Biology Premium, 2024: 5 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online Practice - Wuerth M. 2023
Practice Tests
Practice Test 1
Section I: Multiple-Choice
TIME: 90 MINUTES
DIRECTIONS: For each question or incomplete statement, select the choice that best answers the question or completes the statement.
1.The following figure shows the interaction of water molecules with sodium chloride.
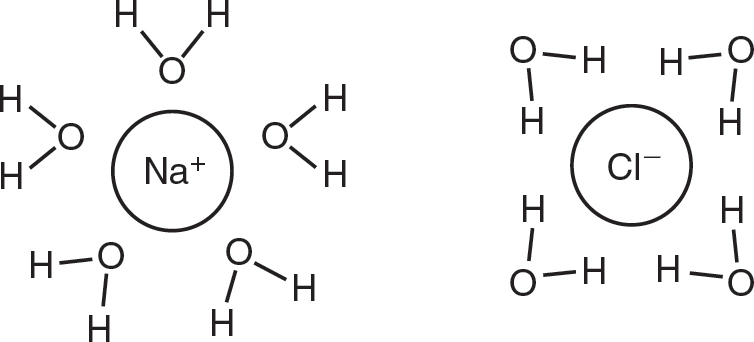
Which of the following statements best explains the arrangement of the molecules in this figure?
(A)Water is nonpolar, and it can easily dissolve ionic compounds by surrounding both negative ions and positive ions with a nonpolar ring of water molecules.
(B)Water is polar, and it can easily dissolve ionic compounds by surrounding negative ions with partially positive hydrogen atoms and by surrounding positive ions with partially negative oxygen atoms.
(C)Water and sodium chloride are both nonpolar molecules, and this allows sodium chloride to dissolve in water.
(D)Hydrogen bonds form between water molecules and the ions in sodium chloride.
2.The following figure shows the interaction between water molecules and a micelle (a spherical formation of lipids dissolved in an aqueous environment).
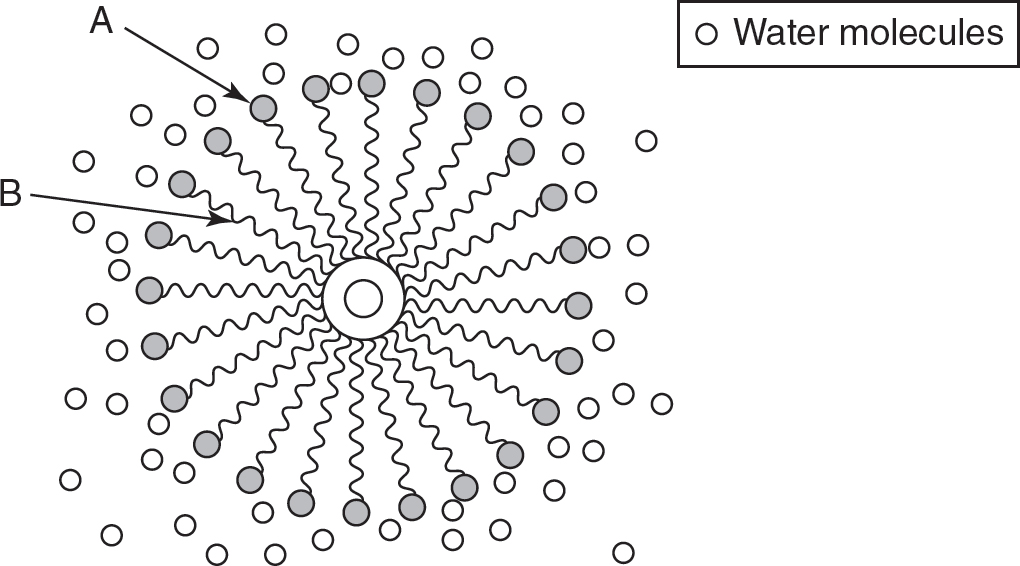
Which of the following correctly describes the parts of the micelle labeled A and B?
(A)Part A represents the hydrophilic phosphate head of a phospholipid, and part B represents the hydrophobic lipid tail of a phospholipid.
(B)Part A represents the hydrophobic phosphate head of a phospholipid, and part B represents the hydrophilic lipid tail of a phospholipid.
(C)Part A represents the glycosidic head of a glycosphingolipid, and part B represents the hydrophilic tail of a phospholipid.
(D)Part A represents the inorganic phosphate compound, and part B represents the fatty sterol cholesterol.
Questions 3—5
A student conducts an experiment to find out how many drops of different liquids can be placed on the surface of a penny before the liquids flow over the sides of the penny. Data are shown in the following table.

3.Which of the following graphs most accurately represents the data, including 95% confidence intervals?
(A)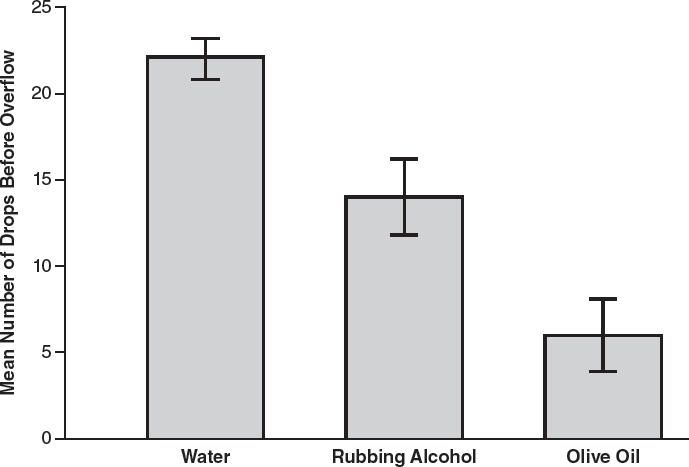
(B)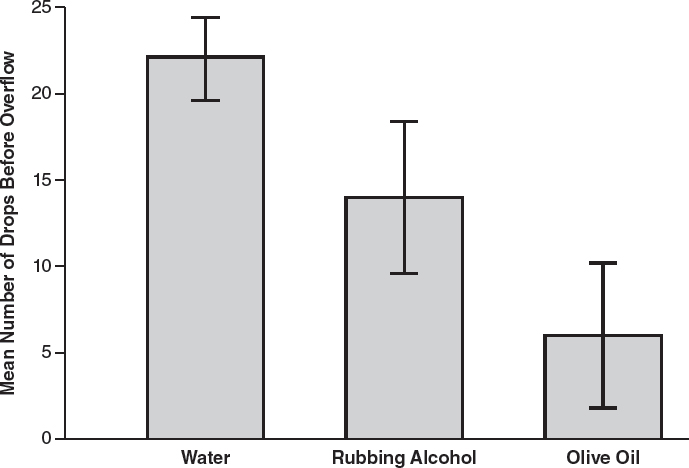
(C)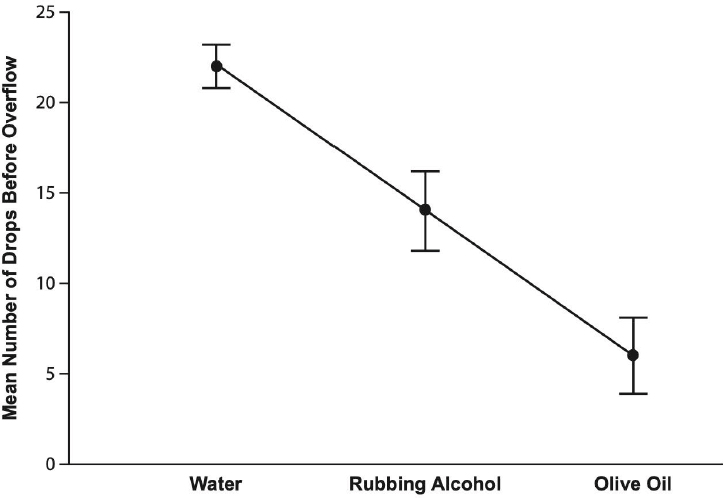
(D)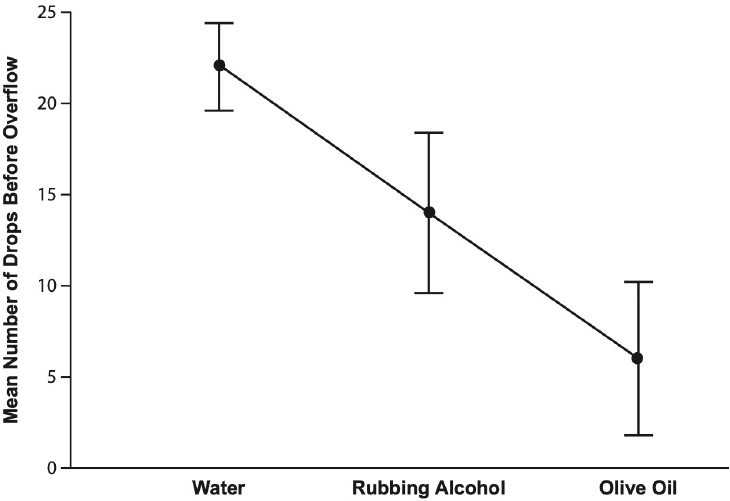
4.Which two liquids are least likely to have a statistically significant difference between their means?
(A)water and rubbing alcohol (because their 95% confidence intervals do overlap)
(B)water and olive oil (because their 95% confidence intervals do not overlap)
(C)water and rubbing alcohol (because their 95% confidence intervals do not overlap)
(D)rubbing alcohol and olive oil (because their 95% confidence intervals do overlap)
5.The student repeats the experiment, but before doing so, first coats the surface of the penny with a thin layer of surfactant (a chemical compound that disrupts the formation of hydrogen bonds). Predict the effect the surfactant will have on the number of drops of water that can be placed on the surface of the penny before overflow occurs, and justify your prediction.
(A)The number of drops of water will decrease due to fewer hydrogen bonds forming between the water molecules.
(B)The number of drops of water will decrease due to fewer polar ends forming within the water molecules.
(C)The number of drops of water will increase due to increased polar covalent bonds within the water molecules.
(D)The number of drops of water will increase due to increased surface tension.
6.Which of the following biological molecules is the carrier of genetic information?
(A)carbohydrates
(B)lipids
(C)nucleic acids
(D)proteins
7.Which of the following correctly describes what would be needed to break down a polypeptide chain into its 15 component amino acids?
(A)dehydration reactions that would produce 15 water molecules
(B)dehydration reactions that would consume 14 water molecules
(C)hydrolysis reactions that would produce 15 water molecules
(D)hydrolysis reactions that would consume 14 water molecules
8.Which of the following is a correct statement about protein structure?
(A)Primary structure is formed by hydrophobic interactions.
(B)Secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds.
(C)Tertiary structure is formed by peptide bonds.
(D)Quaternary structures are found in all proteins.
Questions 9—11
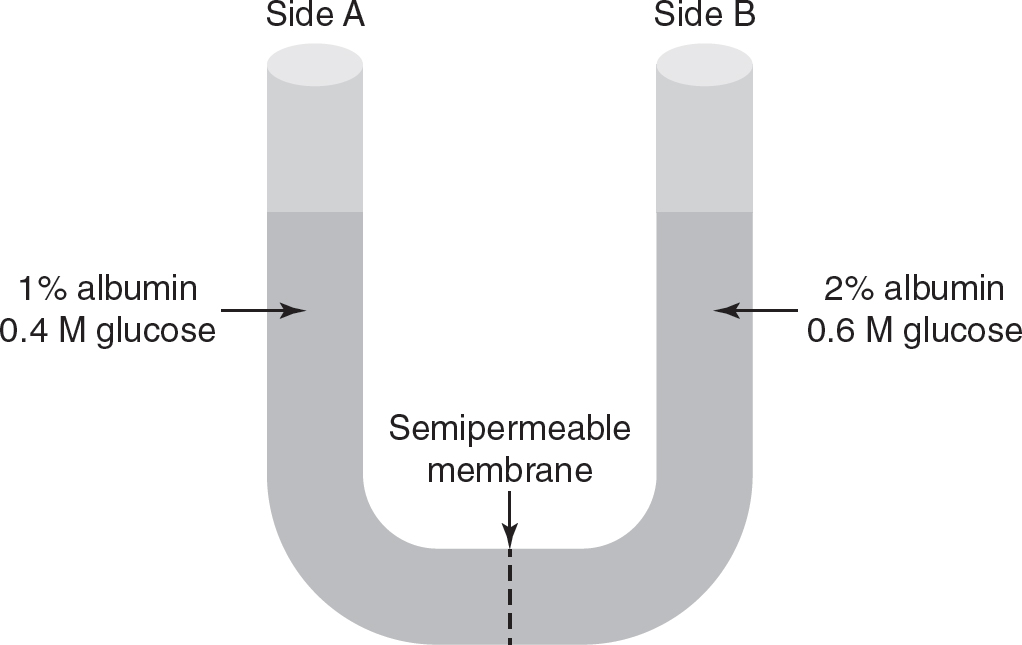
The two sides of the U-tube apparatus are separated by a semipermeable membrane. The aqueous solution on side A of the U-tube contains 1% albumin and 0.4 M glucose. The aqueous solution on side B contains 2% albumin and 0.6 M glucose.
9.Which of the following statements is correct?
(A)Side A initially has a higher water potential than side B because side A has a lower solute concentration than side B.
(B)Side B initially has a higher water potential than side A because side B has a higher solute concentration than side A.
(C)Side A and side B initially have the same water potential because they are both aqueous solutions.
(D)Side A and side B initially have the same water potential because they both contain the same types of solutes.
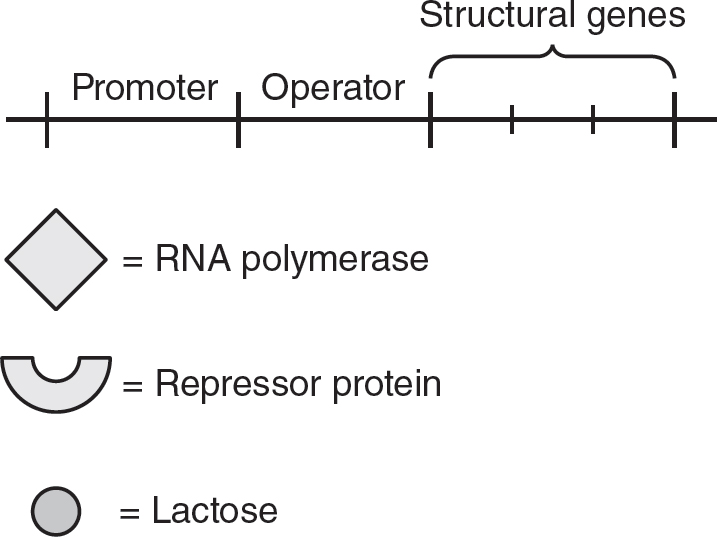
10.Glucose may pass through the semipermeable membrane in the U-tube, but albumin may not. If the solutions on each side of the U-tube apparatus are allowed to equilibrate for 30 minutes, which of the following is the most likely result?
(A)The concentration of glucose on side B will increase.
(B)The concentration of albumin on side A will increase.
(C)The concentration of glucose on side A will increase.
(D)The concentration of albumin on side B will increase.
11.Which of the following correctly predicts and explains the movement of water in the U-tube after 30 minutes?
(A)Water will move from side A to side B because the water potential on side A will be higher than the water potential on side B.
(B)Water will move from side A to side B because the water potential on side B will be higher than the water potential on side A.
(C)Water will move from side B to side A because the water potential on side A will be higher than the water potential on side B.
(D)Water will move from side B to side A because the water potential on side B will be higher than the water potential on side A.
Questions 12—14
Refer to the following table.
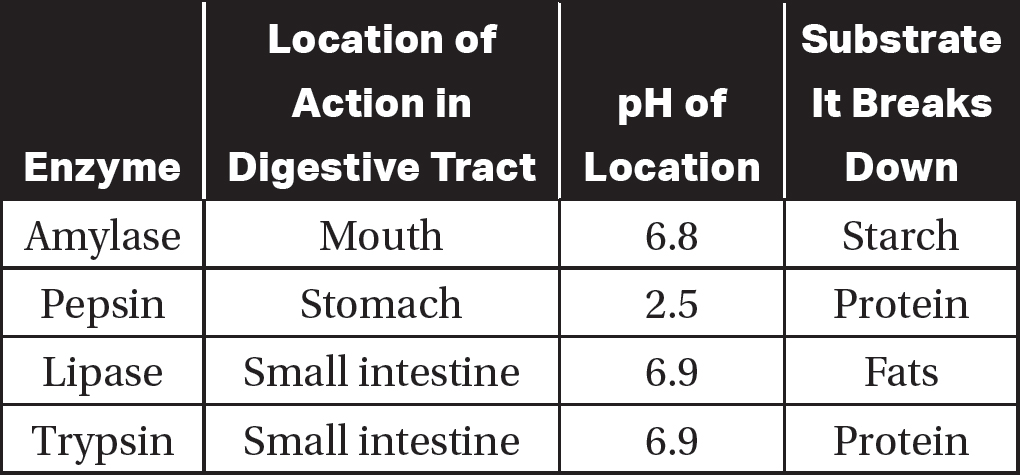
12.Which of the following graphs most likely reflects the activity of pepsin at different pHs?
(A)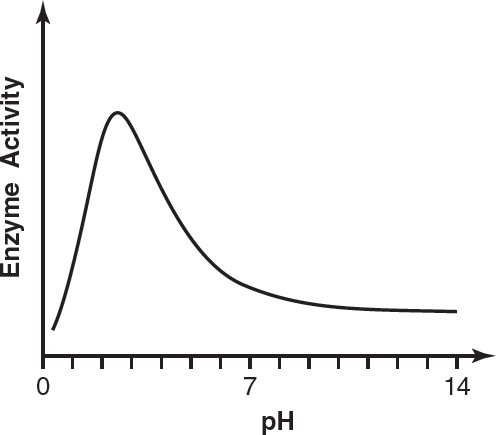
(B)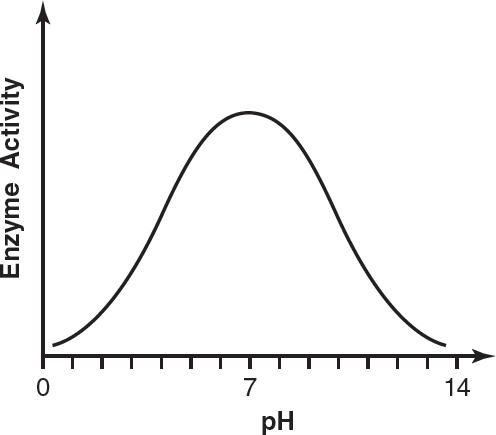
(C)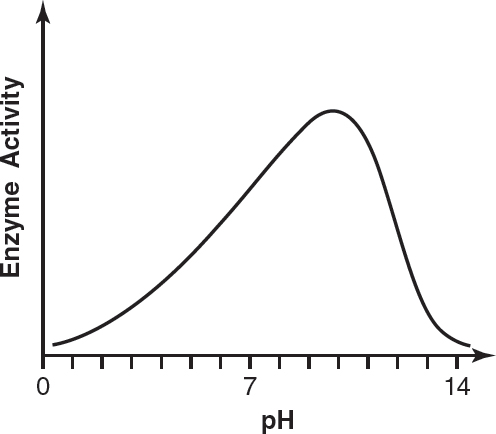
(D)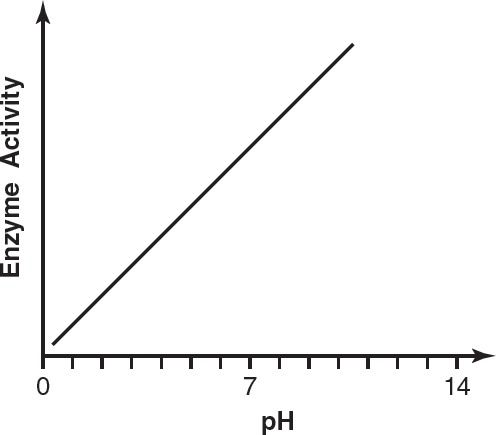
13.A person eats enough antacids to raise the pH of both his mouth and his stomach acid. The activities of which enzymes would most likely be affected by this?
(A)amylase and pepsin
(B)pepsin and lipase
(C)lipase and trypsin
(D)trypsin and amylase
14.The pyloric sphincter controls the flow of the contents of the stomach (chyme) into the small intestine. The pyloric sphincter prevents the acidic chyme from the stomach from entering the small intestine until the pancreas is ready to secrete bicarbonate into the small intestine, which neutralizes the acids in the chyme. If the pyloric sphincter was damaged and could not control the flow of chyme into the small intestine, which enzymes would most likely have reduced activity during digestion?
(A)amylase and pepsin
(B)pepsin and lipase
(C)lipase and trypsin
(D)trypsin and amylase
15.Which of the following processes occurs in anaerobic prokaryotes?
(A)glycolysis
(B)Krebs cycle
(C)oxidation of pyruvate
(D)oxidative phosphorylation
Questions 16—18
In a classic experiment to determine which wavelengths of light produce the greatest amounts of photosynthesis in photosynthetic algae, light was passed through a prism to shine different colors of light onto the photosynthetic algae Spirogyra (that was placed on a microscope slide), as shown in the following figure.
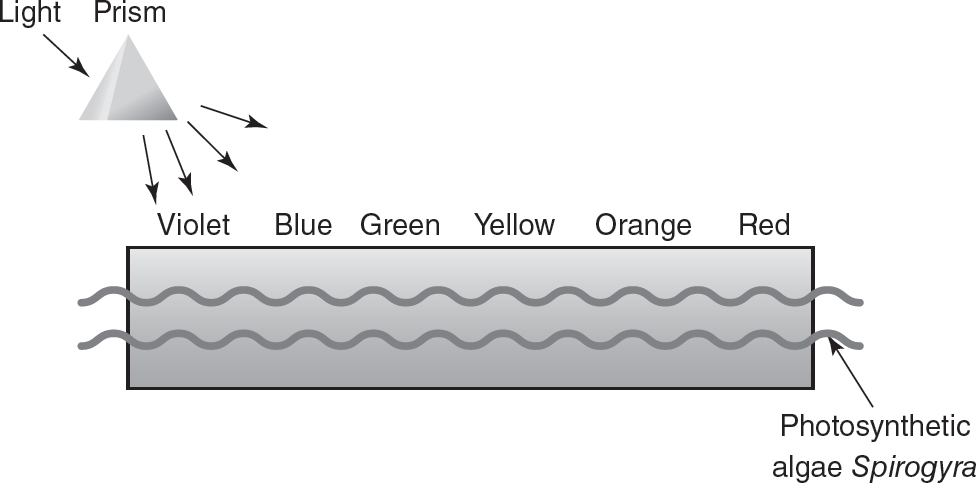
Aerobic bacteria (that need oxygen to survive) were layered on top of the algae. The wavelengths (in nm) of different colors of visible light are noted in the table.
|
Color of Visible Light |
Wavelength (nm) |
Violet |
380—450 |
Blue |
450—495 |
Green |
495—570 |
Yellow |
570—590 |
Orange |
590—620 |
Red |
620—750 |
16.The greatest numbers of aerobic bacteria were found on the slide where the wavelength of light was between 420—470 nm and 660—700 nm. What conclusion could be drawn from this data?
(A)Algae produce the same amount of oxygen when exposed to any color of light.
(B)Algae produce oxygen only when in the presence of aerobic bacteria.
(C)Algae produce the most oxygen when exposed to green light.
(D)Algae produce the most oxygen when exposed to blue-violet or red light.
17.Further research revealed that the light-absorbing pigment in the algae Spirogyra (that was used in this experiment) was chlorophyll, which absorbs the most light energy in the wavelength ranges of 420—470 nm and 660—700 nm. Some photosynthetic red algae use the pigment phycoerythrin, which absorbs the most light energy in the wavelength range of 495—570 nm. If this experiment was repeated with photosynthetic red algae, near which color of light on the slide would you expect to see the greatest number of bacteria?
(A)violet
(B)green
(C)orange
(D)red
18.What is the role of light energy in photosynthesis?
(A)to activate the expression of genes needed for photosynthesis
(B)to trigger a cell signaling pathway that produces carbon dioxide
(C)to excite the electrons in the photosystems
(D)to fix carbon dioxide during the Krebs (citric acid) cycle
Questions 19 and 20
Equal numbers of germinating mung beans were placed in sealed chambers of equal volumes with probes that measured the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide gas over time. One chamber was kept at a temperature of 4° Celsius, and the other chamber was kept at a temperature of 25° Celsius for the duration of the experiment.
19.What is the independent variable in this experiment?
(A)the number of germinating mung beans
(B)the temperature of the chambers
(C)the amount of carbon dioxide produced
(D)the amount of oxygen consumed
20.This graph shows the carbon dioxide levels in both chambers during a 30-minute period.
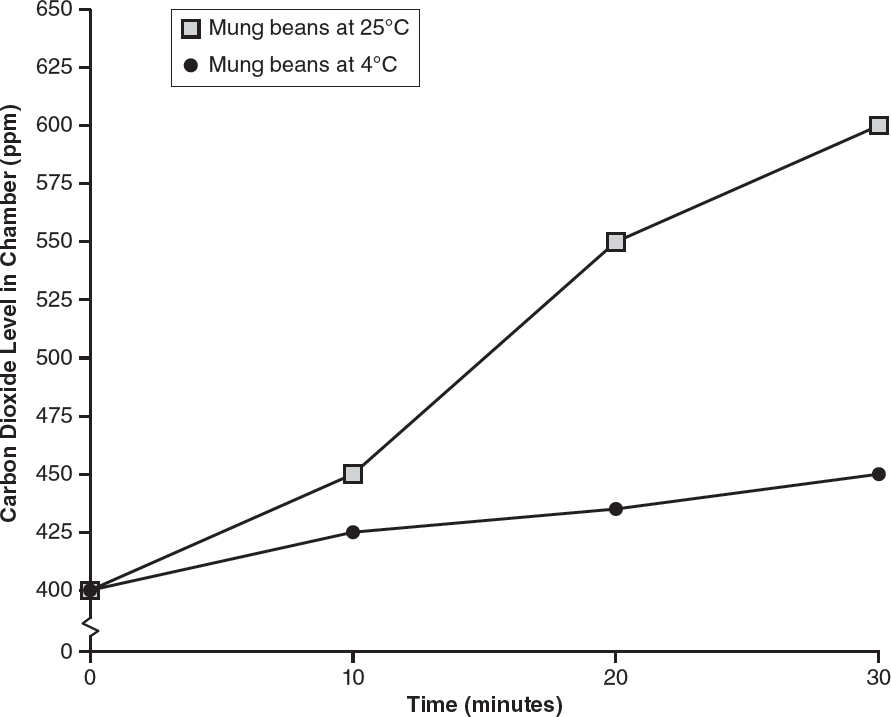
Which of the following correctly states the results of this experiment?
(A)The mung beans at 4° Celsius increased the level of carbon dioxide in the chamber at a rate of 6.67 ppm CO2 per minute and had a higher respiration rate than the mung beans at 25° Celsius.
(B)The mung beans at 4° Celsius increased the level of carbon dioxide in the chamber at a rate of 1.67 ppm CO2 per minute and had a higher respiration rate than the mung beans at 25° Celsius.
(C)The mung beans at 25° Celsius increased the level of carbon dioxide in the chamber at a rate of 6.67 ppm CO2 per minute and had a higher respiration rate than the mung beans at 4° Celsius.
(D)The mung beans at 25° Celsius increased the level of carbon dioxide in the chamber at a rate of 1.67 ppm CO2 per minute and had a higher respiration rate than the mung beans at 4° Celsius.
21.A cell secretes a growth factor that slowly diffuses to nearby cells, stimulating the growth of those cells. This is an example of __________ signaling.
(A)autocrine
(B)juxtacrine
(C)paracrine
(D)endocrine
22.Quorum sensing is used by bacteria to sense the density of bacteria in the area. Bacteria release a signaling molecule that travels short distances to receptors on nearby bacteria. This would best be described as which type of cell signaling?
(A)synaptic
(B)cytokine
(C)paracrine
(D)endocrine
23.Estradiol and testosterone are steroid hormones. Which type of receptor are they most likely to bind to?
(A)a G-protein-linked receptor
(B)a tyrosine kinase receptor
(C)an intracellular cytoplasmic receptor
(D)a membrane ion channel receptor
24.cAMP and Ca2+ ions are examples of ___________.
(A)cell membrane receptors
(B)ligands
(C)intracellular cytoplasmic receptors
(D)secondary messengers
25.Gap junctions in animal cells and plasmodesmata in plant cells are examples of which type of signaling?
(A)autocrine
(B)juxtacrine
(C)paracrine
(D)endocrine
26.How does a cell that has just completed the S stage of the cell cycle compare to the same cell at the start of the S stage?
(A)It has twice the amount of DNA and twice the number of chromosomes.
(B)It has twice the amount of DNA and the same number of chromosomes.
(C)It has the same amount of DNA and twice the number of chromosomes.
(D)It has the same amount of DNA and the same number of chromosomes.
27.During which stage of the cell cycle are you most likely to find cells that have fully differentiated and are not actively dividing?
(A)G0
(B)G1
(C)S
(D)G2
28.___________ are present at near-constant levels during the cell cycle and are dependent on rising levels of ___________ to become active.
(A)Cyclins; mitosis-promoting factor
(B)Cyclins; cyclin-dependent kinases
(C)Cyclin-dependent kinases; cyclins
(D)Cyclin-dependent kinases; phosphatases
29.The three major events of the division of the genetic material during cell replication are (1) replication of the genetic material, (2) alignment of chromosomes, and (3) separation of chromosomes. These events happen during which stages (respectively)?
(A)S, G1, G2
(B)S, metaphase, anaphase
(C)G2, metaphase, telophase
(D)prophase, metaphase, anaphase
30.Which of the following would affect the greatest number of steps in the signal transduction process?
(A)an antibody irreversibly binding to a cell membrane receptor
(B)deletion of the gene for the enzyme adenylyl cyclase
(C)inactivation of a cytoplasmic protein kinase
(D)introduction of an inhibitor of a protein phosphatase
Questions 31 and 32
The ability to taste phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) is a dominant trait. Nontasters of PTC are recessive. In a population that is not in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, there are 520 homozygous dominant tasters, 400 heterozygous tasters, and 80 nontasters of PTC.
31.What is the frequency of the nontaster allele?
(A)0.28
(B)0.44
(C)0.56
(D)0.72
32.What is the frequency of individuals who are carriers of the nontasting allele?
(A)0.08
(B)0.40
(C)0.50
(D)0.52
Questions 33 and 34
Refer to the following table.
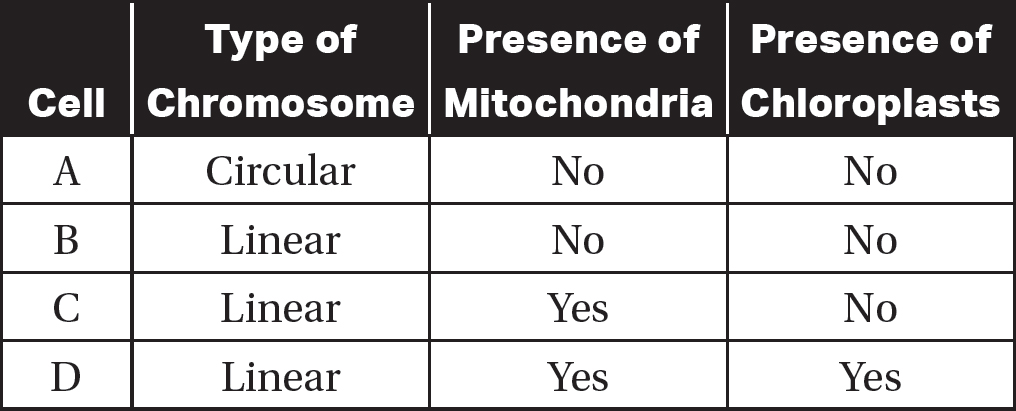
33.Which of the cells in this table shares characteristics of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
(A)A
(B)B
(C)C
(D)D
34.Which of the organisms in the table is most closely related to modern plants?
(A)A
(B)B
(C)C
(D)D
35.Two species of deer live on different mountain ranges separated by 500 miles. Which type of reproductive isolation does this scenario represent?
(A)habitat isolation
(B)temporal isolation
(C)behavioral isolation
(D)mechanical isolation
36.Sea urchins release their sperm and eggs into the water. However, the sperm from red sea urchins cannot fertilize the eggs from purple sea urchins. Which type of reproductive isolation is this?
(A)mechanical isolation
(B)gametic isolation
(C)reduced hybrid fertility
(D)hybrid breakdown
37.A template strand of DNA has the following sequence:
![]()
What is the complementary strand created during DNA replication?
(A)3′-TTA AGG CCT AGC-5′
(B)5′-TTA AGG CCT AGC-3′
(C)3′-UUA AGG CCU AGC-5′
(D)5′-UUA AGG CCU AGC-3′
38.Which of the following statements best explains the mechanism for DNA replication?
(A)DNA replication is reductive, because half of the total DNA present is copied.
(B)DNA replication is semiconservative, because each DNA strand serves as a template for a new strand during replication.
(C)DNA replication is dispersive, because the two resulting DNA molecules are random mixtures of parent and daughter DNA.
(D)DNA replication is conservative, because one resulting molecule is identical to the original and the other consists of two new strands.
39.In DNA replication, DNA “unwinds” to form two template strands: the leading strand and the lagging strand. Which of the following statements about these strands is true?
(A)On the lagging strand, short fragments are formed when the new strand of DNA is synthesized.
(B)The leading strand of DNA is synthesized discontinuously.
(C)DNA polymerase can only synthesize DNA on the leading strand.
(D)The lagging strand can only be synthesized once the leading strand has been completed.
40.Which of the following is the enzyme used during transcription that directly generates the transcript?
(A)helicase
(B)ligase
(C)DNA polymerase
(D)RNA polymerase
41.Which of the following statements about introns is true?
(A)Introns are translated by ribosomes.
(B)Introns have no function in the chromosomes.
(C)Introns are found in eukaryotes.
(D)Introns are found only in prokaryotes.
42.Streptomycin, a commonly used antibiotic, interferes with bacterial ribosomes. Which process would most likely be negatively affected by streptomycin?
(A)DNA replication
(B)posttranscriptional modification of mRNA
(C)transcription
(D)translation
43.A scientist is studying a eukaryotic gene that is 15,000 base pairs long. The scientist isolates the mRNA (produced by this gene) from the cytosol and finds that it is only 12,000 base pairs long. Why is the isolated mRNA not the same length as the DNA that codes for it?
(A)The scientist made a mistake and isolated the wrong mRNA.
(B)Introns are removed from eukaryotic mRNAs, so the mRNA is shorter than the DNA.
(C)RNA is less stable than DNA and is more likely to degrade in the cell.
(D)The poly-A tail on the mRNA results in an mRNA that is shorter than the gene.
44.In the cross AABbCc × AaBbCC, what is the probability of producing an offspring with the genotype AaBbCc?
(A)0
(B)![]()
(C)![]()
(D)![]()
45.Based on this pedigree, what is the most likely mode of inheritance of the trait?
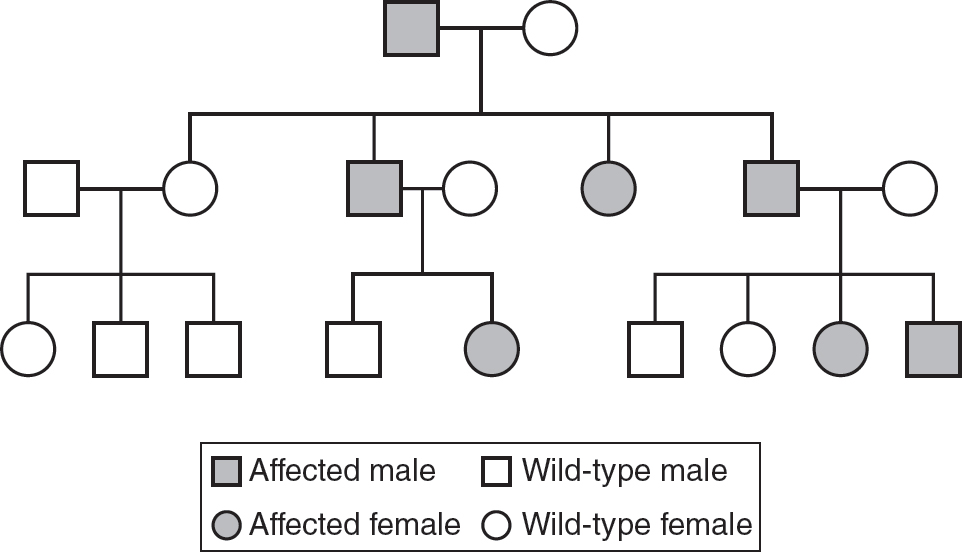
(A)autosomal dominant
(B)sex-linked dominant
(C)sex-linked recessive
(D)mitochondrial inheritance
Questions 46—48
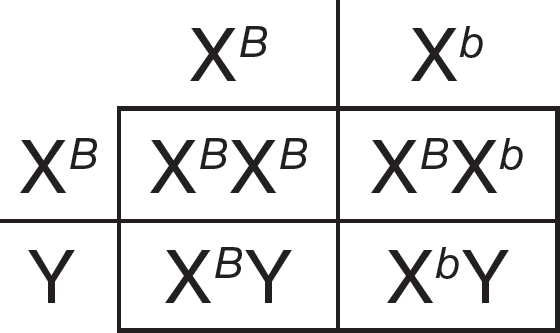
Color blindness in humans is a sex-linked recessive trait. A female who is not color blind, but whose father was color blind, has children with a male who is not color blind.
46.What is the likelihood that their son will be color blind?
(A)0%
(B)25%
(C)50%
(D)100%
47.What is the likelihood that their daughter will be color blind?
(A)0%
(B)25%
(C)50%
(D)100%
48.Which of the following is a likely pedigree for this family? Note that circles indicate females, and squares indicate males. Shaded circles and squares indicate individuals with the trait.
(A)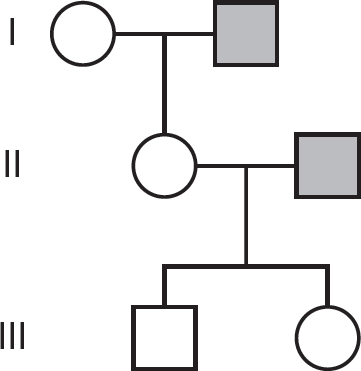
(B)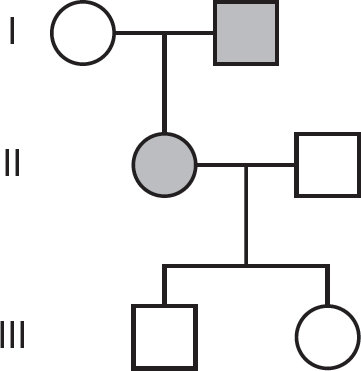
(C)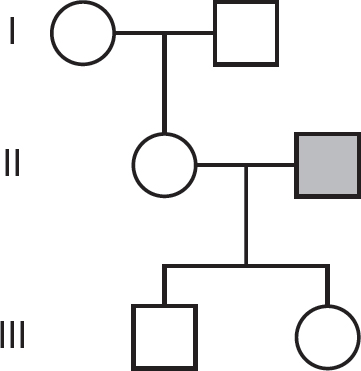
(D)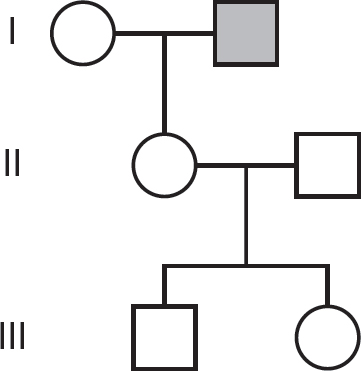
49.Which of the following is a density-independent factor that can limit population size?
(A)competition
(B)disease
(C)predation
(D)weather
Questions 50 and 51
Refer to the following graph.
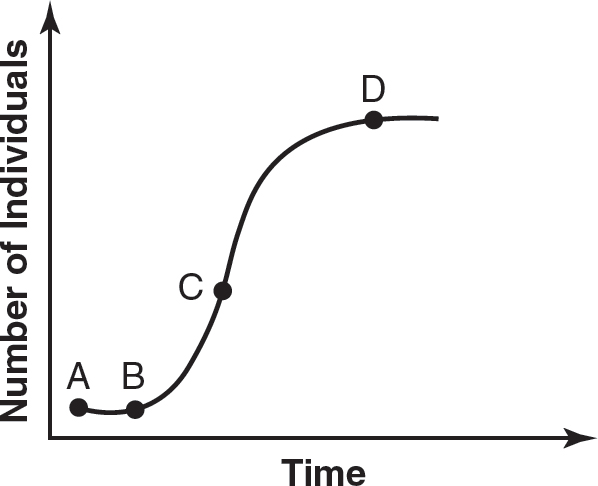
50.Which point on the graph represents the carrying capacity of the environment for this population?
(A)A
(B)B
(C)C
(D)D
51.Which point on the diagram most likely represents a point in which the population is growing exponentially?
(A)A
(B)B
(C)C
(D)D
52.Sea anemones, which live as sessile forms attached to rock surfaces, have stinging nematocysts that release paralyzing toxins (upon contact) into their prey, such as fish. Tentacles move the paralyzed prey into the gastric cavity for ingestion.
Clown fish are covered with a thin layer of mucus that prevents them from being paralyzed by sea anemone toxins. Clown fish live among the tentacles, which provide protection. Predators that attempt to eat clown fish are stung by the sea anemone nematocysts and are then consumed by the sea anemone.
Which of the following correctly describes the relationship between sea anemones and clown fish?
(A)commensalism
(B)competition
(C)mutualism
(D)parasitism
53.In the marine ecosystems on the Pacific Coast of Washington state, sea otters eat sea urchins. Sea urchins eat kelp. Kelp forests provide food and habitat for a wide variety of marine organisms. Due to overhunting from 1750 to 1910, sea otter populations were reduced from over 100,000 to less than 2,000. By 1910, kelp forests off the coast of Washington state virtually disappeared, and the biodiversity of the marine ecosystems on the coast was greatly reduced. Which of the following best describes the ecological role of the sea otter in this ecosystem?
(A)autotroph
(B)detritivore
(C)keystone species
(D)prey species
54.Which of the following is a correct statement about energy in ecosystems?
(A)A net gain in energy can result in the loss of mass and the death of the organism.
(B)Energy is recycled through ecosystems.
(C)Changes in energy availability can disrupt ecosystems.
(D)Heterotrophs capture the energy in sunlight.
55.Which of the following statements about population growth is false?
(A)Reproduction without limiting factors results in the exponential growth of a population.
(B)Density-dependent limits to populations results in logistic growth of a population.
(C)The carrying capacity of an environment depends on resource availability.
(D)K-selected populations can far exceed their environment’s carrying capacity.
56.The synthesis of the amino acid tryptophan in bacteria is controlled by the repressible trp operon. The following figure represents components of the trp operon.
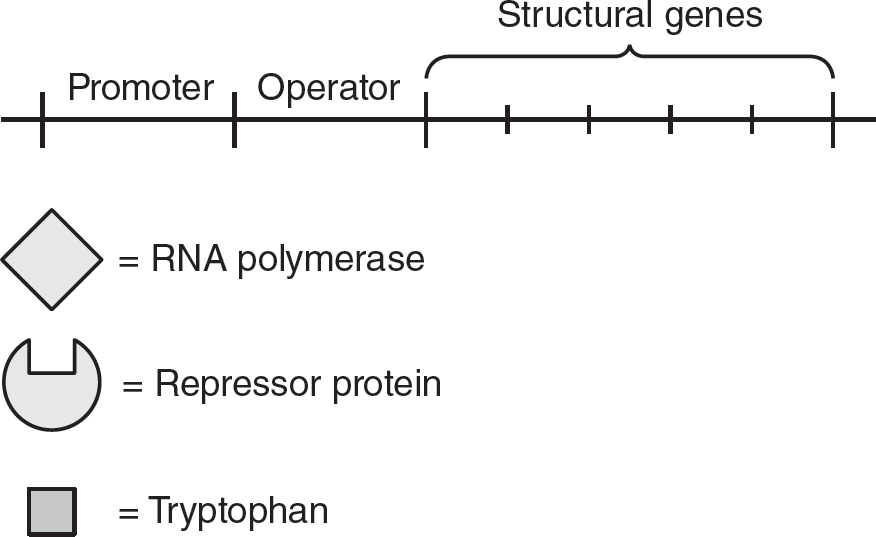
Which of the following best represents the trp operon when the amino acid tryptophan is present in the bacteria’s environment?
(A)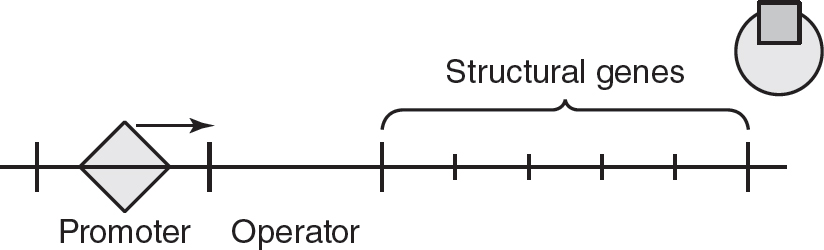
(B)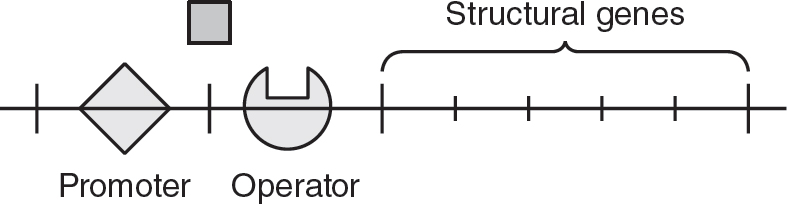
(C)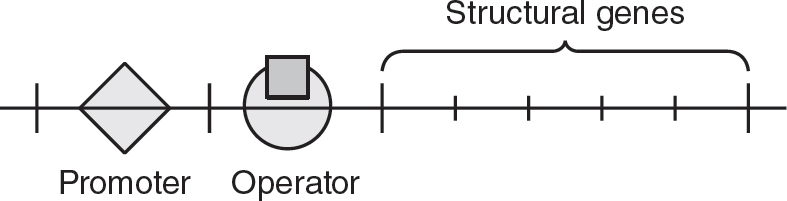
(D)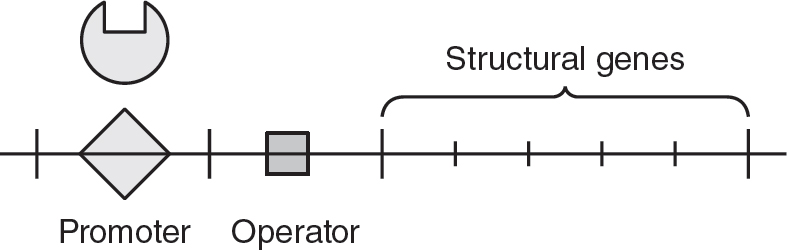
57.The digestion of the sugar lactose in bacteria is controlled by the inducible lac operon. This figure represents the components of the lac operon.
Which of the following best represents the lac operon when the sugar lactose is present in the bacteria’s environment?
(A)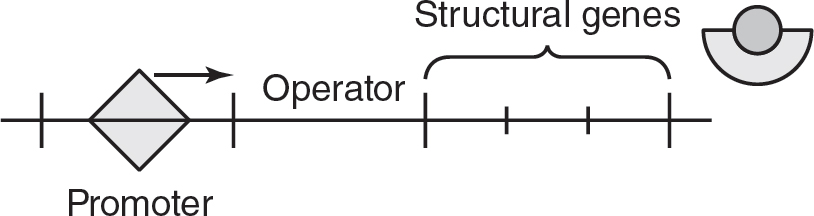
(B)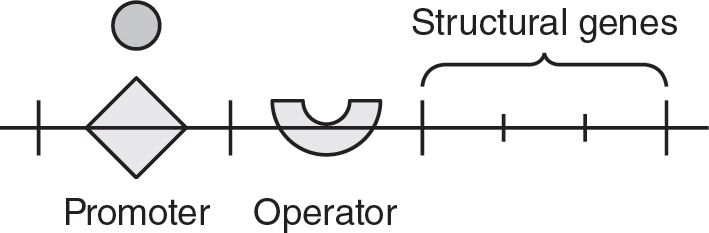
(C)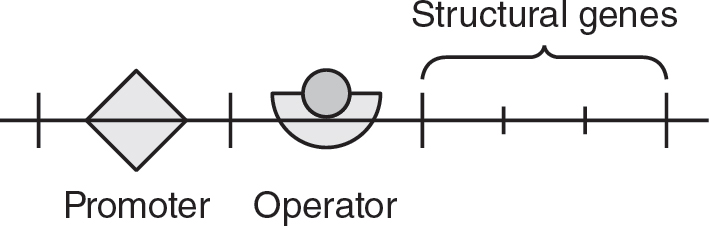
(D)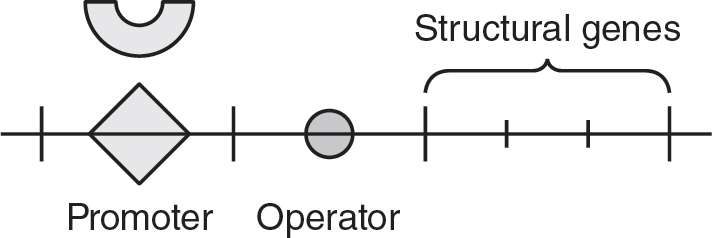
58.Transmembrane proteins span across the entire cell membrane. Where would the hydrophobic amino acids in a transmembrane protein most likely be found?
(A)in contact with the polar phosphates of the phospholipids
(B)on the outer surface of the membrane in contact with the cell’s aqueous surroundings
(C)in contact with the nonpolar fatty acid chains of the phospholipids
(D)on the inner surface of the membrane in contact with the cell’s cytosol
59.In the alpha cells in the pancreas, which produce the peptide hormone insulin, there would likely be a high concentration of which of the following?
(A)lysosomes
(B)centrioles
(C)smooth endoplasmic reticulum
(D)ribosomes
60.A geneticist discovers a previously unknown genetic disorder. Pedigree analysis shows that both males and females can inherit this disorder from their mother but not from their father. Affected females can pass on the allele for this disorder to the next generation, but affected males will not pass on this disorder to the next generation. What is the most likely mode of inheritance of this disorder?
(A)sex-linked recessive
(B)mitochondrial inheritance
(C)autosomal recessive
(D)autosomal dominant

Section II: Free-Response
TIME: 90 MINUTES
DIRECTIONS: Answer each of the following six free-response questions using complete sentences. Allow approximately 20—25 minutes each for the long free-response questions (Questions 1 and 2) and approximately 5—10 minutes each for the short free-response questions (Questions 3, 4, 5, and 6).
1.A scientist completes an analysis of the amino acid sequences of cytochrome c in six different species. The scientist compares how many amino acid differences there are between the cytochrome c protein in humans and that of each of the six different species in the table. The number of amino acid differences is shown in the table.
|
Species |
Number of Amino Acid Differences from Human Cytochrome c |
Chicken |
13 |
Whale |
9 |
Chimpanzee |
1 |
Turtle |
15 |
Tuna |
21 |
Rabbit |
4 |
(a)Explain how amino acid differences in a conserved protein can help scientists determine degrees of relationships between organisms.
(b)Analyze the data, and use it to construct a cladogram of these organisms using the template provided.
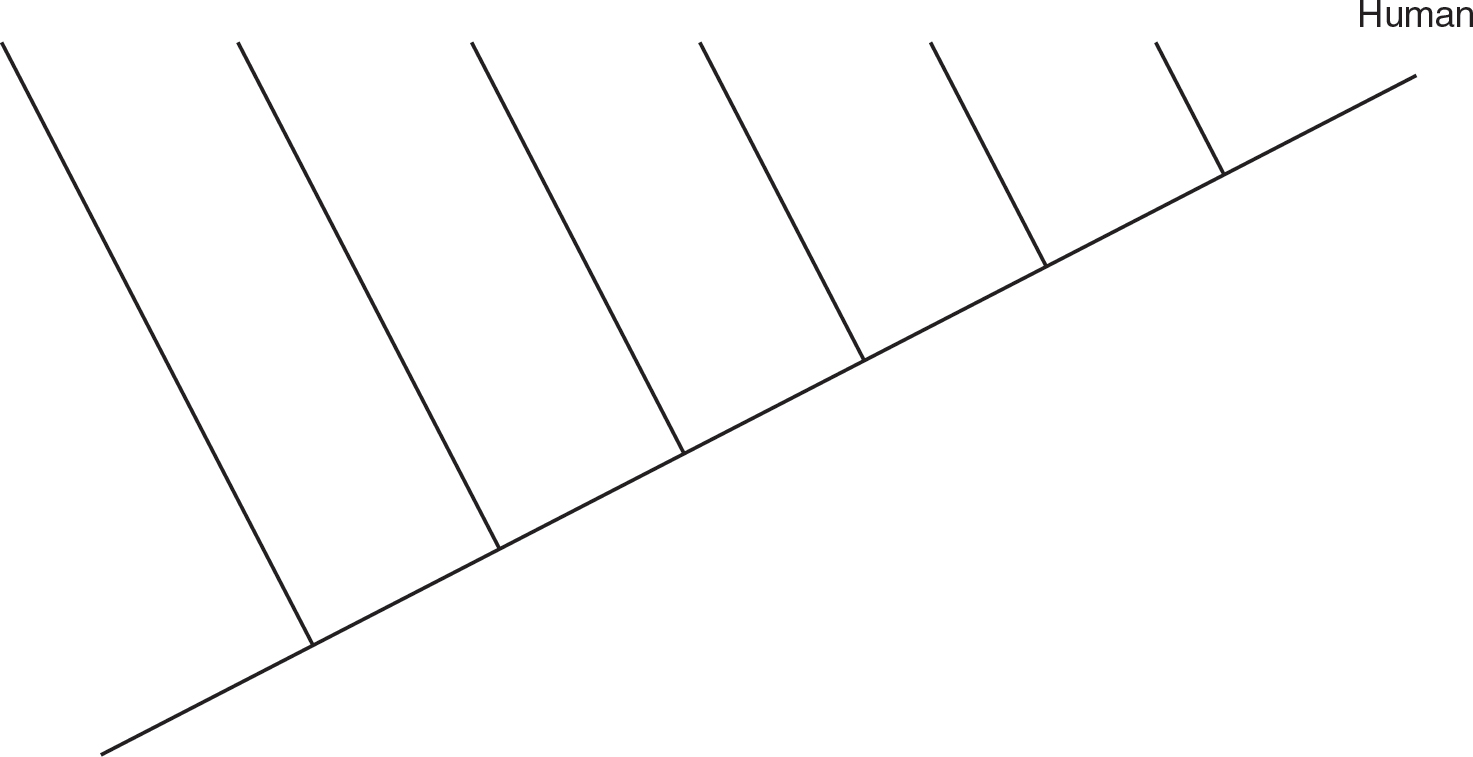
(c)Justify your placement of the organisms on the cladogram in your response to part (b).
(d)A claim is made that chickens share a more recent common ancestor with humans than turtles do. Identify at least one piece of experimental evidence that might be used to support this claim.
2.A botanist measures the stomatal density on both the upper surface (facing the sun) and lower surface (shaded from the sun) of the leaves from two plant species. Purple passionflower, Passiflora incarnata, is native to Florida and Texas and is found in habitats with a humid climate. White oak, Quercus alba, is native to the central and northern United States and prefers a drier climate with seasons. The mean stomatal density and the standard errors of the mean are shown in the following table.
|
Plant Species |
Mean Stomatal Density of Upper Surface (Number of Stomata per mm2) ± SEM* |
Mean Stomatal Density of Lower Surface (Number of Stomata per mm2) ± SEM |
Passiflora incarnata |
90 ± 10 |
345 ± 10 |
Quercus alba |
25 ± 3 |
375 ± 12 |
*Standard Error of the Mean
(a)Describe the role of stomata in water regulation and photosynthesis in plants.
(b)Construct a graph that shows the mean stomatal density for both the upper and lower leaf surfaces of both plants. Be sure to include 95% confidence intervals.
(c)Analyze the data to determine whether there is a statistically significant difference in the mean stomatal densities between the two plants.
(d)Make a claim explaining why the mean stomatal density on the upper surface of the leaves of Passiflora incarnata is different than the mean stomatal density on the upper surface of the leaves of Quercus alba. Justify your claim with your knowledge of the role stomata play in water regulation and photosynthesis in plants.
3.A student conducts an investigation to measure the amount of gas produced by the aquatic plant Elodea. Equal amounts of Elodea are placed in inverted test tubes in four different water baths (at different temperatures) under lights (of the same intensity), as shown in the figure.
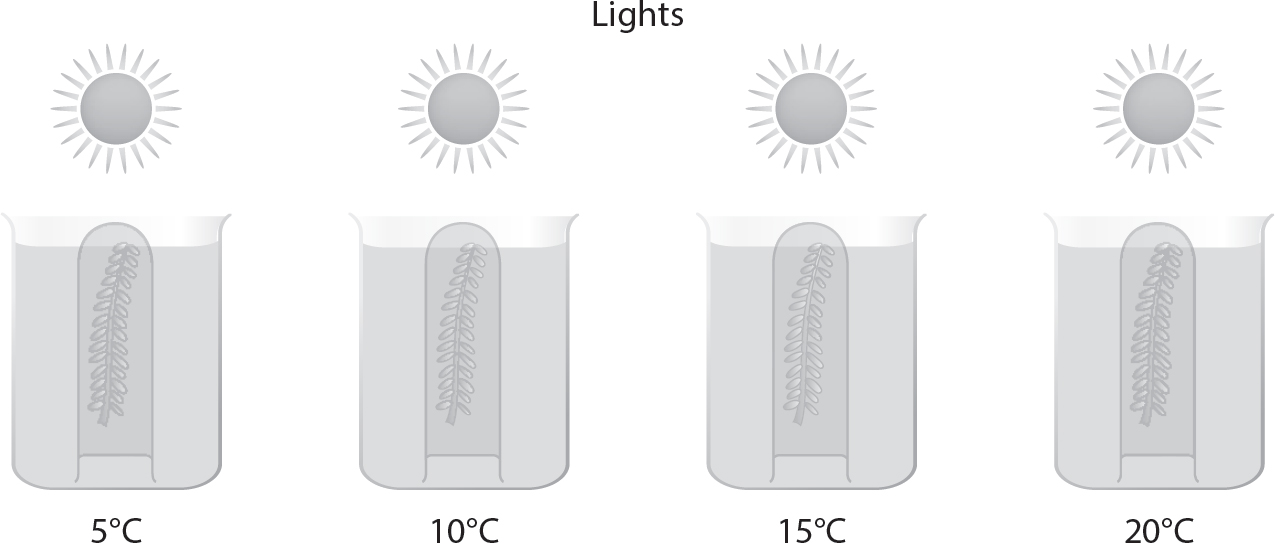
The size of the gas bubble at the top of the inverted test tube is measured after 30 minutes, and that data are displayed in the following table.
|
Temperature |
Size of Gas Bubble After 30 Minutes (mm) |
5°C |
3.5 |
10°C |
5.2 |
15°C |
7.1 |
20°C |
10.4 |
(a)Describe why a gas bubble would form in each tube.
(b)Identify the independent variable, the dependent variable, and at least one experimental control.
(c)Predict the size of the gas bubble if the experiment was repeated with a water bath at a temperature of 25°C.
(d)Justify your prediction from part (c).
4.Acetylcholine (ACh) is a neurotransmitter. The binding of acetylcholine to membrane receptors starts a cell signaling cascade in neurons.
(a)Describe the three steps in cell signaling.
(b)Explain how cell signals are amplified in the cell.
(c)An autoimmune disorder produces antibodies that bind to the acetylcholine receptors, blocking them. Predict the effect this would have on the cell signaling pathway that involves acetylcholine.
(d)Justify your prediction from part (c).
5.A student performs a bacterial transformation experiment. Wild-type E. coli are transformed with a plasmid containing the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene. The GFP gene is attached to the control elements of the repressible tryptophan operon. A diagram of the plasmid is shown in the figure.
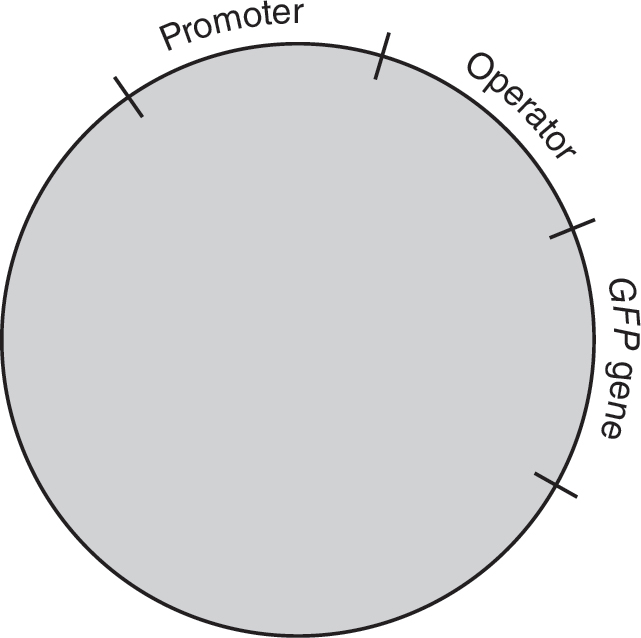
(a)Describe the roles of the promoter and operator in operons.
(b)Explain the effect, if any, of adding tryptophan to the medium in which the transformed bacteria are growing.
(c)Tryptophan is added to the medium in which the bacteria are growing. Using an “X” for tryptophan and an “O” for the repressor protein, represent the likely locations of tryptophan and the repressor protein on or around the operon in the figure above.
(d)Explain how the regulation of the expression of the tryptophan operon relates to negative feedback.
6.In pea plants, round peas are dominant over wrinkled peas, and a purple flower color is dominant over a white flower color. Two pea plants (both of which are heterozygous for round peas and heterozygous for purple flowers) were crossed and produced 1,600 offspring. The number of offspring with each phenotype is shown in the following table.
|
Phenotype |
Number of Offspring |
Round peas, purple flowers |
860 |
Round peas, white flowers |
320 |
Wrinkled peas, purple flowers |
310 |
Wrinkled peas, white flowers |
110 |
(a)Describe the expected numbers of each phenotype. (Assume the genes for pea shape and flower color are on different chromosomes.)
(b)Calculate the chi-square value for this experiment.
(c)Evaluate the data for this dihybrid cross using a p-value of 0.05.
(d)The genes for pea shape and flower color are located on different chromosomes. Explain how the data would have differed if the two genes had been located on the same chromosome.
ANSWER KEY
Practice Test 1
Section I
1.B
2.A
3.B
4.D
5.A
6.C
7.D
8.B
9.A
10.C
11.A
12.A
13.A
14.C
15.A
16.D
17.B
18.C
19.B
20.C
21.C
22.C
23.C
24.D
25.B
26.B
27.A
28.C
29.B
30.A
31.A
32.B
33.B
34.D
35.A
36.B
37.B
38.B
39.A
40.D
41.C
42.D
43.B
44.B
45.A
46.C
47.A
48.D
49.D
50.D
51.C
52.C
53.C
54.C
55.D
56.C
57.A
58.C
59.D
60.B
Section II
See the Answer Explanations section.
Answer Explanations
Section I
1.(B)Ionic compounds have both positive and negative ions. Water is polar, and it has a partially negative end and a partially positive end. When ionic compounds dissolve in water, the partially negative ends of the water molecules are attracted to the positive ions of the ionic compound, and the partially positive ends of the water molecules are attracted to the negative ions of the ionic compound. Choices (A) and (C) are both incorrect because water is polar, not nonpolar. While hydrogen bonds will form between water molecules, hydrogen bonds do not form between water molecules and ions, so choice (D) is incorrect.
2.(A)The hydrophilic phosphate heads will be attracted to the surrounding water molecules. The hydrophobic lipid tails will be repelled by the water and orient themselves in the center of the micelle. Thus, part A represents the hydrophilic portions of the micelle, and part B represents the hydrophobic portions of the micelle. Choice (B) is incorrect because the phosphate heads are hydrophilic, not hydrophobic, and the tails are hydrophobic, not hydrophilic. Although choices (C) and (D) do refer to fats and associated fatty molecules that may be found in a plasma membrane of a cell, that is not what is represented in this image. Thus, both (C) and (D) are incorrect.
3.(B)This graph shows the means correctly plotted with 95% confidence intervals. The upper limit of the 95% confidence interval is the mean plus 2 ![]() , and the lower limit is the mean minus 2
, and the lower limit is the mean minus 2 ![]() . Choice (A) is incorrect because the upper and lower limits were calculated with only 1
. Choice (A) is incorrect because the upper and lower limits were calculated with only 1 ![]() , not 2
, not 2 ![]() . Choice (C) is incorrect because even though it correctly plots the means, it does not correctly plot the 95% confidence intervals. Also, it is a line graph, which is inappropriate for categorical data, such as the data in this question. Choice (D) plots the means and confidence intervals correctly, but it is a line graph, which is inappropriate for the categorical data given in the question, so it is incorrect.
. Choice (C) is incorrect because even though it correctly plots the means, it does not correctly plot the 95% confidence intervals. Also, it is a line graph, which is inappropriate for categorical data, such as the data in this question. Choice (D) plots the means and confidence intervals correctly, but it is a line graph, which is inappropriate for the categorical data given in the question, so it is incorrect.
4.(D)The 95% confidence intervals of rubbing alcohol and olive oil do overlap, so these two liquids are the least likely to have a statistically significant difference. Choice (A) is incorrect because the confidence intervals for water and rubbing alcohol do not overlap. Since the confidence intervals for water and olive oil do not overlap, they are more likely to have a statistically significant difference, so choice (B) is incorrect. Similarly, the confidence intervals for water and rubbing alcohol do not overlap, so they also are likely to have a statistically significant difference, making choice (C) incorrect as well.
5.(A)Surfactants, like soap for example, are amphipathic molecules, which means they have both polar and nonpolar components. So the surfactant will disrupt the formation of hydrogen bonds between the water molecules, reducing the surface tension of the water. So fewer drops of water will be able to stay on the surface of the penny. Choices (B) and (C) are incorrect because the surfactant will neither disrupt nor strengthen the formation of polar ends, or covalent bonds, within the water molecules. The surfactant will decrease the surface tension of water, so choice (D) is incorrect.
6.(C)The nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, are the carriers of genetic information. Choices (A), (B), and (D) are incorrect because carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins do not carry genetic information.
7.(D)A polypeptide chain with 15 amino acids would have 14 peptide bonds. Breaking each peptide bond would require a hydrolysis reaction that would consume 1 molecule of water per bond, so 14 molecules of water would be needed. Choices (A) and (B) are incorrect because dehydration reactions form bonds, not break them. Choice (C) is incorrect because only 14 water molecules would be needed, not 15, and those water molecules would be consumed, not produced.
8.(B)Secondary structure in proteins is formed by hydrogen bonds between the amino acids in the polypeptide chain. Choice (A) is incorrect because primary structure is held together by peptide bonds. Tertiary structure is driven primarily by hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions and is not formed by peptide bonds, so choice (C) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because quaternary structure is only found in proteins that are composed of more than one subunit.
9.(A)Solutions with lower solute concentrations have higher water potentials; side A initially has a lower solute concentration, so it has a higher water potential. Choice (B) is incorrect because solutions with higher solute concentrations would have lower, not higher, water potentials. Aqueous solutions with different solute concentrations would have different water potentials, so choice (C) is incorrect. While sides A and B do contain the same solutes, they have different concentrations of each solute, so their water potentials are different, making choice (D) incorrect.
10.(C)As stated in the question, glucose can cross the membrane. Since side B has an initially higher concentration of glucose than side A, glucose will move down its concentration gradient from side B to side A, and the concentration of glucose on side A will increase. Choice (A) is incorrect because the concentration of glucose on side B will decrease, not increase, as glucose moves down its concentration gradient. Choices (B) and (D) are incorrect because albumin cannot cross the membrane according to the question.
11.(A)Side A has a lower solute concentration and a higher water potential than side B, so water will move from the higher water potential on side A to the lower water potential on side B. Since albumin cannot cross the barrier in order to satisfy equilibrium, water will flow toward side B in order to dilute the solution. Choice (B) correctly states that water will move from side A to side B, but it incorrectly explains the reason for the movement of water in this direction. Choices (C) and (D) are incorrect because water will move from side A to side B, not from side B to side A.
12.(A)Pepsin is found in the stomach, which has a pH of 2.5, so it is most likely to have its optimum activity at a pH of 2.5. Choice (B) shows the optimum activity at a pH of 7.0, so it is incorrect based on the information in the table. The graph in choice (C) shows the optimum activity at a basic pH of 10.0, so it is incorrect. Choice (D) shows a constant rate of increasing enzyme activity as the pH increases, so it is also incorrect.
13.(A)According to the table, amylase is found in the mouth and pepsin is found in the stomach. So changing the pH of those locations would most likely affect the activity of those enzymes. Lipase and trypsin are found in the small intestine, so changes in the pH of the mouth and the stomach acid would not likely affect their activity. Thus, choices (B), (C), and (D) are incorrect.
14.(C)Lipase and trypsin are found in the relatively neutral pH of the small intestine. So if the acidic contents of the stomach were added to the small intestine in an uncontrolled manner, the pH of the small intestine would most likely change. This would affect the activity of lipase and trypsin. Amylase is found in the mouth, so a change in the pH of the small intestine would not affect its activity. This rules out choices (A) and (D). Choice (B) is incorrect because pepsin is most active in the stomach and a change in the pH of the small intestine would not affect its activity.
15.(A)Anaerobic prokaryotes do not have mitochondria nor do they have access to oxygen, so they are limited to performing glycolysis. Choices (B), (C), and (D) would require the presence of oxygen and mitochondria, so those choices are all incorrect.
16.(D)Oxygen is a product of photosynthesis, so the areas where the bacteria congregated would correspond with the areas that carried out the most photosynthesis. According to the table, wavelengths of 420—470 nm and 660—700 nm correspond to blue-violet and red light, respectively, so those colors of light resulted in the greatest amount of photosynthesis. Photosynthetic pigments absorb light of specific wavelengths; not every wavelength of light can drive the process of photosynthesis, making choice (A) incorrect. Choice (B) is incorrect because aerobic bacteria are not required for the algae to produce oxygen; the concentration of aerobic bacteria are used as an indirect measure of the amount of oxygen produced. According to the table, green light has a wavelength in the range of 495—570 nm, which does not correspond to the areas where the greatest numbers of bacteria congregated. Therefore, less oxygen was present in that area and less photosynthesis occurred under green light, so choice (C) is incorrect.
17.(B)Green light has wavelengths between 495—570 nm based on the table. Choices (A), (C), and (D) are incorrect because violet, orange, and red light have wavelengths in the ranges of 380—450 nm, 590—620 nm, and 620—750 nm, respectively.
18.(C)The role of photons of light energy in photosynthesis is to excite the electrons in the photosystems. Light does not activate the genes used in photosynthesis, so choice (A) is incorrect. Choice (B) is incorrect because carbon dioxide is consumed, not produced, during photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide is fixed in the light-independent reactions, not during the Krebs (citric acid) cycle, so choice (D) is incorrect.
19.(B)The temperature of the chambers is the independent variable. The number of germinating mung beans was kept constant, so it is not an independent variable. Thus, choice (A) is incorrect. The amounts of carbon dioxide produced and oxygen consumed are the dependent variables, so choices (C) and (D) are incorrect.
20.(C)The mung beans at 25° Celsius increased the level of carbon dioxide from 400 to 600 ppm over the 30-minute period, so the rate is ![]() per minute. The mung beans at 4° Celsius increased the level of carbon dioxide from 400 to 450 ppm over the 30-minute period, so that rate is
per minute. The mung beans at 4° Celsius increased the level of carbon dioxide from 400 to 450 ppm over the 30-minute period, so that rate is ![]() per minute. Based on this data, the mung beans at 25° Celsius have a higher respiration rate than the mung beans at 4° Celsius. Thus, choice (C) is the only correct statement, and choices (A), (B), and (D) are incorrect.
per minute. Based on this data, the mung beans at 25° Celsius have a higher respiration rate than the mung beans at 4° Celsius. Thus, choice (C) is the only correct statement, and choices (A), (B), and (D) are incorrect.
21.(C)Paracrine signaling stimulates nearby cells. Autocrine signaling stimulates the same cell that produces the signal, so choice (A) is incorrect. Choice (B) is incorrect because juxtacrine signaling occurs between cells that are in direct contact (touching). Endocrine signals travel long distances, either through circulatory systems or through the air, so choice (D) is incorrect.
22.(C)Quorum sensing in bacteria affects nearby bacteria cells and is an example of paracrine signaling. Choice (A) is incorrect because synaptic signaling is specific to neurons that secrete neurochemicals across a synaptic gap. Cytokine signaling occurs between cells that are in direct contact, so choice (B) is incorrect. Endocrine signaling occurs over long distances, whereas quorum sensing occurs over short distances, so choice (D) is incorrect.
23.(C)Steroid hormones can cross the cell membrane unassisted and bind to receptors in the cell’s cytoplasm. G-protein-linked receptors, tyrosine kinase receptors, and membrane ion channel receptors are all types of membrane-bound receptors, which bind to hydrophilic ligands, so choices (A), (B), and (D) are incorrect.
24.(D)Cyclic AMP (cAMP) and the calcium ion are both secondary messengers. Choices (A) and (C) are incorrect because cAMP and the calcium ion do not function as receptors. cAMP and the calcium ion are not ligands, so choice (B) is also incorrect.
25.(B)Gap junctions and plasmodesmata are channels that allow direct contact between cells and an exchange of materials, so they are examples of juxtacrine signaling. Choices (A), (C), and (D) do not describe the correct type of signaling.
26.(B)DNA is replicated during the S stage of the cell cycle. At the start of the S stage, each chromosome has one chromatid; at the end of the S stage, each chromosome has two identical chromatids, with twice the amount of DNA as they had at the beginning of the S stage. Choices (A), (C), and (D) are all incorrect because they list incorrect amounts of DNA and/or incorrect numbers of chromosomes.
27.(A)Cells that are not actively dividing and are fully differentiated will leave the cell cycle and enter the G0 stage. Choice (B) is incorrect because during G1, the cell is growing and getting ready for cell division. During the S stage, the DNA is replicated in preparation for cell division, so choice (C) is also incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because during G2, the cell is making final preparations for mitosis.
28.(C)Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are present at near-constant levels throughout the cell cycle but do not become active until they are bound to cyclins. The levels of cyclins rise and fall during the cell cycle. Choices (A) and (B) are incorrect because cyclins are not present at near-constant levels during the cell cycle. Phosphatases remove phosphate groups from compounds, which usually inactivates them, so choice (D) is incorrect.
29.(B)Replication of the genetic material occurs during the S stage. Chromosomes align along the center of the cell during metaphase. The chromatids of chromosomes separate during anaphase. Choice (A) is incorrect because G1 and G2 are not the stages during which chromosomes align or separate. G2 is not when replication of the genetic material occurs, and telophase involves the formation of two new nuclei. So choice (C) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because prophase involves the condensation of the genetic material into visible chromosomes and the dissolution of the nuclear membrane.
30.(A)The first step in cell signaling is the binding of the ligand to the receptor. So if an antibody irreversibly bound to a receptor, the cell signaling process could not start. Choice (B) would affect the secondary messenger cyclic AMP (cAMP) because adenylyl cyclase catalyzes the formation of cAMP from ATP. Choices (C) and (D) are incorrect because protein kinases and protein phosphatases are involved in the transduction of the signal, which occurs after the binding of the ligand to the receptor.
31.(A)In this problem, it is stated that the population is NOT in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, nor is this population under the conditions necessary for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. So the Hardy-Weinberg equations cannot be used. To find the frequency of the nontaster allele, total up how many recessive alleles are in the population and divide by the total number of alleles in the population. There are a total of 1,000 individuals (520 + 400 + 80 = 1,000), so there are 2,000 alleles in total. Each of the 400 heterozygous individuals contributes one nontaster allele (400 nontaster alleles), and each of the 80 nontaster individuals contributes two nontaster alleles (160 nontaster alleles) for a total of 560 nontaster alleles: ![]() . Choices (B), (C), and (D) do not list the correct frequency.
. Choices (B), (C), and (D) do not list the correct frequency.
32.(B)Carriers of the nontasting allele are heterozygous. There are 400 heterozygous individuals in a total population of 1,000 individuals, so the frequency of carriers is ![]() . Choices (A), (C), and (D) do not list the correct frequency.
. Choices (A), (C), and (D) do not list the correct frequency.
33.(B)Prokaryotic cells do not contain mitochondria or chloroplasts, and eukaryotic cells have linear chromosomes, so cell B has characteristics of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Choice (A) is incorrect because circular chromosomes and the lack of mitochondria and chloroplasts are all characteristics of prokaryotic cells. Choices (C) and (D) are eukaryotic cells because they both have linear chromosomes and membrane-bound organelles.
34.(D)Cell D has both linear chromosomes and chloroplasts. Thus, of the four cells, cell D is most closely related to modern plants. Choice (A) is incorrect because it has circular chromosomes, which are a characteristic of prokaryotic cells. Choices (B) and (C) both do not contain chloroplasts, so neither is closely related to modern plants.
35.(A)Two species that occupy different habitats cannot interbreed and will remain separate species. Choice (B) is incorrect because temporal isolation occurs when organisms are active at different times of the day or have breeding seasons at different times of the year. Behavioral isolation involves different mating behaviors, for example mating dances or bird calls, so choice (C) is incorrect. Mechanical isolation occurs when morphological differences prevent the meeting of gametes, so choice (D) is incorrect.
36.(B)Gametic isolation occurs when the gametes of different species are incompatible, leading to reproductive isolation. Choice (A) is incorrect because mechanical isolation occurs when morphological differences prevent the meeting of gametes. Since both species of sea urchins can release their gametes into the water and their gametes can come into contact, there is no mechanical isolation in this instance. Reduced hybrid fertility occurs when a hybrid of the two organisms is produced but that hybrid is sterile, so choice (C) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because hybrid breakdown occurs when a fertile hybrid is produced but with each successive generation, the offspring of the hybrid are weaker or less fertile.
37.(B)The two strands of DNA are antiparallel, so the new strand would start with a 5′ end. Following the pairing rules for DNA (A-T and C-G), this leaves choice (B) as the correct answer. Choice (A) is incorrect because the new DNA strand is not antiparallel to the original strand. Choices (C) and (D) are incorrect because DNA replication does not incorporate U’s into the new strand; the base pair uracil is only found in RNA.
38.(B)DNA replication is semiconservative, because each strand of DNA produced during DNA replication contains one original strand from the template DNA and one newly synthesized DNA strand. Choice (A) is incorrect because the entire DNA is copied during DNA replication. While newly synthesized DNA does contain parent and daughter DNA, it is not a random mixture of the two (one strand is from the parent molecule and one strand is newly synthesized). Thus, choice (C) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because the original DNA molecule is separated into two strands during DNA replication and each of those strands serves as a template for a new molecule of DNA.
39.(A)On the lagging strand, short fragments of new DNA are synthesized discontinuously during DNA replication. Choice (B) is incorrect because the leading strand of DNA is synthesized continuously, not discontinuously. DNA polymerase is used on both strands to synthesize DNA, so choice (C) is incorrect. Lagging strand and leading strand synthesis occur simultaneously, so choice (D) is incorrect.
40.(D)RNA polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes RNA from a DNA template. Choice (A) is incorrect because helicase is the enzyme that unwinds DNA at the start of DNA replication. Ligase is used to join DNA fragments (for example, the Okazaki fragments created during the discontinuous replication of the lagging strand of DNA), so choice (B) is incorrect. DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA during DNA replication, so choice (C) is incorrect.
41.(C)Introns are found in eukaryotes (and in archaea). Introns are not translated, so choice (A) is incorrect. Although introns are not directly converted into proteins, some introns may have a function in gene regulation, so choice (B) is incorrect. Eukaryotes do contain introns, so choice (D) is incorrect.
42.(D)Ribosomes are involved in translation, so an antibiotic that interferes with ribosomes would negatively impact the process of translation. Choices (A), (B), and (C) are incorrect because none of these processes (DNA replication, posttranscriptional modification of mRNA, or transcription) involve ribosomes.
43.(B)Eukaryotic mRNA contains introns, which are removed before the mRNA exits the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, so eukaryotic mRNA is shorter than the DNA that codes for it. Choice (A) is incorrect because there is no evidence in the question that the scientist made any errors. While RNA is a less stable molecule than DNA due to the extra oxygen atom in RNA’s five-carbon sugar, that is not the reason why eukaryotic mRNAs are shorter than the genes that code for them. Thus, choice (C) is incorrect. The poly-A tail added to eukaryotic mRNAs during posttranscriptional processing would make the mRNA longer, not shorter, so choice (D) is incorrect.
44.(B)The best way to solve this type of problem is to treat each gene separately and then combine the probabilities. The probability that the cross AA × Aa would produce Aa is ![]() . Similarly, the probability that the cross Bb × Bb would produce Bb is also
. Similarly, the probability that the cross Bb × Bb would produce Bb is also ![]() . The probability that the cross Cc × CC would produce Cc is also
. The probability that the cross Cc × CC would produce Cc is also ![]() . Therefore, the probability of all three events occurring is the product of their individual probabilities:
. Therefore, the probability of all three events occurring is the product of their individual probabilities: ![]() . Choices (A), (C), and (D) do not list the correct probability.
. Choices (A), (C), and (D) do not list the correct probability.
45.(A)The trait occurs in every generation and affects both males and females, so it is most likely an autosomal dominant trait. Sex-linked dominant traits would be passed on to every offspring of a female who has the trait. That’s not what’s shown here, so choice (B) is incorrect. Choice (C) is incorrect because sex-linked recessive traits are more often expressed in males than females because males have only one X chromosome. Mitochondrial inheritance occurs from mother to offspring; males do not pass on mitochondrial genes to their offspring, so choice (D) is incorrect.
46.(C)Females have two X chromosomes, and the genes for color blindness are located on the X chromosome. Females inherit one X chromosome from each parent. If the female in the question stem does not express color blindness, one of her X chromosomes does not contain the color blindness allele. Her father was color blind, so the X chromosome she inherited from him must have the color blindness allele, and therefore she must be heterozygous (XBXb). If she has a child with a man who is not color blind (XBY) and that child is a son, the likelihood the son would be color blind would be 50%, as shown in the following Punnett square.
Choices (A), (B), and (D) do not list the correct percentage.
47.(A)The color blindness trait is recessive. In order for the daughter to be color blind, she would have to inherit the allele from each of her parents. Since her father is not color blind, she cannot inherit the allele from him, so there is no probability for her to be color blind. Choices (B), (C), and (D) do not list the correct percentage.
48.(D)The woman in generation II is not color blind but her father in generation I was color blind, so the pedigree shown in choice (D) matches the text description. Choice (A) is incorrect because the male in generation II is not color blind (according to the text), so his square should not be shaded. The woman in generation II is not color blind (according to the text), so her circle should not be shaded. Therefore, choice (B) is incorrect. Choice (C) is incorrect for two reasons. First, the male in generation I was color blind, so his square should be shaded. Second, the male in generation II is not color blind, so his square should not be shaded.
49.(D)Weather is a density-independent factor that is not affected by population density. Choices (A), (B), and (C) all do depend on population density and are therefore incorrect.
50.(D)The number of individuals is reaching its maximum at point D, which represents the carrying capacity of the environment. Choices (A) and (B) represent the lag phase of growth and are therefore incorrect. Choice (C) is when the rate of population growth is the greatest, which is exponential growth. Thus, choice (C) does not represent the carrying capacity and is therefore incorrect.
51.(C)Exponential growth is when the rate of population growth is the greatest. On this graph, exponential growth is shown at point C. Choices (A) and (B) represent points during the lag phase of growth, so those choices are incorrect. The carrying capacity of the environment is represented by point D, so choice (D) is incorrect.
52.(C)Mutualism is a type of symbiotic relationship that results when both organisms benefit: the clown fish is protected from predators, and the sea anemone gains access to prey that is attracted to the clown fish. Commensalism is when one member benefits and the other member is neither helped nor harmed; that is not the case in this scenario, so choice (A) is incorrect. Competition is when two organisms are competing for the same limited resource; that is not what’s happening in this situation, so choice (B) is incorrect. Parasitism is when one member benefits and the other member is harmed; no member is harmed in this relationship, so choice (D) is also incorrect.
53.(C)Keystone species have a disproportionally large effect on their environment relative to their abundance. When the sea otter populations declined in numbers, the biodiversity of the entire ecosystem was affected, so sea otters are a keystone species in this ecosystem. Autotrophs produce their own nutrition, usually through photosynthesis. Sea otters are not autotrophs, so choice (A) is incorrect. Detritivores eat dead organic material, allowing nutrients to be recycled through the ecosystem. This description does not match the role of sea otters in the question, so choice (B) is incorrect. Sea otters are a predator species, not a prey species, in this ecosystem, so choice (D) is also incorrect.
54.(C)Ecosystems can be disrupted and thrown out of balance if energy availability changes. A net gain in energy can result in the gain of mass by an organism; it would not result in the death of the organism, so choice (A) is incorrect. Energy is not recycled through ecosystems; each change in trophic level results in a loss of energy (from the consumer to the environment) as heat. So choice (B) is also incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because autotrophs, not heterotrophs, capture the energy in sunlight.
55.(D)K-selected populations do not far exceed their environment’s carrying capacity; once a K-selected population reaches the carrying capacity, its numbers fluctuate moderately around the environment’s carrying capacity. r-selected populations will fluctuate greatly around their environment’s carrying capacity and far exceed it on occasion. Choices (A), (B), and (C) are all true statements about population growth. Without limiting factors, organisms will exhibit exponential growth. Density-dependent limits will cause populations to grow in a logistic manner. The resources available determine an environment’s carrying capacity.
56.(C)In repressible operons, the repressor protein needs to bind to a corepressor to be capable of binding to the operator. The corepressor is often the product produced by the operon. In the trp operon, the amino acid tryptophan serves as the corepressor. When excess amounts of tryptophan are available, tryptophan binds to the repressor, which then binds to the operator. This prevents transcription of the operon by RNA polymerase and prevents the production of more tryptophan. Choice (A) is incorrect because while it does show tryptophan bound to the repressor, the repressor is not bound to the operator. In choice (B), the repressor is bound to the operator but without its corepressor, so choice (B) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because it shows tryptophan bound to the operator, but tryptophan cannot bind to the operator on its own.
57.(A)In inducible operons, the repressor protein can bind to the operator on its own, shutting down the operon. Inducible operons usually produce enzymes that are involved in digesting a compound. The inducer molecule is often the compound that is digested by the products of the inducible operon. When the inducer molecule is present, the inducer binds to the repressor and the repressor undergoes a shape change, which causes it to be released from the operator. RNA polymerase can then begin transcription of the operon. Choice (B) is incorrect because lactose is present but is not bound to the repressor protein (and the repressor is bound to the operator). In choice (C), lactose is bound to the repressor but the repressor is still bound to the operator, so this choice is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because it shows lactose bound to the operator, but only repressors can bind directly to the operator.
58.(C)The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer in which the polar phosphate heads are on both the inner and outer surfaces of the membrane and the hydrophobic lipid tails are in the interior of the membrane. The hydrophobic portions of transmembrane proteins would most likely be found in contact with the hydrophobic (nonpolar) lipids in the cell membrane. The hydrophobic portions of transmembrane proteins would be repelled by the polar phosphates of the phospholipids, so choice (A) is incorrect. Both the aqueous surroundings of the cell and the cell’s cytosol are largely polar, so the hydrophobic portions of transmembrane proteins would be repelled by those environments, making choices (B) and (D) incorrect.
59.(D)Ribosomes produce proteins, so a cell that produced large amounts of a peptide (protein) hormone would likely have a high concentration of ribosomes. Lysosomes are involved in digesting compounds; they are not involved in protein production, so choice (A) is incorrect. Choice (B) is incorrect because centrioles are involved in organizing microtubules during cell division. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum detoxifies poisons and is involved in lipid production, not the production of peptides, so choice (C) is also incorrect.
60.(B)During fertilization, the vast majority of mitochondria are passed on to offspring from the mother because the eggs are thousands of times larger than the sperm. Thus, mitochondrial DNA is inherited from the mother. Males do not pass on their mitochondrial DNA to their offspring. Choice (A) is incorrect because sex-linked recessive genes can be passed on to offspring by either the mother or the father. Autosomal genes can be passed on to offspring by either parent, so choices (C) and (D) are incorrect.
Self-Analysis Chart for Section I
Use this chart to help identify areas where you need to focus your review. After scoring the multiple-choice section, circle the questions in this chart that you answered incorrectly. Note the units that you scored well in as well as the units that might require further study. Be sure to also review the answer explanations for Section II as all of those questions cover a wide variety of units and topics.
|
Unit |
Questions |
Unit 1: Chemistry of Life |
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 |
Unit 2: Cell Structure and Function |
9, 10, 11, 33, 34, 58, 59 |
Unit 3: Cellular Energetics |
12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20 |
Unit 4: Cell Communication and Cell Cycle |
21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 |
Unit 5: Heredity |
31, 32, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 60 |
Unit 6: Gene Expression and Regulation |
37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 56, 57 |
Unit 7: Natural Selection |
35, 36 |
Unit 8: Ecology |
49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55 |
Section II
1.(a)Organisms that share a more recent common ancestor have had less time during which mutations can accumulate, so their proteins will have fewer amino acid differences than organisms that share a more distant common ancestor.
(b)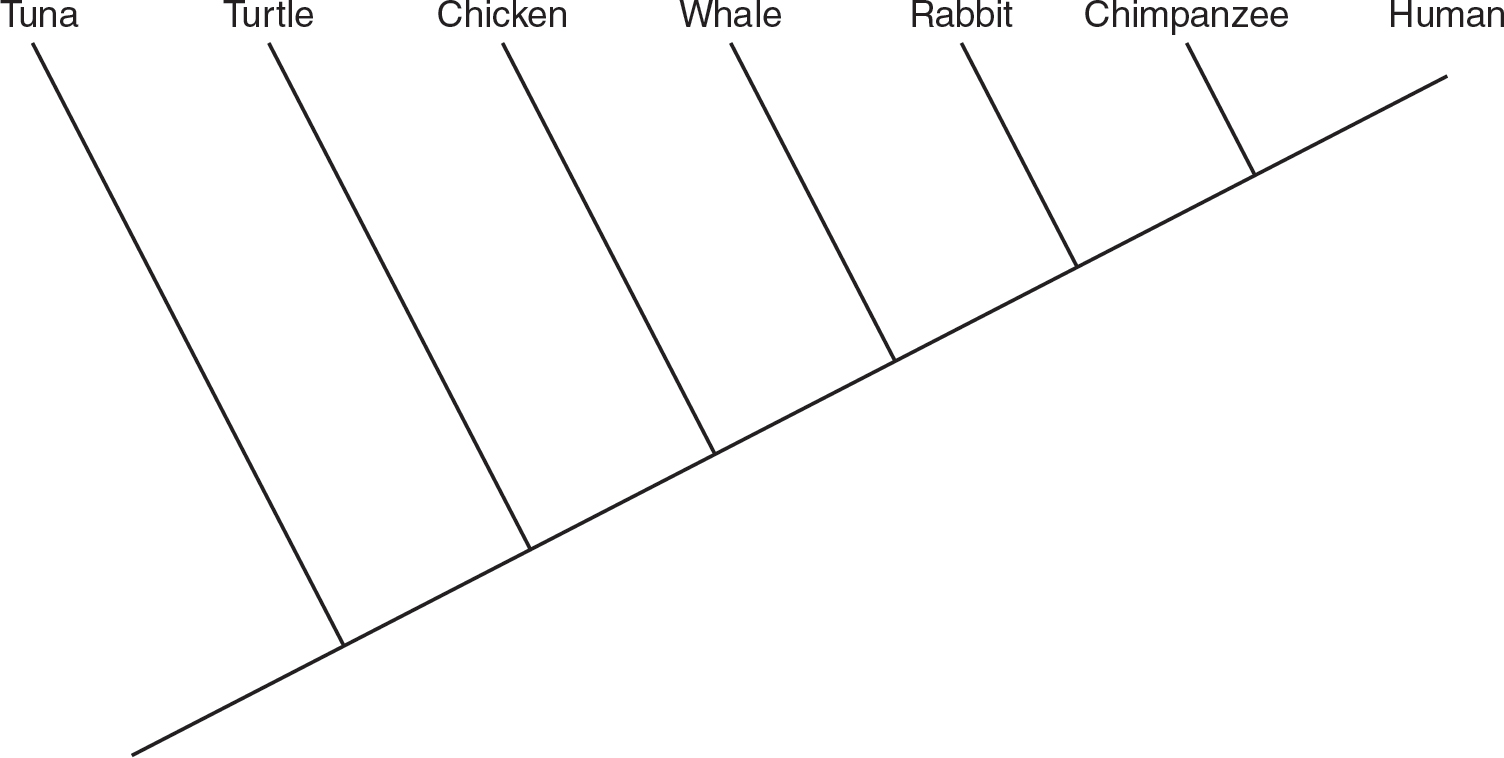
(c)Chimpanzees have the fewest number of amino acid differences from humans in their cytochrome c protein, so they are placed closest to humans on the cladogram as the most recent common ancestor. Tuna have the greatest number of amino acid differences from humans in their cytochrome c protein, so they are placed farthest from humans on the cladogram as the most distant common ancestor. The other organisms are placed in order of the number of amino acid differences from humans. Those with fewer differences are closer to humans, and those with more differences are closer to tuna.
(d)One could look at the number of amino acid differences in a different protein to see if chickens still have fewer amino acid differences from humans than turtles do. One could also look at DNA sequences of the three species or look for homologous structures.
2.(a)When stomata open, the plant can take in the carbon dioxide it needs for photosynthesis. However, when stomata open, the plant can also lose water through the process of transpiration. The lower the water potential in the plant’s surroundings, the more likely the plant is to lose water when its stomata are open.
(b)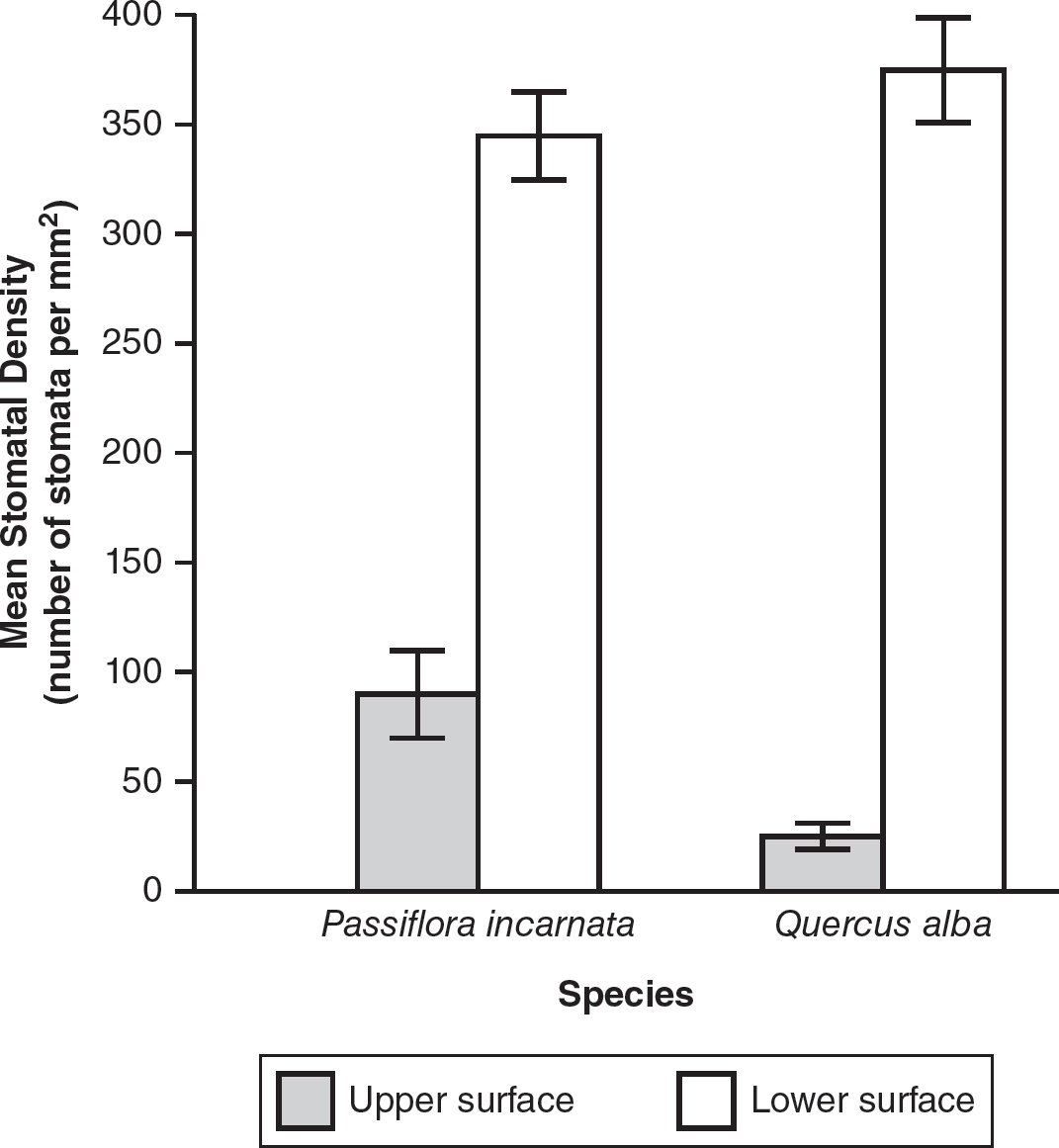
(c)In looking at the data for the lower surfaces of the leaves of the two species, the 95% confidence intervals overlap. So one cannot be sure if there is a statistically significant difference between the mean stomatal densities on the lower surfaces of the leaves of the Passiflora incarnata and Quercus alba. However, the 95% confidence intervals for the upper surfaces of the two species do not overlap. (The lower limit of the 95% confidence interval of Passiflora incarnata is 70 stomata per mm2, and the upper limit of the 95% confidence interval of Quercus alba is 31 stomata per mm2.) Therefore, there is likely a statistically significant difference in the mean stomatal densities found on the upper surfaces of the leaves of the two species.
(d)The mean stomatal density on the upper surface of the leaves of Passiflora incarnata is greater than the mean stomatal density on the upper surface of the leaves of Quercus alba because Passiflora incarnata typically grows in more humid environments than does Quercus alba. If the environment surrounding a plant is more humid, the difference in water potential between the plant and its surroundings will be less, and the plant will likely lose less water to its environment when it opens its stomata to take in the carbon dioxide needed for photosynthesis. In drier environments, like the ones in which Quercus alba is typically found, the difference in water potential between the plant and its environment is greater. When the plant opens its stomata to take in the carbon dioxide needed for photosynthesis, it is more likely to lose water to its environment.
3.(a)Plants produce oxygen during photosynthesis, and the oxygen produced by the Elodea during photosynthesis would accumulate in the inverted tubes.
(b)The independent variable is the temperature of the water baths. The dependent variable is the size of the gas bubbles (in mm) after 30 minutes. Experimental controls include the intensity of the lights, the type of plant, and the amount of the plant in the tubes.
(c)The gas bubble would be expected to be at least 10.4 mm or larger.
(d)Based on the data shown, the increase in the size of the gas bubble with increasing temperature indicates a direct relationship with the temperature. Photosynthesis is a chemical process, and increased kinetic energy from the increased water temperature would increase chemical reactions, producing more oxygen gas at 25°C than at the lower temperatures.
4.(a)The three steps in cell signaling are reception (binding of the ligand to its receptor), transduction (the steps that occur after the binding of the ligand that trigger the appropriate response), and response (the cell’s desired response to the presence of the ligand).
(b)Cell signals are amplified in the cell when one chemical reaction in the transduction process triggers multiple chemical reactions and each of those chemical reactions trigger multiple chemical reactions. This allows one ligand-binding event to trigger hundreds or even thousands of chemical reactions in the cell.
(c)The cell would no longer be able to respond to acetylcholine.
(d)If an antibody irreversibly binds to the acetylcholine receptors, acetylcholine cannot bind to the receptors and can no longer trigger the appropriate response in the cell.
5.(a)The promoter serves as a binding site for RNA polymerase. The operator serves as a binding site for the repressor protein.
(b)Since the tryptophan operon is a repressible operon, the presence of tryptophan would turn the operon off. Tryptophan serves as a corepressor. It would bind to the repressor protein, and then the repressor protein would bind to the operator, blocking RNA polymerase’s ability to transcribe the genes on the plasmid. Green fluorescent protein would not be expressed.
(c)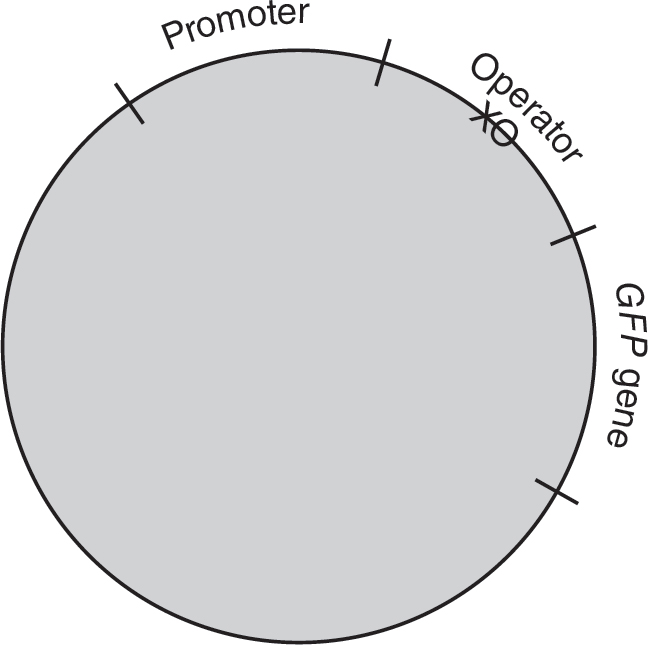
(d)Negative feedback helps maintain homeostasis and near-constant levels of different molecules in a cell. When there is excess tryptophan in a cell, the tryptophan binds to the repressor protein, which then binds to the operator of the tryptophan operon, preventing the production of more tryptophan. This prevents the cell from wasting energy and resources on producing more tryptophan than it needs.
6.(a)If the pea plants are heterozygous for both traits, the cross would be RrPp × RrPp. So ![]() of the offspring would be expected to have round peas, and
of the offspring would be expected to have round peas, and ![]() of the offspring would be expected to have wrinkled peas. Additionally,
of the offspring would be expected to have wrinkled peas. Additionally, ![]() of the offspring would be expected to have purple flowers, and
of the offspring would be expected to have purple flowers, and ![]() of the offspring would be expected to have white flowers. So the expected numbers of offspring would be:
of the offspring would be expected to have white flowers. So the expected numbers of offspring would be:

(b)Using the chi-square formula:
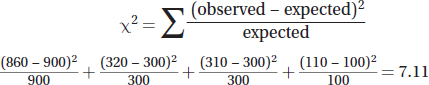
(c)Since there are four possible phenotypic outcomes in the experiment, there are 3 degrees of freedom. Using a p-value of 0.05 and 3 degrees of freedom, the critical value from the chi-square table is 7.81. Since the calculated chi-square value is less than the critical value, fail to reject the null hypothesis that there is no statistically significant difference between the observed and expected data.
(d)If the genes had been located on the same chromosome, they would be linked genes and would not assort independently. Genes that are linked would not follow the Mendelian ratios predicted by Punnett squares.