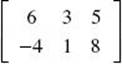SAT SUBJECT TEST MATH LEVEL 2
PART 2
![]()
REVIEW OF MAJOR TOPICS
![]()
CHAPTER 3
Numbers and Operations

3.3 Matrices
![]()
ADDITION, SUBTRACTION, AND SCALAR MULTIPLICATION
A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. The size of a matrix is r by c , where r is the number of rows and c is the number of columns. The numbers in a matrix are called entries, and the entry in the i th row and j th column is named xij. Two matrices are equal if they are the same size and their corresponding entries are equal.
EXAMPLES
1. Evaluate x and y if 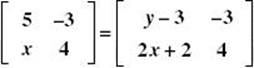 .
.
These two matrices are equal if y – 3 = 5 and x = 2x + 2. Therefore, y = 8 and x = –2.
If r = 1, the matrix is called a row matrix. If c = 1, the matrix is called a column matrix. If r = c , the matrix is called a square matrix. The numbers from the upper left corner to the bottom right corner of a square matrix form the main diagonal.
Scalar multiplication takes place when each number in a matrix is multiplied by a constant. If two matrices are the same size, they can be added or subtracted by adding or subtracting corresponding entries.
2. Simplify: 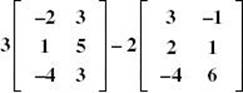
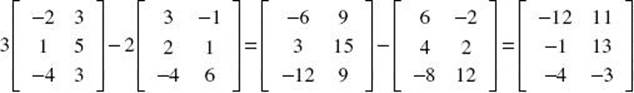
3. Solve the matrix equation: 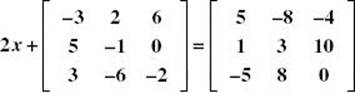
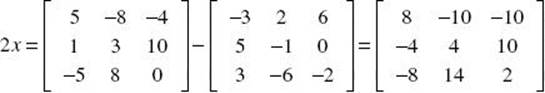
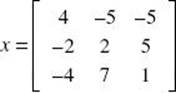
EXERCISES
1.  . Find the value of K + J + M.
. Find the value of K + J + M.
(A) 2
(B) 4
(C) 6
(D) 7
(E) 8
2. Evaluate x and y if 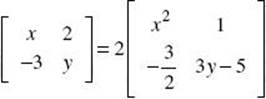 .
.
(A) x = 0; y = 2
(B) x = 1; y = 2
(C) x = −1, 1; ![]()
(D) ![]()
(E) x = 0, ![]() ; y = 2
; y = 2
3. Solve for x: 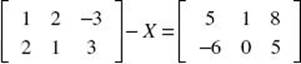 .
.
(A) 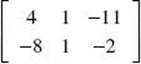
(B) 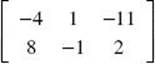
(C) 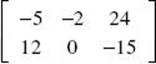
(D) 
(E)