Organic Chemistry: Concepts and Applications - Headley Allan D. 2020
Synthetic Polymers and Biopolymers
20.18 Lipids
Lipids are not polymers, but most are large naturally occurring compounds. A large number of naturally occurring compounds, including cholesterol, fall under a category of compounds called lipids. Lipids are typically insoluble in water, but soluble in most organic solvents, such as diethyl ether. Lipids can be divided into three types: (i) triglycerides and waxes; (ii) phospholipids; and (iii) steroids, prostaglandins, and terpenes (Figure 20.2).
Triglycerides, waxes, and phospholipids can be hydrolyzed under acidic or basic conditions to produce smaller molecules, typically carboxylic acids and alcohols. Phospholipids make up our cells' membrane and are critical to the various functions of the cell. Steroids, prostaglandins, and terpenes are classified based on structural features of these types of molecules and the special functions that they perform (Figure 20.3).
Steroids are compounds used to treat a wide variety of inflammation and to reduce the activity of the immune system. Prostaglandins are hormone-like compounds that participate in a wide range of functions of the body. Functions such as contraction and relaxation of smooth muscles and dilation and constriction of blood vessels are affected by prostaglandins. Terpenes are natural products with unique fragrances; they are widely used in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries for a variety of products, such as cosmetics. Alpha pinene is one of the most commonly known terpenes and is used for its anti-inflammatory properties.
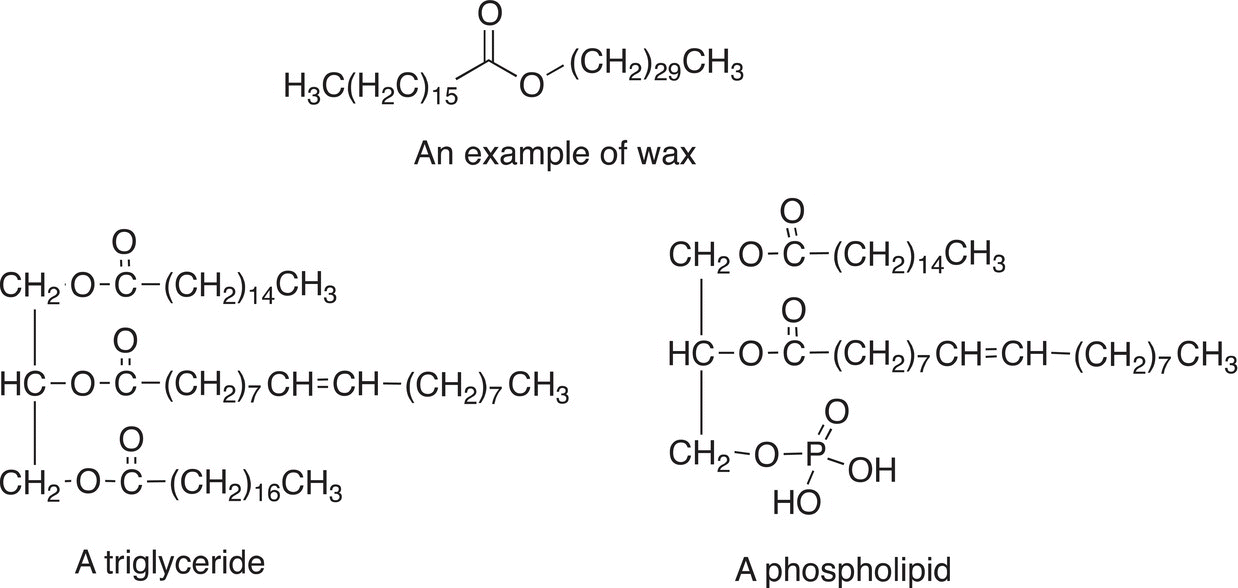
Figure 20.2 Examples of a wax, a triglyceride, and a phospholipid.
α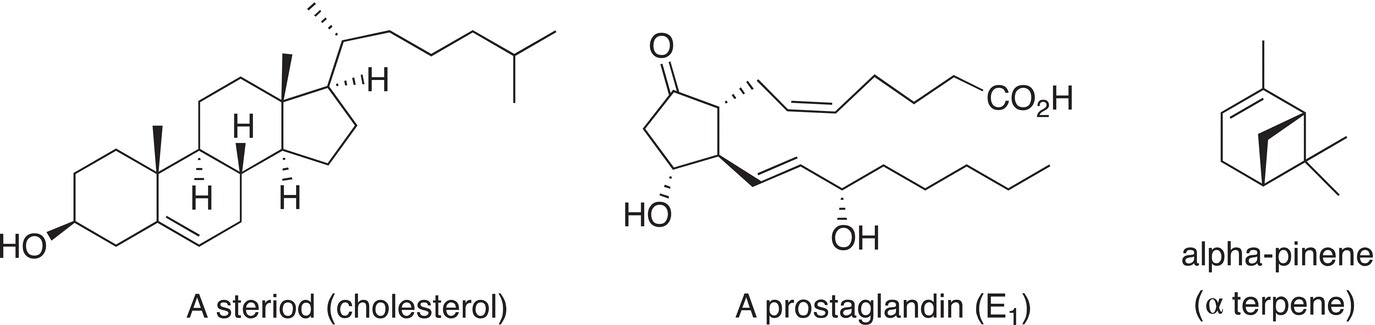
Figure 20.3 Examples of a steroid, a prostaglandin, and a terpene.