Practice Makes Perfect: Spanish Pronouns and Prepositions, Premium 3rd Edition (2016)
Appendix B. Pronouns
1. Personal pronouns
A personal pronoun (also called a subject pronoun) replaces a noun that names the subject or actor in a clause or sentence.
![]()

2. Interrogative pronouns
An interrogative pronoun is used in asking questions. The answer sought will be a noun or pronoun (either a person or thing).
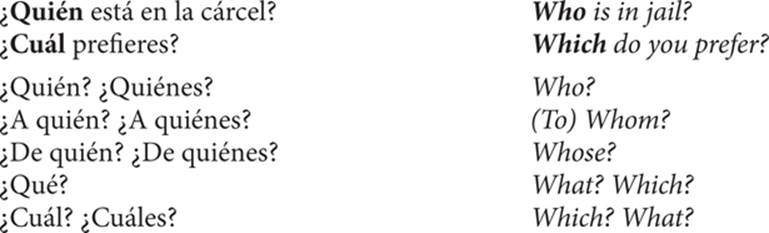
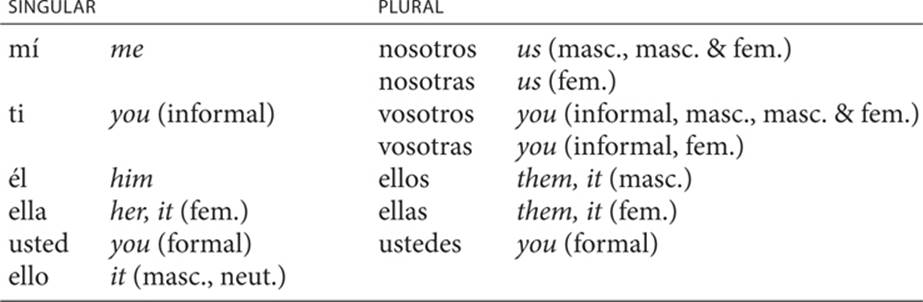
3. Prepositional pronouns
A prepositional pronoun follows a preposition and functions as the object of the preposition, replacing a noun that names a person or thing.

Prepositional pronouns are nearly identical to the subject pronouns, with the exceptions of mí and ti and the addition of the third-person form ello, which represents a masculine or neuter noun.
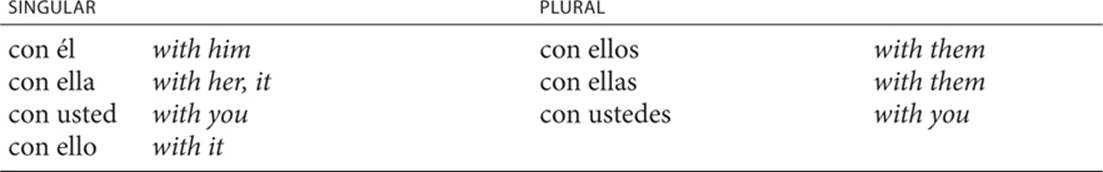
Pronouns with con: Certain pronouns that follow the preposition con (“with”) take on a special form.

In certain situations, the standard prepositional pronouns are used with con (“with”) in the third person, as shown below.
Subject pronouns with prepositions: In Spanish, there are six prepositions that always take a subject pronoun, rather than a standard prepositional pronoun.

Reflexive pronouns following a preposition: A reflexive action (an action that “reflects” back on the performer) can be expressed with a preposition followed by a reflexive pronoun.

4. Possessive pronouns
A possessive pronoun replaces the nouns that name the owner of an object and the object itself.

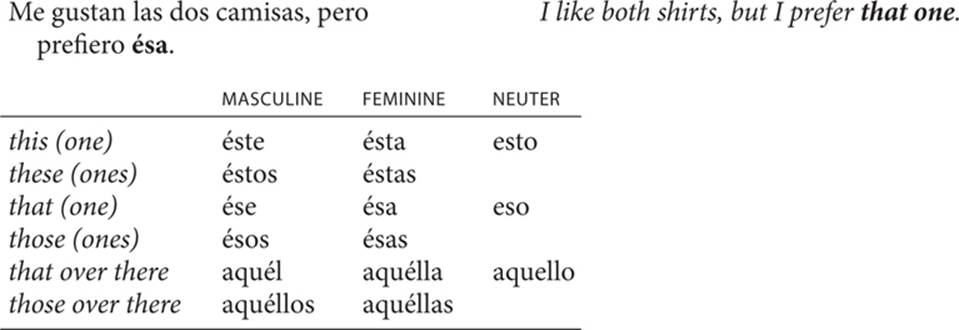
5. Demonstrative pronouns
A demonstrative pronoun replaces an understood noun and points out its location relative to the speaker.
6. Numbers as pronouns
A number used as a pronoun replaces an understood or omitted noun. It assumes the meaning of the noun itself as well as the number.

7. Adjective pronouns
An adjective pronoun is an adjective that assumes the meaning of an understood, irrelevant, or omitted noun. Descriptive, or qualitative, adjectives easily become pronouns.

Many adjective pronouns are quantitative pronouns that correspond to indefinite pronouns in English. Others are adjectives with “clipped”—or omitted—words, which many times refer to unspecified people or things.
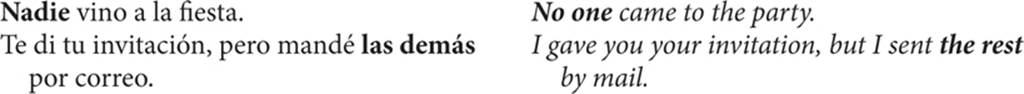
Below are several frequently used adjective pronouns; some are quantitative and others refer to unspecified nouns.

8. Relative pronouns
A relative pronoun represents understood or omitted material and connects a dependent clause with an independent, or principal, clause.

Below are several frequently used relative pronouns.

9. Direct object pronouns
A direct object pronoun replaces a noun that names the direct object of the verb in a sentence or clause. It answers the question “What?” or “Whom?”

10. Indirect object pronouns
An indirect object pronoun replaces a noun that names the indirect object of the verb in a sentence or clause. It answers the questions “To whom?” and “For whom?”

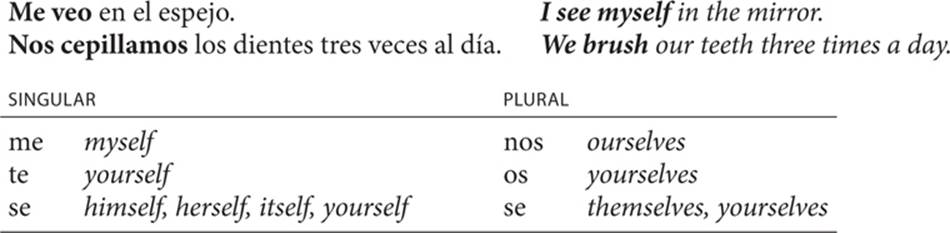
11. Reflexive object pronouns
A reflexive object pronoun indicates that the subject and the object of an action are the same person or thing.
12. Double-object pronoun order: RID
RID is an acronym that is useful for remembering the placement order for two object pronouns in a sentence. Two object pronouns in a sentence are always used in the following order: reflexive object pronoun, indirect object pronoun, direct object pronoun.

In the second example, the indirect and direct object pronouns could also be attached to the infinitive: Debemos decírsela. Note that an accent mark is usually required to retain the original stress in the infinitive. Also note that whenever the two object pronouns begin with the letter l, the l in the first pronoun changes to s: Le la debemos decir becomes Se la debemos decir.
Following are patterns for the more common combinations of double object pronouns.
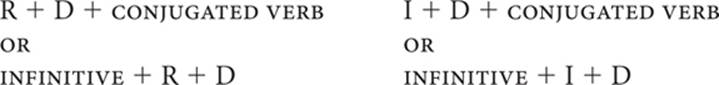
13. Reciprocal pronouns
A reciprocal pronoun expresses reciprocity; it indicates an action that goes back and forth between two or more subjects.

14. The pronoun se and the passive voice
Se is commonly used to indicate that an action is performed by an unspecified subject, expressing the passive voice in Spanish.
![]()
Se also is used to express an unknown, impersonal subject.
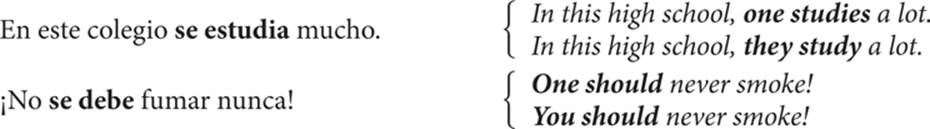
Actions involving inanimate objects often employ se.
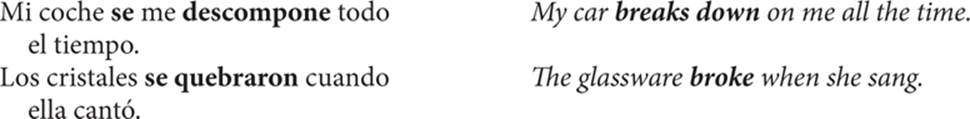
The pattern using se to express the passive voice is shown below.
se + THIRD-PERSON CONJUGATED VERB