Basic Math and Pre-Algebra
APPENDIX A. Check Point Answers
Chapter 1
1. In the number 3,492, the 9 is worth 9 tens.
2. In the number 45,923,881, the 5 is worth 5 millions.
3. In the number 842,691, the 6 is worth 6 hundreds.
4. In the number 7,835,142, the 3 is worth 3 ten-thousands.
5. In the number 7,835,142, the 7 is worth 7 millions.
6. 79,038: seventy-nine thousand, thirty-eight
7. 84,153,402: eighty-four million, one hundred fifty-three thousand, four hundred two
8. “eight hundred thirty-two thousand, six hundred nine” = 832,609
9. “fourteen thousand, two hundred ninety- one” = 14,291
10. “twenty-nine million, five hundred three thousand, seven hundred eighty-two” = 29,503,782
11. 10,000 = 104
12. 100,000,000,000 = 1011
13. 107 = 10,000,000
14. 1012 = 1,000,000,000,000
15. 105 = 100,000
16. 59,400 = 5.94 x 104
17. 23,000,000 = 2.3 x 107
18. 5.8 x 109 = 5,800,000,000
19. 2.492 x 1015 = 2,492,000,000,000,000
20. 1.2 x 1023 = 1.2 x 10 x 1022 = 12 x 1022 > 9.8 x 1022
21. 942 ≈ 900
22. 29,348 ≈ 30,000
23. 1,725,854 ≈ 1,700,000
24. 1,725,854 ≈ 1,726,000
25. 1,725,854 ≈ 2,000,000
Chapter 2
1. 48 + 86 = 134
2. 97 + 125 = 222
3. 638 + 842 = 1,480
4. 1,458 + 2,993 = 4,451
5. 12,477 + 8,394 = 29,871
6. 18 + 32 + 97 = 147
7. 91 + 74 + 139 = 304
8. 158 + 482 + 327 + 53 = 1,020
9. 71,864 + 34,745 + 9,326 = 115,935
10. 9,865 + 7,671 + 8,328 + 1,245 + 3,439 = 30,548
11. 596 - 312 = 284
12. 874 - 598 = 276
13. 1,058 - 897 = 161
14. 5,403 - 3,781 = 1,622
15. 14,672 - 5,839 = 8,833
16. 100 - 62 = 38
17. 250 - 183 = 67
18. 500 - 29 = 471
19. 400 - 285 = 115
20. 850 - 319 = 531
21. 462 x 53 = 24,486
22. 833 x 172 = 143,276
23. 1,005 x 53 = 53,265
24. 1,841 x 947 = 1,743,427
25. 2,864 x 563 = 1,612,432
26. 4,578 ÷ 42 = 109
27. 3,496 ÷ 19 = 184
28. 16,617 ÷ 29 = 573
29. 681 ÷ 14 = 48, remainder 9
30. 1,951 ÷ 35 = 55, remainder 26
Chapter 3
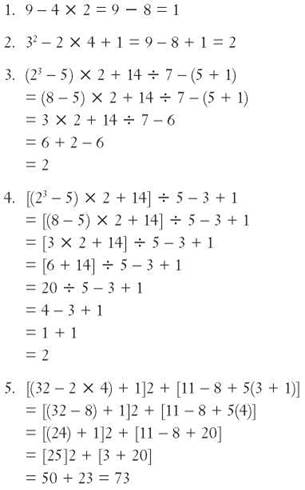
6. 2(35 + 14) = 70 + 28 = 98
7. 3(20 + 8) = 60 + 24 = 84
8. 7(100 - 2) = 700 - 14 = 686
9. 15(40 - 14) = 600 - 15 x 14 = 600 - (150 + 60) = 600 - 210 = 390
10. 250(1,000 - 400) = 250(600) = 150,000
11. |-19| = 19
12. |42| = 42
13. |0| = 0
14. |5 - 3| = |2| = 2
15. 7 + |5 - 3| = 7 + |2| = 9
16. -15 + 25 = 10
17. 19 + -12 = 7
18. -23 + 14 = -9
19. -58 + -22 = -80
20. 147 + -200 = -53
21. -17 - 4 = -17 + (-4) = -21
22. 39 - 24 = 39 + (-24) = 15
23. 26 - -12 = 26 + 12 = 38
24. -83 - 37 = -83 + (-37) = -120
25. -48 - -32 = -48 + 32 = -16
26. -4 X 30 = -120
27. 8 x -12 = -96
28. -7 x 15 = -105
29. -11 x -43 = 473
30. -250 x 401 = -100,250
31. 49 ÷ -7 = -7
32. -125 ÷ -15 = 8, remainder 5
33. -27 ÷ 9 = -3
34. 120 ÷ -6 = -20
35. -981 ÷ -9 = 109
Chapter 4
1. 51 is composite. 51 = 17 x 3
2. 91 is composite. 91 = 13 x 7
3. 173 is prime.
4. 229 is prime.
5. 5,229 is composite. 5,229 = 3 x 1,743 = 7 x 747 = 9 x 581 = 21 x 249 = 63 x 83
6. 78 = 2 x 3 x 13
7. 98 = 2 x 7 x 7
8. 189 = 3 x 3 x 3 x 7
9. 255 = 3 x 5 x 17
10. 512 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2
11. 20 0 = 23 x 52
12. 168 = 23 x 3 x 7
13. 672 = 25 x 3 x 7
14. 2,205 = 32 x 5 x 72
15. 22,000 = 24 x 53 x 11
16. GCF of 18 and 42 is 6.
17. GCF of 42 and 70 is 14.
18. GCF of 144 and 242 is 2.
19. GCF of 630 and 945 is 315.
20. GCF of 286 and 715 is 143.
21. LCM of 14 and 35 is 70.
22. LCM of 45 and 105 is 315.
23. LCM of 286 and 715 is 1,430.
24. LCM of 21 and 20 is 420.
25. LCM of 88 and 66 is 264.
Chapter 5
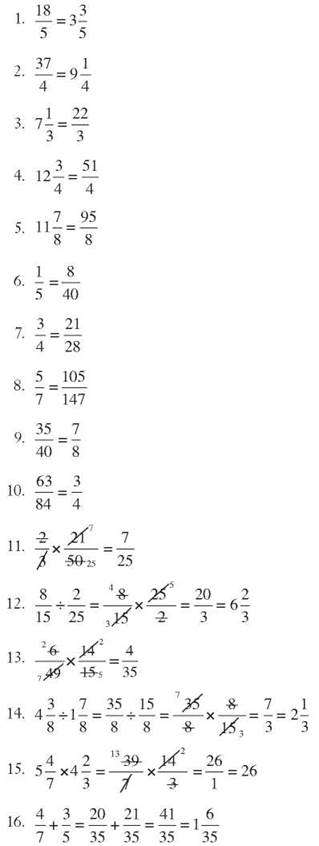
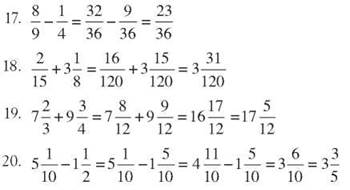
Chapter 6
1. 9.003 is nine and three thousandths.
2. 82.4109 is eighty-two and four thousand one hundred nine ten-thousandths.
3. “forty-two hundredths” is 0.42.
4. “forty-two ten-thousandths” is 0.0042.
5. “three hundred twelve and nine hundred one thousandths” is 312.901.
6. 0.00001 = 10-5
7. 0.000000001 = 10-9
8. 0.000000000000001 = 10-15
9. 10-6 = 0.000001
10. 10-10 = 0.0000000001
11. 0.492 = 4.92 x 10-1
12. 0.0000051 = 5.1 x 10-6
13. 2.7 x 10-5 = 0.000027
14. 8.19 x 10-7 = 0.000000819
15. 5.302 x 10-4 = 0.0005302
16. 45.9 + 19.75 = 65.65
17. 397.256 - 242.81 = 154.446
18. 17,401.12 + 15,293.101 = 32,694.221
19. 159.41006 - 143.0025 = 16.40756
20. 1.00027 + 0.4587332 = 1.4590032
21. 4.92 x 1.5 = 7.380 (or just 7.38)
22. 68.413 x 0.15 = 10.26195
23. 95.94 ÷ 7 7.8 = 12.3
24. 461.44 ÷ 7 1.12 = 412
25. 5,066.518 ÷ 7 8.6 = 589.13
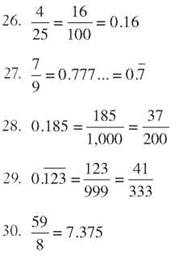
Chapter 7
1. 5x + 3x = 32
8x = 32
x = 4
5x = 20 3x = 12
There are 12 boys in Math Club.
2. 7x + 1x = 40
8x = 40
x = 5
7x = 35 1x = 5
There were 5 hybrids sold.
3. 2x + 3x = 20
5x = 20
x = 4
2x = 8 3x = 12
The florist should use 12 white roses and 8 red roses.
4. 4 x + 7x + 4 x = 45
15x = 45
x = 3
4 x = 12 7x = 21 4 x =12
There are 21 tigers.
5. 21x + 20x + 9x = 900
50x = 900
x = 18
21x = 378 20x = 360 9x = 162
There are 162 white balloons.
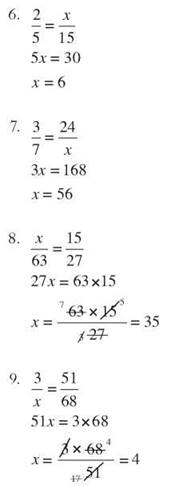
10. ![]()
5 x = 30
x = 6
11. 45 is 20% of 225.
![]()
20x = 4500
x = 225
12. 16 is 25% of 64.
![]()
64 x = 1600
x = 25
13. 15% of 80 is 12.
![]()
100x = 1200
x =12
14. 63 is 300% of 21.
![]()
21x =6300
x = 300
15. 120% of 55 is 66.
![]()
100x = 6600
x = 66
16. ![]()
17. 85.3% = 0.853
18. ![]()
19. 0.049 = 4.9%
20. 5.002 = 500.2%
21. I = prt
I = 18000 x 0.04x5 = $3,600
The interest is $3,600.
22. I = prt
130 = 1000 x r x 2
![]()
The interest rate is 6.5%.
23. tax= 0.047 x 175 = 8.225
You will pay $8.23 tax.
24. tip = 0.20 x $35.84 = 7.168
The tip should be approximately $7.17.
25. A total of 8 people at $22 per person is a bill of $176. The tip will be 0.18 x 176 = 31.68 or $31.68. Adding the tip to the bill brings the total to $207.68. Dividing that total eight ways means that each person’s share is $25.96.
26. The increase is $650 - $500 = $150.
![]()
500x = 15000
x = 30
The investment increased 30%.
27. The decrease is 7.5 - 6.75 = 0.75 minutes.
![]()
7.5x = 75
x = 10
Her time decreased 10%.
28. The change was an increase of 8.5 - 8 = 0.5 pounds.
![]()
8x = 50
x = 6.25
The dog’s weight increased 6.25%.
29. The decrease was 180 - 150 = 30 pounds.
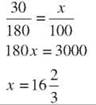
His weight decreased ![]()
30. The increase is 2 - 1.5 = 0.5 quarts.
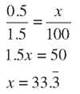
There was ![]() more ice cream.
more ice cream.
Chapter 8

Chapter 9
1. 4x is a term.
2. -12 is a term.
3. -2t7 is a term.
4. 6/y is not a term.
5. a/6 is a term.
6. 7y2 and 11y are unlike.
7. 3t2 and 5t2 are like.
8. 2x and 7x are like.
9. -9a2 and -15a3 are unlike.
10. 132x3 and -83x3 are like.
11. -4x + 9x = 5x
12. 3a2 - 2a3 is not possible.
13. 5xy + 6xy = 11 xy
14. 120xy2 — 80xy2 = 40xy2
15. 15z + 25x is not possible.
16. 6x(2x + 9) = 12x2 + 54x
17. 12 + 5(x + 1) = 12 + 5x + 5 = 5x + 17
18. 6t2(t - 3) - 2? = 6t3 - 18t2 - 2t2 = 6t3 - 20t2
19. 5y(6y + 2) + 7y2(4 - 12y) = 30y2 + 10y + 28y2 - 84y3 = -84y3 + 58y2 + 10y
20. 8a(2b - 5) - 2b(a - 2) = 16ab - 40a - 2ab + 4b = 14ab - 40a + 4b
21. -3a3 + 5a2 - 3a + 12 is degree 3.
22. 6 + 3b — 4b is degree 2.
23. 2t - 9 + 7t2 + 4t3 is degree 3.
24. 11y - 7y4 + 5y2 - 3 is degree 4.
25. 6 - 4x2 + 3x is degree 2.
26. a3 + 10a4 - 11a + 9 = 10a4 + a3- 11a + 9
27. 2b3 - 9b + 12b2 - 5 = 2b3 + 12b2 - 9b - 5
28. 3k4 + 8k5 - 13k - 7 = 8k5 + 3k4 - 13k - 7
29. 4 - 7m2 + 14m4 + 2m3 = 14 m4 + 2m3 - 7m2 + 4
30. 5p - 3 + 6p2 - 15p3 = - 15p3 + 6p2 + 5p - 3
Chapter 10
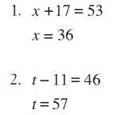
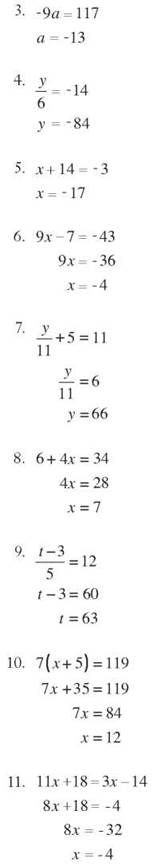
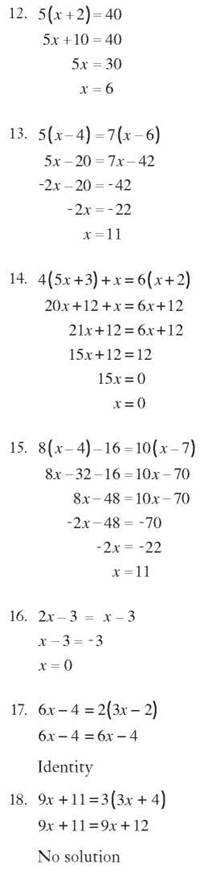
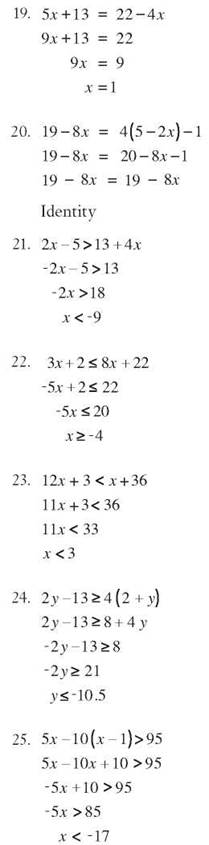
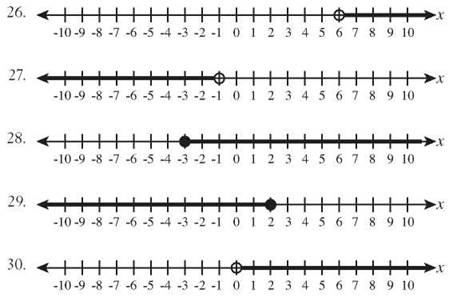
Chapter 11
Answers for questions 1 through 5 are shown on one graph below.
6. x + y = 7
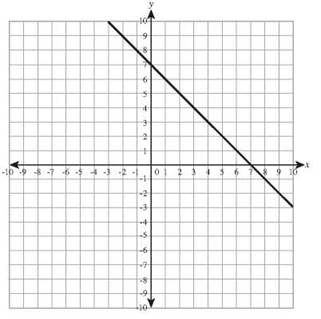
7. 2x - y = 3
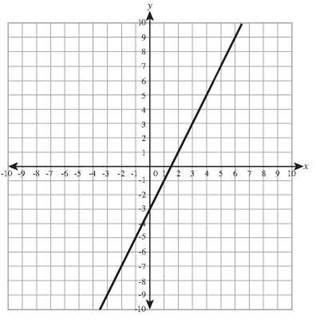
8. y = 3x - 6
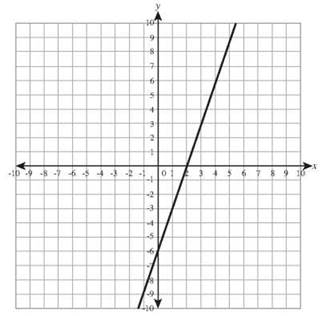
9. y = 8 - 2x
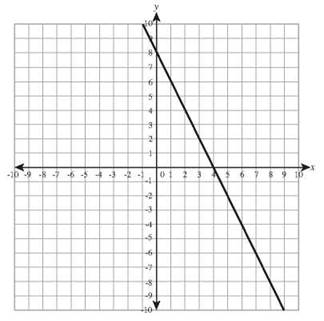
10. ![]()
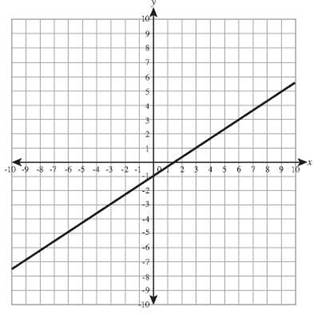
11. x + y = 10 has intercepts (0,10) and (10,0).
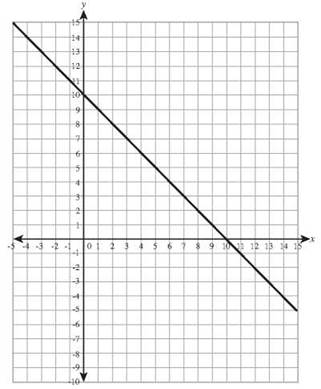
12. 6x + 2y =12 has intercepts (0,6) and (2,0).
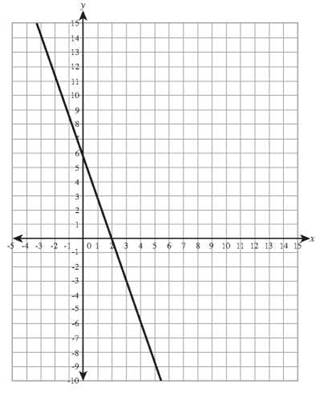
13. 2x- 3y = 9 has intercepts (0,-3) and (4.5,0).
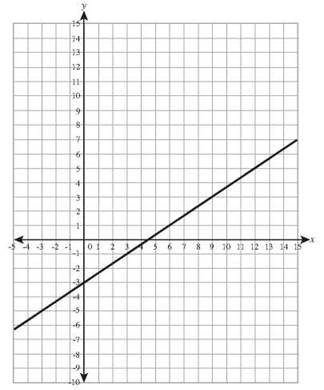
14. x -2y = 8 has intercepts (0,-4) and (8,0).
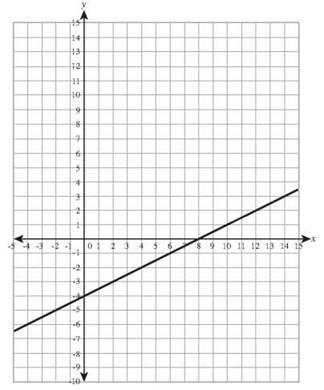
15. 6x + 2y =18 has intercepts (0,9) and (3,0).
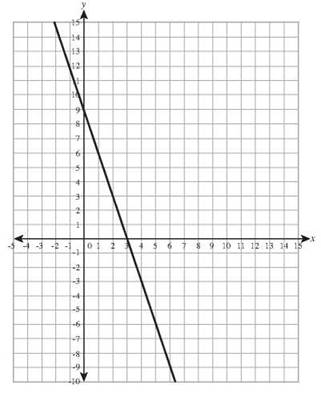
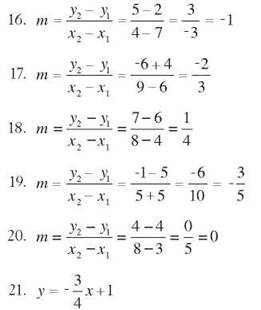
y-intercept: (0,1) slope: -3/4
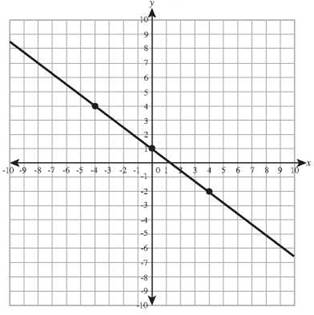
22. y = -4x + 6
y-intercept: (0,6) slope: -4
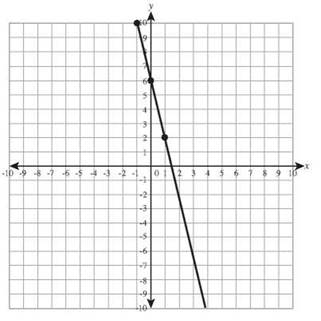
23. y = -3x - 4
y-intercept: (0,-4) slope: -3
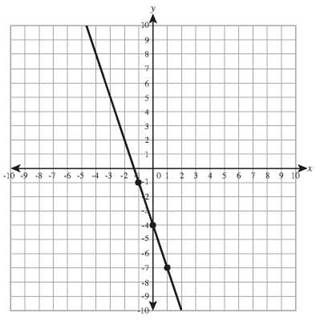
24. 2y = 5x - 6
y-intercept: (0,-3) slope: 5/2
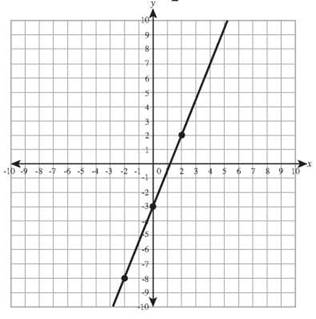
25. y — 6 = 3x +1
y-intercept: (0,7) slope: 3
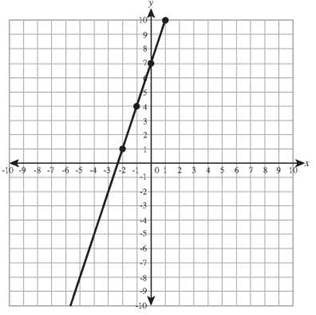
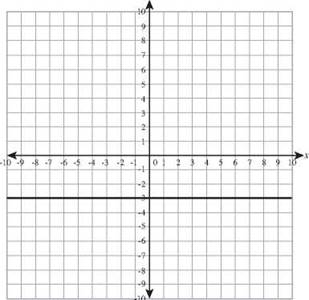
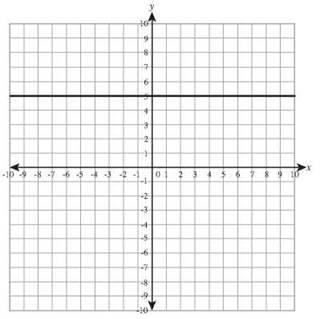
26. y = -3
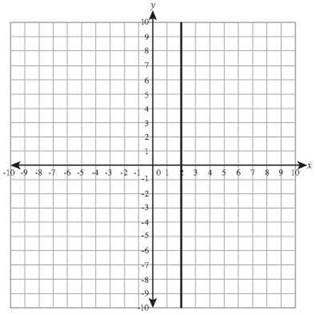
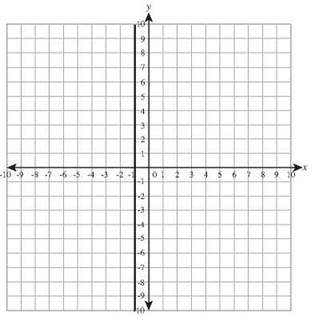
27. x = 2
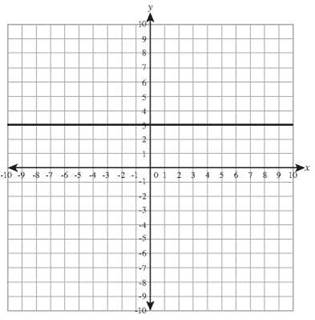
28. y = 5
29. x = -1
30. y + 1 = 4
31. ![]()
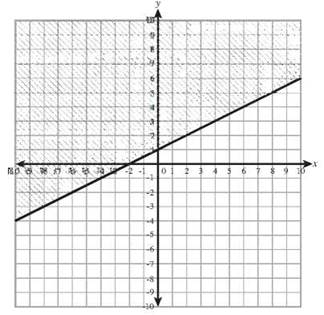
32. y ≤ 2x — 5
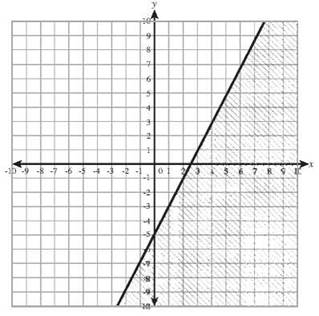
33. y > 5x — 4
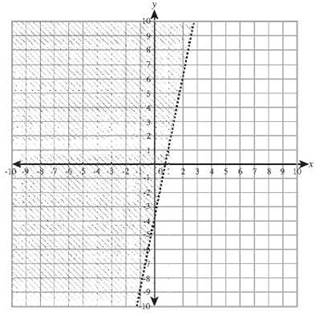
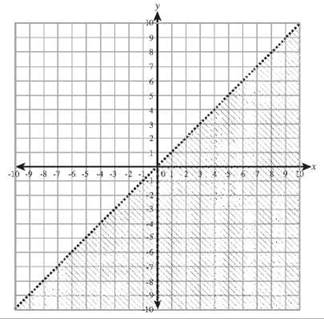
34. y < x
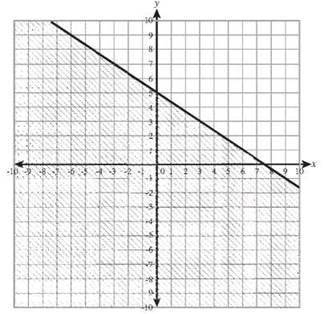
35. ![]()
Chapter 12
Sample answers are shown for questions 1-5.
Many answers are possible.
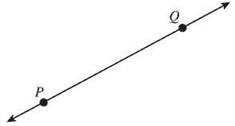
1. Line PQ
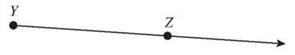
2. Ray YZ
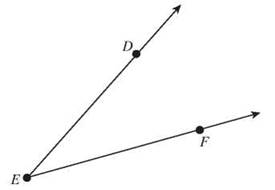
3. Angle ∠DEF
4. Rays AB and AC
![]()
5. Angles ∠PQR and ∠RQT
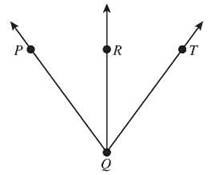
6. If m∠X = 174°, then ∠X is a(n) obtuse angle.
7. If m∠T = 38°, then ∠T is a(n) acute angle.
8. If ∠X and ∠Y are supplementary, and m∠X = 174°, then m∠Y = 6°.
9. If ∠R and ∠T are complementary, and m∠T = 38°, then m∠R = 52°.
10. Lines ![]() and
and ![]() intersect at point Y. If m∠PYR = 51°, then m∠RYA = 129° and m∠TYA = 51°.
intersect at point Y. If m∠PYR = 51°, then m∠RYA = 129° and m∠TYA = 51°.
11. M is the midpoint of segment ![]() If PM = 3 cm, MQ= 3 cm and PQ= 6 cm.
If PM = 3 cm, MQ= 3 cm and PQ= 6 cm.
12. H is the midpoint of ![]() If XY = 28 inches, then XH = 14 inches.
If XY = 28 inches, then XH = 14 inches.
13. Ray ![]() bisects ∠CAT. If m∠CAT = 86°, then m∠HAT = 43°.
bisects ∠CAT. If m∠CAT = 86°, then m∠HAT = 43°.
14. If m∠AXB = 27° and m∠BXC = 27°, then ![]() bisects ∠AXC.
bisects ∠AXC.
15. m∠PYQ= 13°, m∠QYR = 12°, m∠RYS = 5°, and m∠SYT = 20°. True or False: ![]() bisects ∠PYT. m∠PYR = 13° + 12° = 25°. m∠RYT = 5° + 20° = 25°.
bisects ∠PYT. m∠PYR = 13° + 12° = 25°. m∠RYT = 5° + 20° = 25°.
16. ∠PXY and ∠XYT are a pair of alternate interior angles.
17. ∠AXQ and ∠XYT are a pair of corresponding angles.
18. If m∠XYT = 68°, then m∠PXA = 112°.
19. If m∠PXY = 107°, then m∠RYB = 107°.
20. If ![]() then m∠XYR = 901.
then m∠XYR = 901.
21. Line a is parallel to line b. Both have slopes of -3.
22. ![]() is perpendicular to
is perpendicular to ![]() Slopes are negative reciprocals:
Slopes are negative reciprocals: ![]()
23. Line p and line q are neither parallel nor perpendicular.
24. ![]() Line
Line ![]() and line
and line ![]() are neither parallel nor perpendicular.
are neither parallel nor perpendicular.
25. The line 3x - 2y = 12 has slope = 3/2 and the line 2x + 3y = 12 has slope = -2/3. The lines are perpendicular.
Chapter 13
1. m∠S = 180° - (48° + 102°) = 30°.
2. m∠TSQ = 48° + 102° = 150°.
3. m∠TSQ = 150°, m∠TRP = 132°, and m∠STN = 78°. The total of m∠TSQ + m∠TRP + m∠STN = 150° + 132° + 78° = 360°.
4. Placidville is 43 miles from Aurora, and Aurora is 37 miles from Lake Grove. The distance from Placidville to Lake Grove is greater than 6 miles and less than 80 miles.
5. Gretchen lives 5 miles from the library and 2 miles from school. The distance from the library to school is between 3 miles and 7 miles.
6. ∆RST is isosceles with RS = ST. If m∠SRT = 39°, then m∠STR = 39!.
7. In right triangle ∆ABC, m∠A = 90° - 19° = 71°.
8. False: If m∠P = 17° and m∠Q = 25°, m∠R = 180° - (17° + 25°) = 138°. ∆PQR is an obtuse triangle, not an acute triangle.
9. If m∠P = 17° and m∠Q= 25°, then the longest side of ∆PQR is side ![]()
10. If the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle measures 94°, then the base angles measure 43° each.
11. In ∆XYZ, ![]() If XY = 15 cm and YZ = 20 cm, XZ = 25 cm.
If XY = 15 cm and YZ = 20 cm, XZ = 25 cm.
12. In ∆RST, ![]() If ST = 20 inches and RS = 52 inches, RT = 48 inches.
If ST = 20 inches and RS = 52 inches, RT = 48 inches.
13. In ∆PQR, ![]() If PQ = PR = 3 feet, QR = 3√2 ≈ 4.24 feet.
If PQ = PR = 3 feet, QR = 3√2 ≈ 4.24 feet.
14. In ∆CAT, ![]() If CT = 8 meters and CA = 4 meters, AT = 4√3 ≈ 6.93 meters.
If CT = 8 meters and CA = 4 meters, AT = 4√3 ≈ 6.93 meters.
15. In ∆DOG, ![]() If DO = 21 cm and DG = 35 cm, OG = 28 cm.
If DO = 21 cm and DG = 35 cm, OG = 28 cm.
16. ∆ABC is a 30°-60°-90° right triangle, with hypotenuse 8 cm long. The length of the shorter leg is 4 cm.
17. ∆RST is an isosceles right triangle with legs 5 inches long. The length of the hypotenuse is 5√2 inches.
18. ∆ARM is a right triangle with AR = 14 meters, RM = 28 meters, and AM = 14√3 meters. m∠M = 30°.
19. ∆LEG is a right triangle with LE = EG and LG = 7√2 inches. m∠G = 45°.
20. ∆OWL is an isosceles right triangle with OW > OL. ∠L is the right angle.
21. ![]()
22. ![]()
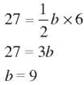
The base is 9 inches.
23. If the legs of the right triangle measure 20 cm and 48 cm, the hypotenuse is 52 cm. P = 20 + 48 + 52 = 120 cm.
24. In an equilateral triangle with a base b, the altitude will be ![]() and the area is
and the area is ![]() If the area is 9√3 square inches,
If the area is 9√3 square inches, ![]() so
so ![]() and b = 6 inches. The perimeter is 18 inches.
and b = 6 inches. The perimeter is 18 inches.
25. The area of a right triangle with legs of 3 cm and 4 cm and hypotenuse of 5 cm is 6 square centimeters.
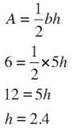
The altitude from the right angle to the hypotenuse is 2.4 centimeters long.
Chapter 14
1. In quadrilateral ABCD, ![]() and
and ![]() ABCD is a parallelogram because both pairs of opposite sides are parallel.
ABCD is a parallelogram because both pairs of opposite sides are parallel.
2. In quadrilateral PQRS, with diagonal ![]() ∠QRP ≅ ∠SPR and ∠QPR ≅ ∠SRP. PQRS is a parallelogram. The congruent alternate interior angles prove that both pairs of opposite sides are parallel.
∠QRP ≅ ∠SPR and ∠QPR ≅ ∠SRP. PQRS is a parallelogram. The congruent alternate interior angles prove that both pairs of opposite sides are parallel.
3. In quadrilateral FORK, ∠F ≅ ∠K and FO = RK. There is sufficient information to say FORK is a parallelogram.
4. In quadrilateral LAMP, with diagonals ![]() and
and ![]() intersecting at S, ∆ALS ≅ ∆PMS and ∆AMS ≅ ∆PLS. The congruent triangles assure that both pairs of opposite sides are congruent, so LAMP is a parallelogram.
intersecting at S, ∆ALS ≅ ∆PMS and ∆AMS ≅ ∆PLS. The congruent triangles assure that both pairs of opposite sides are congruent, so LAMP is a parallelogram.
5. In quadrilateral ETRA, with diagonals ![]() and
and ![]() intersecting at X, TX = RX and EX = AX. There is not enough information to guarantee that ETRA is a parallelogram.
intersecting at X, TX = RX and EX = AX. There is not enough information to guarantee that ETRA is a parallelogram.
6. In quadrilateral FORT, ![]() and
and ![]() FORT is a rectangle.
FORT is a rectangle.
7. In quadrilateral CAMP, CA = AM = MP = CP and ![]() CAMP is a square.
CAMP is a square.
8. In quadrilateral VASE, diagonals ![]() and
and ![]() are congruent, but sides
are congruent, but sides ![]() and
and ![]() are not. VASE is a rectangle.
are not. VASE is a rectangle.
9. In quadrilateral SOAP, ![]() and
and ![]() SOAP is a parallelogram.
SOAP is a parallelogram.
10. In quadrilateral COLD, diagonals ![]() and
and ![]() are perpendicular bisectors of one another, but they are not congruent. COLD is a rhombus.
are perpendicular bisectors of one another, but they are not congruent. COLD is a rhombus.
11. In trapezoid ABCD, ![]() and
and ![]() is a median. AC = 14 cm and BD = 30 cm. Median
is a median. AC = 14 cm and BD = 30 cm. Median ![]() measures 22 cm.
measures 22 cm.
12. In trapezoid FIVE, ![]() and m∠F = 59°. m∠I = 121°.
and m∠F = 59°. m∠I = 121°.
13. In trapezoid TEAR, ![]() and TE = AR. If ∠E = 107°, m∠A = 107°, and m∠R = 73°.
and TE = AR. If ∠E = 107°, m∠A = 107°, and m∠R = 73°.
14. In trapezoid ZOID, ![]() m∠Z = 83° and m∠I = 97°. If ZO = 4 cm, ID = 4 cm, because ZOID is an isosceles trapezoid.
m∠Z = 83° and m∠I = 97°. If ZO = 4 cm, ID = 4 cm, because ZOID is an isosceles trapezoid.
15. In trapezoid PQRT, ![]() and
and ![]() is a median.
is a median. ![]() If MN = 17 inches and PT = 21 inches,
If MN = 17 inches and PT = 21 inches,
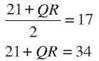
QR = 13 inches.
16. For a square with a side of 17 cm, perimeter is 68 cm and area is 289 cm2.
17. For a rectangle 18 inches long and 9 inches wide, perimeter is 54 inches and area is 162 square inches.
18. For parallelogram ABCD, AB = CD = 7 inches, AC = BD = 21 inches, and the height from B perpendicular to ![]() and
and ![]() 3 inches, perimeter is 56 inches, and area is 63 square inches.
3 inches, perimeter is 56 inches, and area is 63 square inches.
19. For a rhombus with sides 5 inches long and diagonals that measure 6 inches and 8 inches, perimeter is 20 inches and area is 5 square inches.
![]()
20. If the area of a parallelogram with a height of 48 cm is 3,600 square centimeters, the base to which that altitude is drawn (and the opposite side) must measure 75 cm. If the perimeter is 250 cm, the other two sides each measure 50 cm.
21. The number of diagonals in an octagon is ![]()
22. The total of the measures of all the interior angles in a nonagon is 180° (9- 2) = 1260°.
23. If a hexagon is regular, the total of the measures of all the interior angles is 180° (6 - 2) = 720°, and the measure of any one of its interior angles is ![]()
24. If the interior angles of a polygon add up to 900°, then 900° = 180°(n - 2), and n - 2 = 5. The polygon has 7 sides.
25. If a polygon has a total of 119 possible diagonals, ![]() so n(n-3) = 238. The factors of 238 are 2 x 119, 7 x 34, and 14 x 17. The last pair differ by 3, so n = 17.
so n(n-3) = 238. The factors of 238 are 2 x 119, 7 x 34, and 14 x 17. The last pair differ by 3, so n = 17.
26. The area of a regular pentagon with sides 8 cm long and an apothem 5 cm long is ![]()
27. The area of an octagon with a perimeter of 40 inches and an apothem of 5 inches is ![]() square inches.
square inches.
28. The area of a regular decagon in which each of the 10 sides measure 2 meters and the apothem is 1.5 meters is ![]() square meters.
square meters.
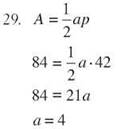
If the perimeter of a regular hexagon is 42 inches and its area is 84 square inches, its apothem is 4 inches.
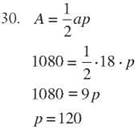
A regular pentagon with an area of 1,080 square inches and an apothem of 18 inches has a perimeter of 120 inches. Each side is 24 inches.
Chapter 15
1. An arc less than half a circle is a minor arc.
2. The distance from the center point to any point on the circle is called the radius.
3. Two circles with the same center are concentric circles.
4. If two circles touch each other at just one point, the circles are tangent.
5. An arc that is exactly half the circle is called a semicircle.
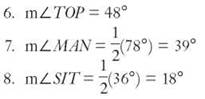
9. ∠ITS is inscribed in a semicircle. m∠ITS = 90°.
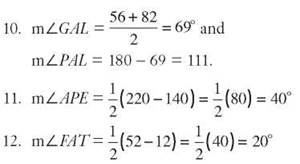
13. ∠RAC intercepts an arc of 360 - 72 = 288°. ![]()
14. Let x = the measure of arc ![]()
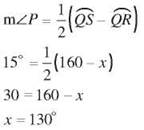
15. ![]() but 2x + x = 360, so x = 120 and m∠P = 60°.
but 2x + x = 360, so x = 120 and m∠P = 60°.
16. The area of a circle with a radius of 9 cm is 81π cm2.
17. The circumference of a circle with a diameter of 12 inches is 12π inches.
18. The area of a circle with a diameter of 32 cm is 162π = 256π cm2.
19. The radius of a circle with an area of 36π square meters is 6 meters, its diameter is 12 meters, and its circumference is 12π meters.
20. The diameter of a circle with a circumference of 24π feet is 24 feet, its radius is 12 feet, and its area is 144π square feet.
21. The equation of a circle with its center at the origin and a radius of 3 units is x2 + y2 = 9.
22.
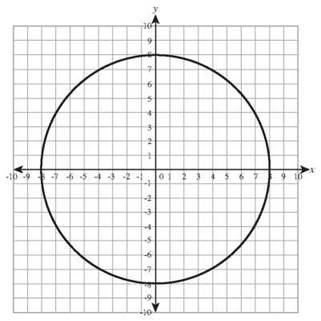
23. The center of the circle (x - 8)2 + (x - 3)2 = 49 is the point (8,3) and radius is 7.
24. The equation of a circle with center (4,9) and radius of 2 units is (x - 4)2 + (y - 9)2 = 4.
25.
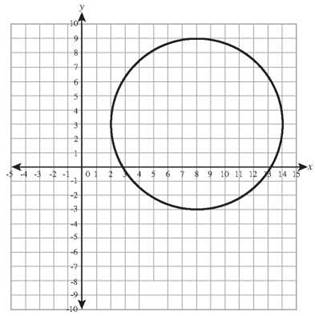
Circle of radius 6 centered at (8,3)
Chapter 16
1. SA = 2(15 x 24) + 2(15 x 10) + 2(24 x 10) = 1,500 cm2
2. SA = 2(1/2 x 5 x 12) + 5(8 + 12 + 13) = 225 square inches
3. SA = 2 x 65 + 42 x 30 = 1,390 cm2
4. SA = 2 x 387 + 5 x 15 x 4 = 1,074 square inches
5. SA = 6 x 172 = 1,734
6. V = 73 = 343 cubic inches
7. V = 12 x 21 x 15 = 3,780 cm3
8. V = 1/2 x 3 x 4 x 6 = 36 cubic inches
9. V = 387 x 8 = 3,096 cubic inches
10. V = 65 x 50 = 3,250 cm3
11. SA = 42 + 1/2(16 x 5) = 16 + 40 = 56 square inches
12. SA = 62.4 + 1/2(36 x 10) = 62.4 + 180 = 242.4 cm2
13. SA = 172 + 1/2(50 x 18) = 172 + 450 = 622 cm2
14. SA = 260 + 1/2(60 x 10) = 260 + 300 = 560 square inches
15. SA = 102 + 1/2(40 x 13) = 100 + 260 = 360 square inches
16. If the slant height is 13 inches and half the side is 5 inches, the height is 12 inches. ![]() cubic inches.
cubic inches.
17. If the slant height is 5 inches and half the side is 2 inches, the height is √21 ≈ 4.58 inches. ![]() cubic inches.
cubic inches.
18. The base of the pyramid is an equilateral triangle with a side of 12 cm and an area of 62.4 square centimeters. The area is half the apothem times the perimeter, so ![]() and the apothem is a ~ 3.47. Use the Pythagorean Theorem with the apothem and slant height to find the height. a2 + h2 = l2 becomes (3.47) + h2 = 102 and h ≈ 9.38. The height is approximately 9.38, and
and the apothem is a ~ 3.47. Use the Pythagorean Theorem with the apothem and slant height to find the height. a2 + h2 = l2 becomes (3.47) + h2 = 102 and h ≈ 9.38. The height is approximately 9.38, and ![]() cubic centimeters.
cubic centimeters.
19. Use the area of the pentagon and its perimeter to find the apothem. ![]() so a ≈ 6.88. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the height. a2 + h2 = l2 so (6.88)2 + h2 =(18)2 and h ≈ 16.63.
so a ≈ 6.88. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the height. a2 + h2 = l2 so (6.88)2 + h2 =(18)2 and h ≈ 16.63. ![]() cubic centimeters.
cubic centimeters.
20. The regular hexagon that forms the base has a perimeter of 60 inches and an area of 260 square inches, so use the formula ![]() to find the apothem.
to find the apothem. ![]() means that the apothem is
means that the apothem is![]() inches long. Use the Pythagorean Theorem with the apothem and the slant height to find the height. a2 + h2 = l2 so
inches long. Use the Pythagorean Theorem with the apothem and the slant height to find the height. a2 + h2 = l2 so ![]() and h ≈ 4.99 inches.
and h ≈ 4.99 inches. ![]() cubic inches.
cubic inches.
21. h = 14 cm, r = 5 cm, SA = 2∙52∙π + 2∙π∙5∙14 = 190π cm2, V = π∙52∙14 = 350π cm3.
22. h = 8 inches, d = 6 inches, r = 3 inches, SA = 2∙32∙π + 2∙π∙3∙8 = 66π square inches, V = π∙32∙8 = 72π cubic inches.
23. h = 2 m, C = 2π m, d = 2 m, r = 1 m, SA = 2∙12∙π + 2∙π∙1∙2 = 6π m2, V = π∙12∙2 = 2π m3.
24. h = 82 cm, d = 90 cm, r = 45 cm, SA = 2∙452∙π + 2∙π∙45∙82 = 11,430π cm2, V = π∙452∙82 = 166,050π cm3.
25. h = 20 inches, C = 20π inches, d = 20 inches, r = 10 inches, SA = 2∙102∙π + 2∙π∙10∙20 = 600π square inches, V = π∙102∙20 = 2,000π cubic inches.
26. r = 10 cm, h = 24 cm, l = 26 cm, SA = π∙102 + π∙10∙26 = 360π cm2, V = 1/3∙π∙102∙24 = 800π cm3
27. d = 8 inches, r = 4 inches, h = 3 inches, l = 5 inches, SA = π∙41 + π∙4∙5 = 36π square inches, V = 1/3∙π∙42∙3 = 16π cubic inches
28. C = 16π cm, d = 16, r = 8, h = 6 cm, l = 10 cm, SA = π∙82 + π∙8∙10 = 144π cm2, V = 1/3∙π∙82∙6 = 128π cm3
29. r = 12 inches, h = 5 inches, l = 13, SA = π∙122 + π∙12∙13 = 300π square inches, V = 1/3∙π∙122∙5 = 240π cubic inches
30. A = 324π cm, r = 18 cm, h = 24 cm, l = 30 cm, SA = π∙182 + π∙18∙30 = 864π cm2, V = 1/3∙π∙182∙24 = 2,592π cm3
31. r = 8 inches, SA = 4∙π∙82 = 256π square inches
32. r = 12 cm, V = 4/3∙π∙123 = 2,304π cm3
33. d = 4 m , r = 2m, SA = 4∙π∙22 = 16π m2
34. d = 6 feet, r = 3 feet, V = 4/3∙π∙33 = 36π cubic feet
35. V = 4500π cm3, r = 15 cm
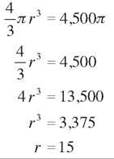
Chapter 17
1. Shaded area = area of large square - area of 2 white squares = 72 = 2∙32 = 49 - 18 = 31 square units.
2. Shaded area = area of rectangle - area of two white strips adjusted for overlap of white strips = 20 x 6 - (20 x 1 + 6 x 1 - 1 x 1) = 120 - 25 = 95.
3. Shaded area = Vi the area of large circle + 1/2 the area of small circle = 72π + 12.5π = 84.5π.
4. Shaded area = 1/2 x 1 x 12 = 6.
5. Flip one shaded section. Shaded area = ![]()
![]()
6. ![]() ∆ABC ≅ ∆XYZ by ASA
∆ABC ≅ ∆XYZ by ASA
7. ![]() ∆ACT ≅ ∆IWN by AAS
∆ACT ≅ ∆IWN by AAS
8. ![]() ∆BIG and ∆MAN cannot be determined.
∆BIG and ∆MAN cannot be determined.
9. ![]() , ∆CAT ≅ ∆DOG by SSS
, ∆CAT ≅ ∆DOG by SSS
10. ![]() ∆BOX ≅ ∆CAR by SAS
∆BOX ≅ ∆CAR by SAS
11. ∆ABC~∆XYZ, ![]()
12. ∆RST~∆FED, ![]()
13. ∆PQR~∆VXW, ![]()
14. ∆MLN~∆LJK, ![]()
15. ∆ZXY~∆BCA, ![]()
16. ∆GHI~∆ARM, GH = 9 ft, GI = 8 ft, AR = 12 ft. Find AM.
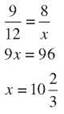
17. ∆JKL~∆DOG, JK = 17 m, JL = 25 m, DG = 30 m. Find DO.
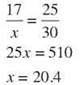
18. ∆ABC~∆XYZ, AB = 21 cm, BC = 54 cm, XY = 7 cm. Find YZ.
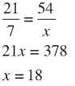
19. ∆DEF~∆CAT, DE = 65 in, EF = 45 in, CA = 13 in. Find AT.
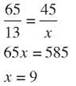
20. ∆MNO~∆LEG, MN = x - 3, NO EG = 21, LE = 2x + 4. Find LE.
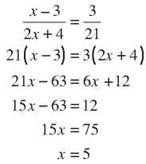
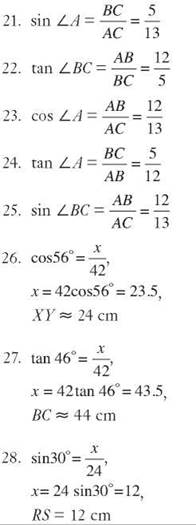
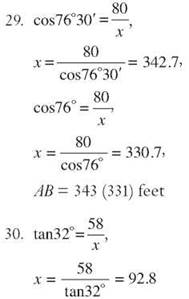
Side ![]() is 58 m. Find the length of
is 58 m. Find the length of ![]() to the nearest centimeter. XY ≈ 93.
to the nearest centimeter. XY ≈ 93.
Chapter 18
1. 2 x 4 = 8
2. 2 x 5 x 4 = 40
3. 2 x 5 x 3 x 4 = 120
4. 2 x 5 x 4 x 4 = 160
5. 2 x 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 4 = 960
6. 6! = 6 x 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 720.
7. 7! = 7 x 6 x 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 5,040.
8. 7! ÷ 6 = 840.
9. The permutations of 9 things taken 3 at a time = 504.
10. The permutations of 10 things taken 4 at a time = 5,040.
11. The number of combinations of 6 things taken 3 at a time = 20.
12. The number of combinations of 7 things taken 4 at a time = 35.
13. The number of combinations of 5 things taken 2 at a time = 10.
14. The number of different committees of 5 people that can be chosen from a group of 12 people is 792.
15. If you are going to choose 3 toppings from a list of 12 possibilities and the order in which you put toppings on does not matter, you have 220 sundaes to choose from.
16. The probability of drawing a heart and then a queen is ![]()
17. The probability of drawing a heart and then a heart is ![]()
18. The probability of drawing a black card and then a red card is ![]()
19. The probability of drawing a king and a queen is ![]()
20. The probability of drawing two black cards is ![]()
21. The probability that the marble chosen is red or blue is ![]()
22. The probability that the chosen marble is yellow or blue is ![]()
23. The probability that the marble is green or white is ![]()
24. The probability that the chosen marble is yellow or red is ![]()
25. The probability that the marble is red or orange is ![]()
Chapter 19
1.
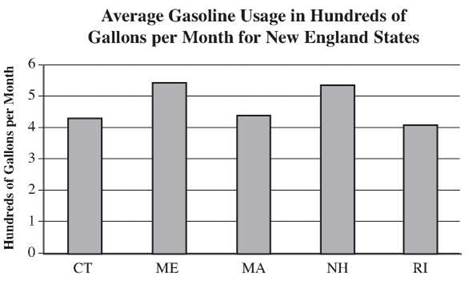
2. Rhode Island had the lowest average gasoline usage, possibly because the small size of the state means commuting distances are smaller.
3. Tacos outsell pasta by approximately 1,000 lunches.
4. Approximately 6,000 chicken lunches are sold per year.
5. Approximately 5,000 burgers are sold per year.
6.
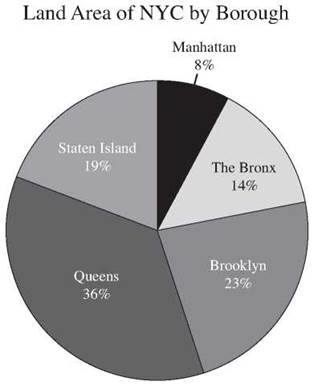
7. Area of Queens ÷ area of Manhattan = 109 ÷ 23 ≈ 4.7. Queens is between 4 and 5 times the size of Manhattan.
8. Percent of the enrollment in music courses = 4% + 22% + 16% = 42%.
9. Chorus had the largest enrollment.
10. Painting and Ceramics had the most similar enrollments.
11. Art History was 20% of enrollment, so 20% of 461 is approximately 92 students.
12.
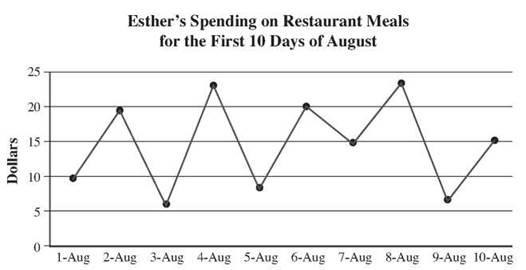
13. Esther’s restaurant spending alternates large and small expenditures.
14. Esther’s spending varied by only 25 cents on August 4th and 8th and on August 7th and 10th.
15. Sales have the greatest positive change from June to July.
16. Sales had the steepest drop from August to September.
17. November had sales most similar to the number of hot dogs sold in February.
Chapter 20
1. For data set A, mean = 3.1
2. For data set B, mean = 71.8
3. For data set C, mean = 5.3
4. For data set D, mean = 35
5. For data set E, mean = 3.2
6. The median of {2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4} is 3.
7. The median of {34, 54, 78, 92, 101} is 78.
8. The median of {3, 4, 5, 4, 7, 8, 9, 2, 10, 1} is 4.5.
9. The median of {32, 34, 36, 38} is 35.
10. The median of {2, 2, 3, 4, 5} is 3.
11. The mode of {2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4} is 4.
12. B = {34, 54, 78, 92, 101} has no mode.
13. The mode of {3, 4, 5, 4, 7, 8, 9, 2, 10, 1} is 4.
14. D = {32, 34, 36, 38} has no mode.
15. The mode of {2, 2, 3, 4, 5} is 2.
16. For data set A, Q1 = 4, Median = 8.5, Q3 = 32.
17. For data set B, Q1 = 3, Median = 4, Q3 = 66.
18. For data set C, Q1 = 25, Median = 64, Q3 = 83.
19. George’s placement at the 54th percentile means that his score is slightly above the mean, but Harry’s 43rd percentile places him below the mean. George did better.
20.
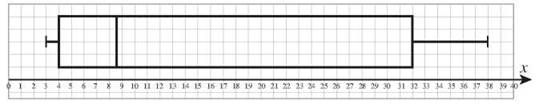
21. The range of {34, 54, 78, 92, 101} is 101 - 34 = 67.
22. The range of {3, 4, 5, 4, 7, 8, 9, 2, 10, 1} is 10 - 1 = 9.
23. The interquartile range of {3, 4, 5, 4, 7, 8, 9, 2, 10, 17, 32, 34, 36, 38} is 32 - 4 = 28.
24. The IQR of {2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 34, 54, 78, 92, 101} is 54 - 3 = 51.
25. The standard deviation of the test scores {69, 70, 73, 74, and 74} is approximately 2.345.