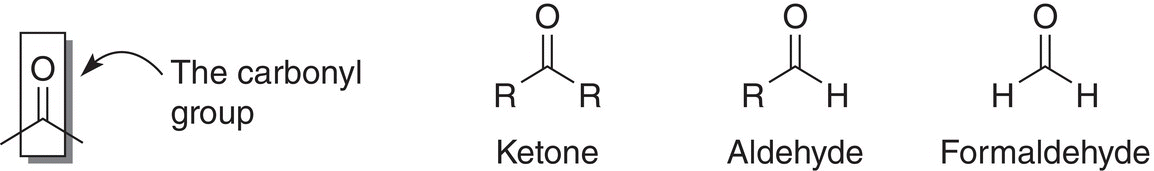
The simplest aldehyde is formaldehyde in which there are two hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon of the carbonyl group. Formaldehyde is commonly used in industry and has a pungent suffocating odor. It is typically sold as formalin, which is a mixture in aqueous solution (about 37—50%). It is easily oxidized to formic acid. Aldehydes that contain large alkyl groups are less toxic and do not penetrate the respiratory track as formaldehyde. Acetone, which is a ketone, dissolves fats and skin. A large number of compounds that are used in the flavoring industry are aldehydes or ketones. Some commonly used aldehydes and ketones are shown below.
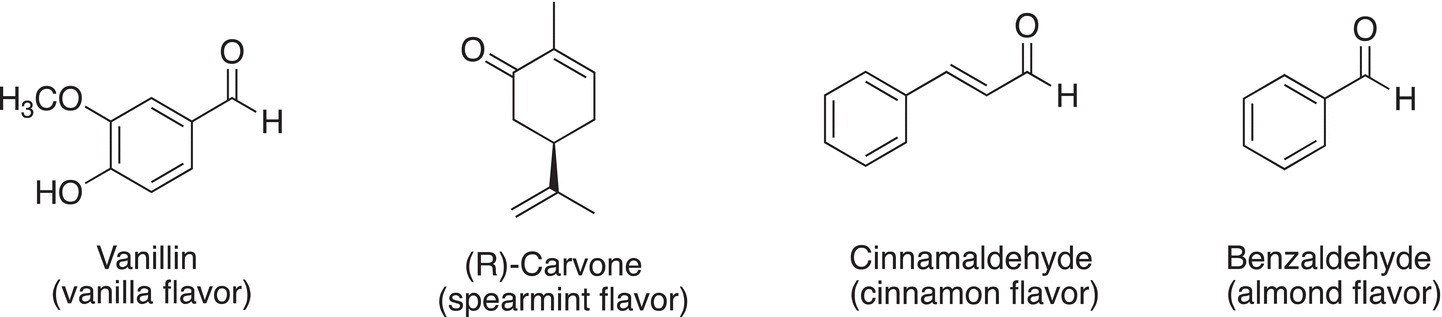
Problem 3.7
For the compounds given in the example above, determine which are aldehydes and ketones.