Cracking the AP Chemistry Exam
Part IV
Content Review for the AP Chemistry Exam
Chapter 3
Big Idea #1: Atoms, Elements, and the Building Blocks of Matter
CHAPTER 3 QUESTIONS
Multiple-Choice Questions
Use the PES spectra below to answer questions 1-4.
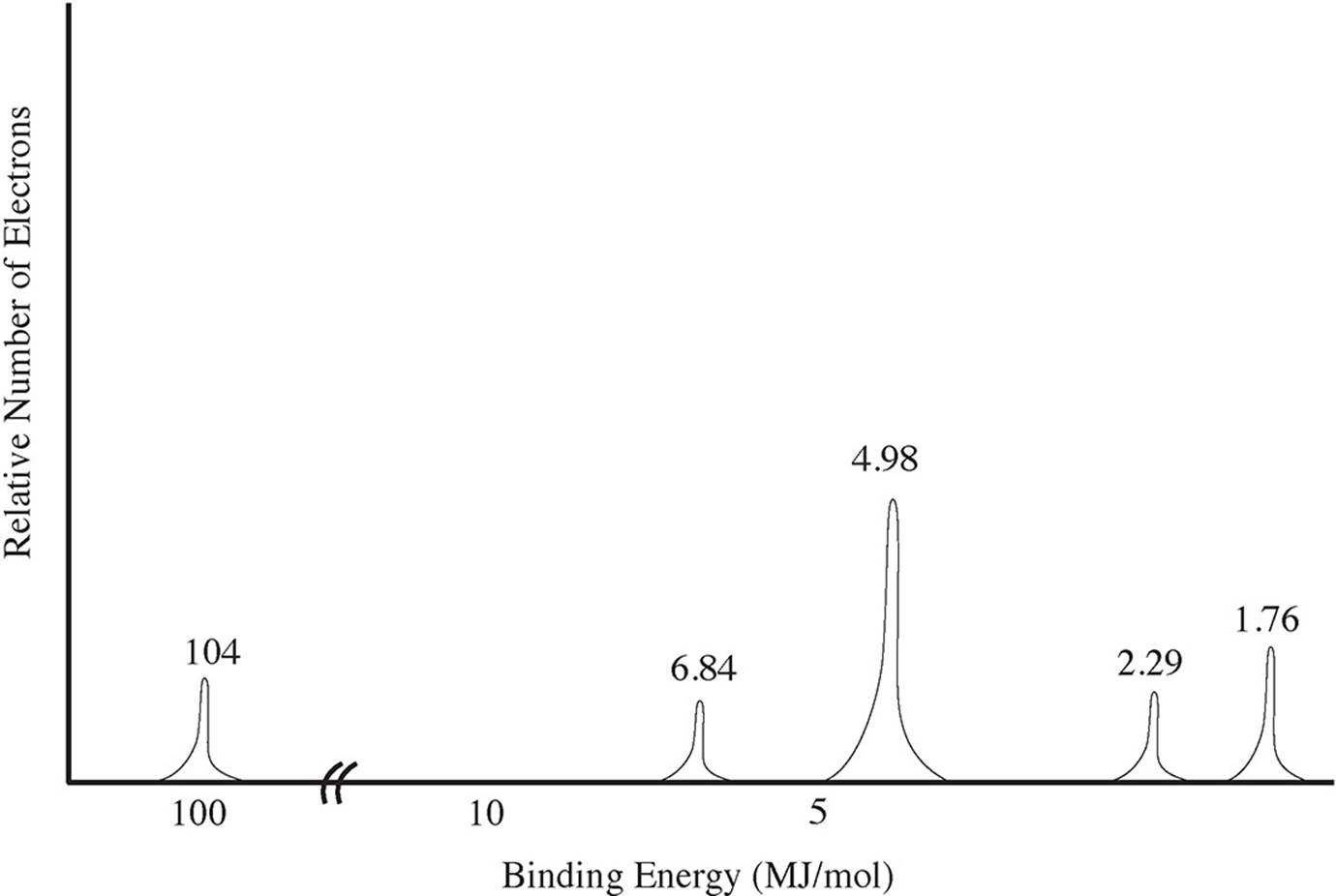
1. What element does this spectra represent?
(A) Boron
(B) Nitrogen
(C) Aluminum
(D) Phosphorus
2. Which peak represents the 2s subshell?
(A) The peak at 104 MJ/mol
(B) The peak at 6.84 MJ/mol
(C) The peak at 2.29 MJ/mol
(D) The peak at 1.76 MJ/mol
3. An electron from which peak would have the greatest velocity after ejection?
(A) The peak at 104 MJ/mol
(B) The peak at 6.84 MJ/mol
(C) The peak at 4.98 MJ/mol
(D) The peak at 1.76 MJ/mol
4. How many valence electrons does this atom have?
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5
5. Why does an ion of phosphorus, P3−, have a larger radius than a neutral atom of phosphorus?
(A) There is a greater Coulombic attraction between the nucleus and the electrons in P3−.
(B) The core electrons in P3− exert a weaker shielding force than those of a neutral atom.
(C) The nuclear charge is weaker in P3− than it is in P.
(D) The electrons in P3− have a greater Coulombic repulsion than those in the neutral atom.
6. Which neutral atom of the following elements would have the most unpaired electrons?
(A) Titanium
(B) Manganese
(C) Nickel
(D) Zinc
7. Which element will have a higher electronegativity value: chlorine or bromine? Why?
(A) Chlorine, because it has less Coulombic repulsion among its electrons
(B) Bromine, because it has more protons
(C) Chlorine, because it is smaller
(D) Bromine, because it is larger
8. Which of the following elements has its highest energy subshell completely full?
(A) Sodium
(B) Aluminum
(C) Chlorine
(D) Zinc
9. Which of the following isoelectric species has the smallest radius?
(A) S2−
(B) Cl−
(C) Ar
(D) K+
10. What is the most likely electron configuration for a sodium ion in its ground state?
(A) 1s2 2s2 2p5
(B) 1s2 2s2 2p6
(C) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
(D) 1s2 2s2 2p5 3s2
11. Which of the following statements is true regarding sodium and chlorine?
(A) Sodium has greater electronegativity and a larger first ionization energy.
(B) Sodium has a larger first ionization energy and a larger atomic radius.
(C) Chlorine has a larger atomic radius and a greater electronegativity.
(D) Chlorine has greater electronegativity and a larger first ionization energy.
12. An atom of silicon in its ground state is subjected to a frequency of light that is high enough to cause electron ejection. An electron from which subshell of silicon would have the highest kinetic energy after ejection?
(A) 1s
(B) 2p
(C) 3p
(D) 4s
13. The wavelength range for infrared radiation is 10−5 m, while that of ultraviolet radiation is 10−8 m. Which type of radiation has more energy, and why?
(A) Ultraviolet has more energy because it has a higher frequency.
(B) Ultraviolet has more energy because it has a longer wavelength.
(C) Infrared has more energy because it has a lower frequency.
(D) Infrared has more energy because it has a shorter wavelength.
14. Which of the following nuclei has 3 more neutrons than protons? (Remember: The number before the symbol indicates atomic mass.)
(A) 11B
(B) 37Cl
(C) 24Mg
(D) 70Ga
15. Which of the following is true of the halogens when comparing them to other elements in the same period?
(A) Halogens have larger atomic radii than other elements within their period.
(B) Halogens have less ionization energy than other elements within their period.
(C) Halogens have fewer peaks on a PES than other elements within their period.
(D) The electronegativity of halogens is higher than other elements within their period.
16. In general, do metals or nonmetals from the same period have higher ionization energies? Why?
(A) Metals have higher ionization energies because they usually have more protons than nonmetals.
(B) Nonmetals have higher ionization energies because they are larger than metals and harder to ionize.
(C) Metals have higher ionization energies because there is less electron shielding than there is in nonmetals.
(D) Nonmetals have higher ionization energies because they are closer to having filled a complete energy level.
17. The ionization energies for an element are listed in the table below.

Based on the ionization energy table, the element is most likely to be
(A) sodium
(B) magnesium
(C) aluminum
(D) silicon
Use the following information to answer questions 18−20.
The outermost electron of an atom has a binding energy of 2.5 eV. The atom is exposed to light of a high enough frequency to cause exactly one electron to be ejected. The ejected electron is found to have a KE of 2.0 eV.
18. How much energy did photons of the incoming light contain?
(A) 0.50 eV
(B) 0.80 eV
(C) 4.5 eV
(D) 5.0 eV
19. If the wavelength of the light were to be shortened, how would that effect the kinetic energy of the ejected electron?
(A) A shorter wavelength would increase the kinetic energy.
(B) A shorter wavelength would decrease the kinetic energy.
(C) A shorter wavelength would stop all electron emissions completely.
(D) A shorter wavelength would have no effect on the kinetic energy of the ejected electrons.
20. If the intensity of the light were to be decreased (that is, if the light is made dimmer), how would that affect the kinetic energy of the ejected electron?
(A) The decreased intensity would increase the kinetic energy.
(B) The decreased intensity would decrease the kinetic energy.
(C) The decreased intensity would stop all electron emissions completely.
(D) The decreased intensity would have no effect.
Free-Response Questions
1. Explain each of the following in terms of atomic and molecular structures and/or forces.
(a) The first ionization energy for magnesium is greater than the first ionization energy for calcium.
(b) The first and second ionization energies for calcium are comparable, but the third ionization energy is much greater.
(c) There are three peaks of equal height in the PES of carbon, but on the PES of oxygen the last peak has a height twice as high as all the others.
(d) The first ionization energy for aluminum is lower than the first ionization energy for magnesium.
2. Use your knowledge of the periodic table of the elements to answer the following questions.
(a) Explain the trend in electronegativity from P to S to Cl.
(b) Explain the trend in electronegativity from Cl to Br to I.
(c) Explain the trend in atomic radius from Li to Na to K.
(d) Explain the trend in atomic radius from Al to Mg to Na.
3. The table below gives data on four different elements, in no particular order:
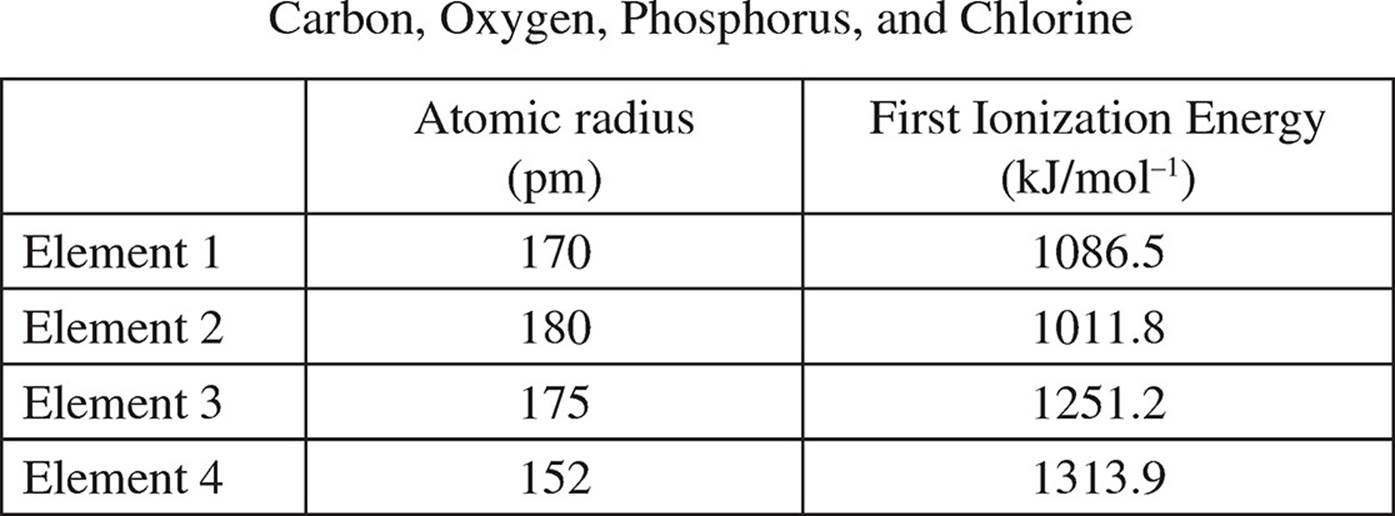
(a) Which element is number 3? Justify your answer using both properties.
(b) What is the outermost energy level that has electrons in element 2? How many valence electrons does element 2 have?
(c) Which element would you expect to have the highest electronegativity? Why?
(d) How many peaks would the PES for element 4 have and what would the relative heights of those peaks be to each other?