GMAT Quantitative Review
3.0 Math Review
3.3 Geometry
9. Rectangular Solids and Cylinders
A rectangular solid is a three-dimensional figure formed by 6 rectangular surfaces, as shown below. Each rectangular surface is a face. Each solid or dotted line segment is an edge, and each point at which the edges meet is a vertex. A rectangular solid has 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices. Opposite faces are parallel rectangles that have the same dimensions. A rectangular solid in which all edges are of equal length is a cube.
The surface area of a rectangular solid is equal to the sum of the areas of all the faces. The volume is equal to
 .
.
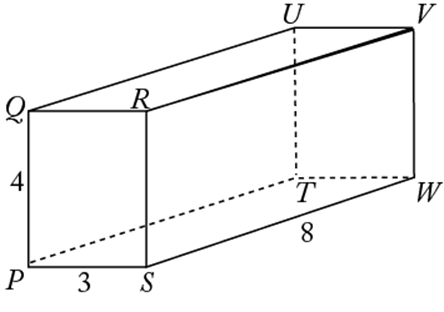
In the rectangular solid above, the dimensions are 3, 4, and 8. The surface area is equal to ![]() . The volume is equal to
. The volume is equal to ![]() .
.
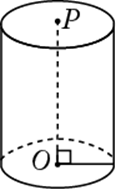
The figure above is a right circular cylinder. The two bases are circles of the same size with centers O and P, respectively, and altitude (height) ![]() is perpendicular to the bases. The surface area of a right circular cylinder with a base of radius r and height h is equal to
is perpendicular to the bases. The surface area of a right circular cylinder with a base of radius r and height h is equal to ![]() (the sum of the areas of the two bases plus the area of the curved surface).
(the sum of the areas of the two bases plus the area of the curved surface).
The volume of a cylinder is equal to ![]() , that is,
, that is,
![]() .
.
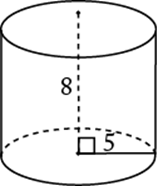
In the cylinder above, the surface area is equal to
![]() ,
,
and the volume is equal to
![]() .
.