Organic Chemistry: Concepts and Applications - Headley Allan D. 2020
An Overview of the Reactions of Organic Chemistry
6.3 Addition Reactions
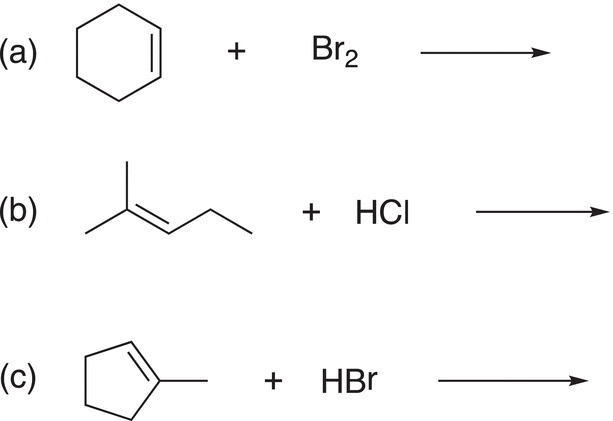
As the name suggests, these reactions involve the addition of a reactant to another reactant to produce the product. The reaction shown in Reaction (6-7) involves the addition of bromine molecule across a carbon—carbon double bond, an alkene functional group, to form an addition product. Hence, this specific type of addition reaction is called bromination reaction of an alkene.
(6-7)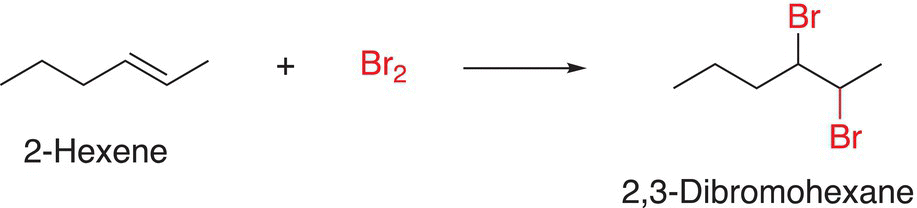
Another example of an addition reaction is given in Reaction (6-8) in which chlorine is added across a carbon—carbon double bond of cyclohexene.
(6-8)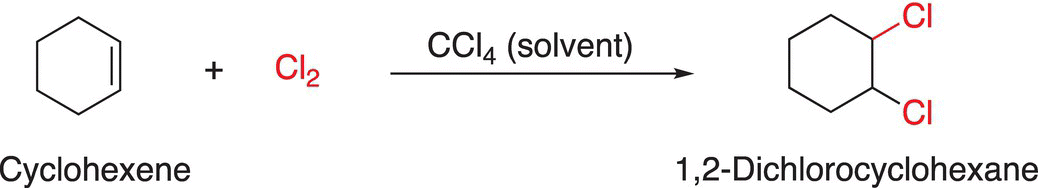
The addition of a molecule such as HBr can also take place to an alkene, as shown in the reaction in Reaction (6-9).
(6-9)
The reaction in Reaction (6-10) involves the addition of HCl to a nonsymmetrical alkene to form two possible products.
(6-10)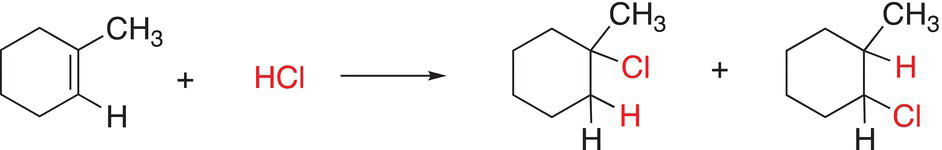
Since the addition can take place in two ways, there are two different products. Since this reaction involves the addition of hydrochloric acid (HCl) across the double bond, this reaction is called hydrochlorination. Reaction (6-11) involves another example of the addition of HCl across the carbon—carbon double bond.
(6-11)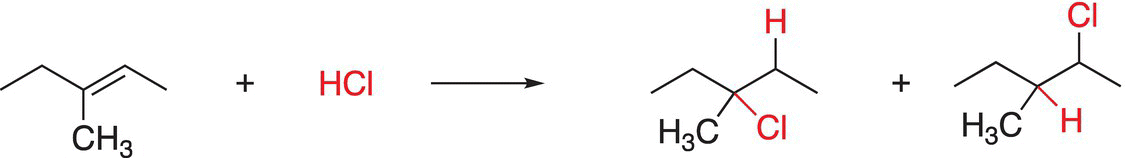
Note that for the reaction shown in Reaction (6-11), there are two possible products since there are two possible addition modes, similar to the addition reaction of HCl to an alkene shown in Reaction (6-10). For addition reactions, there are two important observations: (i) an alkene functionality is transformed into single bonds and (ii) one reactant molecule adds to another molecule at the site of the functional group to form the addition product(s). More details regarding these and other similar addition reaction will be discussed in Chapter 8.
Problem 6.4
Predict all possible products for the following addition reactions.