5 Steps to a 5: AP Calculus AB 2017 (2016)
STEP 4
Review the Knowledge You Need to Score High
CHAPTER 9
Applications of Derivatives
IN THIS CHAPTER
Summary: Two of the most common applications of derivatives involve solving related rate problems and applied maximum and minimum problems. In this chapter, you will learn the general procedures for solving these two types of problems and to apply these procedures to examples. Both related rate and applied maximum and minimum problems appear often on the AP Calculus AB exam.
Key Ideas
![]() General Procedure for Solving Related Rate Problems
General Procedure for Solving Related Rate Problems
![]() Common Related Rate Problems
Common Related Rate Problems
![]() Inverted Cone, Shadow, and Angle of Elevation Problems
Inverted Cone, Shadow, and Angle of Elevation Problems
![]() General Procedure for Solving Applied Maximum and Minimum Problems
General Procedure for Solving Applied Maximum and Minimum Problems
![]() Distance, Area, Volume, and Business Problems
Distance, Area, Volume, and Business Problems
9.1 Related Rate
Main Concepts: General Procedure for Solving Related Rate Problems, Common Related Rate Problems, Inverted Cone (Water Tank) Problem, Shadow Problem, Angle of Elevation Problem

General Procedure for Solving Related Rate Problems
1. Read the problem and, if appropriate, draw a diagram.
2. Represent the given information and the unknowns by mathematical symbols.
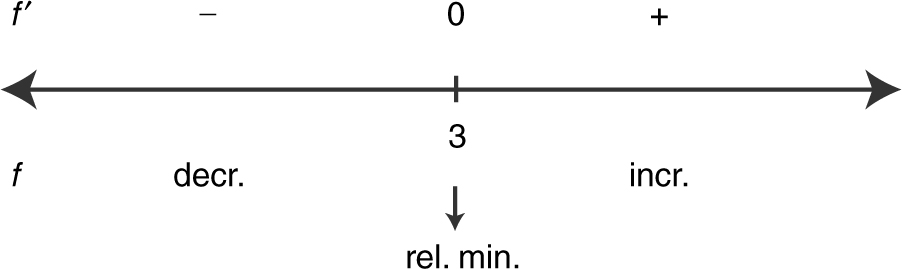
3. Write an equation involving the rate of change to be determined. (If the equation contains more than one variable, it may be necessary to reduce the equation to one variable.)
4. Differentiate each term of the equation with respect to time.
5. Substitute all known values and known rates of change into the resulting equation.
6. Solve the resulting equation for the desired rate of change.
7. Write the answer and indicate the units of measure.
Common Related Rate Problems
Example 1
When the area of a square is increasing twice as fast as its diagonals, what is the length of a side of the square?
Let z represent the diagonal of the square. The area of a square is 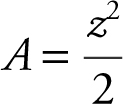 .
.
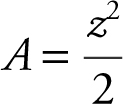
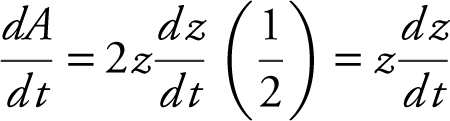 .
.
Since 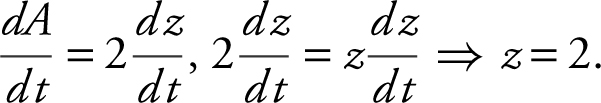 .
.
Let s be a side of the square. Since the diagonal z = 2, then s 2 + s 2 = z 2 .
⇒ 2s 2 = 4 ⇒ s 2 = 4 ⇒ s 2 = 2 or ![]() .
.
Example 2
Find the surface area of a sphere at the instant when the rate of increase of the volume of the sphere is nine times the rate of increase of the radius.
Volume of a sphere: 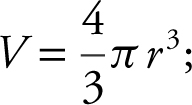 Surface area of a sphere: S = 4πr 2 .
Surface area of a sphere: S = 4πr 2 .
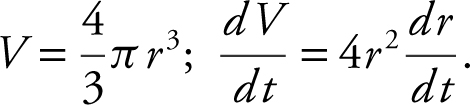 .
.
Since 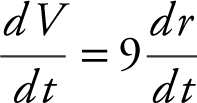 , you have
, you have 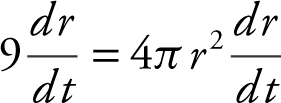 or 9 = 4πr 2 .
or 9 = 4πr 2 .
Since S = 4πr 2 , the surface area is S = 9 square units.
Note: At 9 = 4πr 2 , you could solve for r and obtain 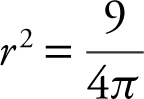 or
or 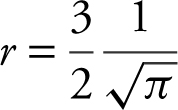 . You could then substitute
. You could then substitute 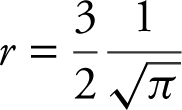 into the formula for surface area S = 4πr 2 and obtain 9. These steps are of course correct but not necessary.
into the formula for surface area S = 4πr 2 and obtain 9. These steps are of course correct but not necessary.
Example 3
The height of a right circular cone is always three times the radius. Find the volume of the cone at the instant when the rate of increase of the volume is twelve times the rate of increase of the radius.
Let r, h be the radius and height of the cone, respectively.
Since h = 3r , the volume of the cone 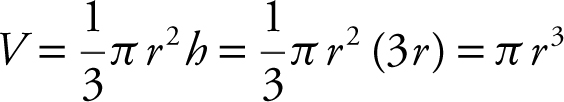 .
.
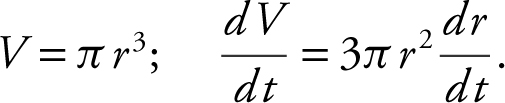
When 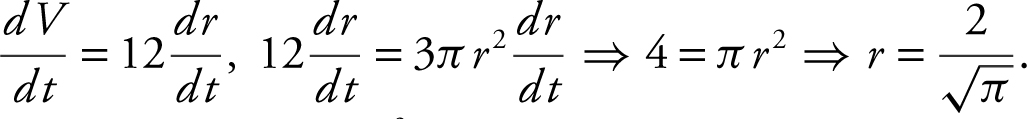
Thus, 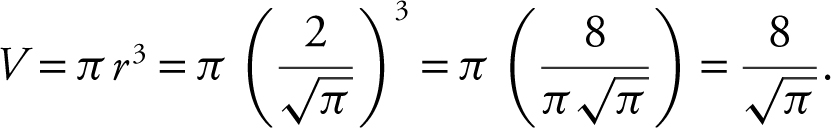
• Go with your first instinct if you are unsure. Usually that is the correct one.
Inverted Cone (Water Tank) Problem
A water tank is in the shape of an inverted cone. The height of the cone is 10 meters and the diameter of the base is 8 meters as shown in Figure 9.1-1 . Water is being pumped into the tank at the rate of 2 m3 /min. How fast is the water level rising when the water is 5 meters deep? (See Figure 9.1-1 .)
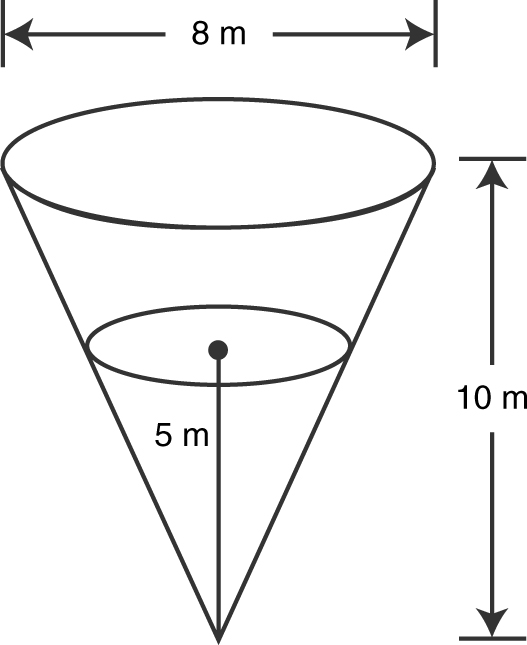
Figure 9.1-1
Solution:
Step 1: Define the variables. Let V be the volume of water in the tank; h be the height of the water level at t minutes; r be the radius of the surface of the water at t minutes; and t be the time in minutes.
Step 2: Given: 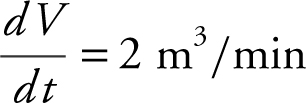 . Height = 10 m, diameter = 8 m.
. Height = 10 m, diameter = 8 m.
Find: 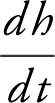 at h =5.
at h =5.
Step 3: Set up an equation: 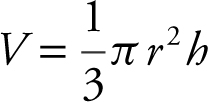 .
.
Using similar triangles, you have 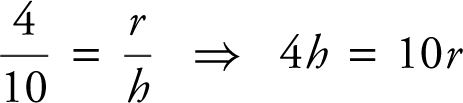 ; or
; or 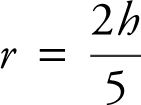 . (See Figure 9.1-2 .)
. (See Figure 9.1-2 .)
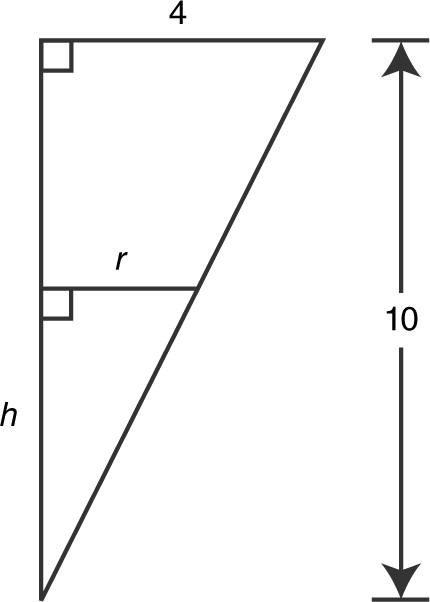
Figure 9.1-2
Thus, you can reduce the equation to one variable:
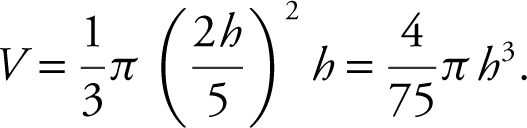 .
.
Step 4: Differentiate both sides of the equation with respect to t .
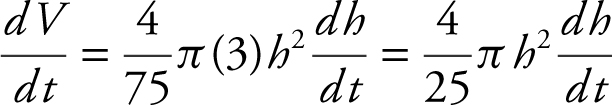
Step 5: Substitute known values.
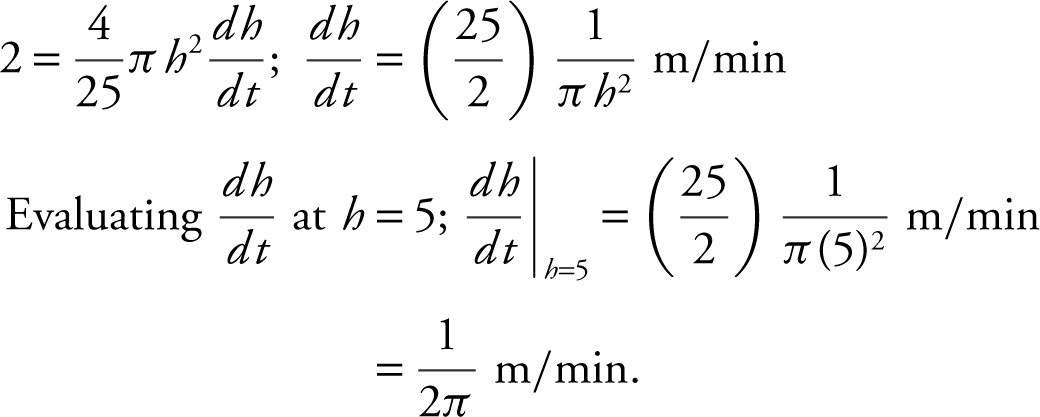
Step 6: Thus, the water level is rising at 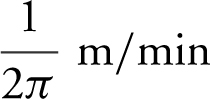 when the water is 5 m high.
when the water is 5 m high.
Shadow Problem
A light on the ground 100 feet from a building is shining at a 6-foot-tall man walking away from the light and toward the building at the rate of 4 ft/sec. How fast is his shadow on the building becoming shorter when he is 40 feet from the building? (See Figure 9.1-3 .)
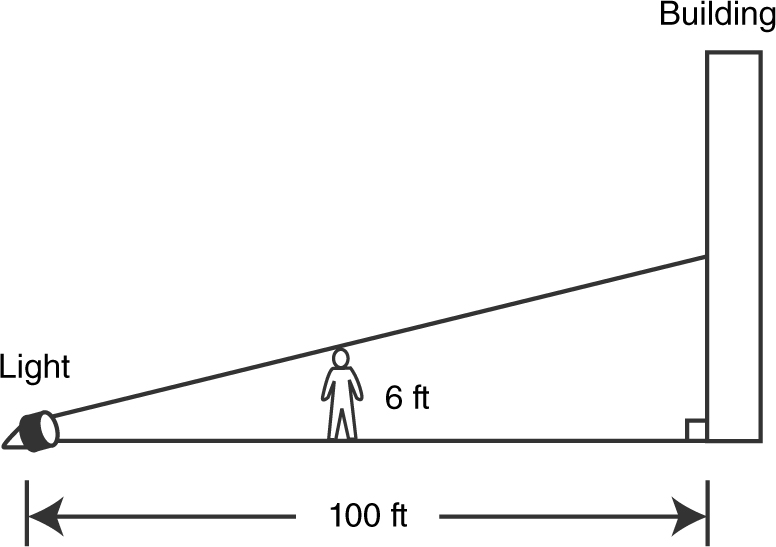
Figure 9.1-3
Solution:
Step 1: Let s be the height of the man’s shadow; x be the distance between the man and the light; and t be the time in seconds.
Step 2: Given: 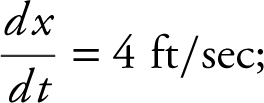 the man is 6 ft tall; distance between light and building = 100 ft. Find
the man is 6 ft tall; distance between light and building = 100 ft. Find 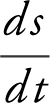 at x = 60.
at x = 60.
Step 3: (See Figure 9.1-4 .) Writing an equation using similar triangles, you have:
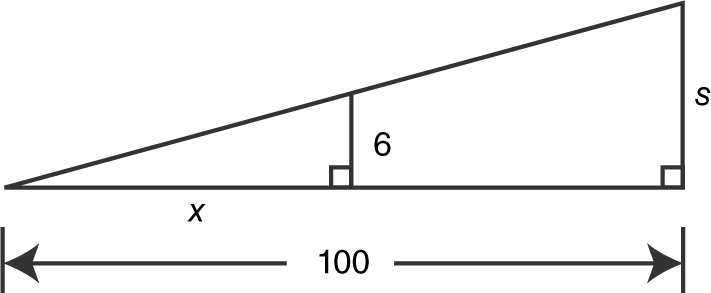
Figure 9.1-4
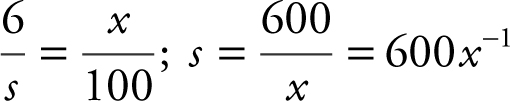
Step 4: Differentiate both sides of the equation with respect to t .
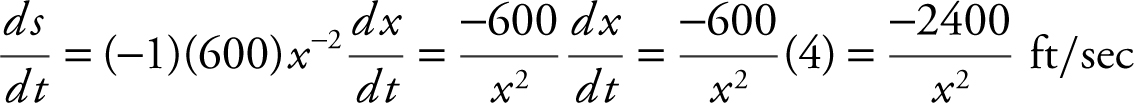
Step 5: Evaluate  at x = 60.
at x = 60.
Note: When the man is 40 ft from the building, x (distance from the light) is 60 ft.
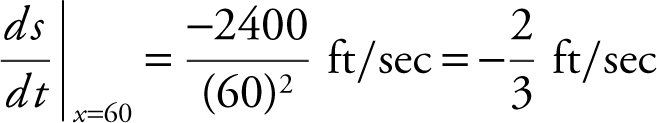
Step 6: The height of the man’s shadow on the building is changing at 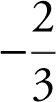 ft/sec.
ft/sec.

• Indicate units of measure, e.g., the velocity is 5 m/sec or the volume is 25 in3 .
Angle of Elevation Problem
A camera on the ground 200 meters away from a hot air balloon (also on the ground) records the balloon rising into the sky at a constant rate of 10 m/sec. How fast is the camera’s angle of elevation changing when the balloon is 150 m in the air? (See Figure 9.1-5 .)
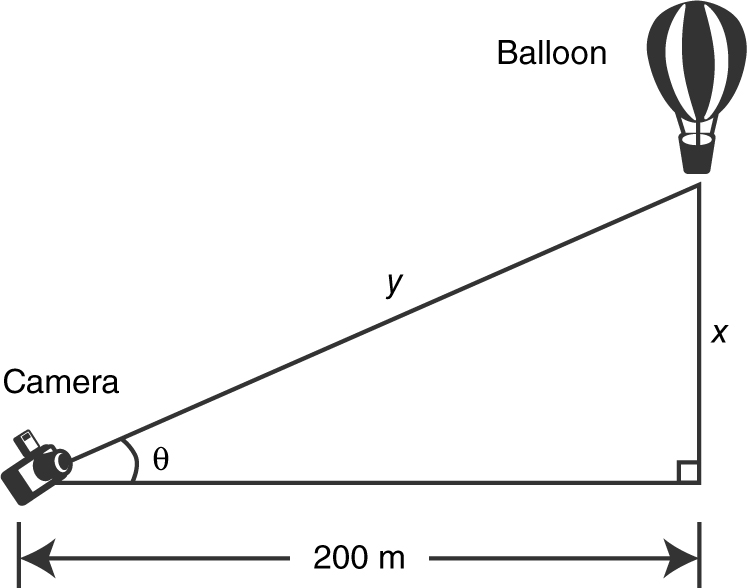
Figure 9.1-5
Step 1: Let x be the distance between the balloon and the ground; θ be the camera’s angle of elevation; and t be the time in seconds.
Step 2: Given: 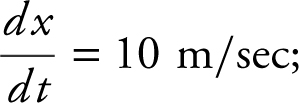 distance between camera and the point on the ground where the balloon took off is 200 m,
distance between camera and the point on the ground where the balloon took off is 200 m, 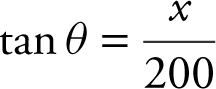 .
.
Step 3: Find 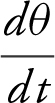 at x = 150 m.
at x = 150 m.
Step 4: Differentiate both sides with respect to t .
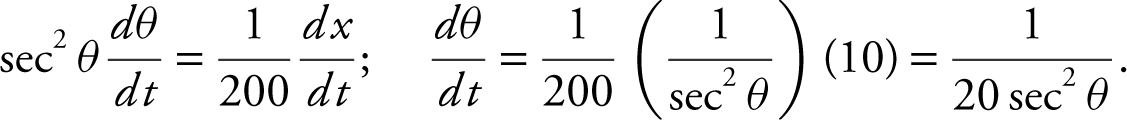 .
.
Step 5: 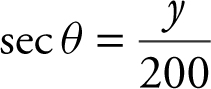 and at x = 150.
and at x = 150.

Since y > 0, then y = 250. Thus, sec 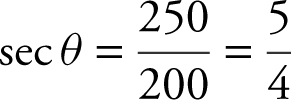 .
.
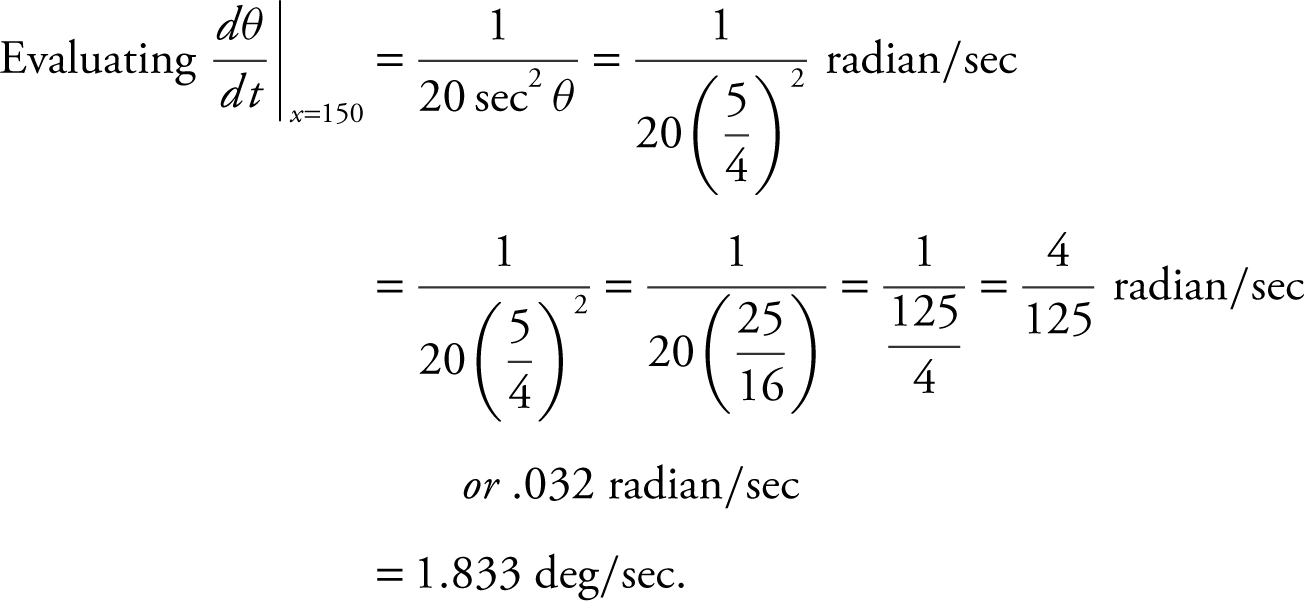
Step 6: The camera’s angle of elevation changes at approximately 1.833 deg/sec when the balloon is 150 m in the air.
9.2 Applied Maximum and Minimum Problems
Main Concepts: General Procedure for Solving Applied Maximum and Minimum Problems, Distance Problem, Area and Volume Problems, Business Problems

General Procedure for Solving Applied Maximum and Minimum Problems
Steps:
1. Read the problem carefully and if appropriate, draw a diagram.
2. Determine what is given and what is to be found, and represent these quantities by mathematical symbols.
3. Write an equation that is a function of the variable representing the quantity to be maximized or minimized.
4. If the equation involves other variables, reduce the equation to a single variable that represents the quantity to be maximized or minimized.
5. Determine the appropriate interval for the equation (i.e., the appropriate domain for the function) based on the information given in the problem.
6. Differentiate to obtain the first derivative and to find critical numbers.
7. Apply the First Derivative Test or the Second Derivative Test by finding the second derivative.
8. Check the function values at the endpoints of the interval.
9. Write the answer(s) to the problem and, if given, indicate the units of measure.
Distance Problem
Find the shortest distance between the point A (19, 0) and the parabola y = x 2 – 2x + 1.
Solution:
Step 1: Draw a diagram. (See Figure 9.2-1 .)
Figure 9.2-1
Step 2: Let P (x , y ) be the point on the parabola and let Z represent the distance between points P (x , y ) and A (19, 0).
Step 3: Using the distance formula,
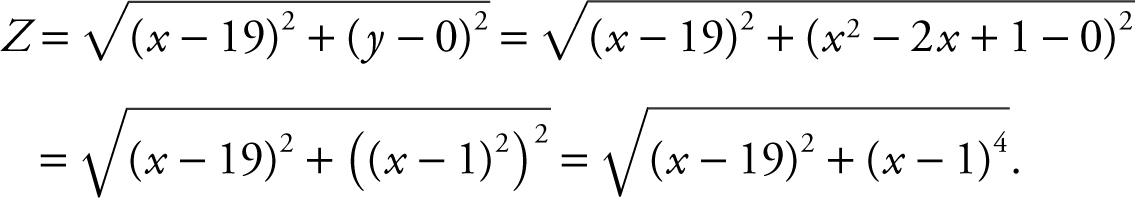
(Special case: In distance problems, the distance and the square of the distance have the same maximum and minimum points.) Thus, to simplify computations, let L = Z 2 = (x – 19)2 + (x – 1)4 . The domain of L is (–∞, ∞).
Step 4: Differentiate: 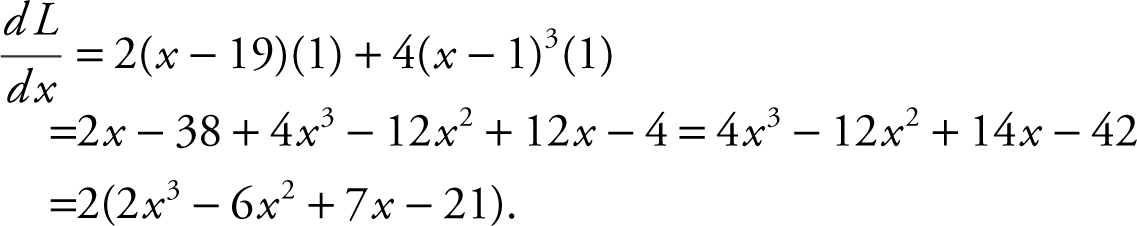
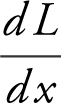 is defined for all real numbers.
is defined for all real numbers.
Set 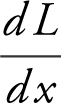 = 0; 2x 3 – 6x 2 + 7x – 21 = 0. The factors of 21 are ±1, ±3, ±7, and ± 21.
= 0; 2x 3 – 6x 2 + 7x – 21 = 0. The factors of 21 are ±1, ±3, ±7, and ± 21.
Using Synthetic Division, 2x 3 – 6x 2 + 7x – 21 = (x – 3)(2x 2 + 7) = 0 ⇒ x = 3.
Thus the only critical number is x = 3.
(Note: Step 4 could have been done using a graphing calculator.)
Step 5: Apply the First Derivative Test.
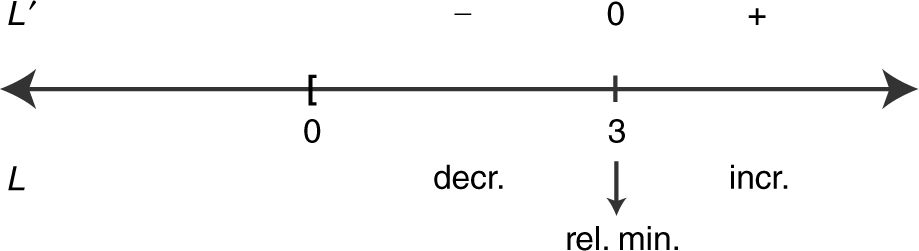
Step 6: Since x = 3 is the only relative minimum point in the interval, it is the absolute minimum.
Step 7: At x = 3, 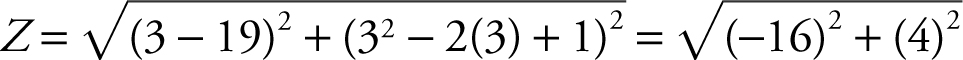
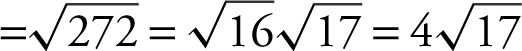 . Thus, the shortest distance is
. Thus, the shortest distance is ![]() .
.

• Simplify numeric or algebraic expressions only if the question asks you to do so.
Area and Volume Problems
Example Area Problem
The graph of 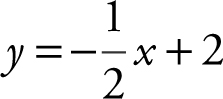 encloses a region with the x -axis and y -axis in the first quadrant. A rectangle in the enclosed region has a vertex at the origin and the opposite vertex on the graph of
encloses a region with the x -axis and y -axis in the first quadrant. A rectangle in the enclosed region has a vertex at the origin and the opposite vertex on the graph of 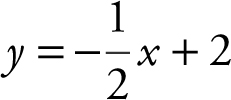 . Find the dimensions of the rectangle so that its area is a maximum.
. Find the dimensions of the rectangle so that its area is a maximum.
Solution:
Step 1: Draw a diagram. (See Figure 9.2-2 .)
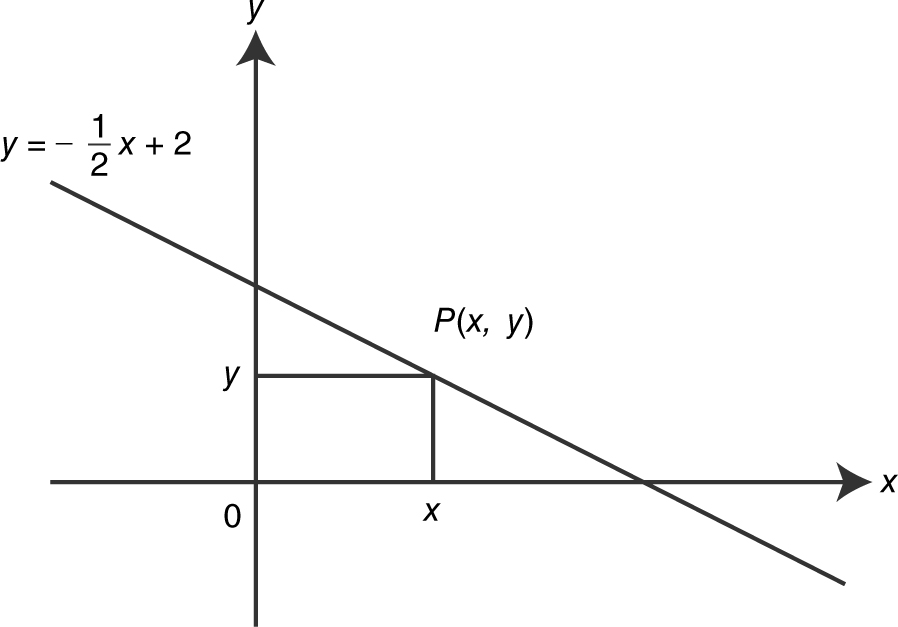
Figure 9.2-2
Step 2: Let P (x , y ) be the vertex of the rectangle on the graph of 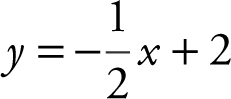 .
.
Step 3: Thus, the area of the rectangle is:
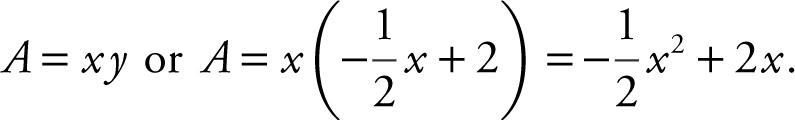
The domain of A is [0, 4].
Step 4: Differentiate:
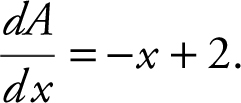
Step 5: 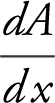 is defined for all real numbers.
is defined for all real numbers.
Set 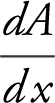 = 0 ⇒ –x + 2 = 0; x = 2.
= 0 ⇒ –x + 2 = 0; x = 2.
A (x ) has one critical number x = 2.
Step 6: Apply the Second Derivative Test:
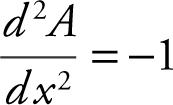 ⇒ A (x ) has a relative maximum point at x = 2; A (2) = 2.
⇒ A (x ) has a relative maximum point at x = 2; A (2) = 2.
Since x = 2 is the only relative maximum, it is the absolute maximum. (Note that at the endpoints: A (0) = 0 and A (4) = 0.)
Step 7: At x = 2, 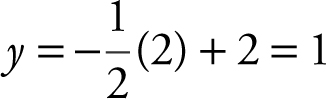 .
.
Therefore, the length of the rectangle is 2, and its width is 1.
Example Volume Problem (with calculator)
If an open box is to be made using a square sheet of tin, 20 inches by 20 inches, by cutting a square from each corner and folding the sides up, find the length of a side of the square being cut so that the box will have a maximum volume.
Solution:
Step 1: Draw a diagram. (See Figure 9.2-3 .)
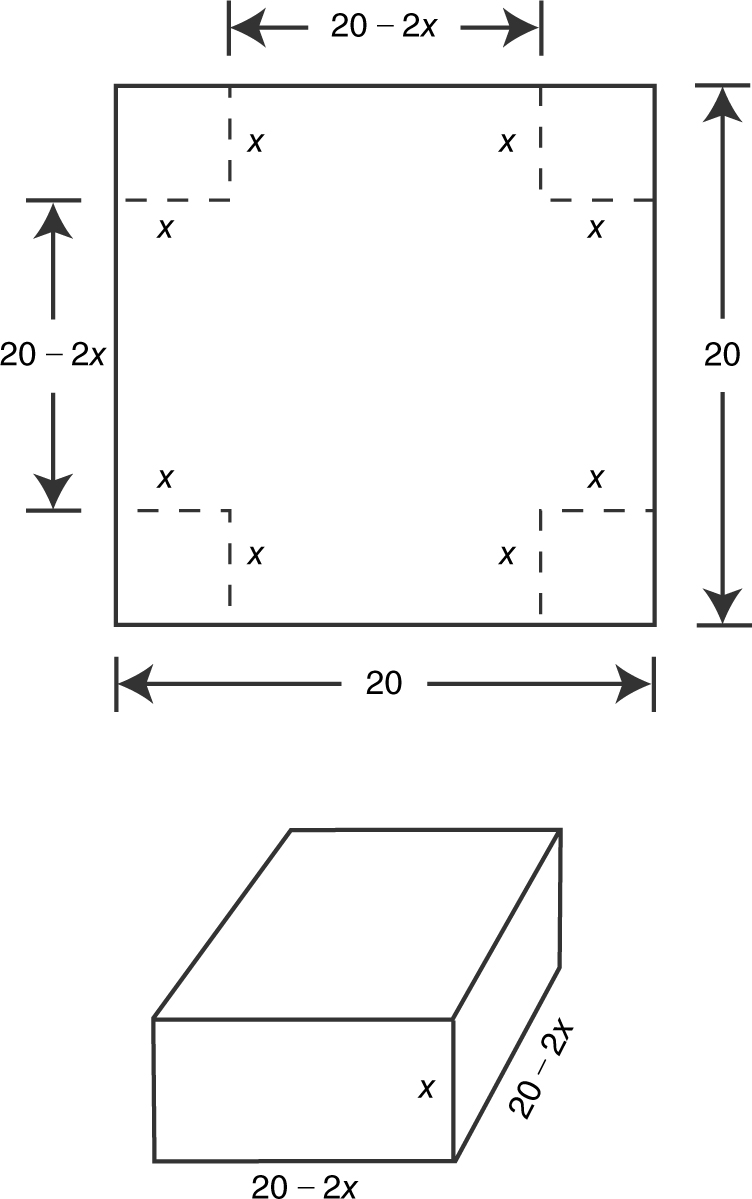
Figure 9.2-3
Step 2: Let x be the length of a side of the square to be cut from each corner.
Step 3: The volume of the box is V (x ) = x (20 – 2x )(20 – 2x ).
The domain of V is [0, 10].
Step 4: Differentiate V (x ).
Enter d (x ∗ (20 – 2x ) ∗ (20 – 2x ), x ) and we have 4(x – 10)(3x – 10).
Step 5: V ′(x ) is defined for all real numbers:
Set V ′(x ) = 0 by entering: [Solve ] (4(x – 10)(3x – 10) = 0, x ), and obtain x = 10 or 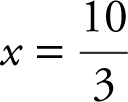 . The critical numbers of V (x ) are x = 10 and
. The critical numbers of V (x ) are x = 10 and 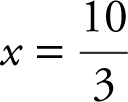 . V (10) = 0 and
. V (10) = 0 and 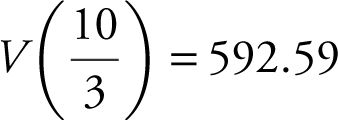 . Since V (10) = 0, you need to test only
. Since V (10) = 0, you need to test only 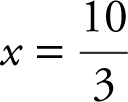 .
.
Step 6: Using the Second Derivative Test, enter d (x ∗ (20 – 2x ) ∗ (20 – 2x ), x ,2)|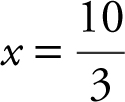 and obtain –80. Thus,
and obtain –80. Thus, 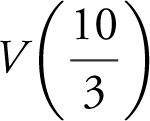 is a relative maximum. Since it is the only relative maximum on the interval, it is the absolute maximum. (Note at the other endpoint x = 0, V (0) = 0.)
is a relative maximum. Since it is the only relative maximum on the interval, it is the absolute maximum. (Note at the other endpoint x = 0, V (0) = 0.)
Step 7: Therefore, the length of a side of the square to be cut is 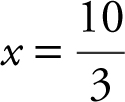 .
.

• The formula for the average value of a function f from x = a to x = b is 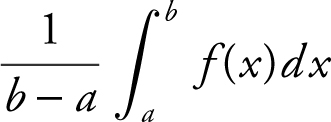 .
.
Business Problems
Summary of Formulas
1. P = R – C : Profit = Revenue – Cost
2. R = xp : Revenue = (Units Sold)(Price Per Unit)
3. 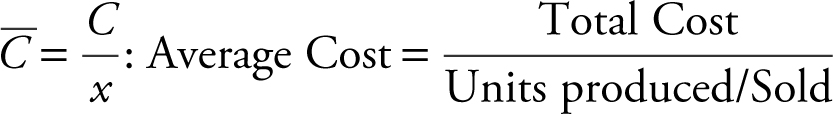 Average
Average
4. 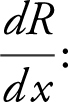 Marginal Revenue ≈ Revenue from selling one more unit
Marginal Revenue ≈ Revenue from selling one more unit
5. 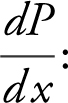 Marginal Profit ≈ Profit from selling one more unit
Marginal Profit ≈ Profit from selling one more unit
6. 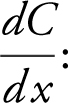 Marginal Cost ≈ Cost of producing one more unit
Marginal Cost ≈ Cost of producing one more unit
Example 1
Given the cost function C (x ) = 100 + 8x + 0.1x 2 , (a) find the marginal cost when x = 50; and (b) find the marginal profit at x = 50, if the price per unit is $20.
Solution:
(a) Marginal cost is C ′(x ). Enter d (100 + 8x + 0.1x 2 , x )|x = 50 and obtain $18.
(b) Marginal profit is P ′(x )
P = R – C
P = 20x – (100 + 8x + 0.1x 2 ). Enter d (20x – (100 + 8x + 0.1x ∧ 2, x )|x = 50 and obtain 2.

• Carry all decimal places and round only at the final answer. Round to 3 decimal places unless the question indicates otherwise.
Example 2
Given the cost function C (x ) = 500 + 3x + 0.01x 2 and the demand function (the price function) p (x ) = 10, find the number of units produced in order to have maximum profit.
Solution:
Step 1: Write an equation.
Profit = Revenue – Cost
P = R – C
Revenue = (Units Sold)(Price Per Unit)
R = xp (x ) = x (10) = 10x
P = 10x – (500 + 3x + 0.01x 2 )
Step 2: Differentiate.
Enter d (10x – (500 + 3x + 0.01x ∧ 2, x )) and obtain 7 – 0.02x .
Step 3: Find critical numbers.
Set 7 – 0.02x = 0 ⇒ x = 350.
Critical number is x = 350.
Step 4: Apply Second Derivative Test.
Enter d (10x – (500 + 3x + 0.01x ∧ 2), x , 2)|x = 350 and obtain –0.02.
Since x = 350 is the only relative maximum, it is the absolute maximum.
Step 5: Write a solution.
Thus, producing 350 units will lead to maximum profit.
9.3 Rapid Review
1. Find the instantaneous rate of change at x = 5 of the function 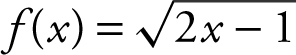 .
.
Answer: 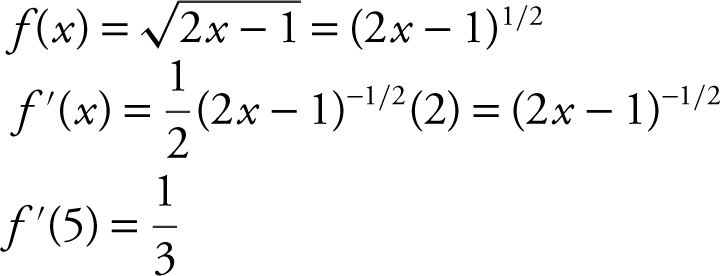
2. If h is the diameter of a circle and h is increasing at a constant rate of 0.1 cm/sec, find the rate of change of the area of the circle when the diameter is 4 cm.
Answer: 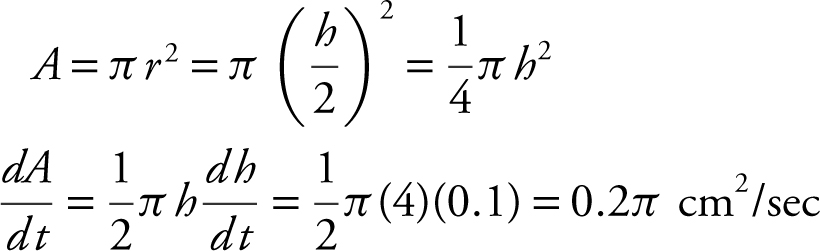
3. The radius of a sphere is increasing at a constant rate of 2 inches per minute. In terms of the surface area, what is the rate of change of the volume of the sphere?
Answer: 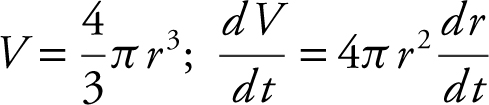 since
since 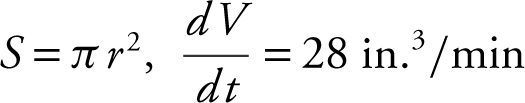
4. Using your calculator, find the shortest distance between the point (4, 0) and the line y = x . (See Figure 9.3-1 .)
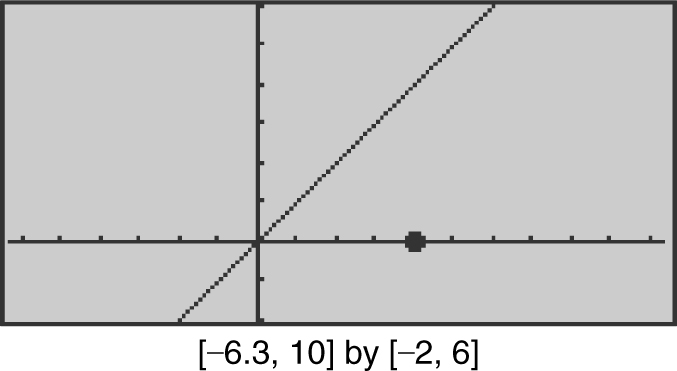
Figure 9.3-1
Answer:
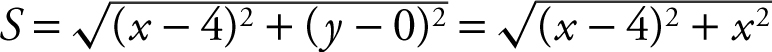
Enter 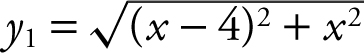
Use the [Zero ] function for y 2 and obtain x = 2. Note that when x < 2, y 2 < 0 which means y 1 is decreasing and when x > 2, y 2 > 0 which means y 1 is increasing and thus at x = 2, y 1 is a minimum. Use the [Value ] function for y 1 at x = 2 and obtain y 1 = 2.82843. Thus, the shortest distance is approximately 2.828.
9.4 Practice Problems
Part A—The use of a calculator is not allowed.
1 . A spherical balloon is being inflated. Find the volume of the balloon at the instant when the rate of increase of the surface area is eight times the rate of increase of the radius of the sphere.
2 . A 13-foot ladder is leaning against a wall. If the top of the ladder is sliding down the wall at 2 ft/sec, how fast is the bottom of the ladder moving away from the wall when the top of the ladder is 5 feet from the ground? (See Figure 9.4-1 .)
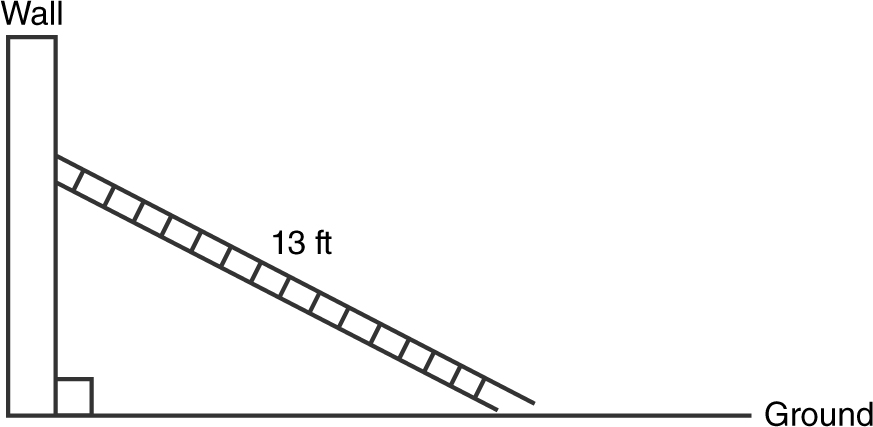
Figure 9.4-1
3 . Air is being pumped into a spherical balloon at the rate of 100 cm3 /sec. How fast is the diameter increasing when the radius is 5 cm?
4 . A woman 5 feet tall is walking away from a streetlight hung 20 feet from the ground at the rate of 6 ft/sec. How fast is her shadow lengthening?
5 . A water tank in the shape of an inverted cone has a height of 18 feet and a base radius of 12 feet. If the tank is full and the water is drained at the rate of 4 ft3 /min, how fast is the water level dropping when the water level is 6 feet high?
6 . Two cars leave an intersection at the same time. The first car is going due east at the rate of 40 mph and the second is going due south at the rate of 30 mph. How fast is the distance between the two cars increasing when the first car is 120 miles from the intersection?
7 . If the perimeter of an isosceles triangle is 18 cm, find the maximum area of the triangle.
8 . Find a number in the interval (0, 2) such that the sum of the number and its reciprocal is the absolute minimum.
9 . An open box is to be made using a piece of cardboard 8 cm by 15 cm by cutting a square from each corner and folding the sides up. Find the length of a side of the square being cut so that the box will have a maximum volume.
10 . What is the shortest distance between the point 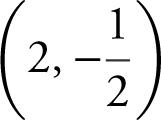 and the parabola y = –x 2 ?
and the parabola y = –x 2 ?
11 . If the cost function is C (x ) = 3x 2 + 5x + 12, find the value of x such that the average cost is a minimum.
12 . A man with 200 meters of fence plans to enclose a rectangular piece of land using a river on one side and a fence on the other three sides. Find the maximum area that the man can obtain.
Part B—Calculators are allowed.
13 . A trough is 10 meters long and 4 meters wide. (See Figure 9.4-2 .) The two sides of the trough are equilateral triangles. Water is pumped into the trough at 1 m3 /min. How fast is the water level rising when the water is 2 meters high?
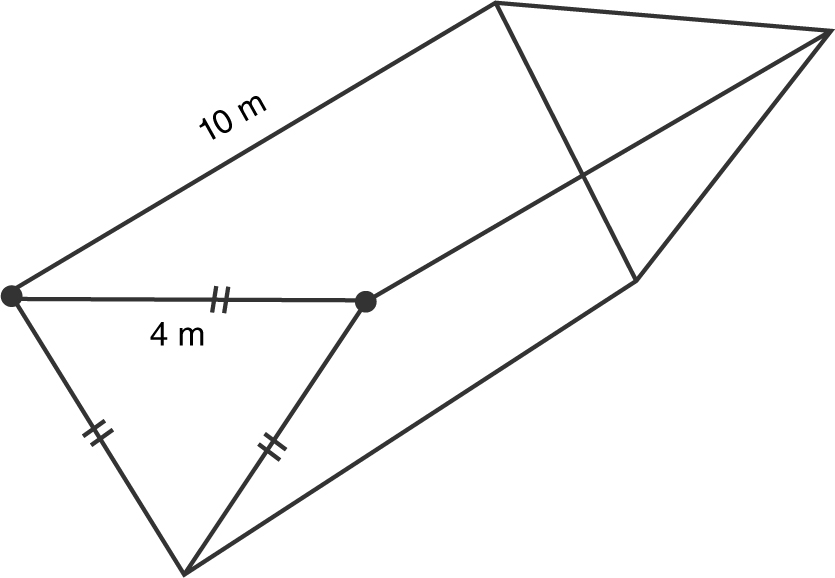
Figure 9.4-2
14 . A rocket is sent vertically up in the air with the position function s = 100t 2 where s is measured in meters and t in seconds. A camera 3000 m away is recording the rocket. Find the rate of change of the angle of elevation of the camera 5 sec after the rocket went up.
15 . A plane lifts off from a runway at an angle of 20°. If the speed of the plane is 300 mph, how fast is the plane gaining altitude?
16 . Two water containers are being used. (See Figure 9.4-3 .)
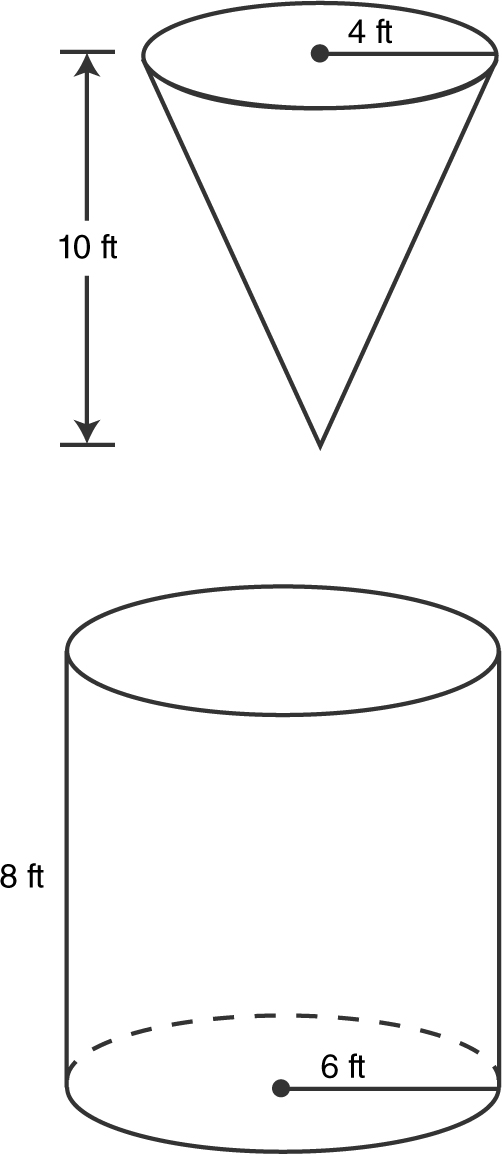
Figure 9.4-3
One container is in the form of an inverted right circular cone with a height of 10 feet and a radius at the base of 4 feet. The other container is a right circular cylinder with a radius of 6 feet and a height of 8 feet. If water is being drained from the conical container into the cylindrical container at the rate of 15 ft3 /min, how fast is the water level falling in the conical tank when the water level in the conical tank is 5 feet high? How fast is the water level rising in the cylindrical container?
17 . The wall of a building has a parallel fence that is 6 feet high and 8 feet from the wall. What is the length of the shortest ladder that passes over the fence and leans on the wall? (See Figure 9.4-4 .)
18 . Given the cost function C(x ) = 2500 + 0.02x + 0.004x 2 , find the product level such that the average cost per unit is a minimum.
19 . Find the maximum area of a rectangle inscribed in an ellipse whose equation is 4x 2 + 25y 2 = 100.
20 . A right triangle is in the first quadrant with a vertex at the origin and the other two vertices on the x – and y -axes. If the hypotenuse passes through the point (0.5, 4), find the vertices of the triangle so that the length of the hypotenuse is the shortest possible length.
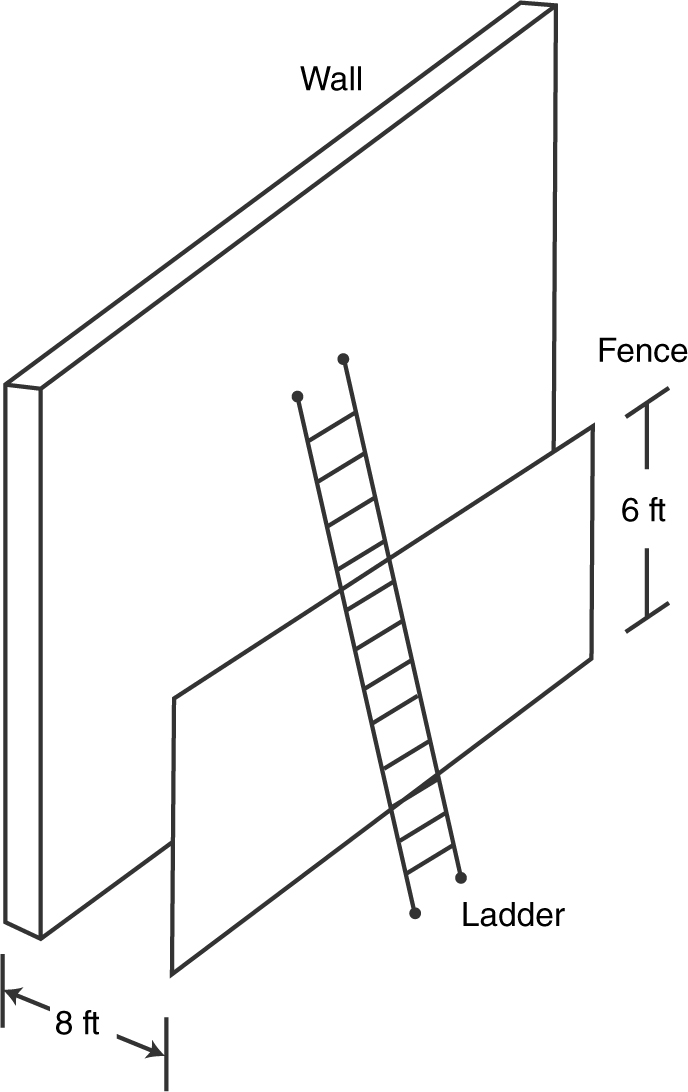
Figure 9.4-4
9.5 Cumulative Review Problems
(Calculator) indicates that calculators are permitted.
21 . If y = sin2 (cos(6x – 1)), find 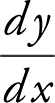 .
.
22 . Evaluate 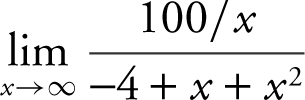 .
.
23 . The graph of f ′ is shown in Figure 9.5-1 . Find where the function f : (a) has its relative extrema or absolute extrema; (b) is increasing or decreasing; (c) has its point(s) of inflection; (d) is concave upward or downward; and (e) if f (3) = –2, draw a possible sketch of f .
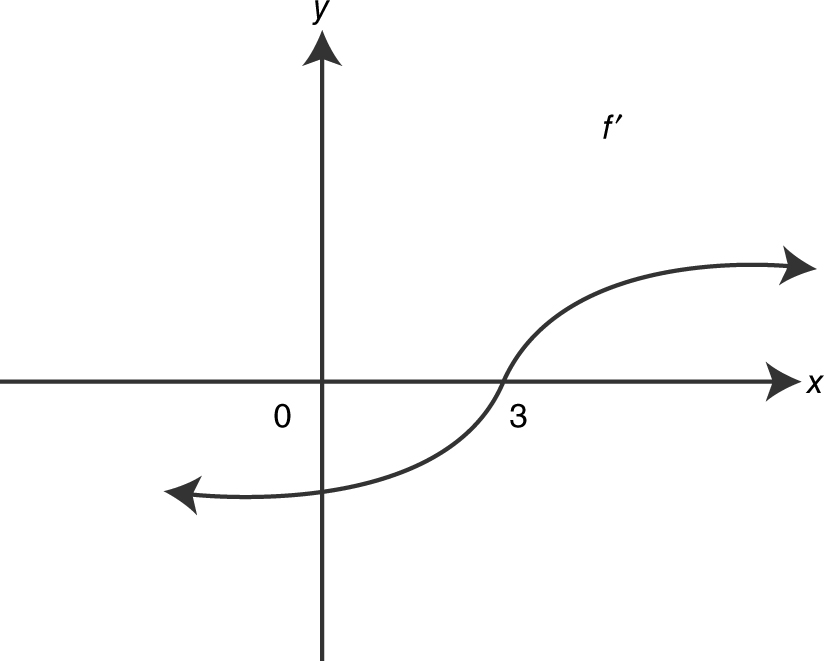
Figure 9.5-1
24 . (Calculator) At what value(s) of x does the tangent to the curve x 2 + y 2 = 36 have a slope of –1?
25 . (Calculator) Find the shortest distance between the point (1, 0) and the curve y = x 3 .
9.6 Solutions to Practice Problems
Part A—The use of a calculator is not allowed .
1 . Volume: 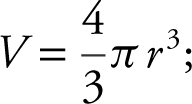
Surface Area: 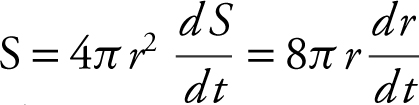 .
.
Since 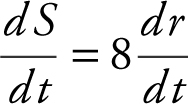 ,
,
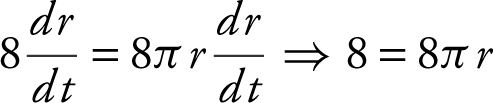
or 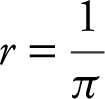
At 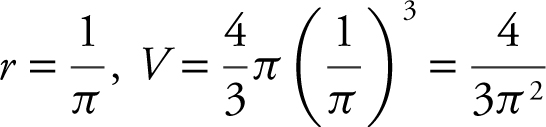 cubic units.
cubic units.
2 . Pythagorean Theorem yields x 2 + y 2 = (13)2 .
Differentiate: 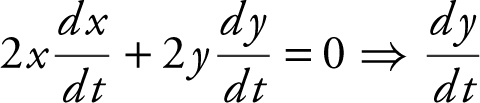
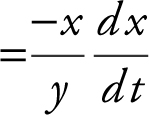 .
.
At x = 5, (5)2 + y 2 = 132 ⇒ y = ± 12, since y > 0, y = 12.
Therefore, 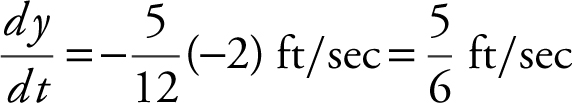 . The ladder is moving away from the wall at
. The ladder is moving away from the wall at 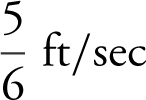 when the top of the ladder is 5 feet from the ground.
when the top of the ladder is 5 feet from the ground.
3 . Volume of a sphere is 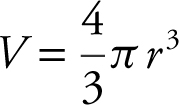
Differentiate: 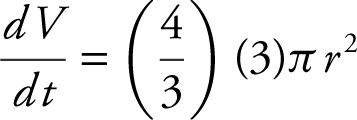
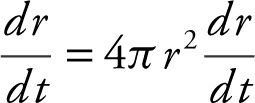 .
.
Substitute: 100 = 4π(5)2 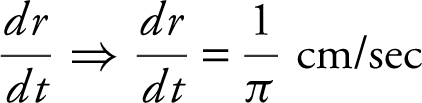 .
.
Let x be the diameter. Since 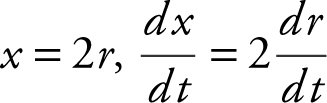 .
.
Thus, 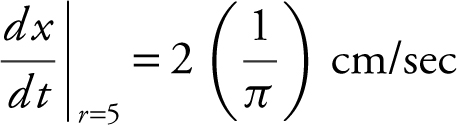
= 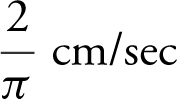 . The diameter is increasing at
. The diameter is increasing at 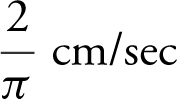 when the radius is 5 cm.
when the radius is 5 cm.
4 . (See Figure 9.6-1 .) Using similar triangles, with y the length of the shadow you have:
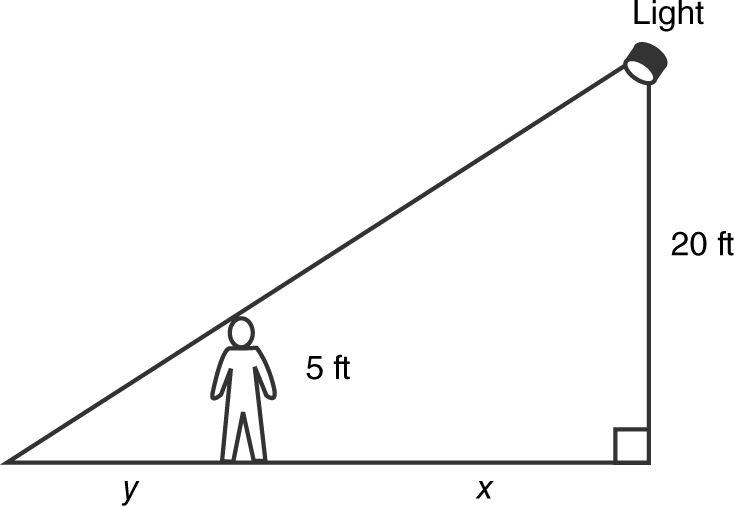
Figure 9.6-1
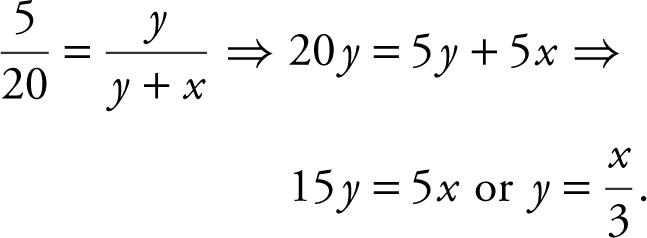
Differentiate:
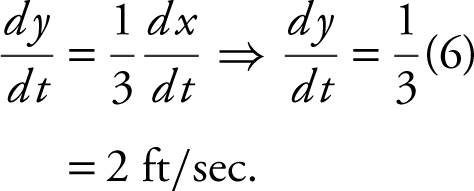
5 . (See Figure 9.6-2 .) Volume of a cone
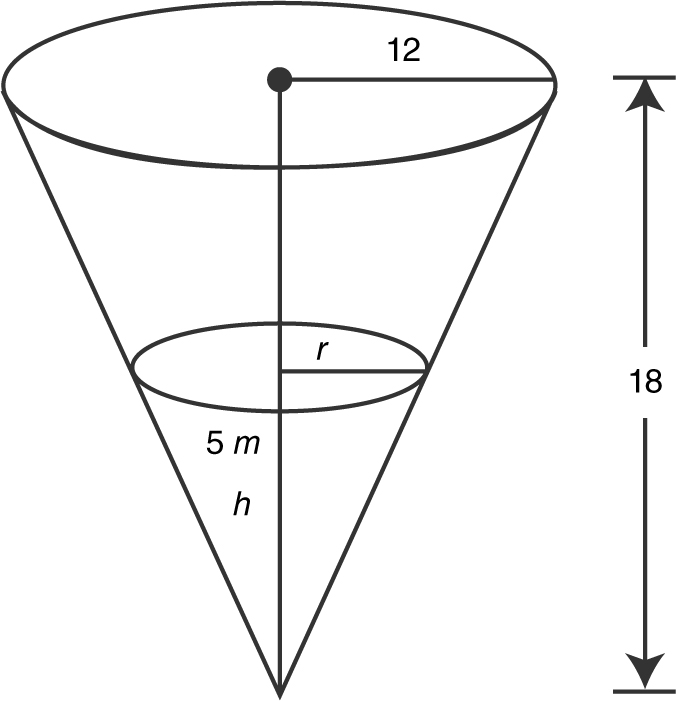
Figure 9.6-2
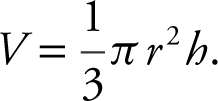 .
.
Using similar triangles, you have
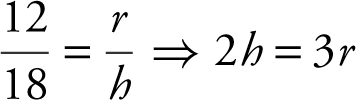 or
or 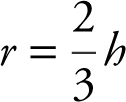 , thus
, thus
reducing the equation to
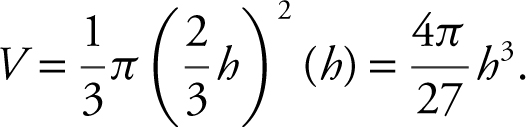
Differentiate: 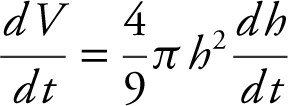 .
.
Substituting known values:
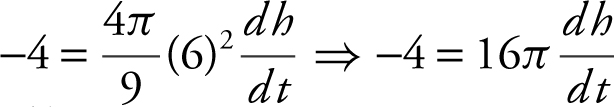 or
or 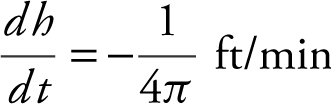 . The water level is dropping at
. The water level is dropping at 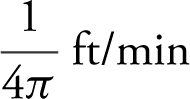 when h = 6 ft.
when h = 6 ft.
6 . (See Figure 9.6-3 .)
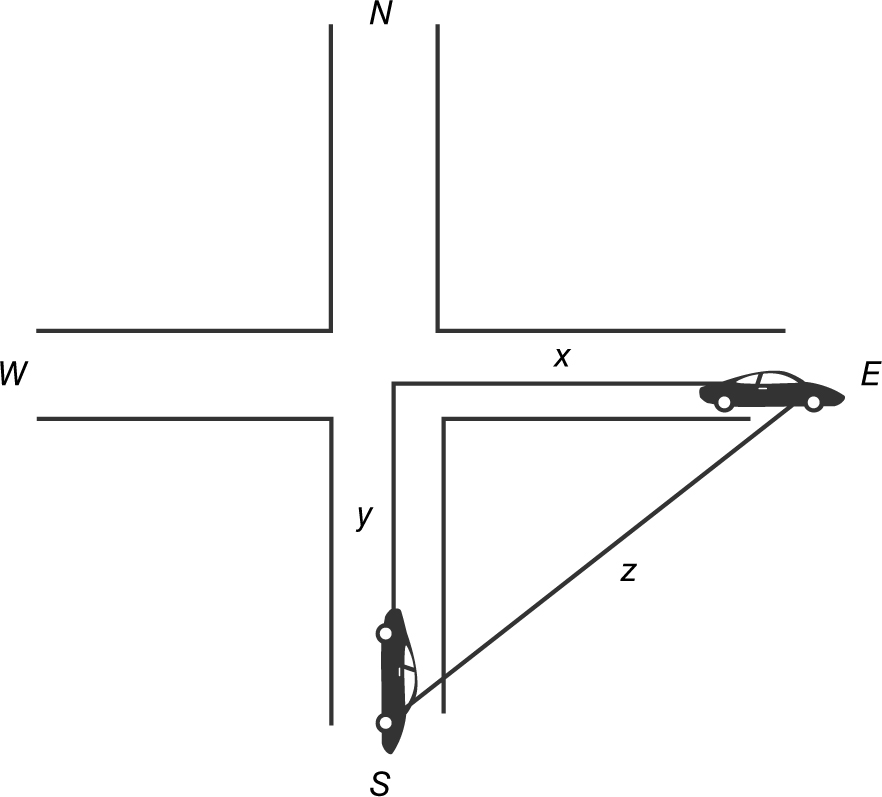
Figure 9.6-3
Step 1: Using the Pythagorean Theorem, you have x 2 + y 2 = z 2 . You also have 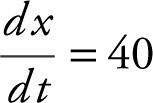 and
and 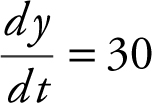 .
.
Step 2: Differentiate: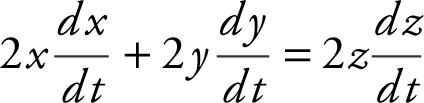 .
.
At x = 120, both cars have traveled 3 hours and thus, y = 3(30) = 90. By the Pythagorean Theorem, (120)2 + (90)2 = z 2 ⇒ z = 150.
Step 3: Substitute all known values into the equation:
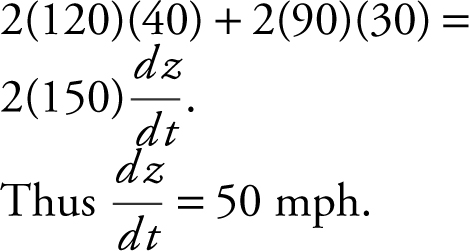
Step 4: The distance between the two cars is increasing at 50 mph at x = 120.
7 . (See Figure 9.6-4 .)
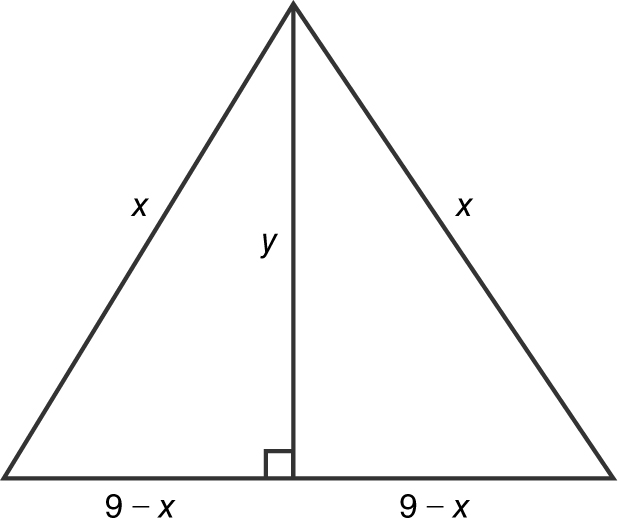
Figure 9.6-4
Step 1: Applying the Pythagorean
Theorem, you have x 2 = y 2 + (9 – x )2 ⇒ y 2 = x 2 – (9 – x )2 = x 2 – 81 – 18x + x 2 = 18x – 81 = 9(2x – 9), or 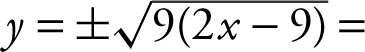
![]() since y < 0,
since y < 0, 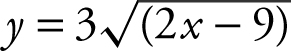 .
.
The area of the triangle 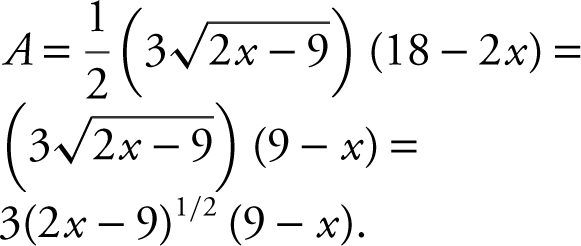
Step 2: 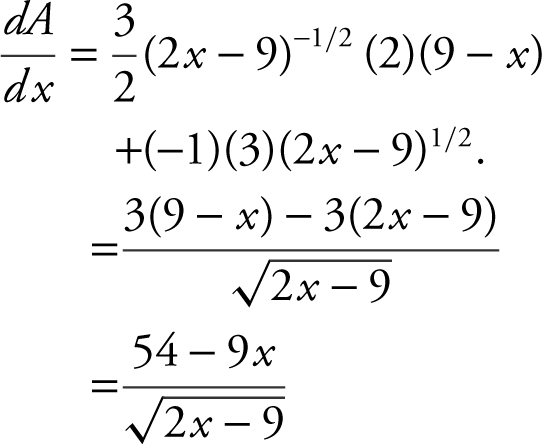
Step 3: Set 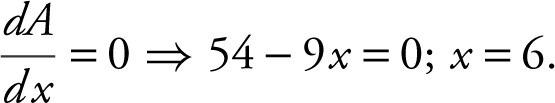
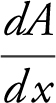 is undefined at
is undefined at 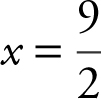 critical numbers are
critical numbers are ![]() and 6.
and 6.
Step 4: First Derivative Test:
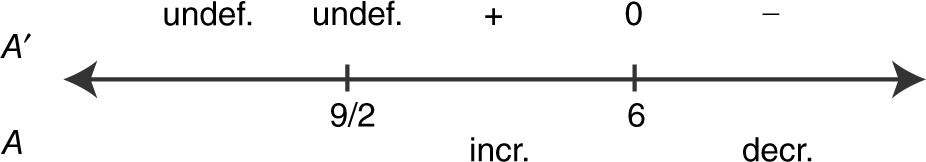
Thus at x = 6, the area A is a relative maximum.
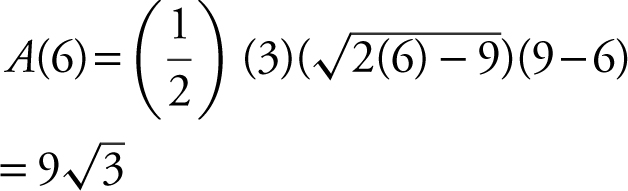
Step 5: Check endpoints. The domain of A is [9/2, 9]. A (9/2) = 0; and A (9) = 0. Therefore, the maximum area of an isosceles triangle with the perimeter of 18 cm is 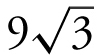 cm2 . (Note that at x = 6, the triangle is an equilateral triangle.)
cm2 . (Note that at x = 6, the triangle is an equilateral triangle.)
8 . Step 1: Let x be the number and ![]() be its
be its
Step 2: 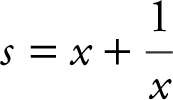 with 0 < x < 2.
with 0 < x < 2.
Step 3: 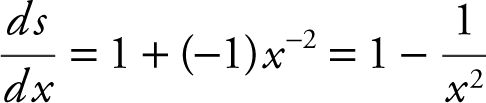
Step 4: Set 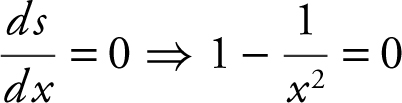 ⇒ x = ±1, since the domain is (0, 2), thus x = 1.
⇒ x = ±1, since the domain is (0, 2), thus x = 1. 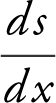 is defined for all x in (0, 2). Critical number is x = 1.
is defined for all x in (0, 2). Critical number is x = 1.
Step 5: Second Derivative Test: 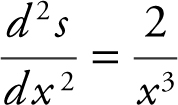 and
and 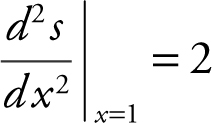 . Thus at x = 1, s is a relative minimum. Since it is the only relative extremum, at x = 1, it is the absolute minimum.
. Thus at x = 1, s is a relative minimum. Since it is the only relative extremum, at x = 1, it is the absolute minimum.
9 . (See Figure 9.6-5 .)
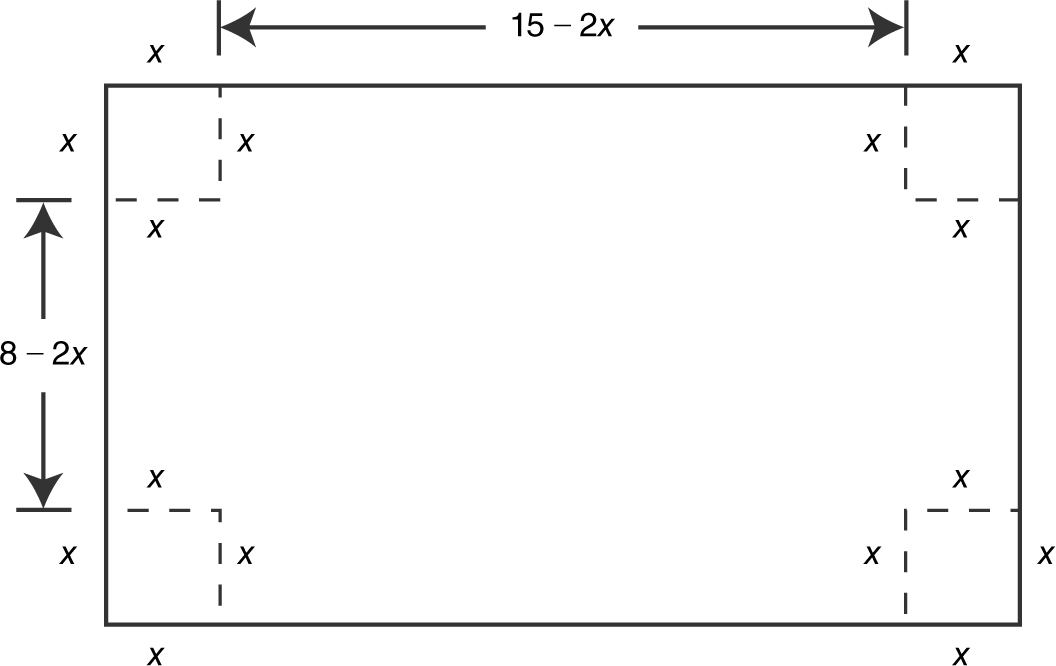
Figure 9.6-5
Step 1: Volume: V = x (8 – 2x )(15 – 2x ) with 0 ≤ x ≤ 4.
Step 2: Differentiate: Rewrite as V = 4x 3 – 46x 2 + 120x
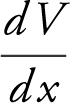 = 12x 2 – 92x + 120.
= 12x 2 – 92x + 120.
Step 3: Set V = 0 ⇒ 12x 2 – 92x + 120 = 0 ⇒ 3x 2 – 23x + 30 = 0. Using the quadratic formula, you have x = 6 or 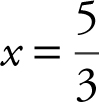 and
and 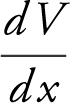 is defined for all real numbers.
is defined for all real numbers.
Step 4: Second Derivative Test:
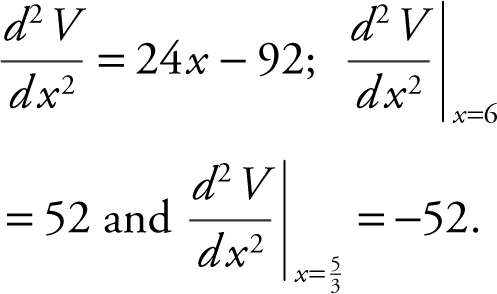 .
.
Thus, 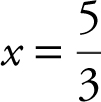 is a relative maximum.
is a relative maximum.
Step 5: Check endpoints.
At x = 0, V = 0 and at x = 4, V = 0. Therefore, at 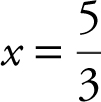 , V is the absolute maximum.
, V is the absolute maximum.
10 . (See Figure 9.6-6 .)
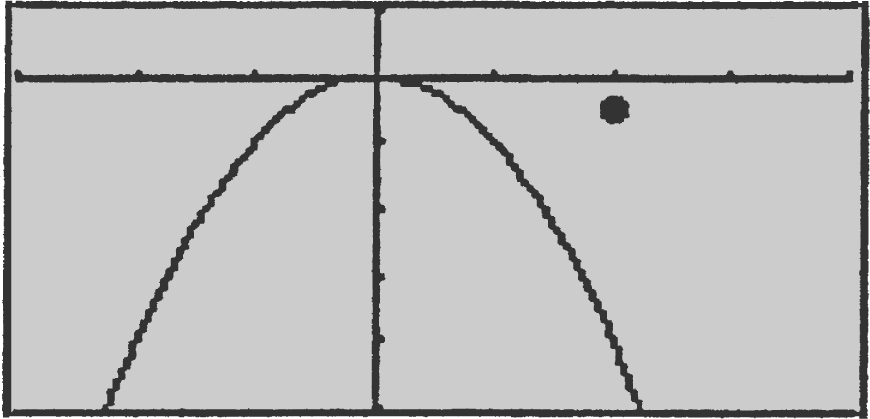
Figure 9.6-6
Step 1: Distance Formula:
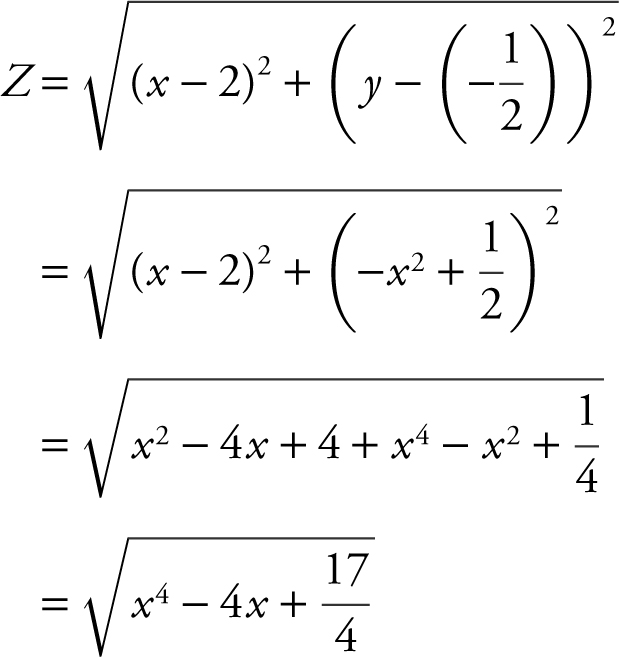
Step 2: Let S = Z 2 , since S and Z have the same maximums and minimums.
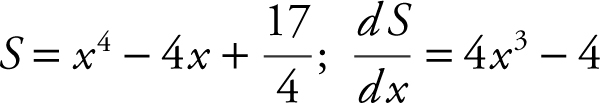
Step 3: Set 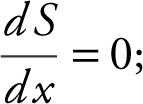 x = 1 and
x = 1 and 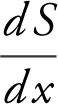 is defined for all real numbers.
is defined for all real numbers.
Step 4: Second Derivative Test:
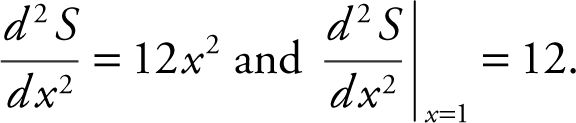
Thus at x = 1, Z has a minimum, and since it is the only relative extremum, it is the absolute minimum.
Step 5: At x = 1,
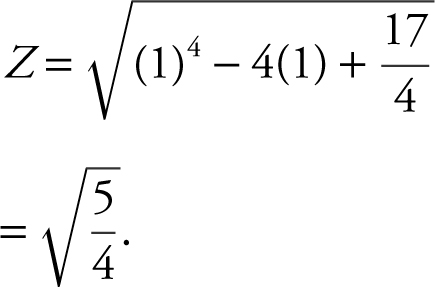
Therefore, the shortest distance is
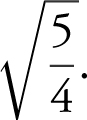
11 . Step 1: Average Cost:
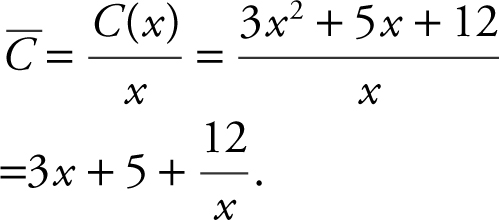
Step 2: 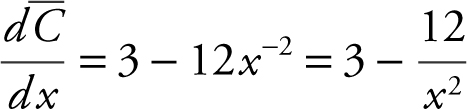
Step 3: Set 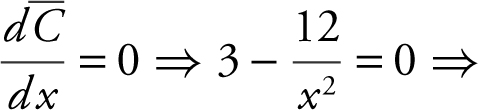
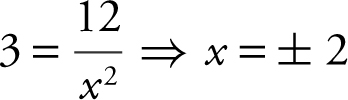 Since x > 0, x = 2 and
Since x > 0, x = 2 and 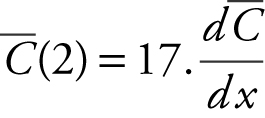 is undefined at x = 0 which is not in the domain.
is undefined at x = 0 which is not in the domain.
Step 4: Second Derivative Test:
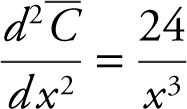 and
and 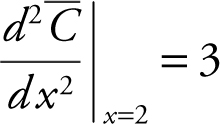
Thus at x = 2, the average cost is a minimum.
12 . (See Figure 9.6-7 .)
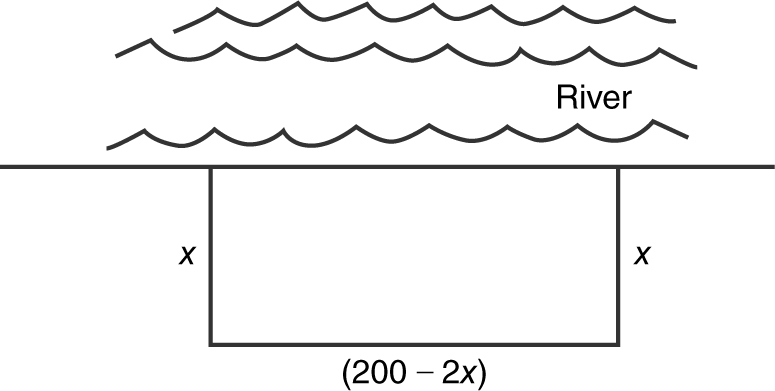
Figure 9.6-7
Step 1: Area:
A = x (200 – 2x ) = 200x – 2x 2 with 0 ≤ x ≤ 100.
Step 2: A ′(x ) = 200 – 4x
Step 3: Set A ′(x ) = 0 ⇒ 200 – 4x = 0; x = 50.
Step 4: Second Derivative Test:
A ″(x ) = –4; thus at x = 50, the area is a relative maximum. A (50) = 5000 m2 .
Step 5: Check endpoints.
A (0) = 0 and A (100) = 0; therefore at x = 50, the area is the absolute maximum and 5000 m2 is the maximum area.
Part B—Calculators are allowed.
13 .
Step 1: Let h be the height of the trough and 4 be a side of one of the two equilateral triangles. Thus, in a 30–60 right triangle, ![]() .
.
Step 2: Volume:
V = (area of the triangle) · 10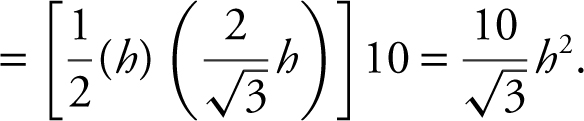 .
.
Step 3: Differentiate with respect to t .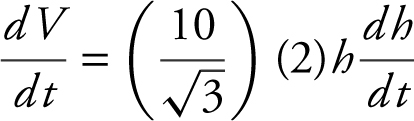
Step 4: Substitute known values: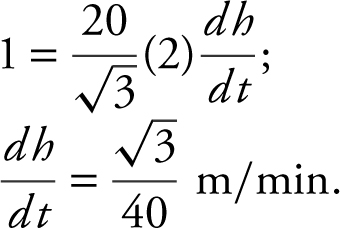
The water level is rising 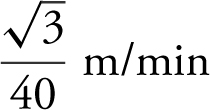 when the water level is 2 m high.
when the water level is 2 m high.
14 . (See Figure 9.6-8 .)
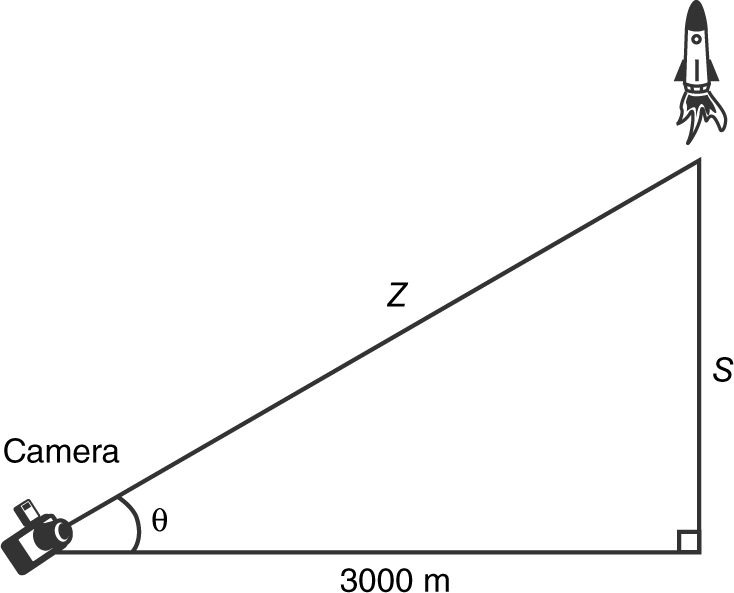
Figure 9.6-8
Step 1: tan θ = S /3000
Step 2: Differentiate with respect to t .
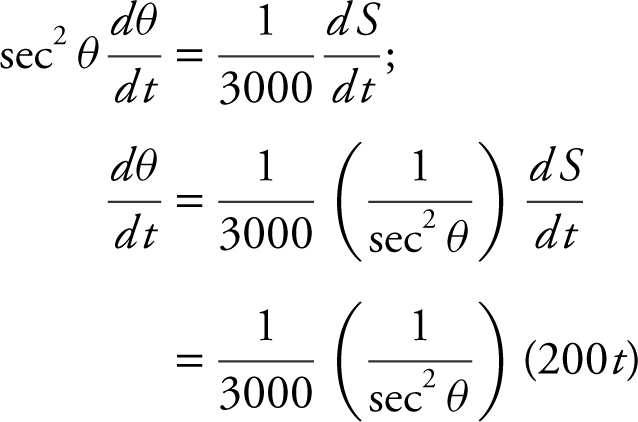
Step 3: At t = 5; S = 100(5)2 = 2500; Thus, Z 2 = (3000)2 + (2500)2 = 15,250,000. Therefore, ![]() , since Z > 0,
, since Z > 0, ![]() . Substitute known values into the equation:
. Substitute known values into the equation:
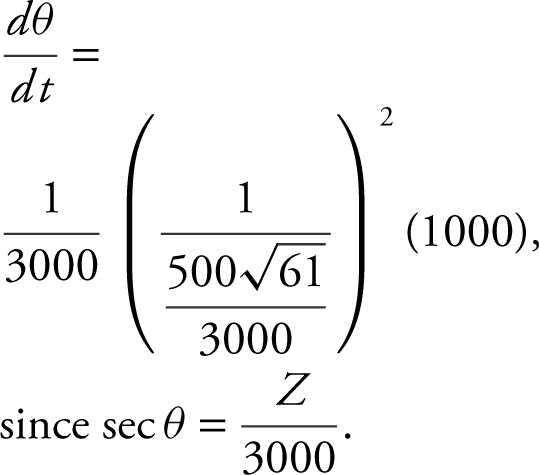
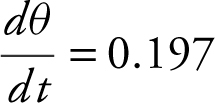 radian/sec. The angle of elevation is changing at 0.197 radian/sec, 5 seconds after liftoff.
radian/sec. The angle of elevation is changing at 0.197 radian/sec, 5 seconds after liftoff.
15 . (See Figure 9.6-9 .)
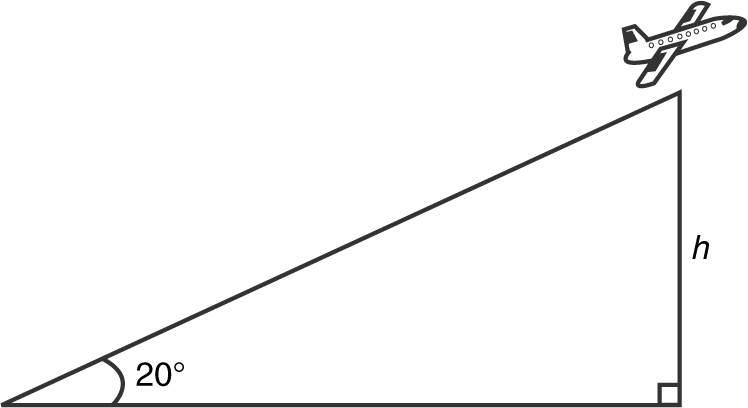
Figure 9.6-9
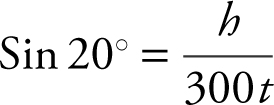
h = (sin 20°)(300)t ; 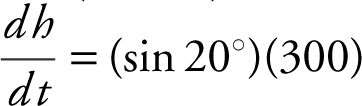 ≈ 102.606 mph. The plane is gaining altitude at 102.606 mph.
≈ 102.606 mph. The plane is gaining altitude at 102.606 mph.
16 . 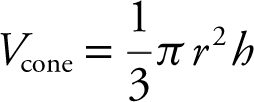
Similar triangles: 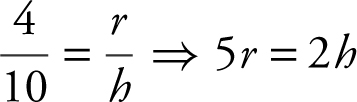 or
or
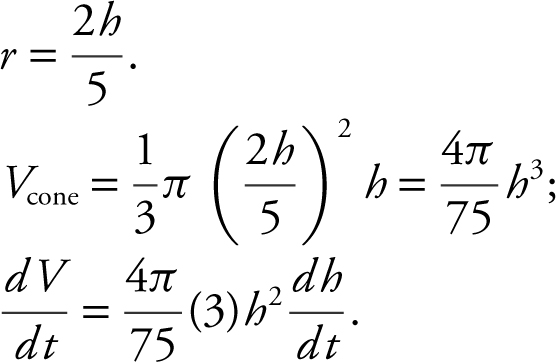
Substitute known values:
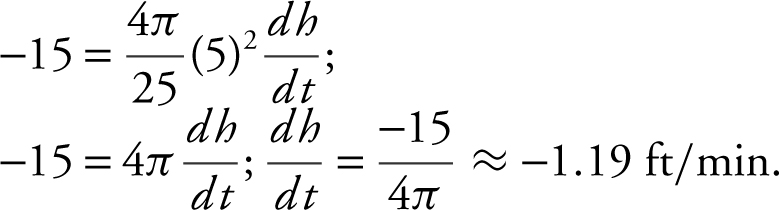
The water level in the cone is falling at
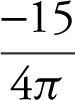 ft/min ≈ 1.19 ft/min when the water level is 5 feet high.
ft/min ≈ 1.19 ft/min when the water level is 5 feet high.
Vcylinder = π R2 H = π(6)2H = 36πH .
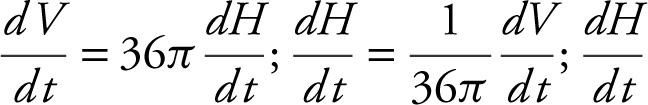
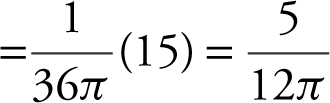 ft/min ≈ 0.1326 ft/min or 1.592 in/min.
ft/min ≈ 0.1326 ft/min or 1.592 in/min.
The water level in the cylinder is rising at 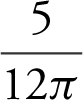 ft/min = 0.133 ft/min.
ft/min = 0.133 ft/min.
17 . Step 1: Let x be the distance of the foot of the ladder from the higher wall. Let y be the height of the point where the ladder touches the higher wall. The slope of the ladder is 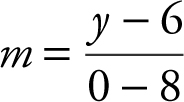 or
or 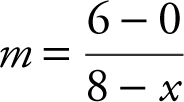 .
.
Thus,
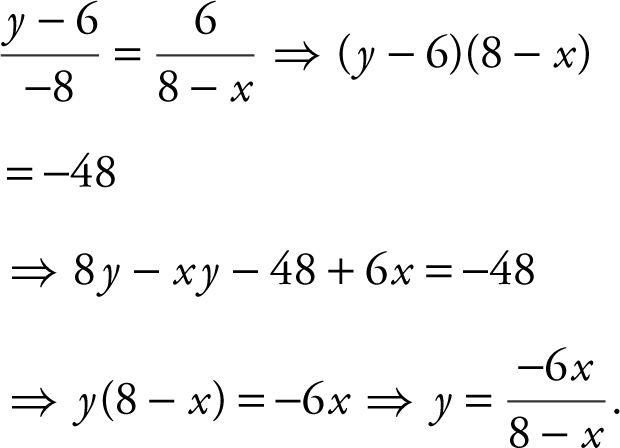
Step 2: Pythagorean Theorem:
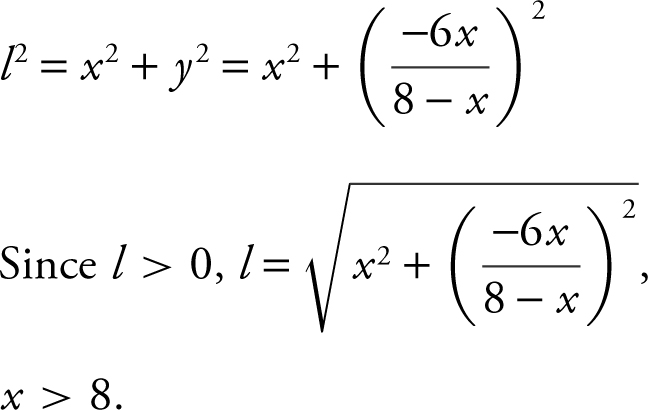
Step 3: Enter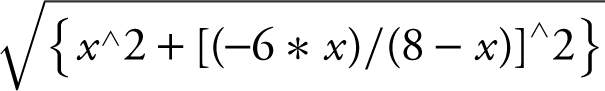
The graph of y 1 is continuous on the interval x > 8. Use the [Minimum ] function of the calculator and obtain x = 14.604; y = 19.731. Thus the minimum value of l is 19.731 or the shortest ladder is approximately 19.731 feet.
18 . Step 1: Average 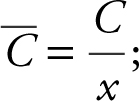 thus,
thus, ![]()
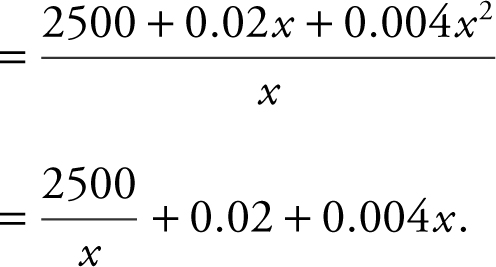
Step 2: Enter: 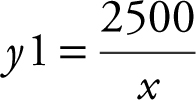 + .02 + .004 * x
+ .02 + .004 * x
Step 3: Use the [Minimum ] function in the calculator and obtain x = 790.6.
Step 4: Verify the result with the First Derivative Test. Enter y 2 = d (2500/x +.02 +.004x , x ); Use the [Zero ] function and obtain x = 790.6. Thus 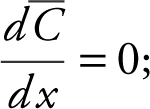 at x = 790.6. Apply the First Derivative Test:
at x = 790.6. Apply the First Derivative Test:
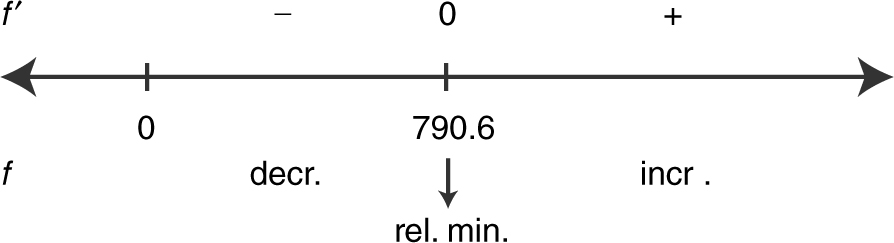
Thus the minimum average cost per unit occurs at x = 790.6. (The graph of the average cost function is shown in Figure 9.6-10 .)
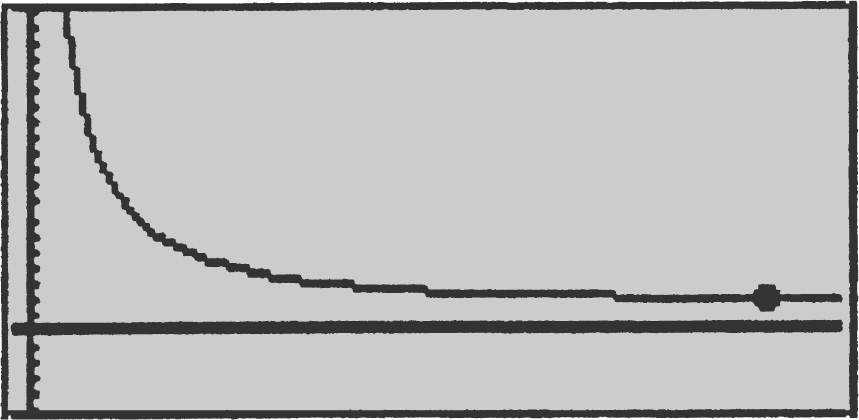
Figure 9.6-10
19 . (See Figure 9.6-11 .)
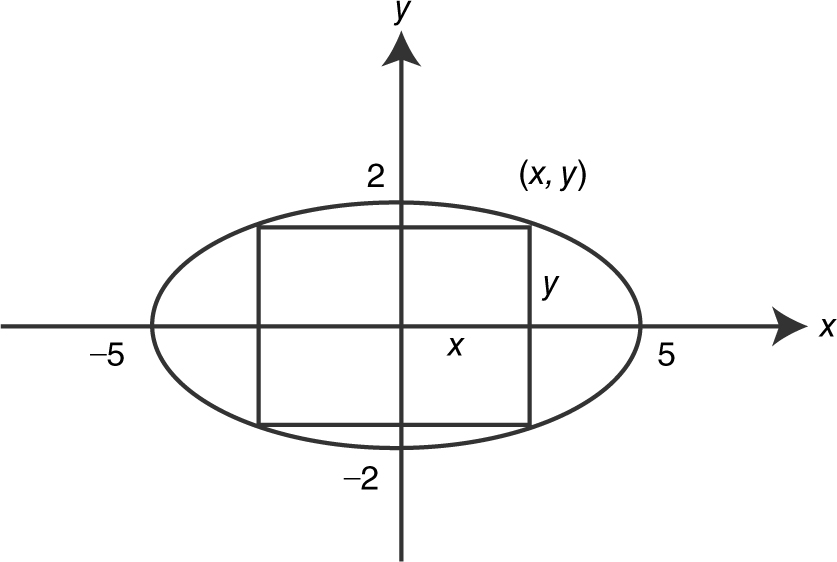
Figure 9.6-11
Step 1: Area A = (2x )(2y ); 0 ≤ x ≤ 5 and 0 ≤ y ≤ 2.
Step 2: 4x 2 + 25y 2 = 100;
25y 2 = 100 – 4x 2 .
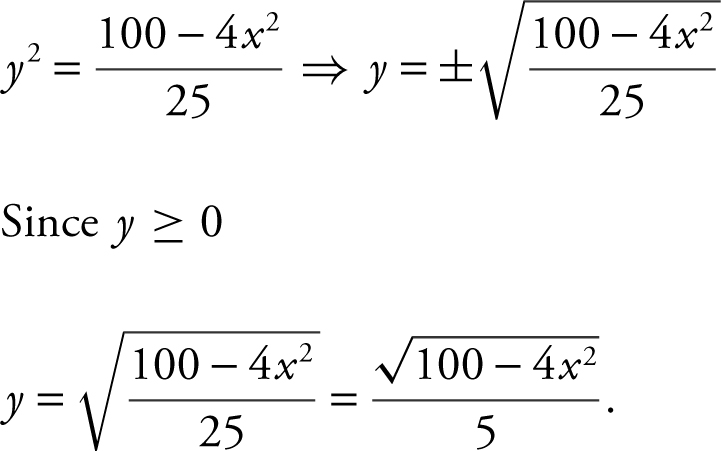
Step 3: 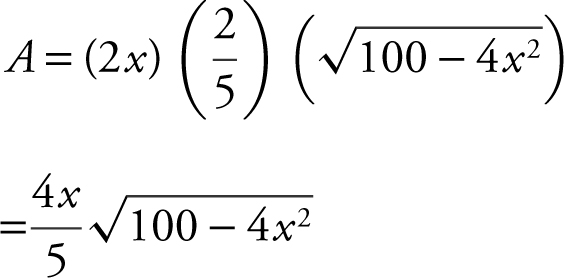
Step 4: Enter 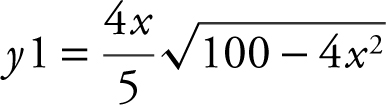
Use the [Maximum ] function and obtain x = 3.536 and y 1 = 20.
Step 5: Verify the result with the First Derivative Test.
Enter
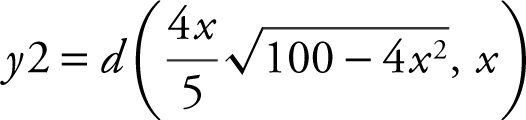 . Use the [Zero ] function and obtain x = 3.536.
. Use the [Zero ] function and obtain x = 3.536.
Note that:
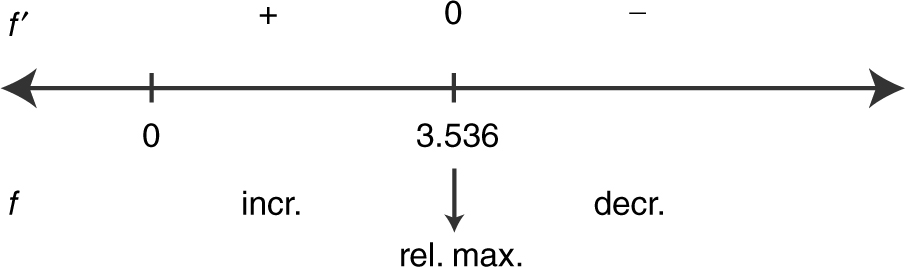
The function f has only one relative extremum. Thus, it is the absolute extremum. Therefore, at x = 3.536, the area is 20 and the area is the absolute maxima.
20 . (See Figure 9.6-12 .)
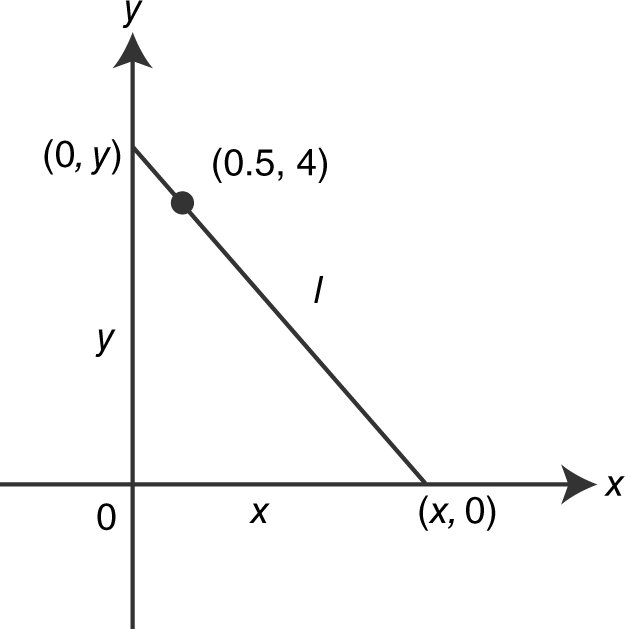
Figure 9.6-12
Step 1: Distance formula:
l 2 = x 2 + y 2 ; x > 0.5 and y > 4.
Step 2: The slope of the hypotenuse:
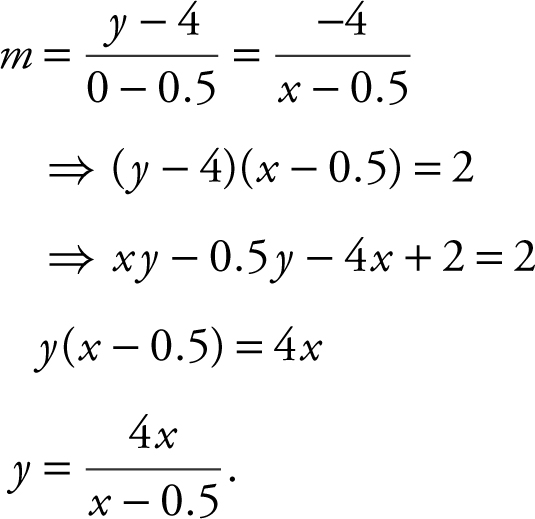
Step 3: 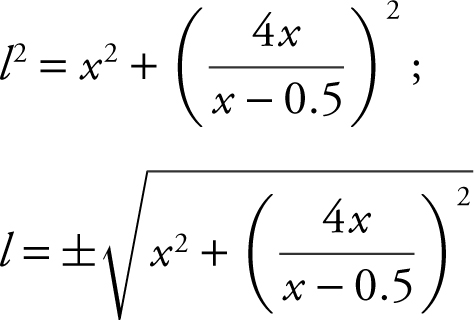 .
.
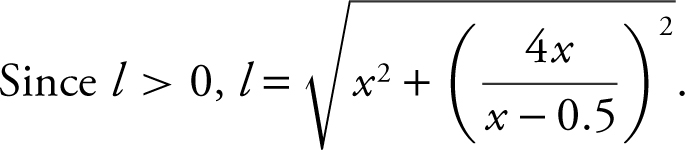
Step 4: Enter 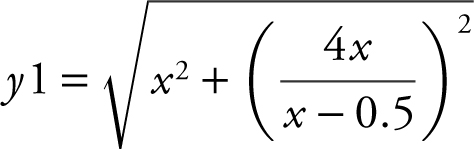 and use the [Minimum ] function of the calculator and obtain x = 2.5.
and use the [Minimum ] function of the calculator and obtain x = 2.5.
Step 5: Apply the First Derivative Test. Enter y 2 = d (y 1(x ), x ) and use the [Zero ] function and obtain x = 2.5.
Note that:
Since f has only one relative extremum, it is the absolute extremum. Thus, at x = 3, it is an absolute minimum.
Step 6: Thus, at x = 2.5, the length of the hypotenuse is the shortest. At x = 2.5, 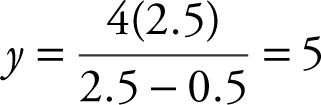 . The vertices of the triangle are (0, 0), (2.5, 0), and (0, 5).
. The vertices of the triangle are (0, 0), (2.5, 0), and (0, 5).
9.7 Solutions to Cumulative Review Problems
21 . 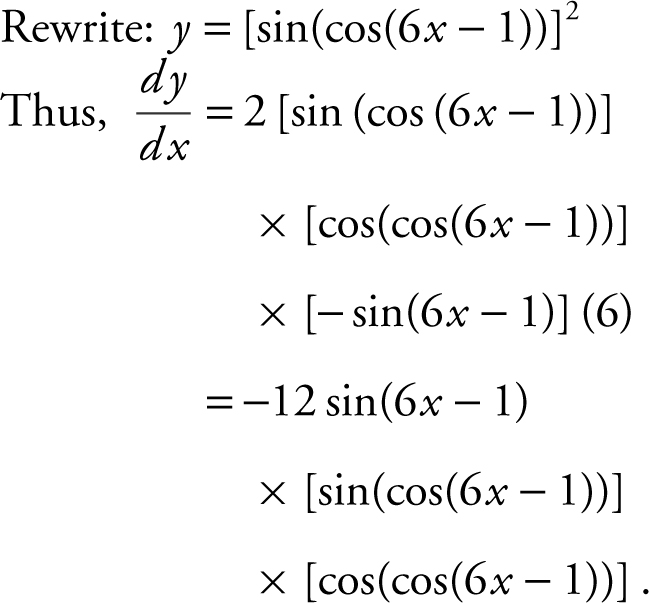
22 . As x → ∞, the numerator 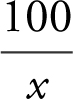 approaches 0 and the denominator increases without bound (i.e., ∞). Thus, the
approaches 0 and the denominator increases without bound (i.e., ∞). Thus, the 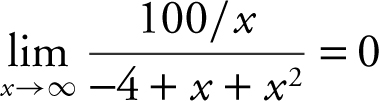 .
.
23 . (a) Summarize the information of f ′ on a number line.
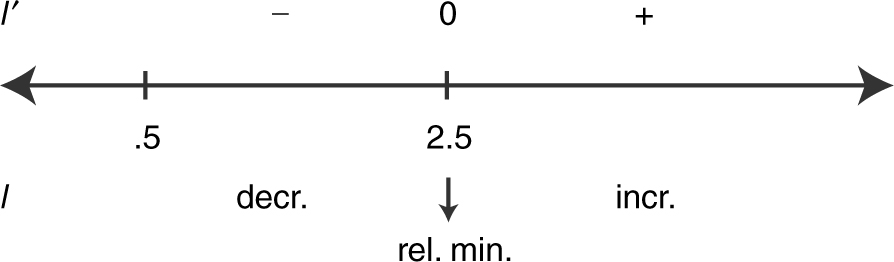
Since f has only one relative extremum, it is the absolute extremum. Thus, at x = 3, it is an absolute minimum.
(b) The function f is decreasing on the interval (–∞, 3) and increasing on (3, ∞).
(c)
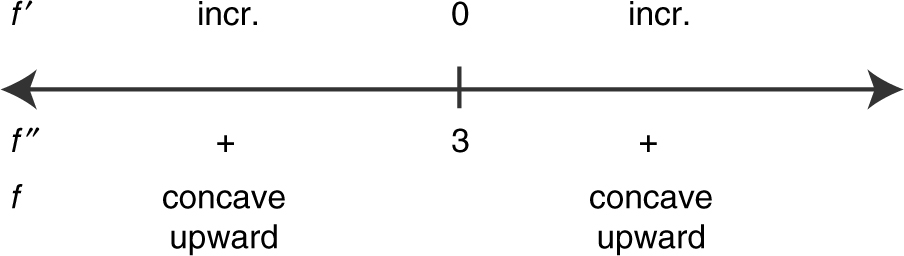
No change of concavity ⇒ No point of inflection.
(d) The function f is concave upward for the entire domain (–∞, ∞).
(e) Possible sketch of the graph for f (x ). (See Figure 9.7-1 .)
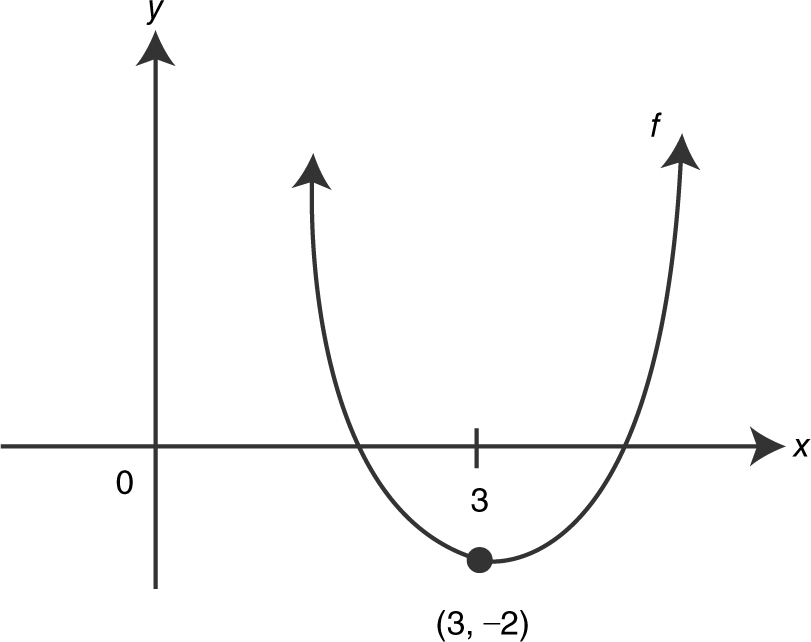
Figure 9.7-1
24 . (Calculator) (See Figure 9.7-2 .)
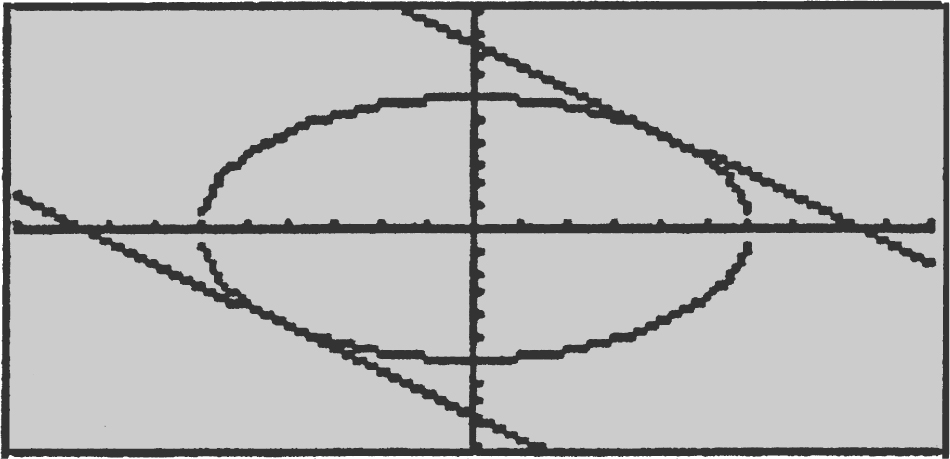
Figure 9.7-2
Step 1: Differentiate: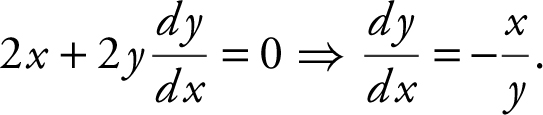
Step 2: Set 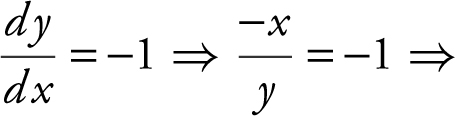 y = x
y = x
Step 3: Solve for y : x 2 + y 2 = 36 ⇒ y 2 = 36 – x 2 ;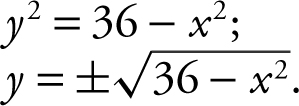 .
.
Step 4: Thus, = x ⇒ ±![]() x ⇒ 36 – x 2 = x 2 ⇒ 36 = 2x 2 or
x ⇒ 36 – x 2 = x 2 ⇒ 36 = 2x 2 or ![]() .
.
25 . (Calculator) (See Figure 9.7-3 .)
Step 1: Distance formula: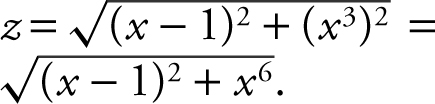
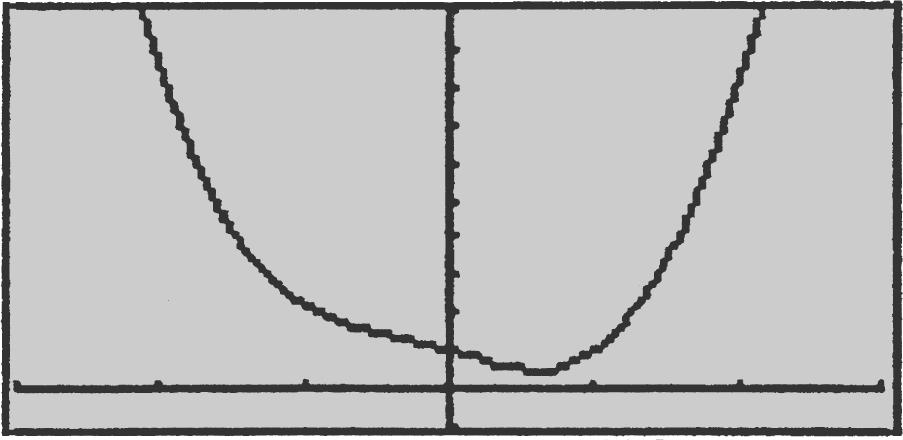
Figure 9.7-3
Step 2: Enter: 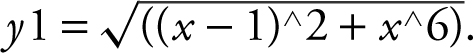
Use the [Minimum ] function of the calculator and obtain x = .65052 and y 1 = .44488. Verify the result with the First Deriative Test. Enter y 2 = d (y 1(x ), x ) and use the [Zero ] function and obtain x = .65052.
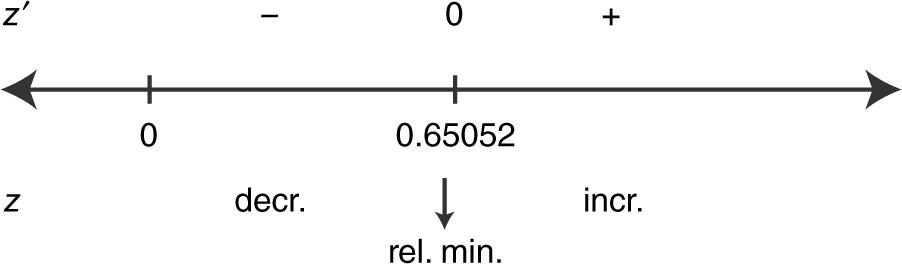
Thus the shortest distance is approximately 0.445.