The MCAT Chemistry Book - Aryangat A. 2012
Solutions
Chapter 1 Solutions
1. The answer is D. This question tests your understanding of the concept of mole. The student is preparing a solution using calcium hydroxide. The formula of calcium hydroxide is Ca(OH)2. The formula weight of calcium hydroxide is 74.1 grams/mol. Here, the student added two moles of it. So the answer is 74.1 x 2 = 148.2 g.
2. The answer is D. The sample weighs 56 g. The formula weight of O2 is 32 g/mol. So the number of moles of oxygen present is roughly 1.75. Remember that 1 mol contains Avogadro number of particles. Since 1.75 moles of oxygen is present, there are 1.75 x 6.0 x 1023 molecules of oxygen. Are we done at this point? No! The question asks for the total number of ions present in the sample. Since each oxygen molecule is composed of oxygen atoms, the total number of atoms in this sample equals 2 x 1.75 x 6.0 x 1023 = 21 x 1023.
3. The answer is B. Gas discharge tubes are vacuum tubes with electrodes connected to very high voltages. Cathode rays are emitted from the cathode of the tube. A cathode ray consists of a beam of electrons. Since electrons are negatively charged, cathode rays will bend away from a negatively charged plate.
4. The answer is D. This question asks for a true statement from the choices. Let’s look at each of those choices. Choice A is incorrect, because neutrons and electrons do not have the same mass. Choice B claims that the mass of a neutron is less than that of an electron. That is not true either. Protons are positive and neutrons are neutral. They cannot together make the nucleus neutral. In fact, the nucleus is positively charged, not electrically neutral. So Choice C is wrong. The last choice makes perfect sense. A proton is more massive than an electron.
5. The answer is B. The actual formula of butane is C4H10. But the question is not about butane’s actual formula. The question asks for the empirical formula of butane. Empirical formula is the most simplified ratio of the actual formula. So the correct answer is C2H5.
6. The answer is C. Let’s look at the question carefully. If you did not get the right answer, carefully think about it again. The question is simply testing your understanding of a definition. The mass of a substance in one mole of it is numerically equal to its molecular weight.
7. The answer is A. Density is equal to mass per volume. Further more, the mass is equal to the product of number moles and molar mass. Equating these two equations we can get the answer. Using the letter notations given in the question, the expression of volume is given by Choice A.
8. The answer is D. The formula of sulfur dioxide is SO2. The formula weight of SO2 is 64 g/mol. This sample of SO2 contains 1.5 moles of it. If we calculate the percentage mass of the oxygen, we can see that the oxygen’s mass contribution is 50% in SO2. So regardless of the amount of SO2 present, half of its mass is due to the presence of oxygen and the other half is due to the presence of sulfur. Here we have 96 g of SO2. Now, one half of 96 g gives 48 g.
9. The answer is A. The formula of carbon tetrachloride is CCl4. The formula weight of CCl4 is 154 g/mol. The percentage composition of Cl can be calculated as follows:
![]()
10. The answer is C. In the question, the percentage compositions of nitrogen and oxygen are given. With that information, we have to find the formula of that compound. Just as discussed in our review, assume that we have 100 grams of this compound. If there are 100 grams, logically it should contain 63.6 grams of nitrogen and 36.4 grams of oxygen.
Step 1
![]()
Step 2
Divide every number of moles with the smallest number of moles calculated in Step 1. Here the smaller one is 2.275. Divide both mole numbers by 2.275. This will give you the simplest ratio between them.
![]()
Since the ratio of nitrogen to oxygen is 2:1, the compound is N2O.
11. The answer is B. Reaction 2 is a typical example of a combustion reaction.
12. The answer is C.
![]()
According to Reaction 2, two moles of ethane will react with 7 moles of oxygen to form 4 moles of carbon dioxide and 6 moles of water. In the question, it is given that 54 g of water was formed. This corresponds to 3 moles of water. From the equation, we can say that 1 mol of ethane must have reacted to form 3 moles of water. We can also say that 3.5 moles of oxygen must have reacted in the formation of 3 moles of water. The last step is the conversion of moles to grams. The corresponding quantities in grams are 30 g of ethane and 112 g of oxygen.
13. The answer is B. From the question, we can say that the empirical formula of dextrose is CH2O. The molecular weight of dextrose is also given. Let’s first calculate the weight of the empirical formula. Maybe the empirical formula represents the actual formula. The weight of the empirical formula is 30 g/mol. But the question says it is 180 g/mol. In this case, the molecular formula is not the same as the empirical formula. By dividing the actual weight by the empirical weight, we will get the coefficient with which we have to multiply the empirical formula to get the actual formula. The coefficient is 180/30 = 6. So the molecular formula is C6H12O6. Have you heard of glucose? Well, dextrose is the same thing. If you knew that, you could have picked the answer right away. But more importantly, it is the process that you have to learn from this question.
14. The answer is C. The formula of methane is CH4. The molecular weight is 16 g/mol. We have 40 g of methane. That means we have 2.5 moles of methane. So the number of hydrogen atoms can be calculated.
![]()
Chapter 2 Solutions
1. The answer is D. This question tests your understanding of the general classification of reactions. The reaction is clearly not a combustion reaction. Combustion reactions occur in the presence of oxygen and involve release of heat. There is no indication of that in the given reaction. You might be tempted to select Choice C since the given reaction is a replacement reaction, but double-replacement reaction best describes the given reaction. In the reaction, the iodine is replaced with the chlorine, and the chlorine is replaced with the iodine.
2. The answer is C. Choices A, B, and D are all acid-base reactions, which are neutralization reactions. Choice C is actually the formation of a base (AlOH3), and it is not a neutralization reaction.
3. The answer is B. Let’s start balancing the equation from the sulfate point of view. You have 3 sulfate groups in aluminum sulfate. It has to come from the sulfuric acid. So the coefficient is 3 for the sulfuric acid. Since there are 2 aluminums in aluminum sulfate, we can assign a coefficient of 2 to the aluminum hydroxide. The rest of the hydrogens and oxygens can be balanced with water.
The balanced equation should look like this:
![]()
4. The answer is B. First, we have to check whether the given reaction is balanced. Without the balanced equation, the calculations will be incorrect. As a matter of fact, the given reaction is not balanced. The balanced equation is this:
![]()
Now we can work out our magic calculations. The question specifies the grams of HCl synthesized. The 73 grams converted to moles should give 2 moles. According to the equation, 2 moles of NaCl are required to synthesize two moles of HCl. All you have to do now is to convert moles to grams. The correct value is 117 grams of NaCl.
5. The answer is D. This is a straightforward definition-type question. The ions that are present in the solution sometimes do not actually participate in the reaction. By writing the complete ionic equation of such a reaction, we can see that the spectator ions on both sides of the equation are in the same state or form. We can cancel them out and get the net equation of the reaction. Spectator ions are not usually depicted in the net ionic equation.
6. The answer is D. This is also a definition-type question. Amphoteric substances can exhibit both acidic and basic properties depending on the environment that they are subjected to.
7. The answer is D. The reaction mentioned in this question is the rusting of iron. The balanced reaction should look like this:
![]()
8. The answer is D. The question tests your understanding of the concept of mole. In Choice A, we have 32 g of O2 which corresponds to 1 mol of oxygen, and 32 g of SO2 which corresponds to half a mol. Choice A is not correct. In Choice B, we have 49 g of NO2 which corresponds to a little more than 1 mol, and 40 g of NaOH which corresponds to 1 mol. So this may be our answer. Choice C is not correct, because we have 20 g of HF which is 1 mol, and 36 g of water which is 2 moles. So Choice C is incorrect. Choice D has 60 g of C2H6 which is 2 moles, and 156 g of C6H6 is also 2 moles. So D is a better choice than B.
9. The answer is B. To answer this question, you have to use your intuition. The reaction occurs by means of the heat supplied to the aluminum hydroxide, and it is a dehydration reaction. So the most plausible answer is water.
10. The answer is D. The reactant coefficients in a balanced equation cannot be used to determine the identity of the limiting reagent. Without comparing the amounts of reactants that are actually present, we cannot determine the identity of the limiting reagent. CO being a gas has nothing to do with being the limiting reagent for the given reaction. Choice C is not logical, because it is a product. The best answer is that we cannot determine the identity of the limiting reagent, if any, without any data regarding the amount of reactants used.
11. The answer is C. Look at the items one by one. Item I says that the second student had the highest yield of products. In Experiment 1, the first student used 40.5 g of Al and 80 g of Fe2O3. This translates to 1.5 moles of Al and roughly 0.5 moles of Fe2O3. Here Fe2O3 is the limiting reagent. What was the second student doing? Well, the second student increased the amount of Fe2O3 used, keeping the same amount of Al. Since Fe2O3 is the limiting reagent, an increase of Fe2O3 will increase the product yield. So the second student must have had more yield than the first student. The first and the third students have the same yield for aluminum oxide, because the amount of limiting reagent present is the same in both cases. So items I and II are true.
12. The answer is C. By increasing the amount of aluminum used by the first student, there will not be an increase in the yield because Fe2O3 is the limiting reagent. Hence, Choice A is not correct. The same reasoning rules out Choice B. Increasing the amount of Fe2O3 by the second student will increase the yield further, because we actually have unreacted Al left according to the amounts used in the experiment. Hence, if we further increase the amount of Fe2O3 used, it will increase the yield until the Al runs out. Choice D is wrong.
13. The answer is A. In the question, we are given that 80 g of Fe2O3 is used in the reaction mixture. How much of this actually reacted is another story. That is to be found out from the yield data. The amount of CO2 produced is 22 g. Based on the balanced equation, we can infer that for every 3 moles of CO reacted, 3 moles of CO2 are produced. So CO and CO2 have a 1:1 ratio. If 22 g or 0.5 moles of CO2 is produced, 0.5 moles of CO must have reacted.
14. The answer is B. Based on the question, we can say that about 0.5 mol of Fe2O3 and 0.5 mol CO was present in the reacting mixture. Since the Fe2O3 to CO reacting ratio is 1:3, CO will completely react, and there will be some leftover unreacted Fe2O3 after the reaction is complete. So the limiting reagent is CO.
15. The answer is B. This question tests your understanding of the mole concept. Since we have excess amounts of Fe2O3, we do not have to worry about it. But, what you should consider is that the amount of CO present dictates the reaction. One mol of CO2 contains Avogadro number (6.02 x 1023) of molecules. The reaction results in 0.1 mol of CO2. So 0.1 mol of CO2 contains 6.02 x 1022 molecules.
Chapter 3 Solutions
1. The answer is A. The correct order of filling from 3s onward is 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, and 4p. For the MCAT, you must know the order of filling of subshells.
2. The answer is D. Inert gases (noble gases) have the completed outermost s and p subshells. Helium is an exception to this.
3. The answer is D. The atomic number of Kr (krypton) is 36. After the representation of Kr, how many electrons do we have? There are 14 more electrons. That adds up to an atomic number of 50. The atomic number 50 corresponds to the element Sn.
4. The correct answer is B. This is a straightforward question. The maximum number of electrons that can occupy the principal energy level is calculated using the formula 2n2.
5. The answer is C. The statement “no two electrons of an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers” is Pauli exclusion principle.
6. The answer is C. The only correct statement in the set of choices is “the 5d subshell has higher energy than the 6s subshell.” All other choices are wrong.
7. The answer is D. The question asks us to pick the species that is not isoelectronic (same number of electrons) with the noble gases. In order to solve this problem, you have to find the number of electrons present in them, and if it matches with the number of electrons in any of the noble gases, you can eliminate that choice. All the ions match with one or the other noble gas in terms of the number of electrons, except Mg+.
8. The answer is D. The nitrogen atom has a total of 7 electrons. The principal quantum number could be 1 or 2. With that alone, we cannot rule out any of the choices. The next quantum number given is the azimuthal quantum number, also known as the angular momentum quantum number. The angular momentum quantum number can have values from 0 to n — 1, where n represents the principal quantum number. Since 2 denotes the maximum n value, we cannot rule out any of the choices yet. Look at the next quantum number, which is the magnetic quantum number. The magnetic quantum number can have values from — l to +l, where l represents angular momentum quantum number. So the magnetic quantum number cannot be +2 for nitrogen.
9. The answer is A. This question tests your ability to recognize a given electronic configuration. The fastest way to approach this type of question is to look at the root element given. The atomic number of argon is 18. We can count 14 more electrons in the given configuration to get a total of 32 electrons. The atomic number 32 is that of germanium (Ge).
10. The answer is B. Osmium, silver, and radium can have the 4d subshell. Copper belongs to the 4th period and therefore cannot have a 4d subshell. All the other elements listed belong to the periods 5, 6 and 7.
Chapter 4 Solutions
1. The answer is B. Sulfur belongs to Group VIA (the representative elements). The inner transition elements are the group of elements that are in the two rows below the main section of the periodic table. The transition elements range from IB through VIIB including the collective group of elements under Group VIII (not the zero group). Choices A and B are ruled out. Sulfur is not classified as a metal. This rules out Choice D.
2. The answer is C. The Group IA metals are collectively called the alkaline metals. The Group IIA metals are the alkaline earth metals. Among the choices, only strontium belongs to this group.
3. The answer is D. Electronegativity increases from left to right along the rows. For this question let’s rephrase this trend. Electronegativity decreases from right to left along the columns, and from top to bottom.
4. The answer is B. The f block contains the inner-transition elements. The only element that is listed among the choices that is an inner-transition element is uranium.
5. The answer is C. This question can be answered on the basis of trivial knowledge. Oxygen, nitrogen, and chlorine are diatomic gases. Neon is a noble gas (zero group element) which is stable on its own.
6. The answer is D. This question tests your knowledge of a periodic trend. Here, the trend of atomic radius is asked. Along a period as the atomic number increases, the atomic radius decreases. Down a group, the atomic radius increases.
7. The answer is A. This question is similar to the previous one. It is again just a matter of comparing the size of the atoms according to the periodic trend of the atomic radius.
8. The answer is D. All the trends listed as choices are wrong. Along a period from left to right, the atomic radius decreases. So Choice A is incorrect. Along a period from left to right, the ionization energy increases. This rules out Choice B. The electronegativity of elements decreases from right to left along a period. Since Choice C contradicts this, it is incorrect.
9. The answer is D. HF is a weak acid and all the other choices are strong acids. This rules out Choice A. Among the other choices, HI is the strongest acid because it can give off the protons more easily than any of the other acids listed. The order of acidity is HI > HBr > HCl.
10. The answer is B. The given configuration is that of Group IVA (carbon family).
Chapter 5 Solutions
1. The answer is A. The central atom of the structure is sulfur. So draw the skeletal (structural) framework. In this structure, sulfur doesn’t have the octet. So the next move is to introduce a double bond.

2. The answer is D. Let us look at the choices one by one. The water molecule is a bent molecule. So there is good reason to believe that it has a net nonzero dipole moment. In HCl, the hydrogen-chlorine bond is a polar bond, and thus there is clearly a separation of charge. This means it has a dipole moment. Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon. This creates a charge separation in the CO molecule. Thus the oxygen has a partial negative charge. So CO is a good candidate, having a net nonzero dipole moment. The CH4 molecule has a tetrahedral structure and the small individual dipoles cancel out. So the net dipole of methane is zero.
3. The answer is B. The electronegativity difference between the nitrogen and the oxygen in NO2 is not enough to cause an ionic interaction. Hence, it is not an ionic bond. The correct answer is covalent bond, because the bond is formed by the sharing of electrons between the nitrogen and the oxygen.
4. The answer is A. Ammonia (NH3) and boron trifluoride (BF3) can undergo a special type of covalent bonding - coordinate covalent bond. Even though this is a covalent bond, the electrons for the bond formation are supplied by one of the partners involved in the bonding. Boron has only three electrons in its outermost shell and they are already involved in the formation of the BF3 molecule itself. There are no more electrons available from boron. But that is not the case with the nitrogen atom in NH3. Two lone electrons are available from the nitrogen in NH3 which make this bond formation possible.
5. The answer is A. To answer this question, we have to use our intuition. We do not have any specific data on any of the compounds listed as choices. But we can do an intelligent elimination. Choices B and D have the same zero dipole moment. Now it is just a matter of deciding which one of the remaining choices (A and C) is the answer. The electronegativity of fluorine is higher than that of bromine. So HF has the highest dipole moment.
6. The answer is B. BCl3 can be drawn as shown below. The geometry is trigonal planar.
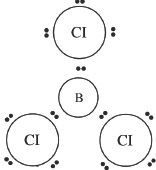
7. The answer is D. If you draw the electron-dot structure of the CCl4 molecule, you can see that there are four electron pairs around the central carbon atom. All these electrons form four carbon-chlorine bonds which make the molecular geometry - tetrahedral.
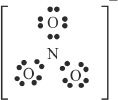
8. The answer is A. The Lewis structure of the nitrate ion is shown. By analyzing the Lewis structure, the best prediction is that the nitrate ion is trigonal planar.
9. The answer is C.
10. The answer is D. All the statements (I, II, III, and IV) are correct. Let’s see why this is the case. All the individual bonds in both compounds are dipoles. This makes items I and II correct. The question says that both molecules are tetrahedral. Hence, these individual bond dipoles cancel out to give a net zero dipole.
11. The answer is C. An ionic bond is formed mainly when there is a noticeable electronegativity difference between the atoms. Usually ionic bonds have the highest electronegativity difference. Choice A is incorrect. Covalently bonded atoms have lesser electronegativity difference. Among Choices B and C, nonpolar covalent bonds obviously have the least electronegativity difference. So our answer is C. Choice D is not true in this case. We do not need any more data to predict this general trend.
12. The answer is C. For Compound A, we should compare the atoms involved in the bond in question. Chlorine is more electronegative than boron. This rules out Choices B and D. For Compound B, the bond dipole should be directed toward the carbon atom. This rules out Choices A and D. So the only choice which has not been ruled out is C.
13. The answer is D. This question is a bit tricky. Many students will quickly select angular as the answer. But you have to be careful. The question is not asking for the molecular geometry of water. It is actually asking for the electronic orientation or electronic geometry of water which is tetrahedral. The four electron pairs (two bonded pairs and two lone pairs) of the water molecule result in a tetrahedral geometry. Moreover, Choices A and B are essentially the same. If one is not correct, the other cannot be correct either.
Chapter 6 Solutions
1. The answer is C. First, we should write the balanced equation. Without the balanced equation there is a good chance we might choose the incorrect answer.
![]()
According to the balanced equation, 2 liters of NO react with 1 liter of O2 to give 2 liters of NO2. According to the question, 4 liters of NO2 were formed. By taking proportionality, we can say that 4 liters of NO and 2 liters of O2 must have reacted so far.
2. The answer is B. Density is mass per unit volume. Since we know the density and the volume, we can find the weight of the gas. Since this represents 1 mol of the gas, that itself is its molecular weight.
![]()
3. The answer is C. One mol of an ideal gas occupies 22.5 L at STP. From the density-volume-mass relationship, we can find the mass of 1 mol of this gas. We know both the density and the volume of the gas.
![]()
This molecular weight is closest to that of oxygen.
4. The answer is B. The objective of this question is to convert the given pressure value (in mmHg) to Pascal units. In order to do this, we should first convert the given value into atmospheres. Since one atm equals 760 mmHg, 1330 mmHg equals 1.75 atm. The conversion of atmospheres to Pascal units is given in the question. The conversion is:
5. The answer is B. This is a simple conversion problem that every MCAT student should know and do without any reference. This conversion should come automatically
![]()
6. The answer is A. The given quantity of CO2 corresponds to 0.26 mol. This quantity of CO2 will occupy 0.26 x 22.5 ≈ 5.9 L. If you still don’t understand this type of calculation, review the chapter again.
7. The answer is B. Gases best behave the most ideally under conditions such as high temperature and low pressure. Choice D is wrong. The passage makes the behavior of gases very clear: They depend on the prevailing temperature and pressure.
8. The answer is C. By rearranging the ideal gas equation, we can find the correct unit of the gas constant.
9. The answer is A. The question is asking for effusion rates of SO2 and O2. The rate of effusion of a molecule is inversely proportional to the square root of its molecular weight. The problem should be solved as follows:
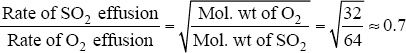
10. The answer is A. A value of zero alone will not ensure ideal behavior. So gas A does not behave ideally. Hence item I is correct. Item II contradicts what we just said. We cannot say whether gas A is xenon. So item III is not a valid statement.
11. The answer is D. The clues to answer this question have to be taken from the given data. What can we infer from the data given about halogens? The correction factor of fluorine is 1.170 L2.atm/mol2. The correction factor of chlorine is 6.340 L2.atm/mol2. By analyzing the trend, we can deduce that bromine must have a correction factor that is higher than that of chlorine. The only value that is higher than that of chlorine is 9.80 L2.atm/mol2. Hence, the best choice is D. If you were looking at the values of b, you probably did not notice the units represented in the answers. All units correspond to that of constant a and not of b.
12. The answer is D.
13. The answer is D. According to the kinetic-molecular theory, all the items are true.
Chapter 7 Solutions
1. The answer is D. The conversion of a gas to a solid is called deposition. Sublimation is the conversion of a solid to a gas. Condensation is the conversion of a gas to a liquid. Freezing is the conversion of a liquid to a solid.
2. The answer is B. Vaporization, sublimation, and melting require heat (consume heat). The only process listed which releases heat is condensation.
3. The answer is D. Potassium fluoride is an ionic compound. See the chapter for descriptions of all types of solids.
4. The answer is C. In order to answer this question we have to think in terms of ionic bonding. What enables the formation of an ionic bond in the first place? The electronegativity differences between the bonded atoms make ionic bonds possible. It is in fact the electrostatic forces that hold the atoms involved in an ionic bond.
5. The answer is B. To answer this question, we need to recall some basic aspects regarding phase diagrams. Just by knowing those, we can eliminate some of the choices right away. In Choices A and D, the phases are wrongly labeled. The phases are correctly labeled only in Choices B and C. This rules out Choices A and D. Water has some anomalous properties. Such properties make water unique. In fact, the solid-liquid segment in the phase diagram of water has a negative slope.
6. The answer is B. See the explanation for Question 5.
7. The answer is B. The question describes a phase change scenario based on the diagram given in the passage. Substance M will be a liquid at point A. If the pressure is decreased, the most likely phase change will be from liquid (the phase before the change) to gas.
8. The answer is C. This is a definition-type question. The point indicated by the X mark is called “triple point.” At the triple point of a substance, the three phases coexist at equilibrium. Below this point, the solid to gas conversion or vice versa is direct without the intermediate liquid phase.
9. The answer is C. The critical temperature is defined to be the temperature above which a gas cannot be changed into a liquid. The choice that best reflects this idea is C.
10. The answer is A. In the phase diagram given in the passage, locate the segment XZ. This segment separates the liquid and the gas phases.
Chapter 8 Solutions
1. The answer is C. Normality of a solution is the number of equivalents of solute per liter of solution.
2. The answer is A.
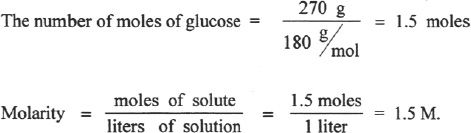
3. The answer is D. First, we should calculate the molar mass of HCl which is 36.5 g/mol. We have a 2.5 molar solution of HCl. That means every liter of the solution will have 2.5 moles of HCl. Here we have 1.25 L of the solution, and a total of 3.125 moles of HCl. That comes closest to 3.125 x 36.5 = 114 g.
4. The answer is B. We can equate the diluted solution with the stock solution as follows: (Molarity of solution made x Volume of solution made) is equal to (Molarity of the stock solution x Volume of the stock solution required). With this in mind, let’s plug in the values that we know.
2 M x 30 ml = 10 M x Volume of the stock solution required
We need not convert the milliliters into liters for this problem, because the molar units will cancel out.
![]()
5. The answer is C. The quickest way to solve this problem is to calculate how many moles of NaCl are present in this solution. Then convert the number of moles to grams of NaCl. The correct answer is 5.1 g.
6. The answer is D. All the solubilities shown in the graph are endothermic. In fact most compounds (solids) dissolve endothermically. The graph shows that as the temperature increases, the solubility of the salts increases. In other words, as the temperature increases, more and more of the salt present is dissociated into ions. This is exactly how an endothermic process works.
7. The answer is D. The first step in answering this question is to find the molality of the solution. Then plug that number into the boiling-point-change equation given in the passage.
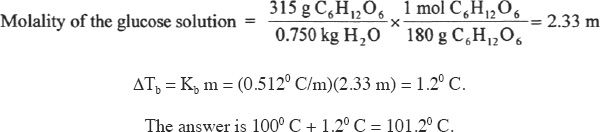
8. The answer is B. The observed changes in colligative properties are less than what was theoretically predicted. This is because the ionization of salts in water is not as complete as we expect. Some of the oppositely charged ions stick together and function as a unit. So the number of particles (units) is lower than what we expect. As the concentration increases, the possibility of the oppositely charged ions sticking together is greater than that in dilute solutions.
9. The answer is D. This question is a bit tricky. You may have selected Choice A. But you have to understand what exactly is asked in the question. The question is not asking about the change in boiling point (ΔT). Instead, it asks what happens to the boiling point. It will not double; it will only increase slightly.
10. The answer is C. Choice C is the only true statement given. Looking closely at Choices A and B, you should realize that they represent the same relationship. Since you cannot have two correct answers, this rules out Choices A and B. Thus, such logical elimination-techniques can be used to solve many MCAT problems and save valuable time.
Chapter 9 Solutions
1. The answer is B. This question tests your understanding of the concept of pH. You also have to use some mathematical skill to answer this question, since you are not allowed to use a calculator.
![]()
To get the hydrogen ion (hydronium or H3O+) concentration, we have to take the antilog. If the pH were 2, the molar concentration would have been 10—2. If the pH were 3, the molar concentration would have been 10—3. Since the pH is 2.5, the best choice is 3.2 x 10—3.
2. The answer is C. NaCl is a salt. Think about its source. NaCl is a salt of sodium hydroxide and hydrogen chloride. NaOH is a strong base and HCl is a strong acid. A salt solution of a strong acid and a strong base is neutral.
3. The answer is D. An acid which can furnish more than one proton per molecule of the acid is called a “polyprotic acid.” Choices A, B and C are all polyprotic acids. So the reasonable choice is ’one of the above.’ Note that the question asked for an acid which is not a polyprotic acid. You should make a habit of underlining or circling key words in the question, especially when the question stem contains words such as “not, except, increasing, decreasing.”
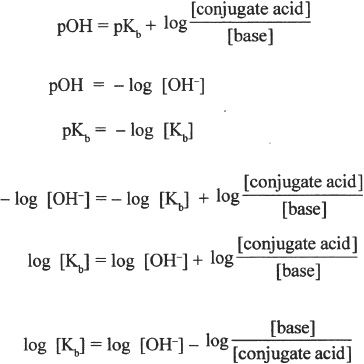
4. The answer is C. To answer this question, you have to manipulate the given equation.
The given equation is:
5. The answer is C.
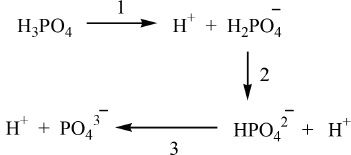
The choices are phosphoric acid and its dissociation products (see above). In a polyprotic acid, such as H3PO4, almost invariably the first dissociation will be of the highest degree. So the highest pKa is for HPO42—. This is Choice C. For a comparison, the Ka values are given below. But as you know, we do not need them to answer this question.
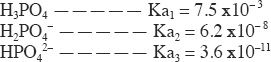
6. The answer is A. The question asks for the net ionic equation of the given acid-base equation. The given reaction is a strong acid-strong base reaction.
7. The answer is A. For this question, we are looking for a strong acid-strong base curve. Why? Well, the answer is simple. In Reaction 1, we have a strong monoprotic acid (HClO4) reacting against a strong base (NaOH). The only curve that satisfies this criterion is given in Choice A.
8. The answer is D. In this question, we are asked to analyze the upper and lower limit ratios of base-to-acid at the best buffering pH. How can we answer this question? Well, there are some clues in the passage. According to the passage, the effective pH range of a buffer system is between pKa — 1 and pKa + 1. What other relevant information do we have in the passage? The passage also gives us an equation with which we can relate the pH and the pKa.
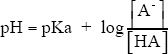
In order to have a pH value of pKa — 1, the second half of the equation with the log should be negative 1. For this the base-acid ratio should be 0.1; log 0.1 = —1. For the other criterion pKa + 1, the log value should be +1. For this, the ratio should be 10.
9. The answer is B. This is a straight forward question. The question asks for the pH of a solution of HCl. HCl is a strong acid, and strong acids completely ionize. So we don’t have to worry about partial ionization such as in weak acids.
![]()
10. The answer is B. This is actually one way of defining pKa value. At the pKa value, the acid-base ratio is 1. So the best answer is Choice B. In addition, it is near the pKa value that the solution will have its best buffering capacity. So Choice D wrong.
Chapter 10 Solutions
1. The answer is A. “Bomb calorimeter” is a device used to determine the energy changes that are associated with reactions by measuring the amount of heat generated or absorbed by a reaction at constant volume. The changes (measurements) are made at constant temperature and constant volume. There is nothing true about Choice B. Keeping the volume constant is not an impossible task! This rules out Choice B. Choice C is wrong, since there is no change in volume, and theoretically there is no work done.
2. The answer is B. The figure shows the conversion of ice (s) to water (l). The process is melting. What happens when a solid is converted to its liquid form? There will be an increase in randomness. This rules out Choice D. Choice C doesn’t make any sense. Since the randomness is increased, the entropy is increased.
3. The answer is C. The change in free energy (ΔG) is related to enthalpy and entropy by the following equation:
![]()
In this question, the change in free energy is zero. This means that there is no net transfer of free energy. This in turn means that the forward and backward reactions are both favorable and thus the reacting system is in equilibrium.
4. The answer is D. This question tests your knowledge and ability to make reasonable judgments based on a limited amount of information. We are given only an equation and a description of that equation. Without further data on this reaction, we cannot be sure whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic. We cannot say whether the reaction is spontaneous or nonspontaneous without pertinent data. Choice C is untrue.
5. The answer is C. According to the third law of thermodynamics, the entropy of a pure, crystalline substance at 0 K is zero.
Chapter 11 Solutions
1. The answer is D. The equilibrium constant is the equilibrium molar concentrations of the products raised to their corresponding coefficients, divided by concentrations of the reactants raised to their corresponding coefficients. The coefficients can be taken directly from the balanced equation of the reaction.
![]()
The equilibrium expression is:
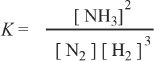
2. The answer is C. From the given equation, we can write the general form of the rate as:
![]()
Our next step is to find m and n using the given information. Examining the first and the second experiments shows that the concentration of X is kept constant, but the concentration of Y is doubled. When the concentration of Y is doubled, the rate also is doubled. So the order (n) with respect to Y is 1. Now compare experiments 2 and 3. In experiments 2 and 3, the concentration of Y is kept constant, but the concentration of X is doubled. This time, the rate is quadrupled. Hence, the order (m) with respect to X should be 2. So the correct expression is Rate = k [ X ]2 [ Y ].
3. The answer is D. This question tests your basic understanding of the factors that affect the rate of reactions. All the listed factors can influence the rate of reactions.
4. The answer is D. This is the potential energy diagram of a reaction. For the MCAT, you should be familiar with diagrams of this type. Since the direction of the reaction-coordinate is indicated in the diagram, we can predict the potential energy level of the reactants and the products. The bump in the graph represents the activation energy of the reaction. So Choice A doesn’t make any sense. According to Choice B, there is a net absorption of energy. But in contrast to this statement, there is a net release of energy. This prediction is based on the fact that the energy level of the products is below that of the reactants. This makes Choice C wrong. That leaves us with Choice D. In fact the diagram is that of an exothermic reaction.
5. The answer is A. Catalysts can change the rate of reactions, by decreasing the activation energy. Catalysts are not consumed by the reactants. If a substance is consumed in the process, it cannot be a catalyst.
6. The answer is B. According to the question, the reverse reaction of Reaction 1 is endothermic. This means the forward reaction is exothermic. For exothermic reactions, the ΔH is negative.
7. The answer is C. In the experiment, the hydrogen is removed. Such a change in concentration will upset the equilibrium. We have to approach this problem in terms of LeChatelier’s principle. Changes in the concentrations of reactants or products of this reaction will turn the system into a non-equilibrium state. The result will be an adjustment of the reaction mode to restore the system to equilibrium. So if we take H2 away, the backward reaction will be favored for restoring the equilibrium.
8. The answer is C. The pressure is decreased in the system. Such a decrease in pressure will not change the reaction mode. Let’s take a look at the reacting system.
![]()
Both sides of the equation have equal number of moles - two on the reactant side and two on the product side. So the pressure change will not affect the reaction in this case.
9. The answer is C.
![]()
In Reaction 2, a pressure change will affect the reaction. Here, the pressure is increased and that will increase the forward reaction. In other words, the reaction shifts to the right. Item I does says that the reaction shifts to the right. But for the wrong reason. According to the equation, we have more moles on the reactant side. So item I is not fully correct. Item II is also ruled out because the reaction shifts to the right. Item III makes perfect sense.
10. The answer is D.
11. The answer is B. There are 2.5 moles (70 g) of nitrogen. The amount of H2 used should also be taken into account. According to the question, 10 g of hydrogen was used, which is equivalent to 5 moles. So the hydrogen acts as the limiting reagent. By the reaction of 5 moles of hydrogen with excess of nitrogen, the number of moles of ammonia produced should equal 10/3 moles. Now, it is a matter of converting moles to grams.
![]()
12. The answer is B. Entropy is a thermodynamic quantity which measures the randomness in a system. An increase in randomness means an increase in the entropy. In general, gas phase has a higher entropy than liquid phase, and liquid phase has a higher entropy than solid phase. But in this reaction, all the components are in their gas phases, and the reactant side has more of them. The production of ammonia causes the entropy to decrease because there is less randomness than before the reaction began.
13. The answer is D. We cannot predict the spontaneity of the reaction accurately based on the information given in the passage. The only fact that we know regarding the reaction is that it has a ΔH value of —92 kJ. Based on that alone, it is not possible to predict the spontaneity accurately.
Chapter 12 Solutions
1. The answer is C. A redox equation is represented in the question. The electrode potential of the reaction is also given. The question also says that the reaction occurred spontaneously. For the given direction of the reaction, the electrode potential is negative. So the reaction must have taken place in the opposite direction of what is given in the question and thus had a positive potential. A net positive potential means a negative free energy change. A negative free energy change denotes spontaneity. We can rewrite the equation:
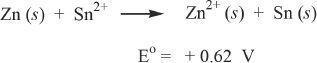
Now we have a positive voltage, where the zinc is oxidized and a tin ion is reduced. Oxidation of zinc means it is losing electrons. Recall that oxidation is losing electrons, and reduction is gaining electrons.
2. The answer is B. The voltage (standard potential) represents the electromotive force, which has nothing to do with the coefficients of the equation. In fact, the two reactions are same. One equation is the simplified version of the other. So the standard potential will remain the same.
3. The answer is C. Based on the given information in the question, we can say that E° is directly related to K. The question also says that the product concentrations are greater than the reactant concentrations. So we can say that the equilibrium constant value is greater than 1. We can rule out Choice A, because there is no such thing as a negative concentration. So K cannot be negative anyway. Since we know that K is greater than 1, the natural logarithm of K will be positive. So from the equation, we can say that E° cannot be negative, which rules out Choice B. Hence, the E° value should be positive. Since we have a positive E° value, the reaction is most likely to be spontaneous. Keep in mind the conditions at which the reaction occurs - standard state (1 atm, 25 °C).
4. The answer is C. Ampere is defined as the total amount of charge that flows per second.
![]()
The charge in coulombs = 5 A x 3.5 min. x 60 s/ 1 min. = 1050 coulombs.
5. The answer is B. For a reaction to be spontaneous, the electrode potential should be positive. Oxidation of copper has a negative electrode potential. That rules out Choice A. Oxidation of fluoride ion and reduction of zinc ion have negative electrode potentials, which rules out Choices C and D respectively. The reduction of chlorine represented below has a positive potential which indicates spontaneity.
![]()
6. The answer is D. The two half-reactions can be written as shown below:
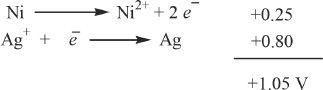
Now, it is just a matter of adding the individual potentials to get the overall potential. A word of caution: when you add the individual half-electrode potentials, make sure that the appropriate sign has been assigned to them.
7. The answer is D. Even though a salt bridge allows an electrical connection between the two half-cells in a galvanic cell, the function of a salt bridge is not to conduct electricity. So Choice A is ruled out. Choice B makes no sense. The salt bridge does not control the voltage. The function of a salt bridge is to maintain electrical neutrality in the half-cells so that excess buildup of charge will not occur in the half-cells. If excess charge builds up in the half-cells, the reaction will slow down and quickly die out.
8. The answer is C. The question asks for the best oxidizing agent. An oxidizing agent gets reduced in the process. So the oxidizing agent (species) should be able to accept electrons with ease. The most positive reduction potential is that of chlorine (Cl2), which makes chlorine the best oxidizing agent among the choices.
![]()
9. The answer is B. The question asks for the species that has the highest oxidation potential. Oxidation is losing electrons. Thus all the half reactions should be considered in the oxidation sense. Since the table gives you reduction half-reactions, you have to reverse all the equations, and when you reverse the equations the sign of the potentials should also be reversed. The most positive value is that of the oxidation of potassium.
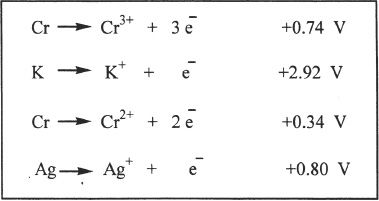
10. The answer is B. The process described in the question is Fe changing to Fe2+, which is oxidation. Oxidation occurs at the anode and reduction occurs at the cathode.
Chapter 13 Solutions
1. The answer is B. We are asked to evaluate the radioactive change. The equation should look like this:
![]()
Notice that the atomic and mass numbers decreased by 2 and 4 units, respectively. The helium nucleus shown in the equation is an alpha particle.
2. The answer is C. In the given radioactive decay, sodium is converted to neon. Notice that the atomic number decreased by one, but the mass number remained the same. The most likely particle that is emitted is a positron. A positron is a positively charged electron. The equation is shown below:
![]()
A gamma particle is also emitted, but that information is not needed to answer this question.
3. The answer is A. This question tests your knowledge of common radioactive emissions. The only emission listed that is a high-energy electromagnetic radiation is the gamma ray. Electromagnetic rays travel at the speed of light. The only emission that travels close to the speed of light are beta particles. But the best choice is gamma ray. So the answer is A. In addition to the greater speed, gamma rays have the highest penetrating power.
4. The answer is C. See the explanation for Question 3.
5. The answer is D. This question tests your knowledge of the concept of half-life. Half-life is defined as the amount of time for a radioactive substance to decay to half its initial quantity. Since the half-life of substance X is 12 years, it takes twelve years for substance X to decay to half its initial quantity. We have 9 grams of substance X present. The amount of substance X that was originally present is 150 grams. So it must have undergone radioactive decay for at least four half-lives. Write the decay mode, starting from the original amount present.
![]()
Each arrow indicates one half-life, for a total of four half-lives. Since one half-life is 12 years, the total time elapsed is 12 x 4 = 48 years. The exact answer is a little above 48 years. But the approximation is correct since the choices are far apart and no values higher than 48 are given.
6. The answer is D. Half-life is the amount of time required for a radioactive substance to disintegrate to half its initial quantity. The sample described in the question has disintegrated to 3% of its original quantity. The disintegration can be analyzed as follows:
![]()
This means, at least 5 half-lives must have elapsed.
7. The answer is A. A beta particle is an electron. By the emission of a β-particle, the nucleus must have changed into protactinium (Pa) which has atomic number 91. Remember that a β emission decreases the atomic number by one.
8. The answer is C. Since alpha particles are positively charged and beta particles are negatively charged, Choices A and B are true. Gamma rays are not deflected because they have no charge. Choice D is also true.
9. The answer is B. According to the figure given in the passage, as the number of protons increases the neutron-proton ratio increases and becomes greater than or equal to one. (Clue: Look at the slope)
10. The answer is D. The mass loss can be equated with the binding energy. In essence, mass loss can be calculated using the equation E = mc2.
Energy = (3.1 x 10—5 kg)(3 x 108 m/s)2 = 2.8 x 1012 kg. m/s2 = 2.8 x 1012 J.
11. The answer is D.
![]()
The question tests your ability to evaluate radioactive emissions by analyzing a given radioactive emission reaction. Notice that the atomic number decreased by 2 and the mass number decreased by 8. If two alpha particles were emitted, that would decrease the mass number to 224, because an alpha particle is a helium nucleus
![]()
It would also decrease the atomic number by 4. But apparently that is not the case here. The atomic number decrease by only 2. This can be accounted for if two β-particles were also emitted.
Chapter 14 Solutions
1. The answer is B. The carbon indicated by the arrow is an sp2 hybridized carbon atom. Notice that the indicated carbon has a double bond and two single bonds. The double bond connects this carbon to the end-carbon. A hydrogen atom and the 3rd carbon are attached to this carbon via single bonds.
2. The answer is A. Acetylene is the first member of the alkyne group. The carbon-carbon bond is a triple bond which contains only one sigma bond.
3. The answer is B. The triple bond of 2-propyne (an alkyne) contains one sigma bond and two pi bonds.
4. The answer is C. The sp3 hybrid orbitals such as those seen in alkanes have a tetrahedral orientation.
5. The answer is D. This question also tests your basic knowledge of hybridization in carbon compounds. A triple bond means three bonds. Since there are three bonds, six electrons are involved in the bond.
6. The answer is B. Methane has a tetrahedral geometry. So the hydrogen-carbon-hydrogen bond angle is closest to 109.5°.
7. The answer is C. The triple bond is the shortest among the bonds indicated by the arrows. The only triple bond-bearing compound given is Choice C.
8. The answer is B. The carbon-hydrogen bond is a single covalent bond.
Chapter 15 Solutions
1. The answer is B.
To answer this question, we can use the following clues from the question:
i) The compound is composed of only carbon and hydrogen atoms.
ii) It is a saturated hydrocarbon.
iii) It does not have a ring structure.
So the compound is an alkane. Alkanes have the general formula CnH2n+2. Now this becomes a simple algebra problem. Since there are 14 hydrogens, 2n+2 = 14.
![]()
2. The answer is A.
3. The answer is D. Constitution isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula, but differ in the order with which the atoms are bonded. This definition matches the relationship between n-butane and isobutane.
4. The answer is C. First, we have to number the carbon chain to get the longest possible chain in the structure. The numbering should be done in such a way that the branches will have the smallest substituent number. The numbering is done as follows:
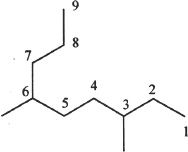
There are 9 carbons in the parent chain. So the parent chain is clear and the complete name ends with “nonane.” This rules out Choices A and B. There are 2 methyl groups on carbons 3 and 6. So the compound is 3,6-dimethyl nonane.
5. The answer is C. Butane contains 4 carbon atoms and if one mole of butane is completely combusted, at least 4 moles of carbon dioxide will be formed provided that there is enough oxygen.
6. The answer is B. A secondary carbon atom should be attached to two other carbon atoms. The carbon atoms indicated by arrows I and III are secondary carbon atoms.
7. The answer is A. A carbonium ion is the same as a carbocation. A carbocation is a positively charged species.
8. The answer is C. Gauche conformation is a form of staggered conformation. The conformation is Gauche if the relative separation of two substituents on adjacent atoms is 60°. The Newman representation of a Gauche conformation is shown:
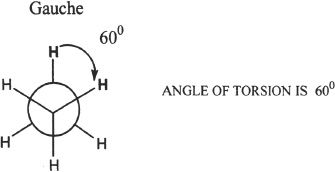
9. The answer is B. The angle closest to 109.5° is 110°. That is the most likely bond angle, having the least angle strain.
10. The answer is A. All the given choices are alkanes. Item I is an unbranched alkane. Items II, III, IV have increasing degrees of branching. Branching decreases the area of contact and thereby decreases the intermolecular interactions. So the unbranched alkane has the highest boiling point. Keep in mind that without actually measuring the properties, we can only compare compounds of comparable weights and number of carbons with reasonable accuracy.
11. The answer is D. The question asks for the type of force that is important with respect to alkanes. Alkanes cannot undergo hydrogen bonding. So Choice A is out. Choice B is generally not important in alkanes. Since there are no ionic bonds in an alkane, Choice C is wrong. The correct choice is Van der Waals forces.
12. The answer is D. To answer this question you have to do some intuitive thinking based on the information given in the passage. Butane is a four-carbon alkane with the formula C4H10. It is a bigger molecule than propane, but a smaller molecule than pentane. So the boiling point of butane should be between propane and pentane. We are talking in terms of the relative boiling points. But the question asks for the melting point. So let’s translate this idea in terms of melting point. Obviously, the melting point of a substance should be below its boiling point. So the answer cannot be either 37.5°C or 55.1°C. This rules out Choices A and B. Choice C is not a sensible answer because butane is a gas at 25°C.
13. The answer is C. Choice A is an initiation step. Choice B is a chain termination step. Choice D is also a chain termination step. The only choice which represents a chain propagation step is Choice C.
14. The answer is A. This question tests your knowledge of intermolecular forces and other interactions that give rise to some of the chemical and physical properties of compounds. Let’s take a look at the compound 2,3-dimethylbutane. We do not have a clue about the precise properties of the compound asked in this question. But what we do know is the boiling point of one of its relatives. In the table given in the passage, we are told that the boiling point of 3-methylpentane is 63.3° C. If we compare these two compounds, we see that they have the same number of carbons and hydrogens — both are six-carbon alkanes. If the boiling point of 3-methylpentane is 63.3° C, then 2,3-dimethylbutane will have a boiling point lower than that. The only choice with a lower value is Choice A.
15. The answer is C. The only way to answer this question is to draw the possible isomers by trial and error. There is no choice other than drawing out the possible structures, starting from the straight chain form of heptane.
Chapter 16 Solutions
1. The answer is B. Acid-catalyzed dehydration of the alcohol shown will result in a mixture of alkenes. All the given choices are alkenes. But Choice B is different, because it has 8 carbons. The parent alcohol has only 7 carbons. So Choice B is not possible as one of the products. All the other compounds given are possible products because of the rearrangement involved in this type of reaction.
2. The answer is C. The question asks for the number of double bonds present in the unsaturated alkene that undergoes complete hydrogenation. Each double bond to be converted to a saturated bond requires 2 hydrogen atoms. If 8 moles of hydrogen (hydrogen is diatomic) is used per mole of the compound, the compound should have 8 double bonds.
3. The answer is D. Ozonolysis is a two-step reaction sequence in which carbonyl groups are generated. The double bonded carbon atoms become the carbon of the carbonyl groups that are created.
4. The answer is B. In this reaction, 2-butene is reacted with peroxyacetic acid. This reagent converts the alkene into an epoxide, which is a compound that has a three-sided ring with an oxygen atom in the ring.
5. The answer is C. This reaction (hydroboration-oxidation) involves the conversion of 1-butene into an alcohol by hydration. The hydration follows anti-Markovnikov’s rule. There is no rearrangement in this reaction.
![]()
6. The answer is A. The heat of hydrogenation decreases as there are more and more substituents in the alkene group. Among the choices, the least amount of substitution is for ethylene.
7. The answer is A. The reaction between 1-propene and HBr in the presence of peroxides results in the addition of HBr into the alkene group. The addition follows anti-Markovnikov’s rule. The reaction is shown below:
![]()
8. The answer is B.
9. The answer is C. Since acid-catalyzed dehydration sequence may involve rearrangement depending on the alcohol involved, Choice A is wrong. Choice B is only partially correct. Even though it is true that there can be rearrangement, the process of rearrangement results in more stable intermediates rather than less stable intermediates. The major product is the most substituted product, because the most substituted product translates to higher stability.
10. The answer is B. Rearrangement is possible in acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols. The intermediate is a carbocation, not a carbanion. This eliminates statements I and III. Depending on the type of alcohol, the rearrangement may involve either methyl shift or hydride shift.
11. The answer is D. All the compounds listed in the choices can be synthesized by the oxidation of alkenes.
12. The answer is B.
13. The answer is B.
14. The answer is D.
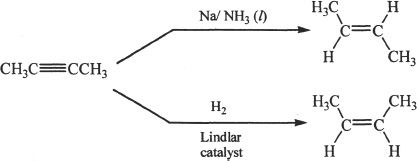
These two products are cis-trans isomers and are commonly called geometric isomers.
15. The answer is B.
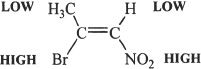
The given structure has Z-configuration. Recall that the priorities are based on the atomic number of the atom bonded to the double bonded carbon.
Chapter 17 Solutions
1. The answer is B. The shortest bond here is the triple bond.
2. The answer is B.

Compare the carbon-carbon bonds that distinguish these compounds. cis-2-Butene is an alkene which has a carbon-carbon double bond. 1-Butyne is an alkyne and has a carbon-carbon triple bond and butane has carbon-carbon single bonds. The triple bonded carbon-carbon bonds have the highest bond dissociation energy. Bottle B contains 1-propyne.
3. The answer is C. Of the given choices, acetylene is the most acidic and has the lowest pKa value.
4. The answer is B. Lindlar catalyst is a combination catalyst which does selective or restrictive hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes. Furthermore, the product is a cis-alkene.
5. The answer is C. When 1-butyne is treated with sulfuric acid in the presence of mercuric oxide as catalyst, hydration occurs. The hydration follows Markovnikov’s rule and forms a ketone. The reaction is given below:
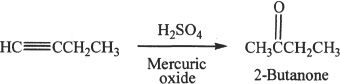
6. The answer is D. When 3-hexyne undergoes ozonolysis, propanoic acid is formed.
![]()
7. The answer is B.
The general structure of a vicinal dihalide:
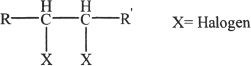
The double dehydrohalogenation (two dehydrohalogenations or eliminations) of vicinal dihalide results in an alkyne.
8. The answer is D. There is nothing there to dehydrate or dehydrohalogenate in an alkyne. This eliminates Choices A and B. Hydrolysis will not help the direct conversion of an alkyne to alkane. A simple hydrogenation is the best way to accomplish this conversion.
9. The answer is A. The liquid ammonia-sodium combination can be used to convert an alkyne to a trans-alkene. In essence, this reaction involves the restrictive hydrogenation of an alkyne to an alkene (trans-product).
10. The answer is D. Alkynes have higher boiling points than corresponding alkanes. So Choice A is true. Alkynes have sp hybridized carbons. So Choice B is true. Choice C is also true, since a terminal alkyne like acetylene can form acetylide ions when exposed to strong bases.
![]()
11. The answer is C. Alkynes are characterized by hybrid orbitals called sp orbitals. In the sp orbitals, there is 50% s character and 50% p character.
12. The answer is B.
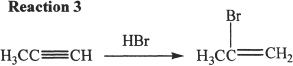
Alkynes, just like alkenes, can undergo addition reactions. Reaction 2 is a typical example of an addition reaction.
13. The answer is D.
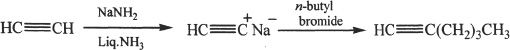
14. The answer is C. Oxidizing agents oxidize other compounds; they do not reduce! This rules out Choice D. Choice B does not make any sense either. The alkyne is not being reduced to an alkane, but is being reduced to an alkene. This is not the most reduced form. Choice A is incorrect. The function of quinoline is to moderate the activity of the catalyst so that the double bonded alkenes that are formed will not undergo further reduction to form alkanes. Moreover, quinoline is not the actual catalyst.
15. The answer is D. According to the passage, quinoline is a heterocyclic amine.
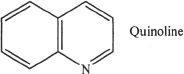
16. The answer is D. The product of this catalytic conversion reaction is a trans-alkene. The combination of reagents (group I metal with liquid ammonia) used is unique in the sense that the product formed is a trans-product. The intermediate involved in this reaction, called the alkenyl radical, readily forms the resulting trans-product.
Chapter 18 Solutions
1. The answer is B. Dimethylated benzenes are called xylenes.
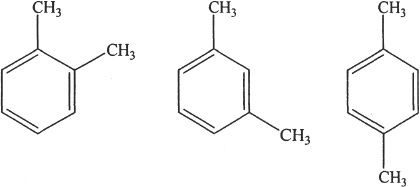
2. The answer is B.
The carbons in the benzene ring are sp2 hybridized.
3. The answer is C. See explanation for Question 1.
4. The answer is B. For a compound to be aromatic, it should have 4n+2 number of pi electrons. So the numbers satisfying the 4n+2 condition are 2, 6, 10, 14, …. Four is not in this series and that is the answer.
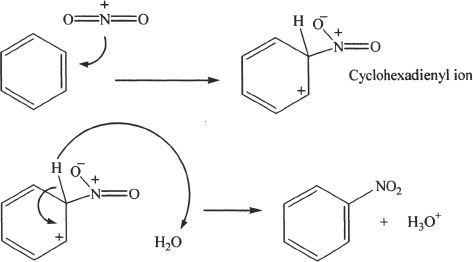
5. The answer is A. This reaction is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The product formed is nitrobenzene. In the reaction, nitronium ion acts as the electrophile which attacks the benzene to form the cyclohexadienyl intermediate, followed by the elimination of the proton to form nitrobenzene. The reaction mechanism follows:
6. The answer is D. This reaction is best described as a Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction.
7. The answer is A. This reaction is commonly called the Clemmenson reaction.
8. The answer is D. The nitro group (-NO2) is a strongly electron withdrawing group, and thus a meta deactivating group. So it favors meta substitutions the most.
9. The answer is C. The regioselectivity of halogens favor ortho/para positions. Halogens are electron withdrawing entities that are ortho/para directing and also deactivating groups.
10. The answer is B. The -CHO group present in the ring is best described as a meta-directing group. So the most likely position of substitution is the meta position.
11. The answer is D. This reaction is a Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction. This rules out Choice A. In an alkylation reaction, there is a possibility of rearrangement. The primary alkyl halide (n-propyl chloride) can form secondary carbocations by rearrangement. To avoid this type of rearrangement, chemists often use Friedel-Crafts acylation reactions which do not involve rearrangement. The carbonyl group in the acylation product can be easily reduced to get the desired hydrocarbon.
12. The answer is A. An alkoxy group can be represented as -OR, where R stands for an alkyl group. It is an ortho/para-directing group and also a good activating group.
13. The answer is C. The substituent -OH is an ortho/para activator. The resulting product is a bromine substitution product. The only choice that fits the reasoning is C.
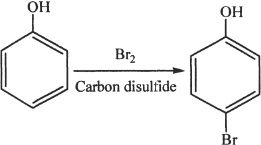
14. The answer is A. The reaction shown is neither an addition reaction, nor an elimination reaction. So the Choices B, C, and D can be ruled out. This is a typical electrophilic substitution reaction.
15. The answer is C. The inscribed circle stands for the pi-system of electrons present in the benzene ring. Let’s be more precise: The circle represents the 6 pi electrons of the benzene ring. Choice D states “8 pi-electrons” which is wrong.
16. The answer is D. To answer this question, we have to think about the substituent; the nitro group. The nitro group is a meta deactivating group. So the substitution predominantly results in a meta-product (1,3 substituted). According to the passage, compound C is the major product.
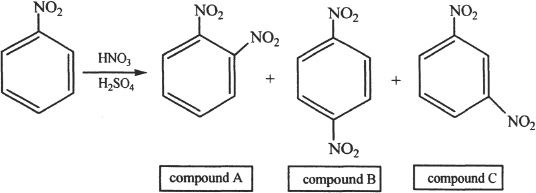
Chapter 19 Solutions
1. The answer is B. Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images. These compounds are enantiomers.
2. The answer is A. The two compounds are stereoisomers. To be precise, they are diastereomers. Diastereomers are not mirror images. Hence, the two compounds given are not mirror images.
3. The answer is D. Since the enantiomer is what is asked for, the answer can be ascertained by visualizing the mirror image.
4. The answer is C. The given representation is called Fischer projection. The Fischer projection is a 2-dimensional way of representing structures. To manipulate the Fischer projection, we should think in terms of 3-D. This can be done by interchanging two pairs of substituents at a time. If only one pair is interchanged, we will not get the equivalent structure. Let’s say we interchanged only one pair. This will result in its enantiomer. Such an example is Choice C which is the only non-equivalent structure.
5. The answer is D. The given structure is an ethane derivative, not a methane derivative. This rules out Choices A and B. In the Fischer projection, the horizontal lines represent the bonds extending out of the plane of the paper toward you. The vertical lines represent the bonds pointing into the plane of the paper (away from you). With this in mind, we can start the switching of groups as follows:
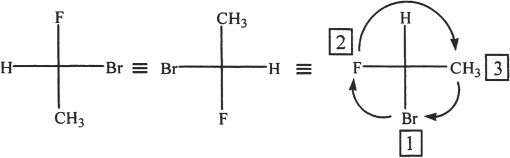
The switching is done so that the lowest ranking substituent (here, it is H) points away (into the plane of paper). The numbering or priority is based on decreasing atomic number. That means the substituent atom with the highest atomic number gets number 1, the next highest gets number 2, and so on. Since the order is clockwise, the configuration is R.
6. The answer is B. Only statements I and II are true. All enantiomers are stereoisomers, but not all stereoisomers are enantiomers. Diastereomers are also stereoisomers.
7. The answer is B.
Chapter 20 Solutions
1. The answer is B.
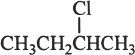
This is straightforward question, involving an important idea. The halogen is attached to a secondary carbon atom and hence it is a secondary alkyl halide.
2. The answer is C. In general, as the number of carbons increases, the boiling point increases. But in this question, all the given choices are derivatives of the same alkane. In other words, they all have the same number of carbon atoms. The compound 1-chloroethane is monochlorinated, the compound 1,1-dichloroethane is dichlorinated, and the compound 1,1,3-trichloroethane is trichlorinated. As the number of Cl atoms increases, the attractive forces also increase, which means the boiling point increases.
3. The answer is D. The reactivity-trend of alcohols with hydrogen halides: Tertiary alcohol > Secondary alcohol > Primary alcohol
4. The answer is B. The generalization in Choice A is not correct. Alkyl halides are generally insoluble in water. Choice C is wrong. The only reasonable choice is B.
5. The answer is C. The question asks for the order of reactivity of bimolecular substitution reactions. The general order of reactivity is: Methyl halide > Primary halide > Secondary halide > Tertiary halide.
6. The answer is D. Choice A is not true because tertiary halides usually undergo substitution by SN1 mechanism. Choice B doesn’t make any sense at all. Choice C is not correct, because SN2 mechanism generally does not involve a carbocation intermediate, whereas SN1 mechanism does involve a carbocation intermediate. Hence, by elimination the answer is D.
7. The answer is D. For this reaction, Choices A, B, and C are possible products. Besides substitution, elimination is also possible, resulting in three products.
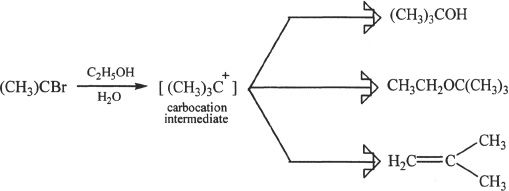
8. The answer is B. The inversion of configuration (at the stereogenic carbon involved in the substitution) is a characteristic of SN2 reactions.
9. The answer is A. Among alkyl halides, alkyl fluorides have the lowest nucleophilic substitution rate. The fastest are alkyl iodides, followed by alkyl bromides and alkyl chlorides.
Chapter 21 Solutions
1. The answer is C. One of the most important properties of alcohols is their ability to undergo hydrogen bonding. The higher boiling points exhibited by alcohols when compared to similar alkanes and ethers are caused by the ability of alcohols to undergo hydrogen bonding.
2. The answer is C.
3. The answer is D. All the listed processes are possible ways of making alcohols.
4. The answer is B. The oxymercuration-demercuration reaction converts an alkene to an alcohol. The hydration follows Markovnikov’s rule and thus the hydrogen adds to the carbon atom with greater number of hydrogens.
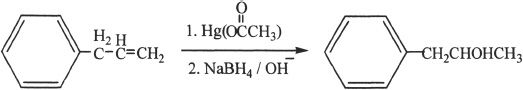
5. The answer is A. Alcohols are much more acidic than alkanes. Among alcohols, primary alcohols are the most acidic ones. Compound A is a primary alcohol. Compound B is a secondary alcohol and Compound C is a tertiary alcohol.
6. The answer is C. Primary alcohols can be converted (oxidized) directly to carboxylic acids. Oxidation of secondary alcohols results in ketones. In some rare cases, secondary alcohols can be converted into carboxylic acids using very strong oxidizing agents, but generally that is not the case. Tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidized. So the best choice is C.
7. The answer is B. Reduction of a ketone usually results in a secondary alcohol.
8. The answer is D. When ethyl magnesium bromide is reacted with ethylene oxide, the carbon chain extends by two more carbons. The product is an alcohol with four carbon atoms.
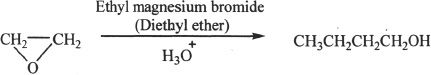
9. The answer is B.
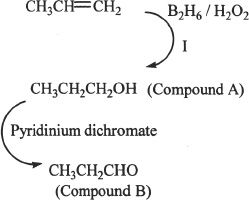
Reaction I sequence results in the alcohol shown above (Compound A). The alcohol formed is oxidized by pyridinium dichromate. The product formed is an aldehyde (propanal).
10. The answer is B. The given organic compound is an aldehyde. The reduction of an aldehyde results in a primary alcohol.
11. The answer is A. The numbering of carbon in the ring should be done as follows:
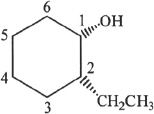
The substituents are cis to each other.
12. The answer is D. Primary alcohols are more acidic than secondary alcohols, and secondary alcohols are more acidic than tertiary alcohols. Ammonia is much weaker than any other compound in the remaining choices. In fact NH3 has a pKa of roughly 36. All the alcohols listed have pKa values ranging from 16 through 18.
13. The answer is C. The complete reaction is shown below:
![]()
14. The answer is A. Primary alcohols are the most reactive alcohols toward metals. Methanol is a primary alcohol. The other choices are tertiary and secondary alcohols.
15. The answer is D. The question asks for a compound which can be directly converted to propanol by oxidation. If an aldehyde is oxidized, it is converted to a carboxylic acid. Oxidation of compounds in Choices B and C cannot produce an alcohol directly by oxidation.
Chapter 22 Solutions
1. The answer is B. Aldehydes can undergo nucleophilic addition reaction with Grignard reagents. The major product here is 3-pentanol which is a five carbon alcohol.
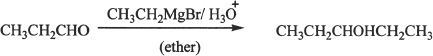
2. The answer is B.
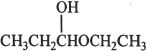
The product formed as a result of nucleophilic addition reaction between an alcohol and an aldehyde is called a hemiacetal. The given structure is a hemiacetal.
3. The answer is B. The reaction described in the question is an oxidation reaction.
4. The choice is A. The reaction can be written as follows:
5. The answer is B. The carbonyl group can act as an electron-withdrawing group. This greatly increases the acidity of a carbonyl compound. Proximity to the carbonyl group is of very great influence in the case of acidity. In essence, carbonyl groups increase the acidity of protons that are connected to the adjacent carbon atoms. The closest protons influenced by the carbonyl group are indicated by the arrows a and b. Among these positions, the protons indicated by b are more acidic because they are influenced by the carbonyl groups from both sides.
6. The answer is D.
7. The correct answer is D.
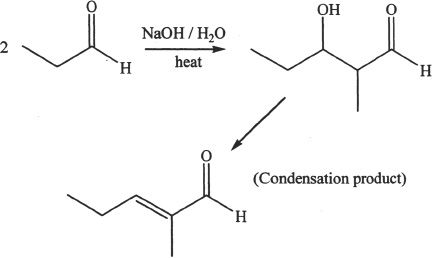
8. The answer is C.
9. The answer is D. Iodoform test is used to identify methyl ketones. Methyl ketones give a positive iodoform test which is indicated by a yellow precipitate.
10. The answer is B. Chromic acid test is a qualitative test that can be used to confirm whether a given unknown compound is an aldehyde or not. Even though aldehydes give a positive response to this test, ketones do not. A sample reaction is shown below:
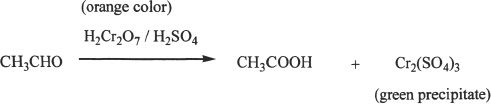
A green precipitate confirms a positive test.
11. The answer is B. The product that is formed in Experiment 2 is an acetal. When one mol of the given compound reacts with two moles of the alcohol, the product formed is an acetal. A simple acetal does not have the -OH group, whereas a hemiacetal has the -OH group.
12. The answer is B. This question tests your ability to judge the type of reaction presented. The conversion is a reduction reaction.
13. The answer is D.
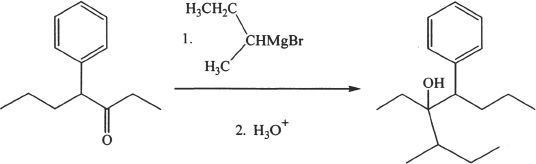
The compound shown in Experiment 4 can be converted to an alcohol by the addition of Grignard reagents. The proper Grignard reagent that should be used for this conversion can be found by comparing the reactant and the desired product.
14. The answer is C. In the experiment, 3-propanal is converted to 2-butanol. Direct oxidation is not an option because there aren’t enough carbons in propanal to form an alcohol with four carbons. So Choice A is ruled out. Choice B is not completely true. With appropriate steps, the reaction is possible. One of the best ways to accomplish the reaction is to first treat the reactant with the appropriate Grignard reagent. Since Grignard reagents are nucleophilic, they can add to the carbonyl group. This extends the carbon chain. The product formed can be then hydrolyzed to form the alcohol.
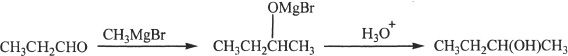
15. The answer is D. By definition, an organometallic compound should have a bond between a carbon atom and a metal atom. The only compound listed here which does not satisfy the definition is Choice D.
16. The answer is C. The conversion is an oxidation reaction.
Chapter 23 Solutions
1. The answer is D. Alkyl magnesium halide or Grignard reagent can react with carbon dioxide to form carboxylic salts. The description of the reaction mentioned in the question also says that the reaction occurred in acidic conditions. Under acidic conditions, the salt is converted to a carboxylic acid. So statement II is true. Furthermore, alkyl magnesium halide (Grignard reagent) acts as the nucleophile in the reaction. So statement III is true.
2. The answer is C. The first step results in n-butyl cyanide (Compound A). n-Butyl cyanide on hydrolysis produces pentanoic acid.
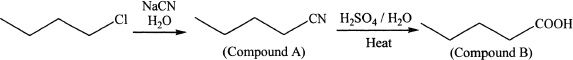
3. The answer is C. Butanoic acid reacts with methanol in the presence of an acid catalyst to form methyl butanoate.
4. The answer is A. Alkanes and ketones have lower boiling points compared to carboxylic acids and alcohols. This aspect rules out Choices C and D. Comparing Choices A and B, we can say that carboxylic acid is a better choice since it can undergo extensive hydrogen bonding. In essence, carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than comparable alcohols.
5. The answer is D. Compound A is more acidic because it is a carboxylic acid. In general, carboxylic acids are more acidic than alcohols.
6. The answer is D. Substituents, especially electronegative ones, increase the acidity of carboxylic acids. Choice D has more substituents of this type than the other choices. So the carboxylic acid represented in Choice D is the most acidic.
7. The answer is D. LiAlH4 is a very good reducing agent. The product is benzyl alcohol.
8. The answer is D.
9. The answer is B.
10. The answer is B.
11. The answer is C. Choice A is true. Carboxylic acids can undergo hydrogen bonding. Choice B is also true and so is Choice D. Choice C is not true. In fact, the hydroxyl group makes its carbonyl group less electrophilic. In a ketone there is no hydroxyl group and that makes its carbonyl group more electrophilic than that of a carboxylic acid.
12. The answer is C. The conversion is an oxidation reaction. This rules out Choices B and D. LiAlH4 is a reducing agent. So Choice A is wrong. KMnO4 is a good oxidizing agent which can accomplish this conversion.
13. The answer is B.
14. The answer is D.
Formic acid is HCOOH.
15. The answer is C. The question asks for the compound that has the highest pKa value. Highest pKa value means the weakest acid. The inductive effects become less and less pronounced as the electronegative substituents are farther away from the carboxylic group.
16. The answer is C. NaOCH3 is basic. Carboxylic acids are much more acidic than alkynes. Choices B and D are ruled out. It is a tough call between Choices A and C. The carboxylic group of acetic acid is attached to an alkyl group. The carboxylic group of benzoic acid is attached to an aryl group. The sp2 carbons in the benzoic acid ring are more electron withdrawing than the sp3 carbon in the acetic acid. This makes benzoic acid more acidic than acetic acid.
Chapter 24 Solutions
1. The answer is B. Among the acid derivatives, the acyl chloride is the least stable and the most reactive compound toward hydrolysis.
2. The answer is A.
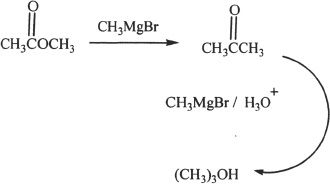
3. The answer is C. Esters can react with Grignard reagents to form tertiary alcohols. The intermediary compound formed is a ketone which reacts with the second Grignard reagent molecule to form the tertiary alcohol. A representative reaction is shown below:
4. The answer is B.
5. The answer is C.
6. The answer is B.
7. The answer is D. Choices A, B, and C describe possible ways of preparing carboxylic acids. Oxidation of an aldehyde can result in a carboxylic acid.
Chapter 25 Solutions
1. The answer is A.
2. The answer is D. Alcohols, water, and carboxylic acids can undergo intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Ethers cannot undergo intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Alkanes cannot form intermolecular hydrogen bonding either. So the best conclusion is that ethers have boiling points similar to that of alkanes.
3. The answer is D. Ethers are polar. Hence, Choice A is true. Ethers are relatively less reactive and are widely used as solvents. Hence, Choices B and C are true.
4. The answer is A. It is true that ethers are not very reactive. Hence, statement I is true and statement II is false. Ethers are flammable. Hence, statement III is true. Ethers have very low boiling points compared to that of alcohols. Hence, statement IV is false.
5. The answer is A. The reaction given in the passage is called Williamson ether synthesis. By looking at the reaction we cannot answer this question. But a clue is given in the question. According to the question the reaction is most effective if it undergoes by SN2 mechanism. Now we have something to hang on to. Since the reaction is mostly effective when undergoing by SN2 mechanism, the alkyl halide most appropriately used must be a primary alkyl halide. The only primary halide among the choices is methyl chloride.
6. The answer is D. In the Williamson ether synthesis, if the alkyl halide is either tertiary or secondary, there is a good chance that elimination reaction can prevail. However, this is not desired in this reaction. In fact, the compounds given in Choices A, B, and C can undergo elimination reaction. Only the compound in Choice D is exempt from undergoing elimination.
7. The answer is A. Ethers are usually not so reactive, but they will react with concentrated acids. This is exactly the type of reaction given in the question. Methyl bromide is the product formed, and the reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
8. The answer is B. All the compounds given are ethers except in Choice B. Choice B is an ester.
Chapter 26 Solutions
1. The answer is B.
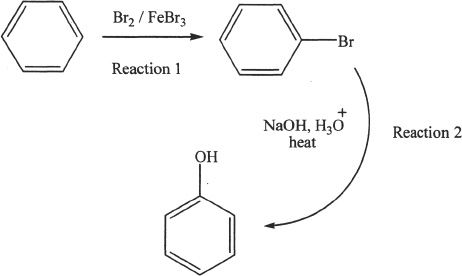
Reaction 1 results in bromobenzene (Compound A). In Reaction 2, the bromobenzene formed is hydrolyzed to phenol.
2. The answer is B. Phenol has the hydroxyl group which is an ortho/para activator. So the substitutions are more likely to be in the ortho and para positions of the ring.
3. The answer is A.
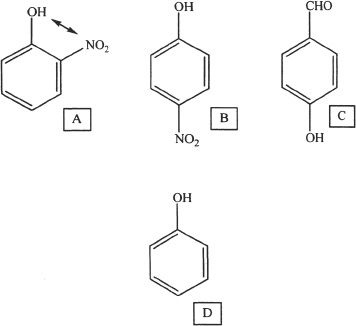
As you can see in the diagram, the intramolecular hydrogen bonding is most pronounced in ortho-nitrophenol because of the proximity of the -NO2 group to the hydroxyl group.
Chapter 27 Solutions
1. The answer is B. The lowest boiling point is likely to be exhibited by Compound B which is an alkane. The highest boiling point is attributed to Compound A which can undergo extensive intermolecular hydrogen bonding, followed by the alcohol, and trailed by Compound D.
2. The answer is D. In general, aryl amines are less basic than ammonia. Alkyl amines are more basic than ammonia. Among alkyl amines, secondary amines are generally more basic than primary amines.
3. The answer is D.
4. The answer is D. This is a straightforward question. The given reaction is a reduction reaction.
5. The answer is D. In general, alcohols (comparable) are more acidic than amines. In the choices, the only alcohol given is ethanol.
6. The answer is B. Tertiary amines cannot have hydrogen bonds themselves, because they have no nitrogen-hydrogen bond connections unlike the other compounds listed.
7. The answer is D. From the values in Table 1, we can compare the basicity of the compounds. It appears that the weakest base is the conjugate base of aniline, which also makes it the most acidic.
8. The answer is B. The conversion that is asked for in the question is accompanied by the loss of carbon dioxide (CO2). This is a typical example of a decarboxylation reaction.
9. The answer is D. The conversion is best described as a reduction reaction.
10. The answer is A.
Chapter 28 Solutions
1. The answer is C.
2. The answer is D. All amino acids are optically active except glycine. Glycine has a simple structure and is achiral.
The structure of glycine.:
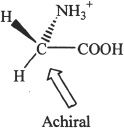
3. The answer is D. At a certain pH (unique for each amino acid), the net charge of an amino acid equals zero. When this pH is achieved, it is said to be at the amino acid’s isoelectric point. At the isoelectric pH of an amino acid, the net movement of that particular amino acid will be zero when the amino acid is subjected to an electric field.
4. The answer is C. The general structure of an amino acid is shown below:
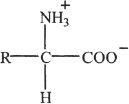
5. The answer is D.
6. The answer is D.
7. The answer is D. Proteases are enzymes that can affect the structural integrity of proteins. Strong bases and acids can also affect the structural mode of proteins.
8. The answer is D.
9. The answer is D. All amino acids have at least one carboxyl group. Hence, statement I is true. Amino acids have high melting points since they can have multiple charges. This results in strong ionic interactions and hence much energy is required to break the ionic interactions between them. Thus it is hard to break the crystal lattice, and they have high boiling points. Hence, statement II is true. Depending on the pH and the particular amino acid’s nature, amino acids can have either a net positive charge, a net negative charge, or a net zero charge. Hence, statements III and IV are true.
10. The answer is C. See the explanation for Question 3.
11. The answer is C. Peptide bond is a covalent bond which connects amino acids in the formation of a peptide or the primary structure of a protein. The peptide link is formed between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of the adjacent amino acid.
12. The answer is B.
13. The answer is D. From the table, we can assess the behavior of amino acids by comparing the pKa values of the amino acids. At pH 7 only glutamate will have a net negative charge.
14. The answer is D.
Chapter 29 Solutions
1. The answer is D. Galactose, glucose, and ribose are monosaccharides. Maltose is a disaccharide made of glucose units.
2. The answer is B. We can rule out Choices A and C, because the given sugar is not a D-sugar. Ribose is a 5-carbon sugar. So Choice D is also ruled out.
3. The answer is D. The synthesis of sugar probably resulted in mostly one form of the sugar. According to the question, there was a change in optical activity. This is due to a phenomenon called mutarotation. The sugar solution that was made mutarotated to form its corresponding anomer, which changed the observed optical activity. The mutarotation will continue until an equilibrium is established.
4. The answer is C. Glycogen is the only non-disaccharide listed. All the other molecules are disaccharides. In animals, carbohydrates are stored mainly in the form of glycogen. It is mostly stored in the liver and the skeletal muscles.
5. The answer is B.
There are two chiral carbons in the given structure. So the number of possible optical isomers is 22 = 4.
6. The answer is A. Fructose, glucose, and galactose are monosaccharides. The only choice that is not a monosaccharide is sucrose. Sucrose is a disaccharide formed by glucose and fructose.
7. The correct answer C. The given structure is not glucose. Ribose is a five-carbon sugar. The given structure is a six-carbon sugar. Maltose is a disaccharide. Further, the given structure is a ketose sugar, and the only ketohexose sugar listed is fructose.
8. The answer is A.
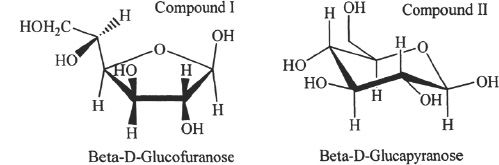
Statements 1 and 2 are true. Both given structures are glucose; one is in the furanose ring form, and the other is in the pyranose ring form. The five-membered ring of glucose is called glucofuranose. The six-membered ring of glucose is called glucopyranose.
9. The answer is B. Glucose and mannose are not anomers, nor are they are mirror images. So Choices A and C are ruled out. Choice D is not true. In fact, they are epimers. Epimers are isomeric sugars that differ in their configurations only at one of their stereogenic centers.
10. The answer is A. Disaccharides are formed by the combination or bonding of two monosaccharides by a linkage called the glycosidic linkage.
11. The answer is C. Anomers differ only in stereogenicity at the anomeric carbon. The structures of a-D-glucose and b-D-glucose are drawn below. They are anomers.
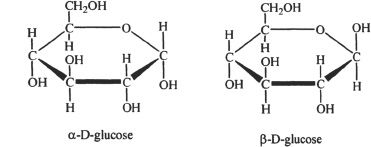
Chapter 30 Solutions
1. The answer is B. Triglycerides are triesters of glycerol. A triglyceride can be represented as follows:
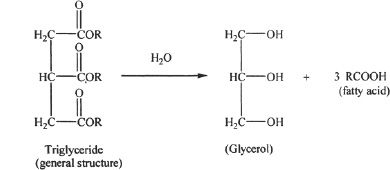
As a result of hydrolysis, each mole of a triglyceride can give 1 mol of glycerol and 3 moles of fatty acids.
2. The answer is D.
Chapter 31 Solutions
1. The answer is B. The indicated bond is best described as a phosphate anhydride bond.
2. The answer is D. The given reaction is a hydrolysis reaction.
3. The answer is B. The interconversion between the compounds X and Y is a typical example of tautomerism. Compound X is the enol form of pyruvate. Compound Y is the keto form of pyruvate. The interconversion of such forms is called tautomerism.
4. The answer is D. The bond indicated by the arrow is an example of N-glycosidic bond.
5. The answer is A. According to the passage, the hydrolysis of ATP has a negative change in free energy (ΔG). So it is sensible to say that the products have less energy than that of the reactants.
6. The answer is C. ATP is a higher energy-currency than AMP. So the hydrolysis of AMP will have a ΔG that is less negative than —31 kJ/mol (given in the passage). Moreover, the conversion represented in the question is the formation of AMP rather than the hydrolysis of AMP. This eliminates Choices B and D. According to the clue given in the question, the products have higher free energy than the reactants. This can give only a positive ΔG.
7. The answer is C.
Chapter 32 Solutions
1. The answer is A.
2. The answer is D.
3. The answer is D. According to the passage, the reactions in Experiment 3 are based on unimolecular substitution mechanism. Based on this information, we can say that compound B has the fastest reaction rate. The second fastest is Compound C. These observations rule out Choices A, B, and C. Compound A is a primary alcohol and is not likely to undergo SN1 reaction.
4. The answer is B. According to the passage, propanone is reacted with the reagent to form a product that lacks the carbonyl group. Note that the compound propanone is a ketone and contains a carbonyl group. But after the reaction, the carbonyl group is not present in the product formed. So the peak that disappeared is the carbonyl peak.
5. The answer is C. The conversion results in the formation of a glycol (an alcohol). Such a conversion is best described as an oxidation reaction.
6. The answer is C. The compounds A, B and C are alcohols. They do not have carboxyl groups. They have different reaction rates in terms of substitution reactions. Since they are alcohols, they all will exhibit broad IR peaks around 3400 cm—1.
7. The answer is A.
The compound B is tert-butyl alcohol.
Even though there are three methyl groups, all the methyl groups are equivalent and so are their protons. So the methyl protons give rise to one peak. The hydroxylic proton will give rise to another peak, totaling two sets of NMR peaks.
8. The answer is B. Since the compound is insoluble in water, statement I is true. Since the compound is insoluble in 5% aqueous sodium hydroxide, statement II is false. Since the compound is an aromatic compound, statement III is true. The compound is not a strong base. Hence, statement IV is false.