The Calculus Primer (2011)
Reference Material from Other Branches of Mathematics
ALGEBRA
FACTORS:
a2 ± 2ab + b2 = (a ± 6)2
a2 − b2 = (a + b)(a − b)
a3 ± b3 = (a ± b)(a2 / ab + b2)
a4 − b4 = (a2 + b2) (a + b) (a − b)
a4 + b4 = (a2 + b2 + ![]() ab)(a2 + b2 −
ab)(a2 + b2 − ![]() ab)
ab)
a2n − b2n = (an + bn)(an − bn)
EXPONENTS:
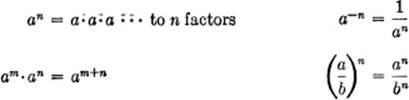

ROOTS:
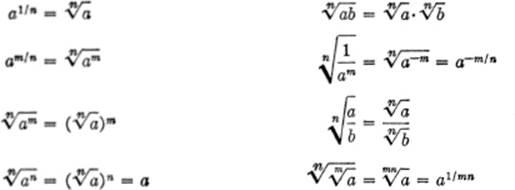
LOGARITHMS:
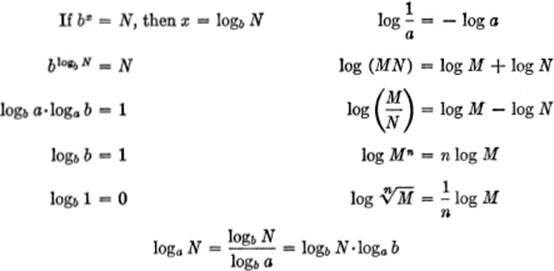
QUADRATIC EQUATIONS:
If r1 and r2 are the roots of the equation
ax2 + bx + c = 0,
![]()
The discriminant Δ = b2 − 4ac;
if Δ > 0, the roots are real and distinct;
if Δ = 0, the roots are real and equal;
if Δ < 0, the roots are complex.
(x − r1) (x − r2) = ax2 + bx + c = 0;
![]()
PROGRESSIONS:
Arithmetic.l = a + (n − 1) d;
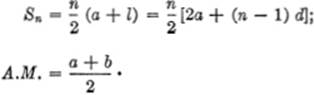
Geometric.l = arn−1;
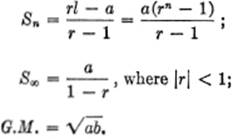
COMPLEX NUMBERS:
![]()
Ifa + bi = x + yi,then a = x and b = y.
Ifa + bi = r(cos θ + i sin θ),
thena = r cos θ,b = r sin θ,
![]()
[r(cos θ + i sin θ)]n = rn(cos nθ + i sin nθ).
FACTORIALS:
n! = 1·2·3·4 ··· to n factors.
nPn = n!0! = 1
![]()
nCr = nCn−r
nCn = nC0 = 1
nC1 + nC2 + nC3 + ··· + nCn = 2n − 1;
nC0 + nC1 + nC2 + ··· + nCn = 2n.
BINOMIAL EXPANSION:
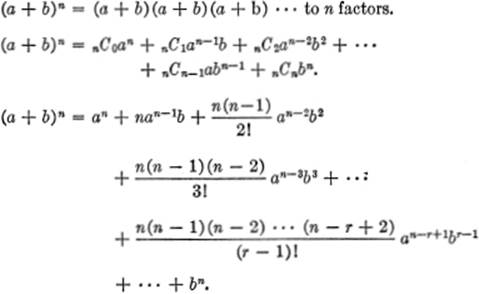
The rth term of (a + b)n is:
![]()
DETERMINANTS:
![]()
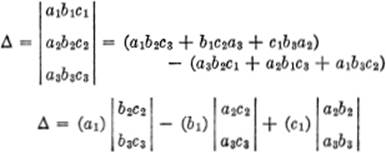
ZERO AND INFINITY:
The symbols 0 and ∞ are not to be regarded as “numbers” in these formulas:
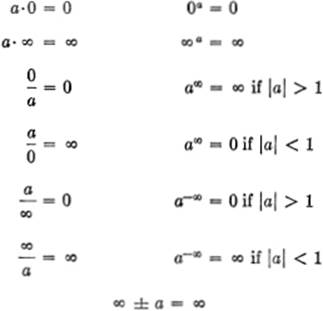
GEOMETRY
In the following formulas,
b = length of base
h = altitude
l = slant height
r = radius
m = median
d = diameter
θ = angle (in radians)
P = perimeter
C = circumference
S = arc length
s = semiperimeter
K = area
B = area of base
V = volume
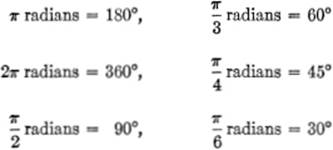
Triangle: P = a + b + c
K = ![]() bh =
bh = ![]()
Trapezoid: m = ![]() (b1 + b2)
(b1 + b2)
K = ![]() h(b1 + b2) =
h(b1 + b2) = ![]() mh
mh
Circle: C = πd = 2πr
![]()
Sector: S = rθ
K = ![]() r2θ
r2θ
Prism: V = Bh
Cylinder: (right circular) K = 2πrh + 2πr2
V = Bh = πr2h
Pyramid: V = ![]() Bh
Bh
Cone: (right circular) K = πrl + πr2; l = ![]()
V = ![]() Bh =
Bh = ![]() πr2h
πr2h
Sphere: K = 4πr2
V = ![]() πr3
πr3
Spherical triangle: K = ![]() , where E = (a° + b° + c°) − 180°.
, where E = (a° + b° + c°) − 180°.
TRIGONOMETRY
FUNDAMENTAL IDENTITIES:
![]()
sin2x + cos2 x = 1;sec2 x = 1 + tan2 x;csc2 x = 1 + cot2 x.
TRANSFORMATIONS:
Functions of the Sum and Difference of Two Angles:
sin (x ± y) = sin x cos y ± cos x sin y,
cos (x ± y) = cos x cos y / sin x sin y,
![]()
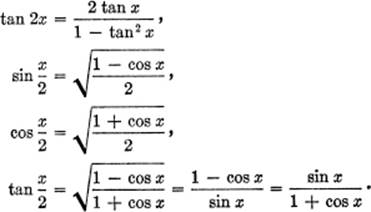
Multiple Angle Formulas:
sin 2x = 2 sin x cos x,
cos 2x = cos2 x − sin2 x = 2 cos2 x − 1 = 1 − 2 sin2 x,
Sum and Product Formulas:
sin x + sin y = 2 sin ![]() (x + y) cos
(x + y) cos ![]() (x − y),
(x − y),
sin x − sin y = 2 cos ![]() (x + y) sin
(x + y) sin ![]() (x − y),
(x − y),
cos x + cos y = 2 cos ![]() (x + y) cos (x − y),
(x + y) cos (x − y),
cos x − cos y = −2 sin ![]() (x + y) sin
(x + y) sin ![]() (x − y),
(x − y),
sin x sin y = ![]() cos (x − y) −
cos (x − y) − ![]() cos (x + y),
cos (x + y),
sin x cos y = ![]() sin (x − y) +
sin (x − y) + ![]() sin (x + y),
sin (x + y),
cos x cos y = ![]() cos (x − y) + cos (x + y).
cos (x − y) + cos (x + y).
sin2 x − sin2 y = sin (x + y) sin (x − y),
cos2 x − cos2 y = − sin (x + y) sin (x − y),
cos2 x − sin2 y = cos (x + y) cos (x − y),
sin2 x = ![]() −
− ![]() cos 2x,
cos 2x,
cos2 x = ![]() +
+ ![]() cos 2x.
cos 2x.
PLANE TRIANGLES:
a, b, c = sides of the triangle
A, B, C = opposite angles of the triangle

R = radius of the circumscribed circle
K = area of the triangle
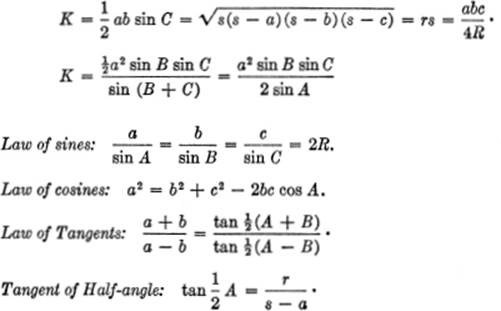
FUNCTIONS OF SPECIAL ANGLES:
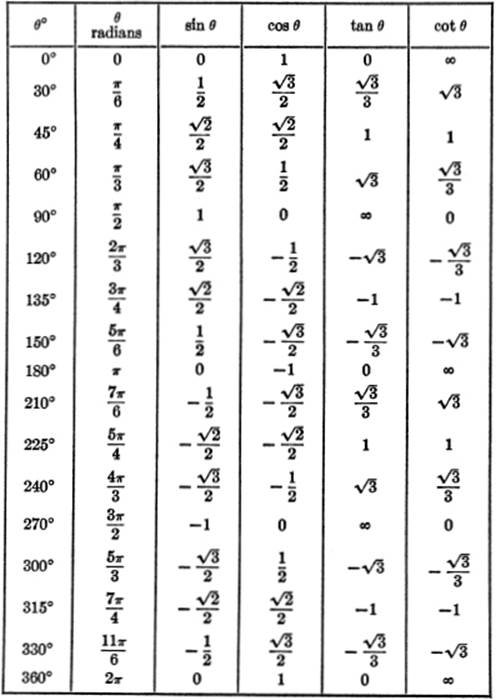
PLANE ANALYTIC GEOMETRY
FUNDAMENTAL RELATIONS:
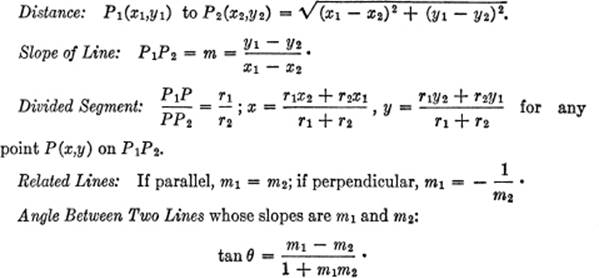
EQUATIONS OF A STRAIGHT LINE:
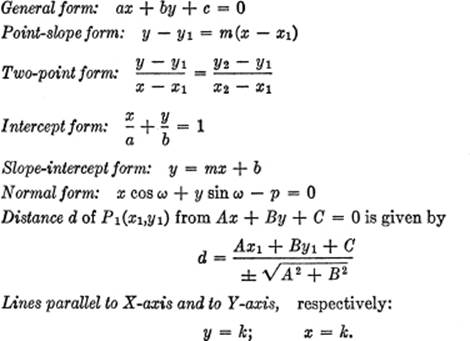
POLAR COORDINATES:
If P(x,y) ≡ P(r,θ), then
![]()
CONIC SECTIONS:
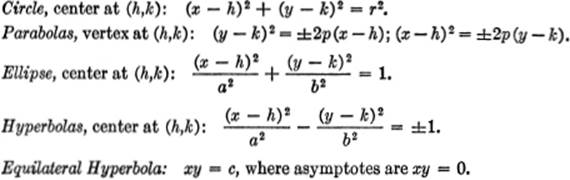
CURVES FOR REFERENCE
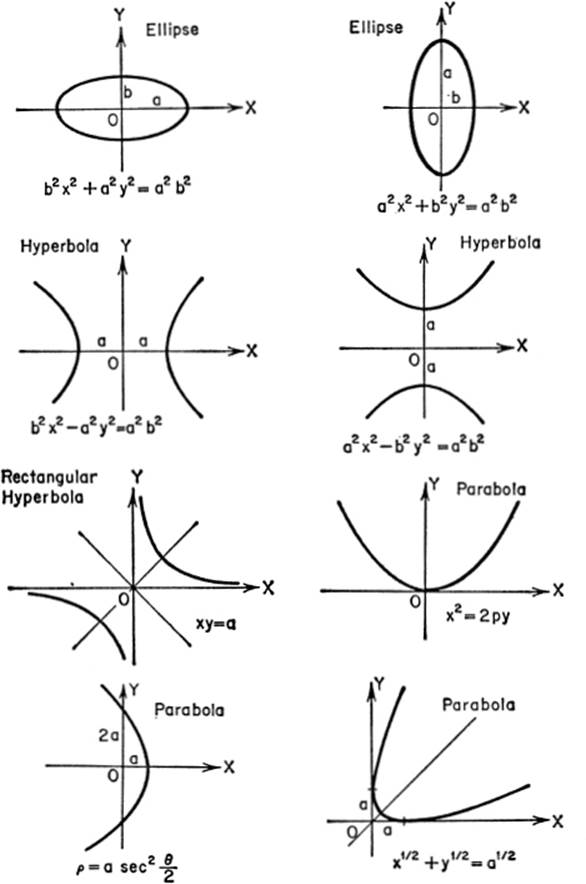
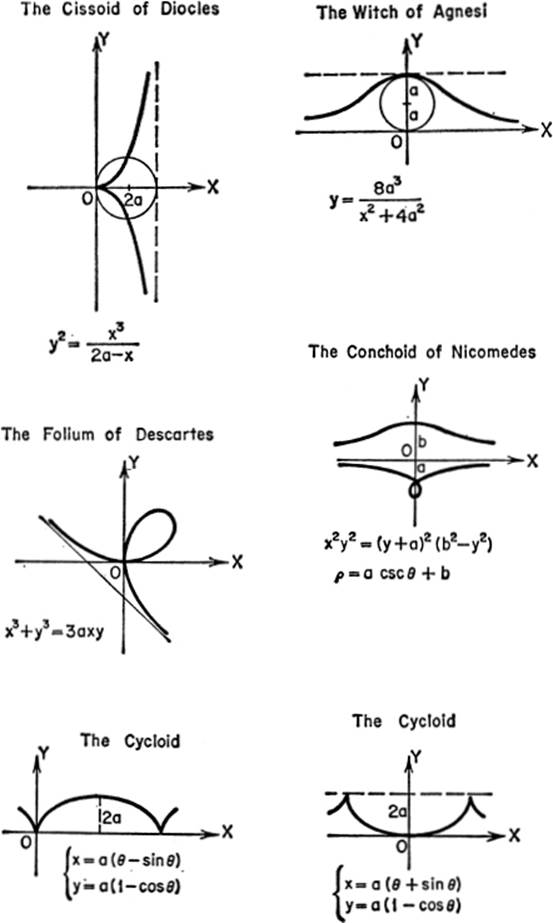
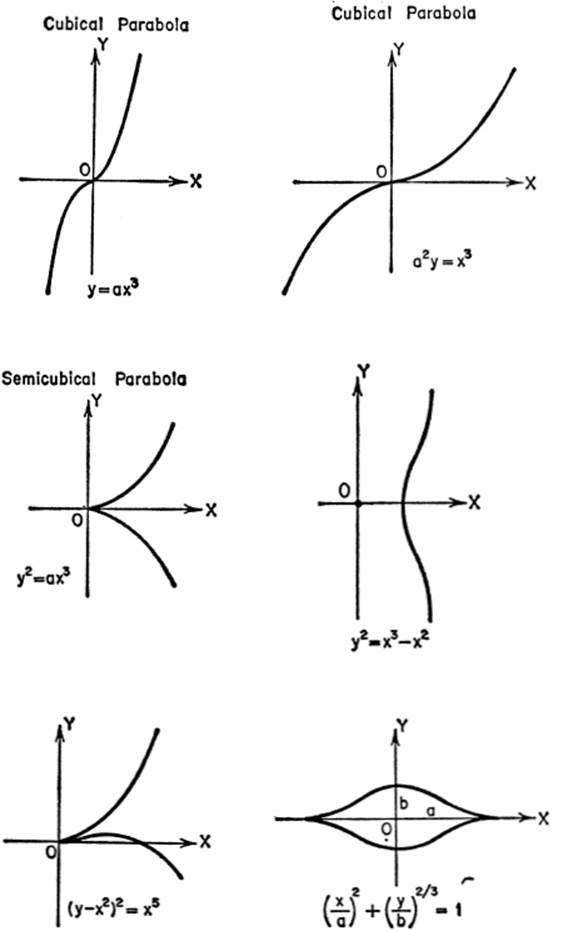
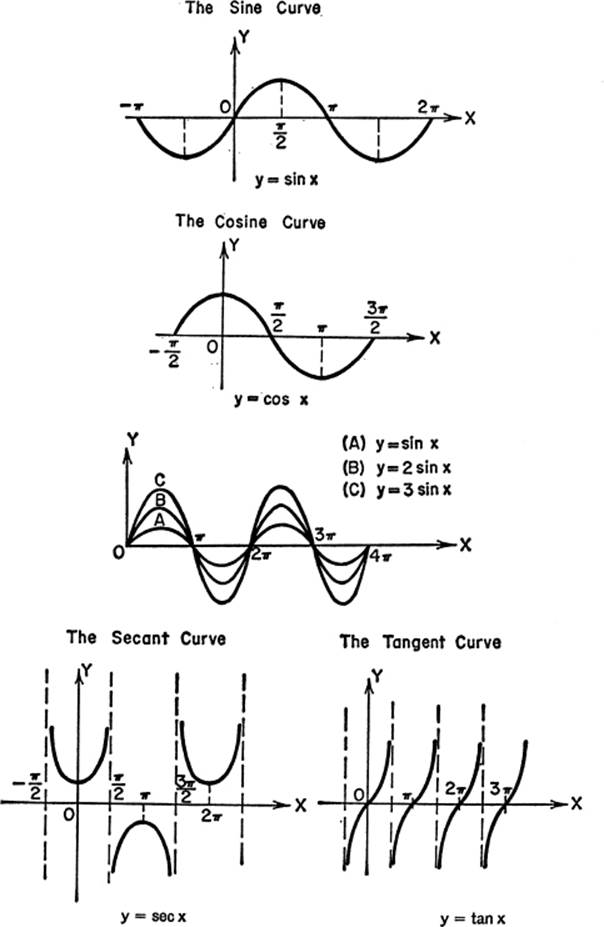
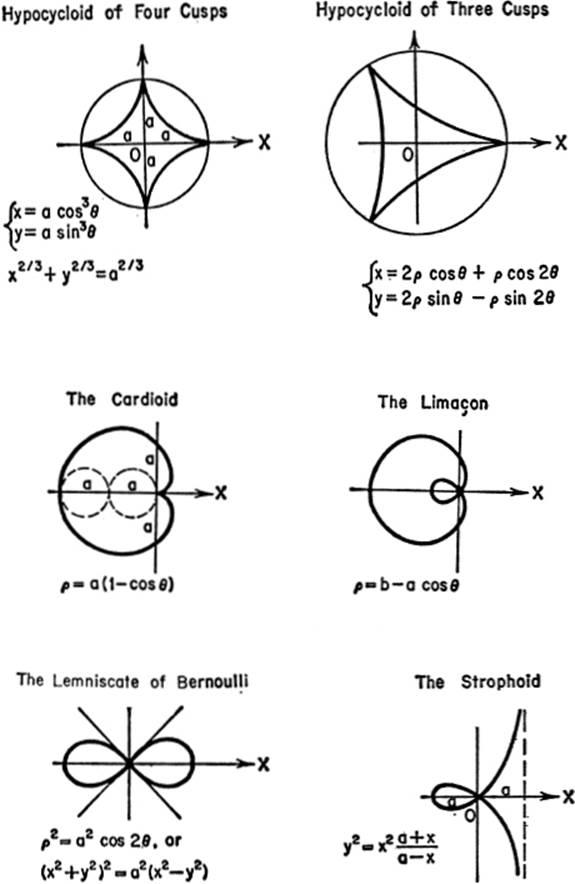
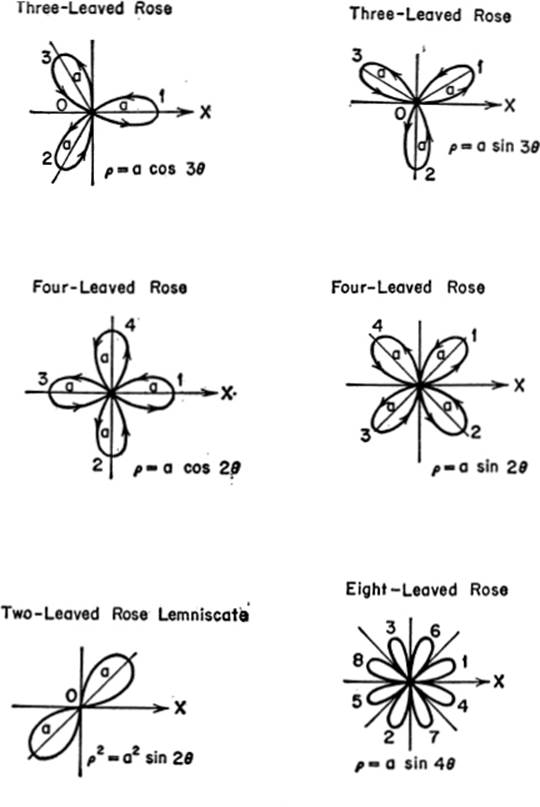
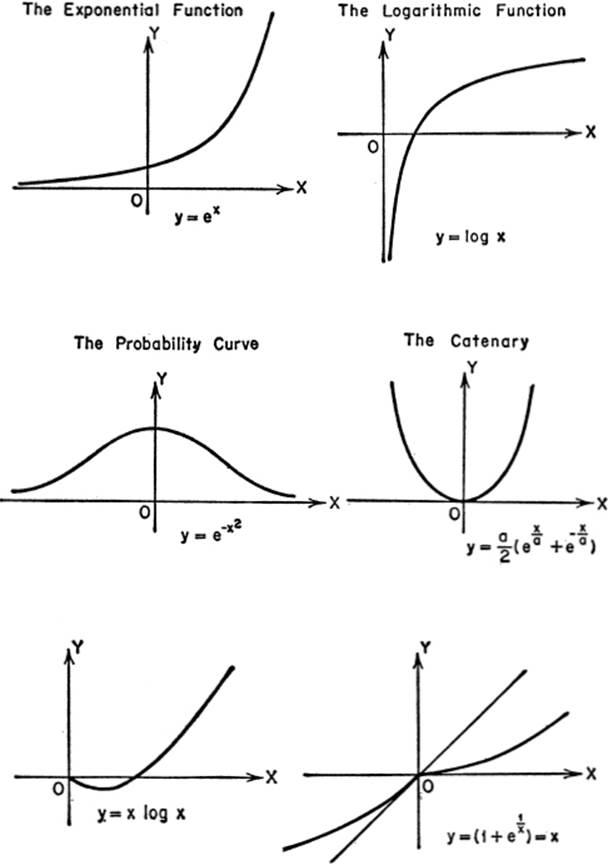
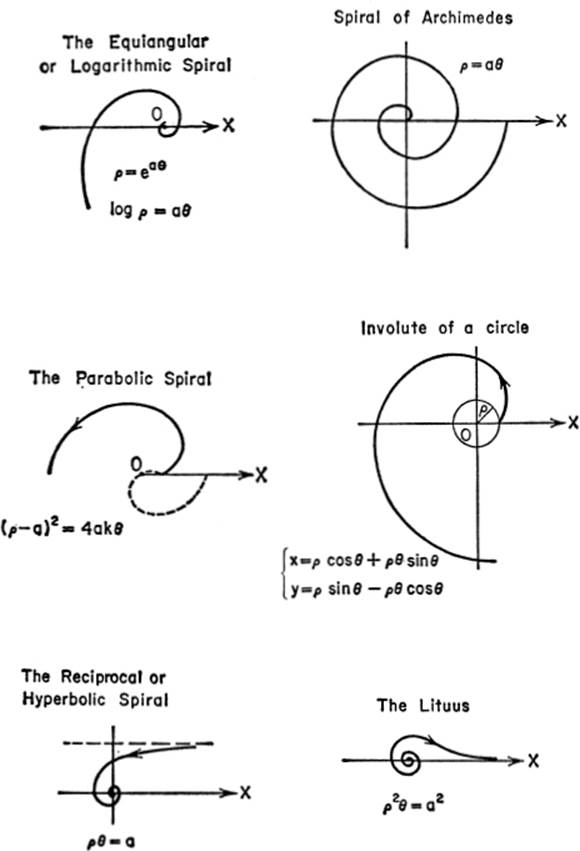
SOLID ANALYTIC GEOMETRY
FUNDAMENTAL RELATIONS
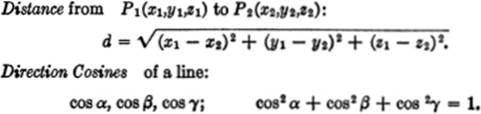
EQUATIONS OF A PLANE:
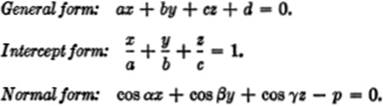
EQUATIONS OF A LINE:

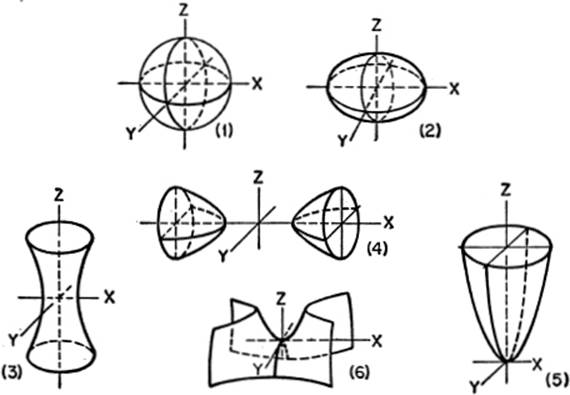
QUADRIC SURFACES
(1)Sphere with center at (0,0,0):
x2 + y2 + z2 = r2.
(2)Ellipsoid with center at (0,0,0):
![]()
(3)Hyperboloid of one sheet:
![]()
(4)Hyperboloid of two sheets:
![]()
(5)Elliptic Paraboloid:
![]()
(6)Hyperbolic Paraboloid (saddle surface) :
![]()
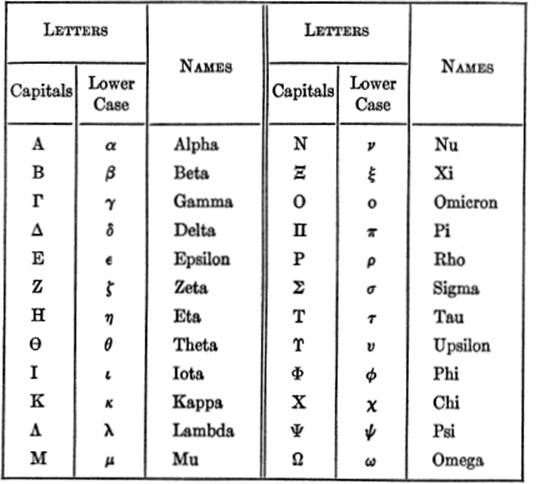
GREEK ALPHABET