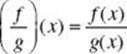SAT SUBJECT TEST MATH LEVEL 2
PART 2
![]()
REVIEW OF MAJOR TOPICS
![]()
CHAPTER 1
Functions

1.1 Overview
![]()
COMBINING FUNCTIONS
Given two functions, f and g, five new functions can be defined:
|
Sum function |
( f + g)(x) = f (x) + g(x) |
|
|
Difference function |
( f – g)(x) = f (x) – g(x) |
|
|
Product function |
|
|
|
Quotient function |
|
|
|
if and only if |
||
|
Composition of functions |
|
|
EXAMPLE
If f(x) = 3x – 2 and g(x) = x2 – 4, write an expression for each of the following functions:
(A) (f + g)(x)
(B) (f – g)(x)
(C) f · g (x)
(D) ![]()
(E) (f ![]() g)(x)
g)(x)
(F) (g ![]() f )(x)
f )(x)
SOLUTIONS
(A) 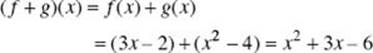
(B) 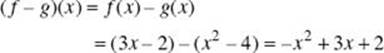
(C) 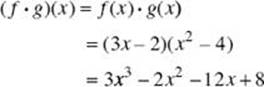
(D) 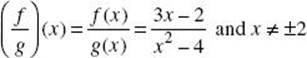
(E) 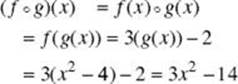
(F) 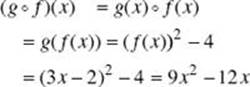
|
TIP (f |
EXERCISES
1. If f(x) = 3x2 – 2x + 4, f(–2) =
(A) –12
(B) –4
(C) –2
(D) 12
(E) 20
2. If f(x) = 4x – 5 and g(x) = 3x, then f(g(2)) =
(A) 3
(B) 9
(C) 27
(D) 31
(E) none of the above
3. If f(g(x)) = 4x2 – 8x and f(x) = x2 – 4, then g(x) =
(A) 4 – x
(B) x
(C) 2x – 2
(D) 4x
(E) x2
4. What values must be excluded from the domain of ![]() (x) if f(x) = 3x2 – 4x + 1 and g(x) = 3x2 – 3?
(x) if f(x) = 3x2 – 4x + 1 and g(x) = 3x2 – 3?
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) 3
(D) both ±1
(E) no values
5. If g(x) = 3x + 2 and g(f(x)) = x, then f(2) =
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) 6
(E) 8
6. If p(x) = 4x – 6 and p(a) = 0, then a =
(A) −6
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
(E) 2
7. If f(x) = ex and g(x) = sin x, then the value of (f ![]() g)(
g)(![]() ) is
) is
(A) –0.01
(B) –0.8
(C) 0.34
(D) 1.8
(E) 2.7