Organic Chemistry: Concepts and Applications - Headley Allan D. 2020
Heteroatomic Functional Groups and Organic Nomenclature
3.7 Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acids
As the name of these compounds suggests, these are acids and they have the functional feature ─COOH; shown below are different ways of writing the carboxylic acid functional group.
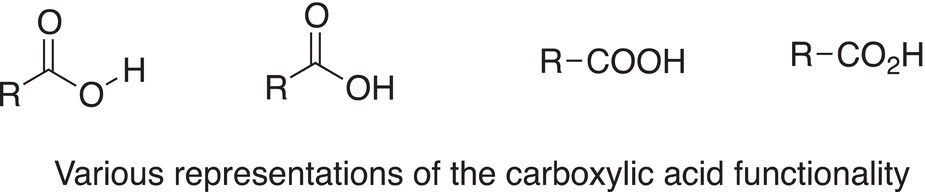
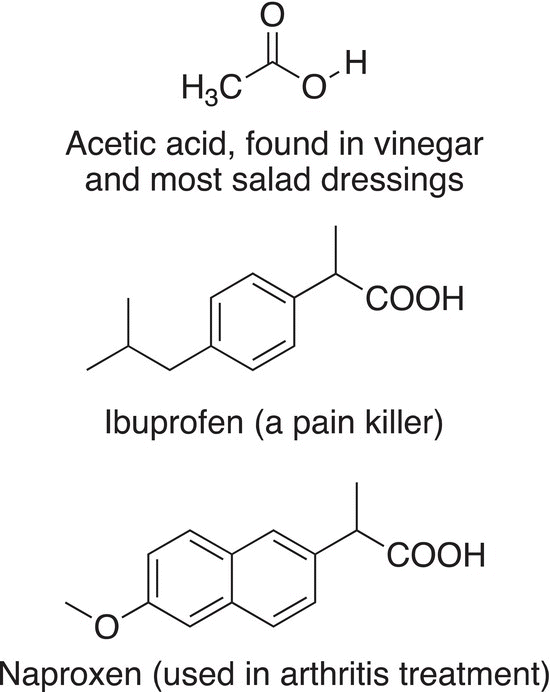
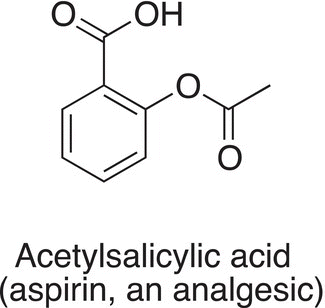
The simplest carboxylic acid is formic acid, in which a hydrogen atom is bonded to the carbonyl carbon of the carboxylic acid functionality. Formic acid is fairly acid and can cause damage to tissues. Formic acid is the main constituent of ant venom, which causes severe irritation when one is stung by an ant. Other carboxylic acids are very important compounds in our everyday lives, and some common ones are shown below.
DID YOU KNOW?
Formic acid is the main constituent of ant venom, which causes severe irritation when one is stung by an ant.
Carboxylic acids have an acidic hydrogen that is bonded to the electronegative oxygen of the carboxylic acid functionality, and as a result, it will be involved in hydrogen bonding. Thus, carboxylic acids are typically high boiling liquids, compared to other liquids of comparable molecular weights that do not have intermolecular hydrogen bonds, as shown below.
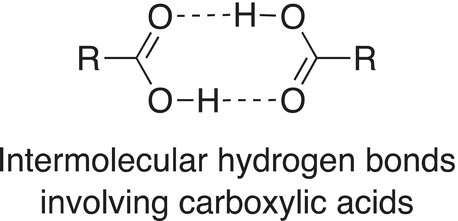
Owing to the type of hydrogen bond shown above, the boiling point of acetic acid is higher than expected, compared to other type compounds of similar molecular weights, the boiling point of acetic acid is 118 °C, and it is soluble in polar solvents such as water.
Carboxylic acids that have long chains are typically classified as saturated fatty acids or unsaturated fatty acids. Unsaturated fatty acids can be broken further into cis and trans fatty acids as shown below.
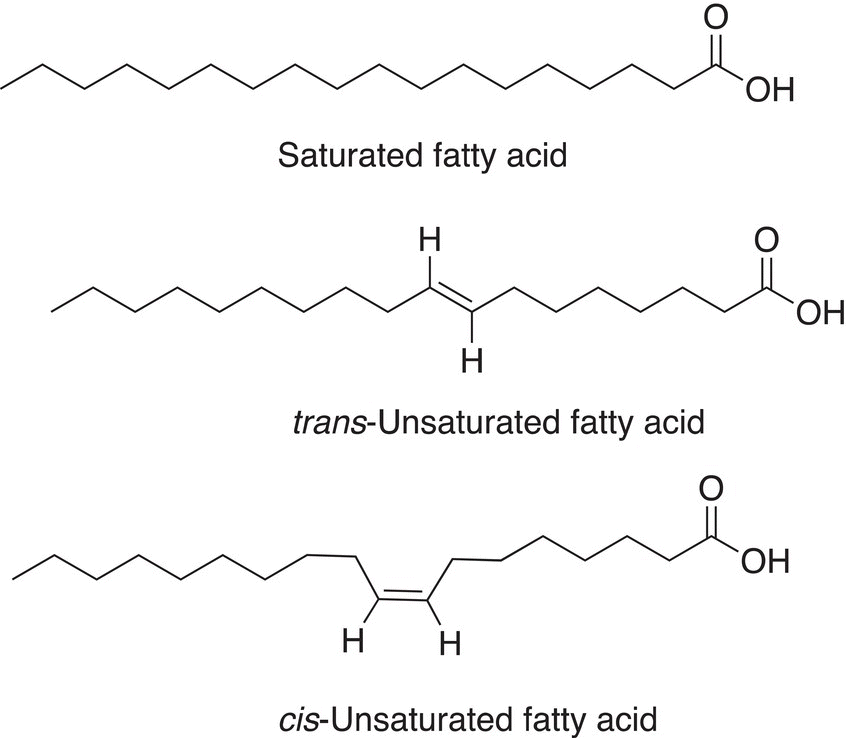
Unsaturated fatty acids have lower melting points than saturated fatty acids with the same number of carbons owing to the structured arrangement of the molecules. For example, the melting point of stearic acid (C18H36O2) is 69.6 °C, but the melting point of oleic acid (C18H34O2), which contains one cis-double bond, is 13.4 °C. Polyunsaturated fatty acids have even lower melting points.