1,001 Calculus Practice Problems
Part I
The Questions
Chapter 6
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions and Tangent Lines
After becoming familiar with the derivative techniques of the power, product, quotient, and chain rules, you simply need to know basic formulas for different functions. In this chapter, you see the derivative formulas for exponential and logarithmic functions. Knowing the derivative formulas for logarithmic functions also makes it possible to use logarithmic differentiation to find derivatives.
In many examples and applications, finding either the tangent line or the normal line to a function at a point is desirable. This chapter arms you with all the derivative techniques, so you'll be in a position to find tangent lines and normal lines for many functions.
The Problems You'll Work On
In this chapter, you do the following types of problems:
· Finding derivatives of exponential and logarithmic functions with a variety of bases
· Using logarithmic differentiation to find a derivative
· Finding the tangent line or normal line at a point
What to Watch Out For
Although you're practicing basic formulas for exponential and logarithmic functions, you still use the product rule, quotient rule, and chain rule as before. Here are some tips for solving these problems:
· Using logarithmic differentiation requires being familiar with the properties of logarithms, so make sure you can expand expressions containing logarithms.
· If you see an exponent involving something other than just the variable x, you likely need to use the chain rule to find the derivative.
· The tangent line and normal line are perpendicular to each other, so the slopes of these lines are opposite reciprocals.
Derivatives Involving Logarithmic Functions
377–385 Find the derivative of the given function.
377. f (x) = ln (x)2
378. f (x) = (ln x)4
379. ![]()
380. ![]()
381. ![]()
382. ![]()
383. ![]()
384. 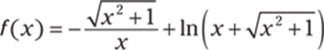
385. 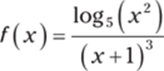
Logarithmic Differentiation to Find the Derivative
386–389 Use logarithmic differentiation to find the derivative.
386. ![]()
387. ![]()
388. 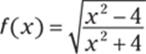
389. 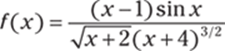
Finding Derivatives of Functions Involving Exponential Functions
390–401 Find the derivative of the given function.
390. f (x) = e5x
391. ![]()
392. ![]()
393. ![]()
394. ![]()
395. ![]()
396. ![]()
397. 
398. ![]()
399. ![]()
400. ![]()
401. ![]()
Finding Equations of Tangent Lines
402–404 Find the equation of the tangent line at the given value.
402. f (x) = 3 cos x + πx at x = 0
403. f (x) = x2 – x + 2 at (1, 2)
404. ![]() at x = 2
at x = 2
Finding Equations of Normal Lines
405–407 Find the equation of the normal line at the indicated point.
405. f (x) = 3x2 + x – 2 at (3, 28)
406. f (x) = sin2 x at ![]()
407. f (x) = 4 ln x + 2 at x = e2