Organic Chemistry: Concepts and Applications - Headley Allan D. 2020
Synthetic Polymers and Biopolymers
20.5 Copolymerization of Alkenes
So far, we have examined polymers that have the same type of repeating unit, but it is possible to have polymers that have different types of repeating units. There are different ways in which the different monomers can be arranged in the polymer. Some examples are shown below.
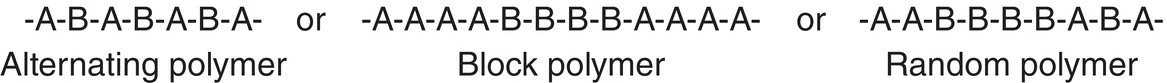
Such type polymers are referred to as copolymers.
20.5.1 Cationic Copolymerization
An example of the copolymerization of styrene and isobutylene is shown below.
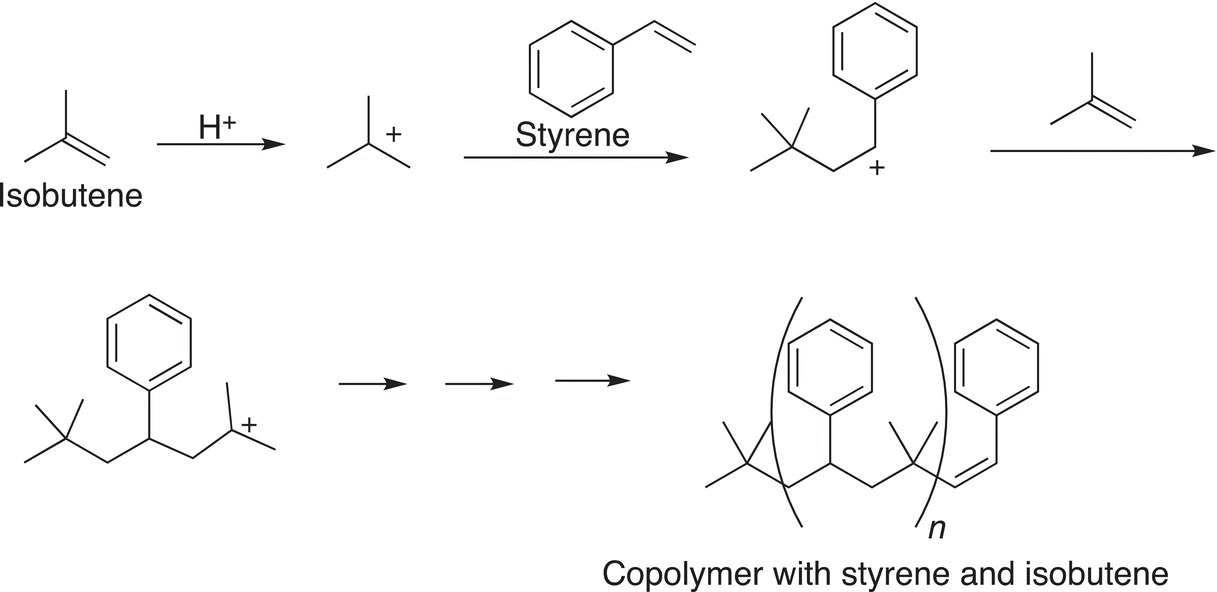
Copolymers have different properties and as a result have different uses. For example, butyl rubber is a copolymer of isobutylene and isoprene that was first produced in 1937 by William Sparks and Robert Thomas of Exxon Corporation. Butyl rubber is impermeable to air and, as a result, is used as liners for airtight containers. Another copolymer is styrene-butadiene rubber, which is a copolymer of styrene and butadiene, which was developed by Goodyear and used in car tires
20.5.2 Epoxy Resin Copolymers
Resins are polymers that are typically solids or highly viscous. Resins that are made by copolymerization of an epoxide with another compound, typically one having two hydroxyl groups. Resins are mainly used as adhesives and coatings. An example of the synthesis of epoxy resin is shown in Reaction (20-14).
(20-14)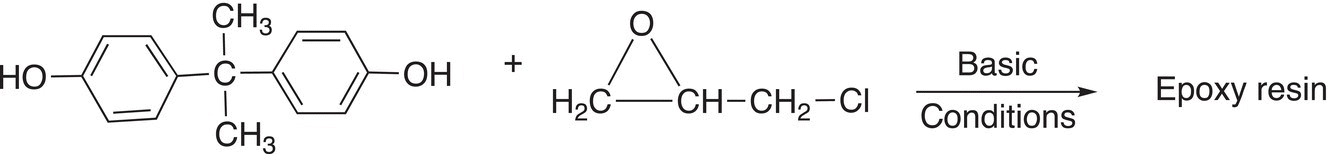
The reaction mechanism shown below explains the reaction and the formation of the epoxy resin as product.
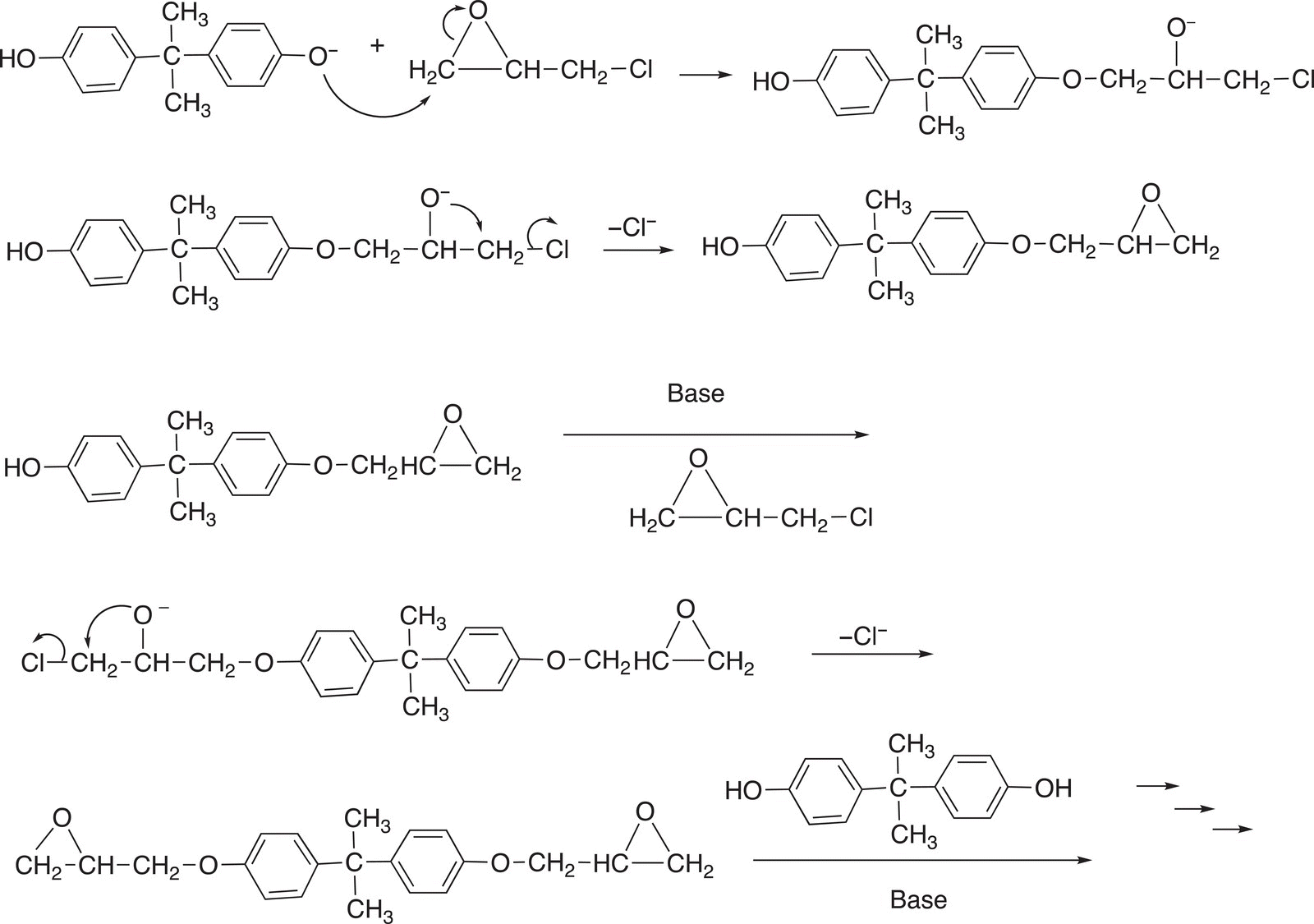
The product that is isolated is the resin. As you will notice, there are many possible molecules that can be used to accomplish a similar reaction leading to slightly modified resins. In industry, various starting compounds are used to make different types of resins.