Organic Chemistry: Concepts and Applications - Headley Allan D. 2020
An Overview of the Reactions of Organic Chemistry
6.9 Catalytic Coupling Reactions
Catalytic coupling reactions are very important reactions in organic chemistry since these reactions involve the coupling of carbons to form new carbon—carbon bonds in the presence of a transition metal catalyst. An example of a famous reaction of this type is shown in Reaction (6-35), which is also known as the Heck reaction in which the palladium is used to catalyze this reaction.
(6-35)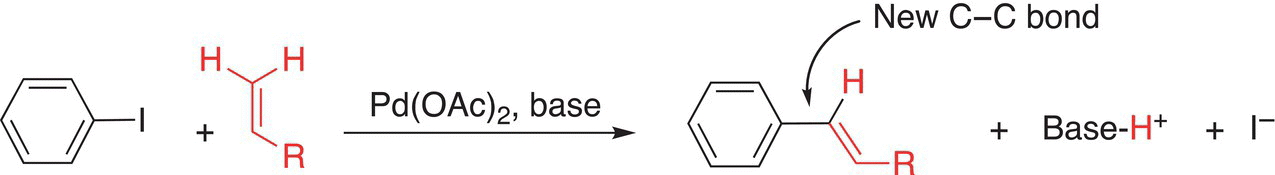
The Heck reaction is named after Richard F. Heck (1931—2015), an American chemist who worked at the University of Delaware, USA. He shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2010 with Ei-ichi Negish and Akira Suzuki, two Japanese chemists who discovered this type of coupling reaction. The Heck reaction involves the carbon—carbon bond-forming reaction in the presence of the catalyst, palladium. These catalytic coupling reactions are of extreme importance in the formation of new carbon—carbon bonds, which are sometimes challenging type of bonds to make in organic chemistry. More details on these reactions will be discussed in Chapter 19, but at this point, students should be able to recognize the features of these types of catalytic coupling reactions, which are carried out using sp2 carbons and students should be able to predict the coupled organic product. Problem 6.12 is designed to get students to recognize the features of a catalytic coupling reaction.
Problem 6.12
i. Give the product for the following catalytic coupling reactions.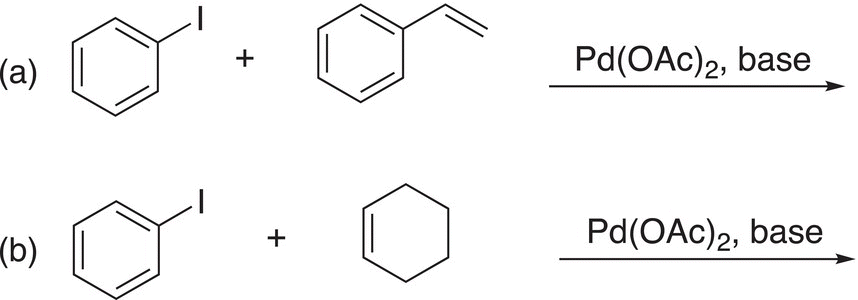
ii. Give the reactants for the following catalytic coupling reactions.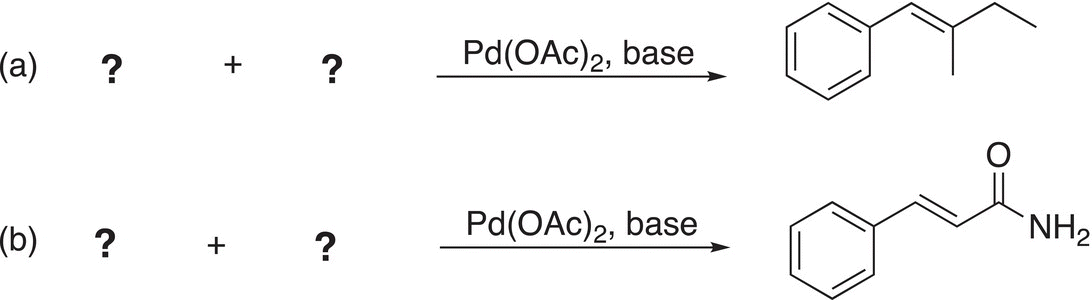
With this overview of the different types of important reactions of organic chemistry, students can better appreciate the versatility of the reactions of organic chemistry in producing an extremely wide variety of organic products. In later chapters, we will discuss in detail, the mechanisms for these types of reactions and how these types of reactions can be used to produce desired organic products. This aspect of organic chemistry is called organic synthesis and is routinely used in industry and research labs.