Advanced Spanish Step-by-Step: Master Accelerated Grammar to Take Your Spanish to the Next Level (2012)
Part III. Future and Conditional Tenses; Past Subjunctive; Idioms
Chapter 11. The Conditional Tense
The conditional tense is used to describe actions that are uncertain in the future. Unlike the future tense, which expresses future certainty, the conditional expresses an action that would happen if another condition were met. This is a simple tense, in that it uses no helping verb in Spanish. It corresponds to the conditional tense in English, which uses would as an auxiliary verb: I would go, but I don’t have time, for example.
Formation of the Conditional Tense
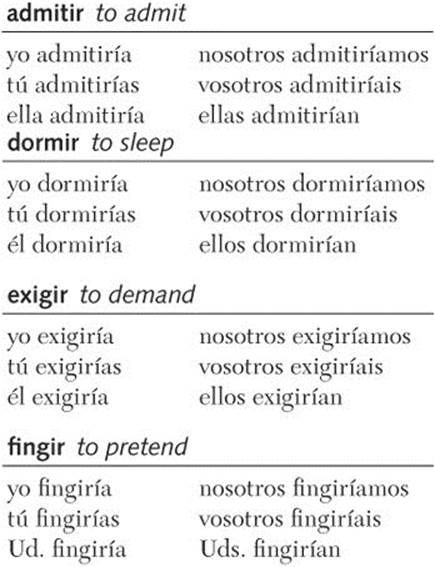
Most verbs are regular in the conditional tense. To form the conditional, use the infinitive as the stem and add the following endings to the infinitive: -ía, -ías, -ía, -íamos, -íais, -ían. These endings are used for all verbs, both regular and irregular, in the conditional tense. Practice pronouncing the following conditional verb forms aloud and be sure to stress the accented syllable.
![]() Pronunciation Reminder
Pronunciation Reminder
Practice pronouncing the d with a soft th sound.
Regular Verbs
-Ar Verbs



![]() Pronunciation Reminder
Pronunciation Reminder
The r at the beginning of a breath group is pronounced as an rr trill. Practice pronouncing these forms of recordar with the trilled r.
-Er Verbs


-Ir Verbs
![]() Pronunciation Reminder
Pronunciation Reminder
The g before an i is pronounced like the English h as in hot.

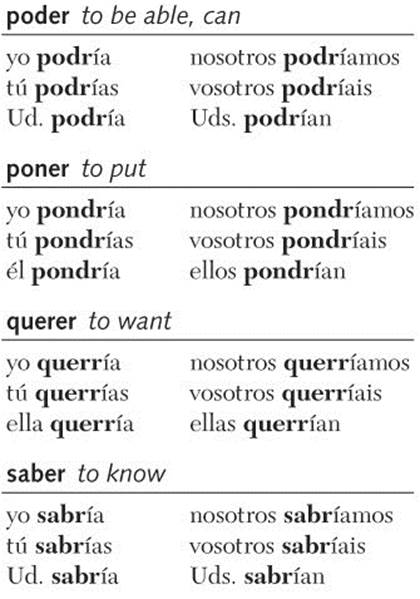
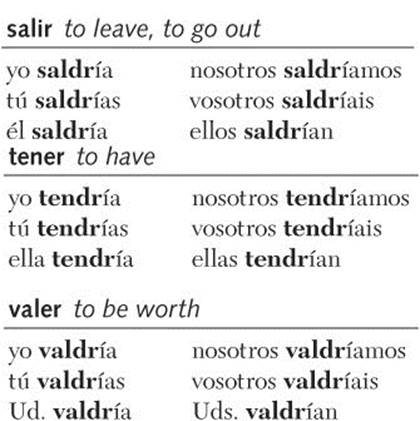
Irregular Verbs
There are 12 basic irregular verbs in the conditional tense. The conditional and future tenses have the same stems in their irregular verbs. Add -ía, -ías, -ía, -íamos, -íais, -ían to the irregular stem. Practice pronouncing these verb forms aloud, and learn them so that you will be able to use the conditional tense freely.

![]() Reminder
Reminder
As noted, valer is most often used in the third person:


![]() A Word About haber
A Word About haber
Habría means there would be and would there be? It is the conditional tense of the verb haber.

Compound forms of verbs are conjugated in the same way as the main verb.
decir
![]()
hacer
![]()
poner
![]()
tener

venir
![]()
Uses of the Conditional Tense
The conditional tense expresses action that is uncertain in the future. This tense corresponds to the English conditional tense: I would go, for example.

![]() A Word About English would
A Word About English would
In English, the translation of the Spanish imperfect tense sometimes uses the word would as a helping verb when expressing repeated action in the past. Following are examples of the imperfect tense:

![]() Exercise 11.1
Exercise 11.1
Complete the following sentences with the correct conditional form of the verb in parentheses.
1. Yo_________________________. (producir)
2. Nosotros lo_________________________. (hacer)
3. ¿Qué_________________________Uds.? (decir)
4. Él_________________________pero no quiere. (venir)
5. ¿Cuánto me_________________________Ud. por mi libro? (dar)
6. Ellos_________________________temprano. (acostarse)
7. Los niños y sus padres_________________________pronto. (regresar)
8. ¿Por qué_________________________Ud. tacones? (llevar)
9. ¿A Uds. les_________________________salir esta noche? (gustar)
10. ¿_________________________luz sin electricidad? (haber)
11. Yo_________________________esa película. (ver)
12. Nosotros no_________________________esta noche. (salir)
13. Laura dijo que_________________________mañana. (llegar)
14. Yo sabía que ella_________________________. (entender)
15. ¿Quién_________________________hacer tal cosa? (poder)
16. ¿Por qué_________________________Samuel al teatro si siempre se duerme? (ir)
Placement of Reflexive, Indirect, and Direct Object Pronouns
The reflexive, indirect, and direct object pronouns have two possible positions when used with the conditional tense.
• Object pronouns can be placed directly before the conjugated verb.
• Object pronouns can be attached to an infinitive if one is used in the phrase or sentence.

![]() Exercise 11.2
Exercise 11.2
Rewrite the following sentences in the conditional tense. Be sure to include all necessary written accents. Pronounce your answers aloud.
EXAMPLE Nadie duerme aquí. Nadie dormiría aquí.
1. Yo la ayudo.__________________________________________________
2. Ella va de compras.__________________________________________________
3. ¿Miras tú televisión?__________________________________________________
4. Ellos venden la comida.__________________________________________________
5. Los mozos les dan la comida a los clientes.__________________________________________________
6. Tenemos mucho que hacer.__________________________________________________
7. El conductor maneja rápidamente.__________________________________________________
8. ¿Cantas?__________________________________________________
9. ¿Vienen Uds. a mi casa?__________________________________________________
10. Yo lo hago.__________________________________________________
11. No le digo nada.__________________________________________________
12. Te cobro cien dólares.__________________________________________________
13. Los niños no leen mucho.__________________________________________________
14. Sé nadar.__________________________________________________
15. Hay mucha gente en los trenes.__________________________________________________
16. No caben más.__________________________________________________
17. Le traigo las flores a su hermana.
18. Nos ponemos los zapatos.__________________________________________________
19. ¿Puede Ud. acompañarme al bus?__________________________________________________
20. ¿A Uds. les gusta ir al cine?
![]() Exercise 11.3
Exercise 11.3
Complete the following sentences with the correct conditional form of the verb in parentheses.
1. Ella_________________________tocar el piano, pero nunca practica. (poder)
2. La enfermera le prometió al paciente que él_________________________. (mejorarse)
3. Yo no_________________________de la situación. (quejarse)
4. Nosotros no le_________________________nada. (decir)
5. Enrique y su esposa sabían que sus hijos_________________________en sus vacaciones. (divertirse)
6. Emanuel y su hermano nos aseguraron que todo_________________________bien. (estar)
7. Los gemelos_________________________una fiesta pero no es su cumpleaños. (tener)
8. La terapeuta física me dijo que no me_________________________más los pies. (doler)
![]() Exercise 11.4
Exercise 11.4
Translate the following sentences into Spanish.
1. José would like to learn to swim, but he is afraid of the water.
__________________________________________________
2. I would not say anything to him, because I do not know him well.
__________________________________________________
3. Our Mexican friends would come to California to visit their family, but they prefer to travel to Europe this year.
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
4. Juan told me that he would give the book to you if you want to study it.
__________________________________________________
5. We would go to Julia’s party, but we don’t know where she lives.
__________________________________________________
The conditional tense may be used to express speculation or conjecture in the past. The translation I wonder or It was probably indicates doubt or conjecture. You will know from context whether the sentence or question expresses the simple conditional or probability in the past.

The Conditional Progressive Tense
The conditional progressive tense expresses doubt about action in the future.
Formation of the Conditional Progressive Tense
The conditional progressive is a compound tense. To form this tense, conjugate estar in the conditional and follow it with the gerund of the main verb.

Uses of the Conditional Progressive Tense
The conditional progressive tense expresses doubt in the future and emphasizes the action. When you don’t need to emphasize the action, use the simple conditional. You’ll find that the simple conditional is used more frequently in everyday speech.
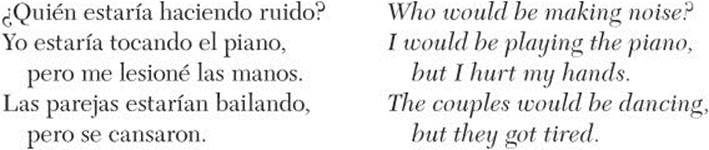
The Conditional Perfect Tense
The conditional perfect tense is used to express an action that would have taken place, but did not: I would have paid you, but I left my money at home, for example.
Formation of the Conditional Perfect Tense
The conditional perfect is a compound tense. To form this tense, conjugate the helping verb haber in the conditional tense and follow it with the past participle of the main verb.

Uses of the Conditional Perfect Tense
The conditional perfect tense, which is used to refer to an action that would have occurred but did not, is often followed by English but.

Remember that reflexive, indirect, and direct object pronouns precede the verb form. The object pronouns are never attached to the past participle.

The conditional perfect tense may also express speculation or conjecture in the past.

![]() Exercise 11.5
Exercise 11.5
Translate the following sentences into Spanish.
1. He would have arrived on time, but he lost the directions.
__________________________________________________
2. We would not have told our secret to anyone.
__________________________________________________
3. Juan and his companion would have gone to Mexico, but they decided to save their money for the following year.
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
4. Antonio and I would have traveled to Colombia, but the flight cost too much.
__________________________________________________
5. Enrique would have been a good president, but he wanted to have more time to spend with his family.
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
6. Elvira would have returned the money that she found, but she gave it to her son.
__________________________________________________
![]() Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension
¿Qué haría Ud. en las siguientes situaciones?
Answer the following questions orally.
1. ¿Diría Ud. una mentira para proteger a su amigo?
2. ¿Compraría Ud. algo antes de verlo?
3. Si vas a un casino, ¿cuánto dinero apostarías antes de irte?
4. Ud. está en una clase de veinte estudiantes y todos están copiando excepto Ud. (Ellos reciben el examen de antemano y aprenden de memoria las respuestas sin saber nada. Ud. está estudiando.) ¿Le diría Ud. al maestro lo que está pasando en la clase?
5. Su hijo tiene catorce años y quiere jugar al fútbol americano para su escuela. Ud. sabe que es peligroso y que muchos niños se lesionan. ¿Lo dejaría jugar o firmaría el documento prohibiéndole que juegue?
6. Su mejor amigo está para casarse. Ud. está en un restaurante y ve a su prometida besar a otro hombre. ¿Se lo diría a su amigo?
7. Ud. encuentra una cantidad de dinero en las montañas con la identificación de una persona que se había muerto en un accidente. ¿Le devolvería Ud. el dinero a la familia?
8. ¿Viajaría Ud. solo?
9. ¿Tomaría Ud. crédito por un libro que no había escrito?
10. Su mejor amigo es pintor. ¿Le diría Ud. la verdad si a Ud. no le gusta su pintura?
Verbos
