Biology Premium, 2024: 5 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online Practice - Wuerth M. 2023
Practice Tests
Practice Test 2
Section I: Multiple-Choice
TIME: 90 MINUTES
DIRECTIONS: For each question or incomplete statement, select the choice that best answers the question or completes the statement.
Questions 1 and 2
Refer to the following table, which describes some of the birds known as “Darwin’s finches,” which live on the Galapagos Islands.
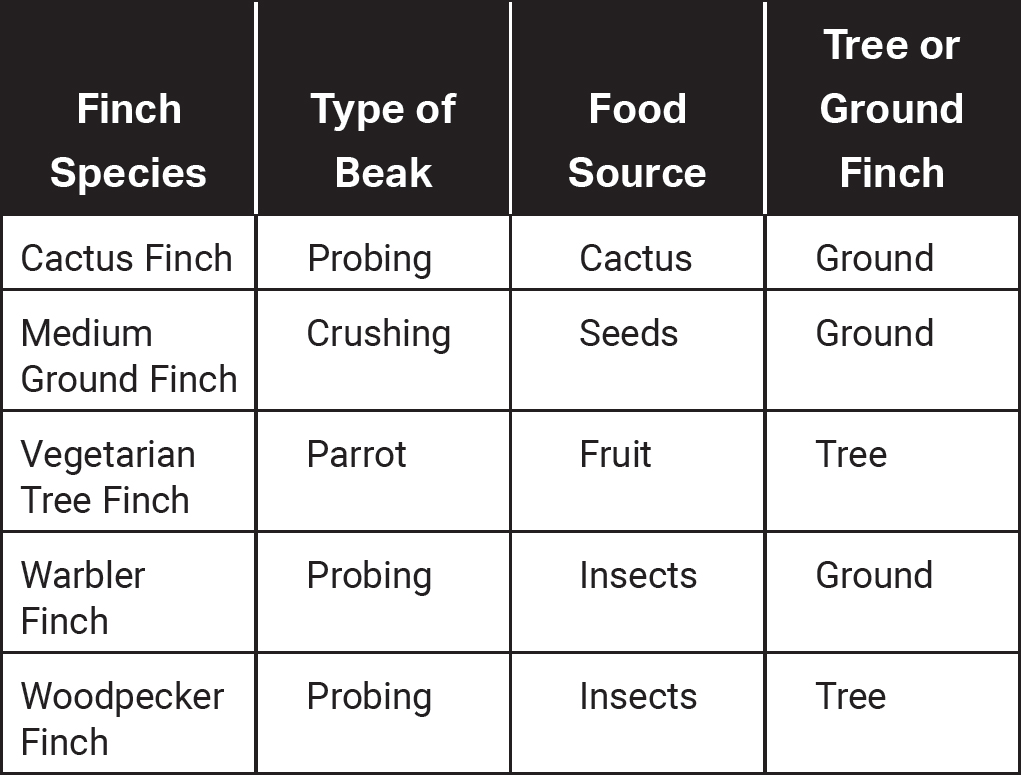
1.A drought eliminates most insects and fleshy fruits from the islands, and the predominant food source is now hard-shelled seeds. Birds with which types of beaks would be expected to increase in numbers?
(A)parrot beaks
(B)grasping beaks
(C)probing beaks
(D)crushing beaks
2.A hurricane eliminates most trees from the island. Which types of birds would be expected to decrease in numbers?
(A)cactus finch
(B)warbler finch
(C)woodpecker finch
(D)medium ground finch
3.The lyrebird (Menura novaehollandiae) is an Australian songbird and is known for its ability to mimic other sounds and produce birdsongs with great complexity. The more complex the birdsong, the more female lyrebirds are attracted. This is an example of which type of selection?
(A)artificial
(B)directional
(C)disruptive
(D)sexual
Questions 4—6
In Drosophila, body color can be brown or black, with the B (brown) allele dominant to the b (black) allele. A large population of Drosophila in Hawaii was studied over a period of 10 years, and the frequency of Drosophila with black bodies is shown over time in the figure.
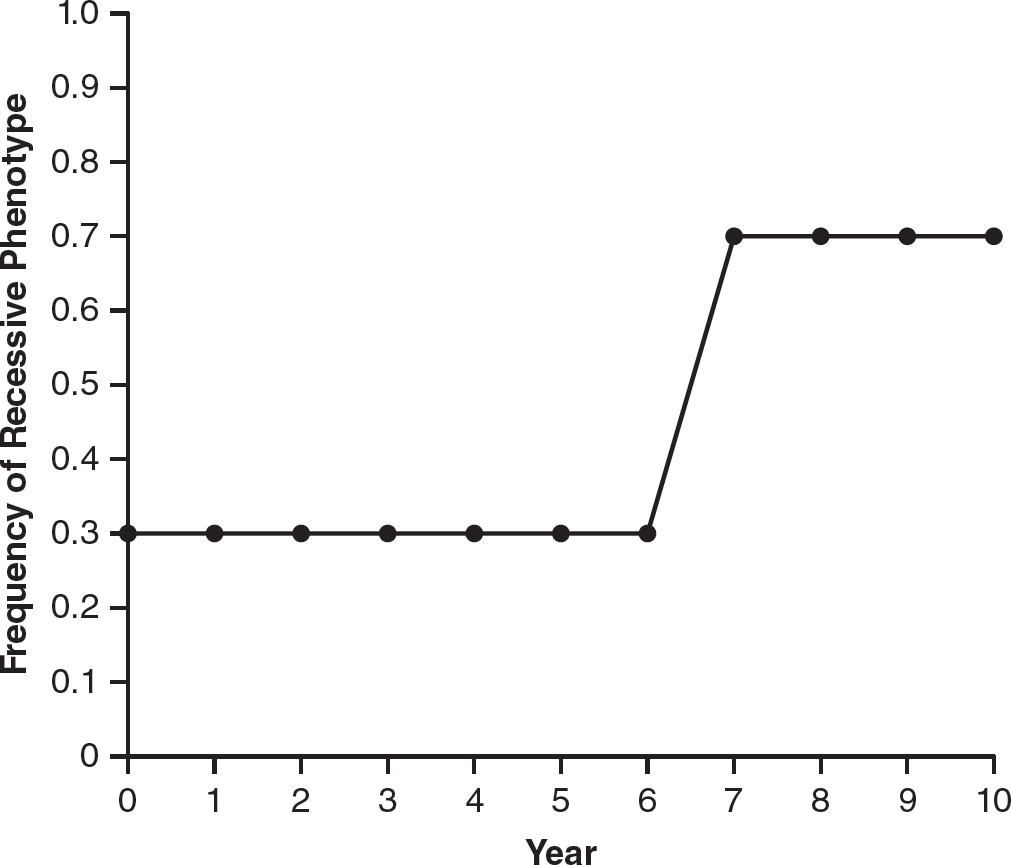
4.Assuming the population was in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium during year 4, what percentage of the population was heterozygous during year 4 of the study?
(A)30.0%
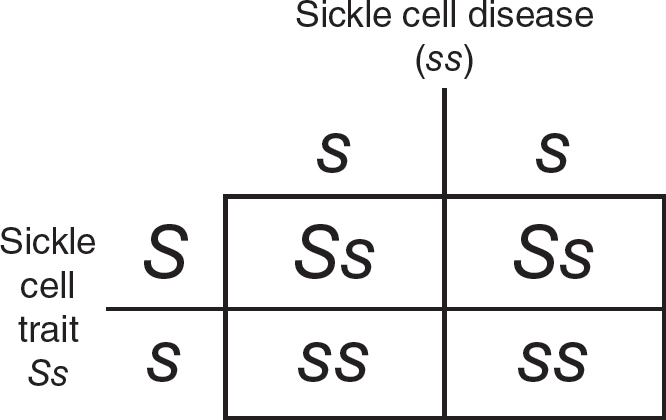
(B)49.5%
(C)54.8%
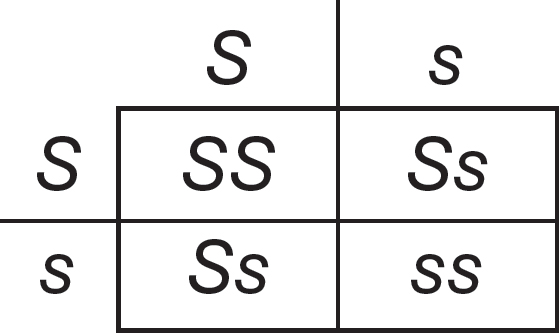
(D)70.0%
5.Assuming the population was in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium during year 10, what would be a characteristic of the population during year 10 of the study?
(A)small population size
(B)random mating
(C)extensive migration
(D)heterozygote advantage
6.Which of the following statements best describes the change in the population between year 6 and year 7 and a possible reason for the change?
(A)The frequency of the recessive phenotype decreased because the black body phenotype was 100% lethal.
(B)The frequency of the recessive phenotype increased because a change in the environment provided a selective advantage to flies with the black body phenotype.
(C)The frequency of the recessive phenotype decreased because the dominant phenotype is always the most common phenotype.
(D)The frequency of the recessive phenotype increased because individual flies adapted to a new, darker environment.
7.In a rural area of the country, there is a high incidence of a rare condition called methemoglobinemia, in which a mutation causes the skin of affected individuals to take on a bluish tint when under low oxygen conditions. All of the individuals with methemoglobinemia are descendants of one individual who immigrated to the area from another country. This is an example of
(A)natural selection.
(B)heterozygote advantage.
(C)bottleneck effect.
(D)founder effect.
Questions 8 and 9
The table shows the presence (+) or absence (—) of five traits in species L, M, N, O, and P.
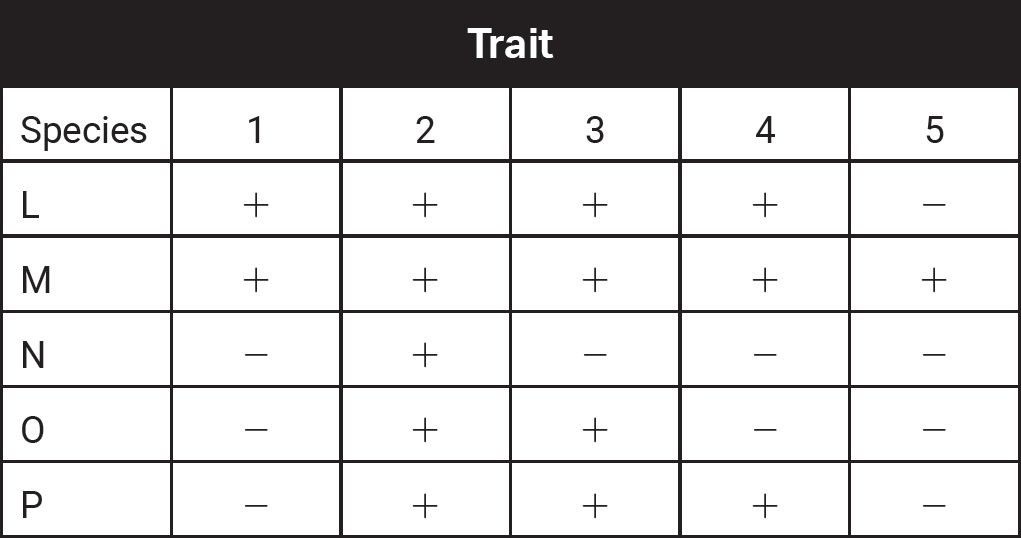
8.Which of the following cladograms best represents the data in the table?
(A)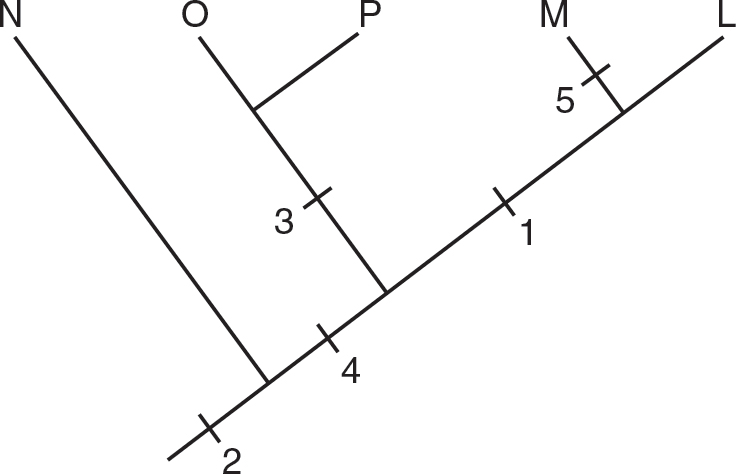
(B)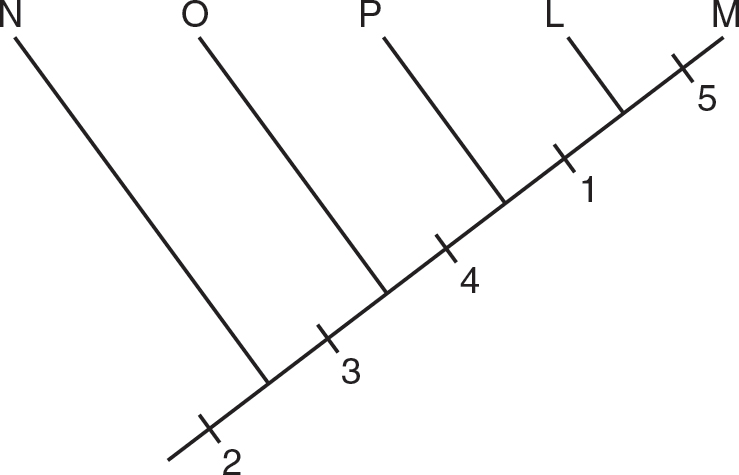
(C)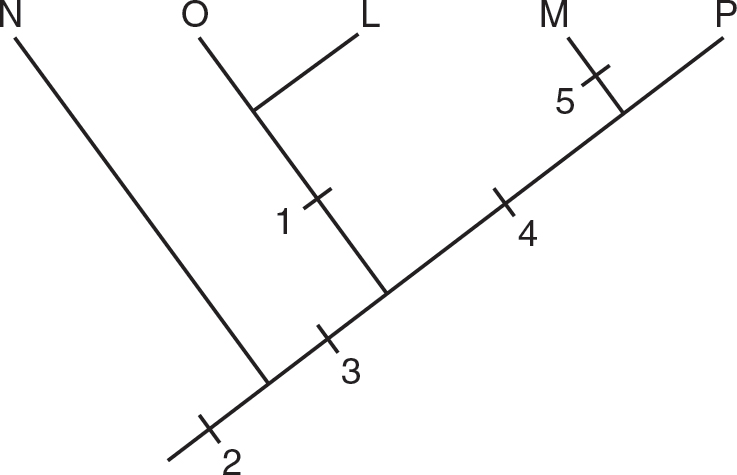
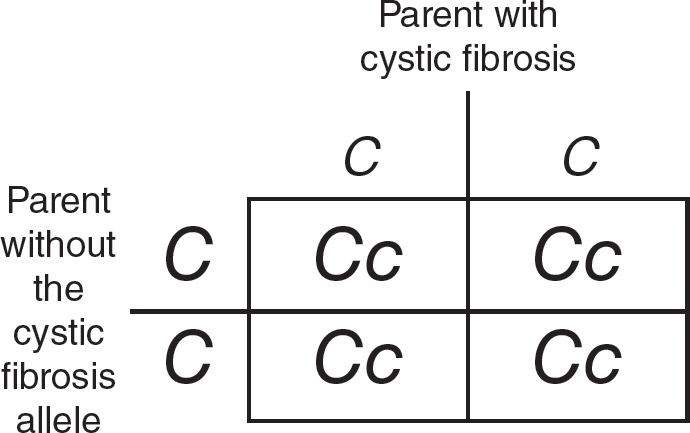
(D)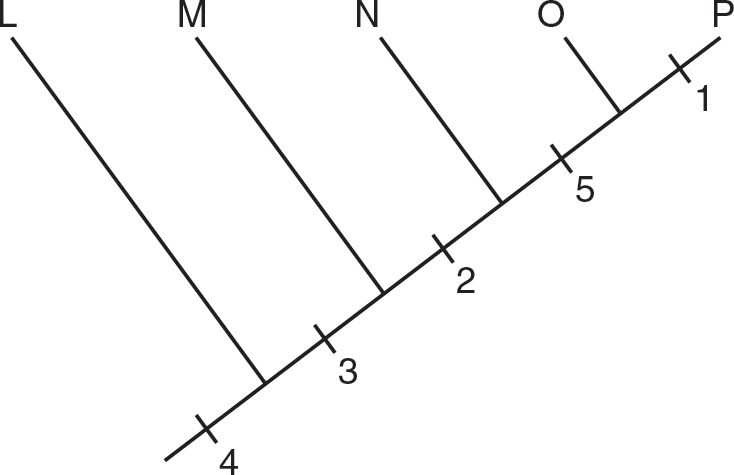
9.Which species represents the outgroup in the cladogram?
(A)M
(B)N
(C)O
(D)P
10.Two species of blind mole rats, Spalax ehrenbergi and Spalax galili, live in the same habitat and breed during the same season. However, Spalax ehrenbergi and Spalax galili do not interbreed. Studies have revealed that while they share a common ancestor, the DNA of the two species is significantly different. This is an example of
(A)allopatric speciation.
(B)sympatric speciation.
(C)polygenic inheritance.
(D)temporal isolation.
11.Fossil evidence shows that throughout Earth’s history, there were long periods of time in which the number and types of species found on Earth were relatively constant, followed by short periods of rapid change in the number and types of species found on Earth. Which of the following best describes this observation?
(A)gradualism
(B)punctuated equilibrium
(C)convergent evolution
(D)coevolution
12.Which of the following is an example of natural selection?
(A)A farmer breeds her two biggest cattle in an effort to obtain the largest offspring.
(B)A person spends time in the sun and his skin tans and becomes darker.
(C)A horse breeder breeds two winners of the Kentucky Derby in order to produce a faster horse.
(D)A mouse with lighter-colored fur is more likely to survive and reproduce in a sandy environment than a mouse with darker-colored fur.
Questions 13—16
Catalase is an enzyme that breaks down hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as shown in the following reaction:
![]()
A student isolates catalase from potato tissue and places it on ice. The student uses a hole punch to make equally sized paper disks, saturates each disk in the catalase solution, and then places them in beakers with different concentrations of H2O2. As the enzyme-catalyzed reaction proceeds, oxygen bubbles are produced and they cling to the paper disks, which then float to the surface. The time required for the catalase-saturated filter paper to float is recorded. The experiment is repeated five times for each concentration of hydrogen peroxide. The data are shown in the table.
|
Concentration of H2O2(l) |
Mean Time (sec) ±1 SEM* |
1% |
100 ± 7.0 |
3% |
75 ± 5.2 |
6% |
45 ± 4.3 |
9% |
30 ± 3.9 |
*Standard Error of the Mean
13.Which of the following would be a valid control for the experiment?
(A)changing the size of the paper disk
(B)saturating the paper disk in distilled water
(C)reducing the temperature of the hydrogen peroxide
(D)pureeing the potatoes with a pH 3 buffer instead of water
14.Based on the data obtained, there is least likely to be a statistically significant difference between which two concentrations of hydrogen peroxide?
(A)1% and 3%
(B)3% and 6%
(C)6% and 9%
(D)1% and 6%
15.What is the most likely explanation for the relationship between time for the disk to float and concentration of hydrogen peroxide?
(A)Higher hydrogen peroxide concentrations generate more heat, causing disks to rise faster.
(B)Increasing the concentration of hydrogen peroxide changes the active site on the catalase, increasing its reaction rate.
(C)The increasing levels of oxygen produced in the reaction functioned as an allosteric inhibitor of the enzyme.
(D)More substrate was available to the enzyme.
16.In a follow-up experiment, the student placed the enzyme in a boiling water bath for one minute before saturating the paper disks with the enzyme. Which of the following best predicts the expected results?
(A)The time required for the paper disks to float will decrease because the heat will cause a faster breakdown of hydrogen peroxide.
(B)The time required for the paper disks to float will not change because heating the enzyme does not change the hydrogen peroxide.
(C)The time required for the paper disks to float will increase because boiling will denature the enzyme.
(D)The time required for the paper disks to float will increase because all enzymes are less effective at higher temperatures.
17.Why is O2 required for aerobic cellular respiration?
(A)O2 is required in glycolysis, the first step in the breakdown of glucose.
(B)O2 serves as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain.
(C)O2 is a substrate for the enzymes used in fermentation.
(D)O2 is used to transport pyruvate to the matrix of the mitochondria.
18.Which of the following questions is most relevant in understanding the Krebs cycle?
(A)How is glucose broken down into pyruvate?
(B)How is the proton gradient in the mitochondria formed?
(C)How is NAD+ reduced to NADH?
(D)How does ATP synthase produce ATP?
19.Which of the following is a correct statement about fermentation and the electron transport chain?
(A)Both processes require O2.
(B)Both processes oxidize NADH to NAD+.
(C)Both processes occur in the mitochondria.
(D)Both processes result in the formation of metabolic water.
20.Telomeres are repetitive sequences of DNA found on the ends of linear chromosomes. With each cycle of DNA replication, a few bases are lost from the telomeres and the length of telomeres decrease. What is the function of telomeres?
(A)to assist in the synthesis of proteins
(B)to protect the genetic information in chromosomes during cell division
(C)to correct mutations in DNA
(D)to inhibit cell division
21.A celery stalk placed in distilled water for a few hours becomes stiff while a celery stalk placed in a 1.0 molar sodium chloride solution wilts. Which of the following best explains these observations?
(A)Celery cells have a higher water potential than both the distilled water and the 1.0 molar sodium chloride solution.
(B)Celery cells have a lower water potential than both the distilled water and the 1.0 molar sodium chloride solution.
(C)Celery cells have a higher water potential than the distilled water and a lower water potential than the 1.0 molar sodium chloride solution.
(D)Celery cells have a lower water potential than the distilled water and a higher water potential than the 1.0 molar sodium chloride solution.
22.When carbon dioxide is added to water, carbonic acid forms and the pH of the solution decreases. Ten alginate beads of the photosynthetic algae Chlorella vulgaris are placed in clear glass vials, along with a pH indicator dye. One vial is wrapped in foil to exclude all light. Both vials are placed under a light source for 40 minutes. The pH is recorded every 10 minutes. The data are shown in the table.
|
Time (minutes) |
pH of Vial with Foil |
pH of Vial Without Foil |
0 |
7 |
7 |
10 |
6.5 |
7.2 |
20 |
6.0 |
7.7 |
30 |
5.5 |
8.2 |
40 |
5.0 |
8.5 |
Which of the following best explains the changes in pH seen in the vials?
(A)The vial covered with foil only performs cellular respiration, and the vial not covered with foil only performs photosynthesis.
(B)The vial covered with foil only performs cellular respiration, and the vial not covered with foil performs both photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
(C)The vial covered with foil only performs photosynthesis, and the vial not covered with foil performs both photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
(D)The vial covered with foil only performs photosynthesis, and the vial not covered with foil only performs cellular respiration.
Questions 23 and 24
A study compared cancer rates in five species with their different body masses. The results are shown in the table.
|
Species |
Cancer Rate (%) |
Body Mass (kg) |
Elephant |
3 |
5,000 |
Marmoset |
16 |
0.4 |
Prairie Dog |
18 |
2.0 |
Tasmanian Devil |
50 |
10 |
Tiger |
12 |
150 |
23.A scientist proposes that since larger animals experience more cell divisions over their lifetimes, they should have a greater cancer rate. Do the data shown support this theory?
(A)yes, because the largest animals have the greatest cancer rates
(B)yes, because the smallest animals have the lowest cancer rates
(C)no, because the largest animals have the greatest cancer rates
(D)no, because the largest animals have the lowest cancer rates
24.The gene TP53 is a tumor suppressor gene, which produces a gene product that lowers cancer rates. Which animal is most likely to have the highest number of copies of the cancer-reducing TP53 gene?
(A)elephant
(B)marmoset
(C)Tasmanian devil
(D)tiger
25.In Drosophila melanogaster, the gene for eye color is on the X chromosome. Female Drosophila have two X chromosomes, and male Drosophila have one X chromosome. The allele for red eye color is dominant, and the allele for white eye color is recessive. A female with white eyes is mated with a male with red eyes. Which of the following best predicts their probable offspring?
(A)Half of the male offspring and half of the female offspring will have white eyes, and half of the male offspring and half of the female offspring will have red eyes.
(B)Half of the male offspring will have white eyes, half of the male offspring will have red eyes, and all of the female offspring will have white eyes.
(C)All of the male offspring will have red eyes, and all of the female offspring will have white eyes.
(D)All of the male offspring will have white eyes, and all of the female offspring will have red eyes.
26.The bacteria Streptococcus pneumonia has a rough strain (R) and a smooth strain (S). The S strain is covered in a capsule, which makes the virulent (disease-causing) bacteria more difficult to detect by the immune system. In a classic experiment, Frederick Griffith injected different combinations of live and heat-killed R strain and S strain Streptococcus pneumonia bacteria into mice and obtained the following results.
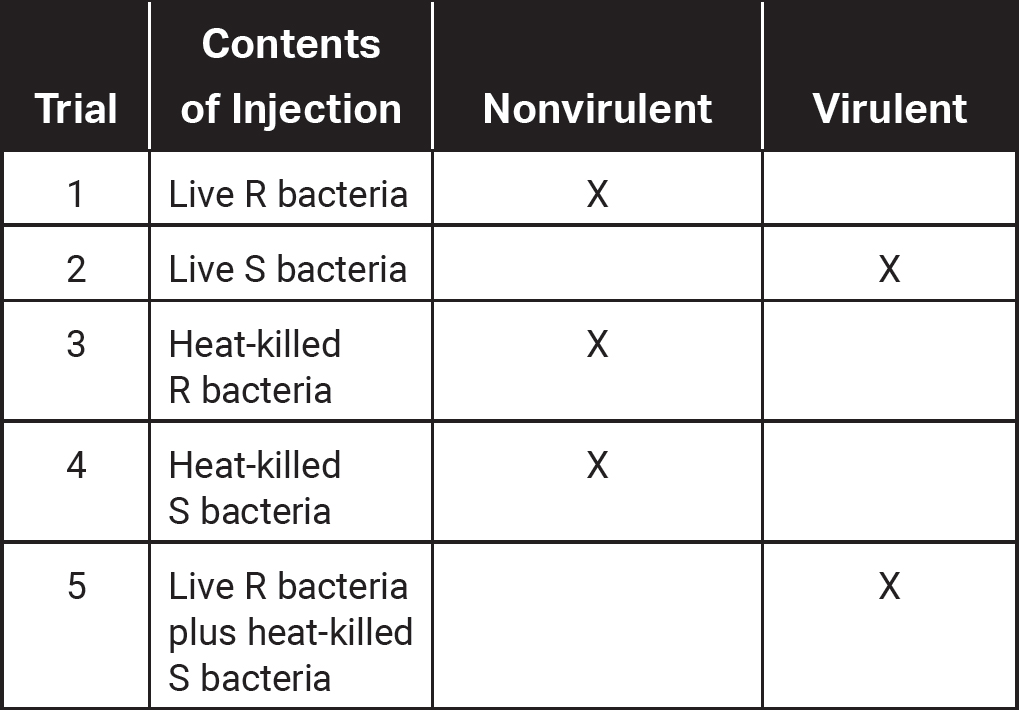
Which process most likely occurred in trial 5?
(A)transcription
(B)transduction
(C)transformation
(D)translocation
Questions 27—29
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is an autosomal recessive disorder. If an individual has just one copy of the sickle cell allele, the person has sickle cell trait (SCT) and is more resistant to malaria than individuals with no copies of the sickle cell allele.
27.If a person with sickle cell disease has a child with a person who has the sickle cell trait, what is the likelihood the child will have sickle cell disease?
(A)0%
(B)25%
(C)50%
(D)75%
28.The fact that individuals with sickle cell trait (SCT) are more resistant to malaria than the general population is an example of which phenomenon?
(A)polygenic inheritance
(B)sexual selection
(C)sex-linked inheritance
(D)heterozygote advantage
29.If an individual who has the sickle cell trait (SCT) has a child with a person who does not have sickle cell disease (SCD) but whose father did have SCD, what is the likelihood the child will have the SCT?
(A)0%
(B)25%
(C)50%
(D)75%
30.Research by climate scientists indicates that rising ocean temperatures may be causing El Niño storms to increase in frequency. These El Niño storms bring more rainfall to the Galapagos Islands. Increased water availability allows an invasive species of the fly Philornis downsi to flourish on the islands. This fly feeds on the blood of finch nestlings. What is the ecological relationship between the fly Philornis downsi and these finches?
(A)commensalism
(B)competition
(C)mutualism
(D)parasitism
31.Since the early 20th century, over 90% of the seagrass plants off of the coast of the United Kingdom have disappeared. Over one million seagrass seeds are being planted in the area to offset this loss. Which of the following would be the most likely benefit of this effort?
(A)reduction of habitats for some invasive species
(B)removal of oxygen from the atmosphere as seagrass performs photosynthesis
(C)absorption of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere as seagrass performs photosynthesis
(D)increased soil erosion in the area where seagrass is planted
32.A student performed an experiment to investigate how many drops of different liquids could be placed on a penny before the liquids would overflow off of the surface of the penny. The table shows the data obtained.
|
Liquid |
Mean Number of Drops (±2 SEM*) |
Ethanol |
22 ± 1.26 |
Vegetable Oil |
6 ± 1.16 |
Distilled Water |
28 ± 1.26 |
0.5 Molar NaCl |
16 ± 1.08 |
*Standard Error of the Mean
Which of the following best explains the experimental results?
(A)Vegetable oil forms more hydrogen bonds than the other liquids tested.
(B)Distilled water forms more hydrogen bonds than the other liquids tested.
(C)The ions in NaCl are repelled by the metal in the penny.
(D)Ethanol is a larger molecule than water, so ethanol forms more hydrogen bonds than water.
33.A U-tube apparatus is separated into two chambers by a semipermeable membrane, as shown in the figure. Water and iodine molecules can pass through the membrane, but starch molecules cannot pass through the membrane. Starch molecules are stained a dark blue or black color when in direct contact with iodine.
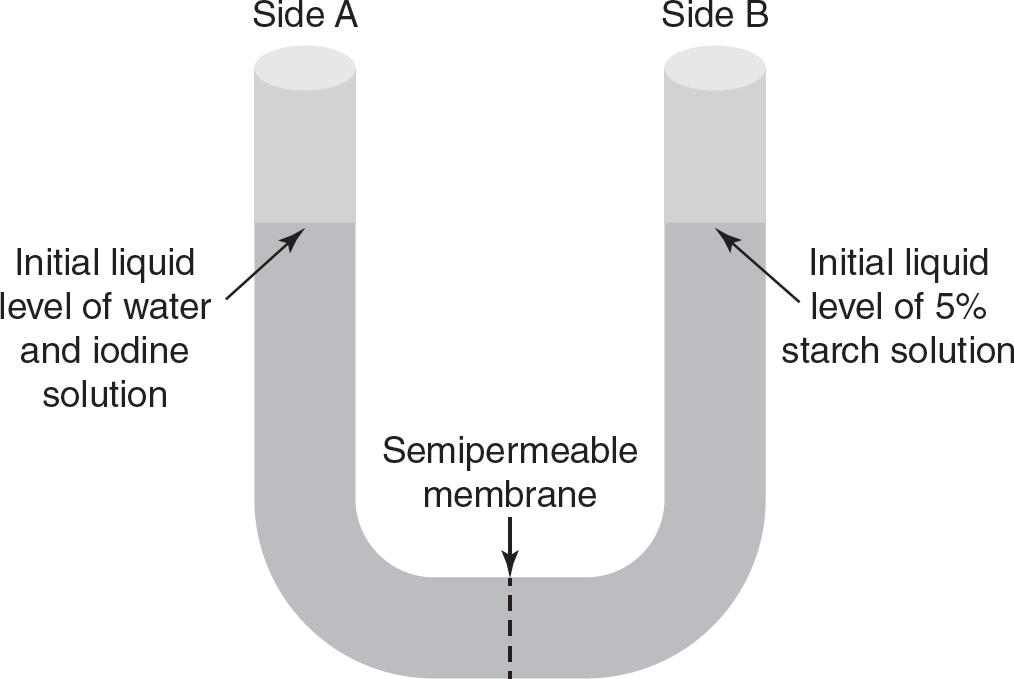
One hundred milliliters of an aqueous iodine solution are placed in the chamber on the left side of the U-tube apparatus (side A). One hundred milliliters of a 5% starch solution are placed in the chamber on the right side of the U-tube apparatus (side B). Which of the following is the most likely result after allowing the liquids to equilibrate for six hours?
(A)The water level on side A will rise, and side A will turn dark blue when the iodine and starch interact.
(B)The water level on side A will rise, and side B will turn dark blue when the iodine and starch interact.
(C)The water level on side B will rise, and side A will turn dark blue when the iodine and starch interact.
(D)The water level on side B will rise, and side B will turn dark blue when the iodine and starch interact.
34.A translocation between human chromosomes 9 and 22 results in the creation of a fusion gene called BCR-ABL. The BCR-ABL fusion can lead to an abnormally high cell division rate and can result in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). Which of the following would most likely slow the rate of cell division in cells that contain the BCR-ABL kinase?
(A)addition of a cofactor
(B)addition of a coenzyme
(C)addition of a competitive inhibitor
(D)addition of a transcription factor
35.Red blood cells are placed in distilled water. Which of the following would be the most likely result?
(A)The red blood cells will shrivel as water moves from the area of higher water potential inside the red blood cells into the area of lower water potential in the beaker.
(B)The red blood cells will swell and lyse as water moves from the area of higher water potential inside the red blood cells into the area of lower water potential in the beaker.
(C)The red blood cells will shrivel as water moves from the area of higher water potential in the beaker to the area of lower water potential inside the red blood cells.
(D)The red blood cells will swell and lyse as water moves from the area of higher water potential in the beaker to the area of lower water potential inside the red blood cells.
36.Rinderpest is a viral disease that affects cattle and wildebeests on the plains of the Serengeti in Africa. In the 1950s, a vaccine against rinderpest became available, and the number of wildebeests on the plains of the Serengeti increased. As the number of wildebeests increased, park rangers found that more grass was eaten by the wildebeests, and the number of wildfires in the area decreased. The decrease in frequency of wildfires led to increased tree density in the area. This increased tree density led to greater biodiversity of species in the area. Based on this information, what role in this ecosystem do the wildebeests play?
(A)apex predator
(B)keystone species
(C)producer
(D)secondary consumer
Questions 37—39
The chart indicates the presence (+) or absence (—) of components in different cells.
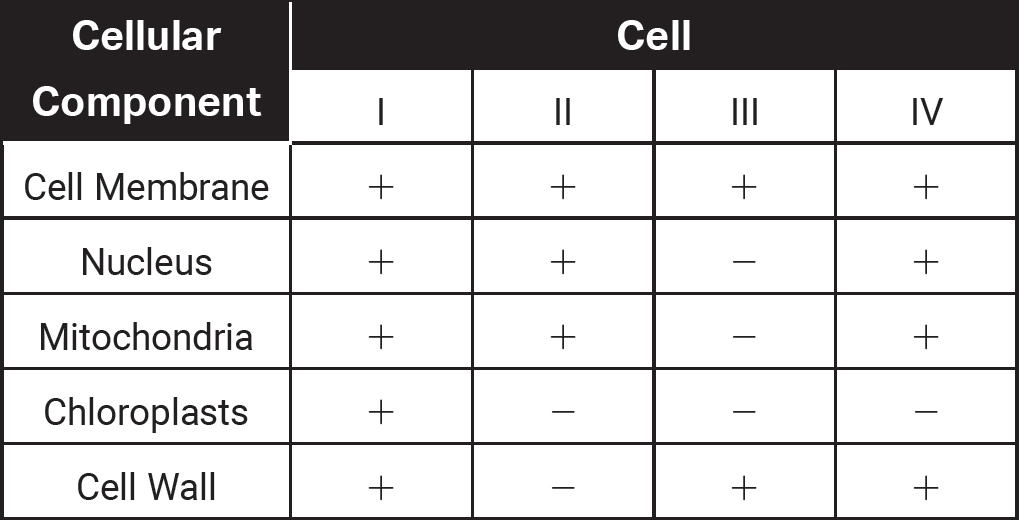
37.Which cell is most likely a bacterium?
(A)I
(B)II
(C)III
(D)IV
38.Which cell comes from an organism that is more likely to be dependent on pollinators for reproduction?
(A)I
(B)II
(C)III
(D)IV
39.Which cell is most likely from human muscle tissue?
(A)I
(B)II
(C)III
(D)IV
40.Which of the following best summarizes the relationship between hydrolysis and dehydration reactions?
(A)Hydrolysis builds monomers, and dehydration reactions break down monomers.
(B)Hydrolysis breaks down polymers into monomers, and dehydration reactions link monomers to form polymers.
(C)Hydrolysis reactions release water into the environment, and dehydration reactions consume water from the environment.
(D)Hydrolysis reactions only occur in carbohydrates and proteins, and dehydration reactions only occur in lipids and nucleic acids.
41.Which of the following contributes to the high specific heat of water?
(A)covalent bonds between oxygen atoms of two adjacent water molecules
(B)hydrogen bonds between oxygen atoms of two adjacent water molecules
(C)covalent bonds between a hydrogen atom on one water molecule and the oxygen atom on an adjacent water molecule
(D)hydrogen bonds between a hydrogen atom on one water molecule and the oxygen atom on an adjacent water molecule
42.Alpha helixes and beta sheets are examples of a protein’s ________ structure and are formed by ________ bonds.
(A)primary; peptide
(B)primary; hydrogen
(C)secondary; peptide
(D)secondary; hydrogen
43.A molecule is analyzed and found to contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. This molecule is most likely to be a __________.
(A)carbohydrate
(B)lipid
(C)nucleic acid
(D)protein
44.Which part of an amino acid is unique and would most likely determine how the amino acid would interact with the aqueous environment of a cell?
(A)the carboxyl group attached to the central carbon
(B)the amino group attached to the central carbon
(C)the R-group attached to the central carbon
(D)the hydrogen atom attached to the central carbon
45.Which of the following is an example of signal amplification?
(A)a steroid hormone binding to a gene and activating its transcription
(B)a kinase adding a phosphate group to an enzyme and activating the enzyme
(C)opening a membrane ion channel, allowing hundreds of ions to enter a cell
(D)a single ligand binding to a single receptor, triggering activation of dozens of enzymes
46.During which phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur?
(A)G1
(B)G2
(C)S
(D)M
47.Which of the following is an example of a positive feedback mechanism?
(A)Adenylyl cyclase catalyzes the formation of cyclic AMP from ATP.
(B)Ripening fruits release ethylene, and ethylene stimulates fruit ripening.
(C)When a cell has an adequate supply of tryptophan, the operon containing the genes that code for the production of tryptophan is shut down.
(D)When blood glucose levels rise, the pancreas releases insulin, which lowers blood glucose levels.
Questions 48—51
Cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. The CFTR gene codes for a protein that functions as a gated membrane channel that helps control the flow of chloride ions from inside the cytosol of the cell to the extracellular fluid outside the cell. When the CFTR protein is not functioning properly, not enough chloride ions exit the cell and the mucus in the extracellular fluid becomes dehydrated, thick, and viscous.
The fully functional form of the CFTR protein is translated from 27 exons in the CFTR gene. Not everyone with cystic fibrosis has the same mutation in the CFTR gene; currently five classes of mutations that can cause cystic fibrosis have been identified.
48.In one type of cystic fibrosis, the sections of the protein coded by exon 10 and exon 17 are missing from CFTR protein. Which type of mutation is most likely the cause of this?
(A)nonsense mutation
(B)translocation between two nonhomologous chromosomes
(C)mutation in a splice site
(D)point mutation, which changes a codon for a hydrophilic amino acid to a codon for a hydrophobic amino acid
49.The most common mutation, F508del, deletes a single amino acid, resulting in slight misfolding of the protein. The cell detects and destroys these abnormal proteins. A combination of two medications (Lumacaftor and Ivacaftor) can help reduce some of the symptoms in patients with this mutation. What is the most likely mechanism of action of the two medications?
(A)activation of CFTR gene transcription in patients with the F508del mutation
(B)repression of the number of ribosomes in patients with the F508del mutation
(C)correction of a premature stop codon in the middle of the F508del mutation
(D)help for the CFTR protein to fold into a more correct shape
50.Another type of mutation causes reduced levels of protein production. Which of the following medications would be effective?
(A)a drug that keeps the gate on the CFTR ion channel open for longer periods of time
(B)a drug that suppresses expression of the CFTR gene
(C)a drug that decreases the number of chloride ions exiting the cell
(D)a drug that stimulates the Na+/K+ pump in the cell membrane
51.A person with cystic fibrosis has a child with a person who does not have the cystic fibrosis allele. What is the probability that the child will have cystic fibrosis?
(A)0%
(B)25%
(C)50%
(D)75%
52.The arginine (arg) operon is a repressible operon in bacteria. What is the most likely result when excess arginine is added to the environment of bacteria?
(A)Arginine acts as an inducer, binding to the repressor protein and changing its shape so that transcription of the arginine operon starts.
(B)Arginine binds to RNA polymerase, stimulating transcription of the arginine operon.
(C)Arginine acts as a corepressor, helping the repressor bind to the operator and stopping transcription of the operon.
(D)Arginine stimulates the enzyme adenylyl cyclase, causing the production of cyclic AMP.
53.Which of the following biotechnology techniques amplifies the number of copies of a specific DNA sequence?
(A)gel electrophoresis
(B)polymerase chain reaction
(C)CRISPR-Cas9
(D)DNA sequencing
54.Conjugation, transformation, and transduction are all examples of which of the following?
(A)horizontal gene transfer
(B)mutations caused by an incorrect number of chromosomes
(C)processes that occur only in eukaryotic cells
(D)methods of reducing genetic diversity
55.Ecologists studying a population of 250 deer in the hills north of San Francisco, California, find that the birth rate for the population is 0.25 and the death rate is 0.15. Which of the following is the most likely prediction regarding the size of this population the following year?
(A)The population size will decrease because the birth rate is less than 1.0.
(B)The population size will decrease because the death rate is greater than 0.
(C)The population size will increase because the deer population in the area has an unlimited food source.
(D)The population size will increase because the birth rate is greater than the death rate.
56.Which of the following is a density-independent factor that can limit population size?
(A)competition for mates
(B)competition for food
(C)predation
(D)a natural disaster
Questions 57 and 58
Fordinae geoica and Fordinae formicaria are two species of gall-forming aphids. By creating galls, nutrient-rich sap from the phloem of the host plant is suctioned into these voids, providing food for the aphids.
F. geoica were introduced onto a rose bush upon which F. formicaria had already inhabited and built galls. Three months later, the number of F. formicaria was reduced by 84%, while the number of F. geoica increased by over 300%. Analysis of the gall contents of the two species of aphids revealed that galls formed by F. geoica had a much higher sap content than galls formed by F. formicaria.
57.The ecological relationship between F. geoica and F. formicaria is best described by which of the following?
(A)intraspecies competition
(B)interspecies competition
(C)mutualism
(D)parasitism
58.The relationship between Fordinae and the rose bush is best described by which of the following?
(A)intraspecies competition
(B)interspecies competition
(C)mutualism
(D)parasitism
Questions 59 and 60
An invasive species of carp is introduced into a lake in 1986. The species of fish present in the lake and the number of each species before and after the introduction of the carp are shown in the table.
|
Species |
Number Present in 1985 |
Number Present in 1991 |
Trout |
1,375 |
934 |
Bass |
1,410 |
733 |
Catfish |
501 |
45 |
Carp |
0 |
2,003 |
Steelheads |
662 |
238 |
Pikes |
52 |
47 |
59.Which species had the greatest percent population decline after the introduction of carp to the lake?
(A)bass
(B)catfish
(C)steelheads
(D)trout
60.If an ecological disturbance occurred in the lake, which lake community (preintroduction or postintroduction) could be hypothesized to recover from the ecological disturbance?
(A)There is no difference because the total number of individuals in 1985 and 1991 was the same, meaning that the Simpson’s Diversity Index was equal in both communities.
(B)The population in 1985 would have a greater ability to recover from an ecological disturbance because its Simpson’s Diversity Index was higher.
(C)The population in 1991 would have a lower ability to recover from an ecological disturbance because its Simpson’s Diversity Index was higher.
(D)The population in 1991 would have a greater ability to recover from an ecological disturbance because the number of species present in 1991 was higher.

Section II: Free-Response
TIME: 90 MINUTES
DIRECTIONS: Answer each of the following six free-response questions using complete sentences. Allow approximately 20—25 minutes each for the long free-response questions (Questions 1 and 2) and approximately 5—10 minutes each for the short free-response questions (Questions 3, 4, 5, and 6).
1.Five equally sized cubes of turnips are massed and placed in five different sucrose solutions at 21°C. The turnip cubes are massed again after 24 hours, and the percent change in mass is calculated. A graph of the data is constructed.
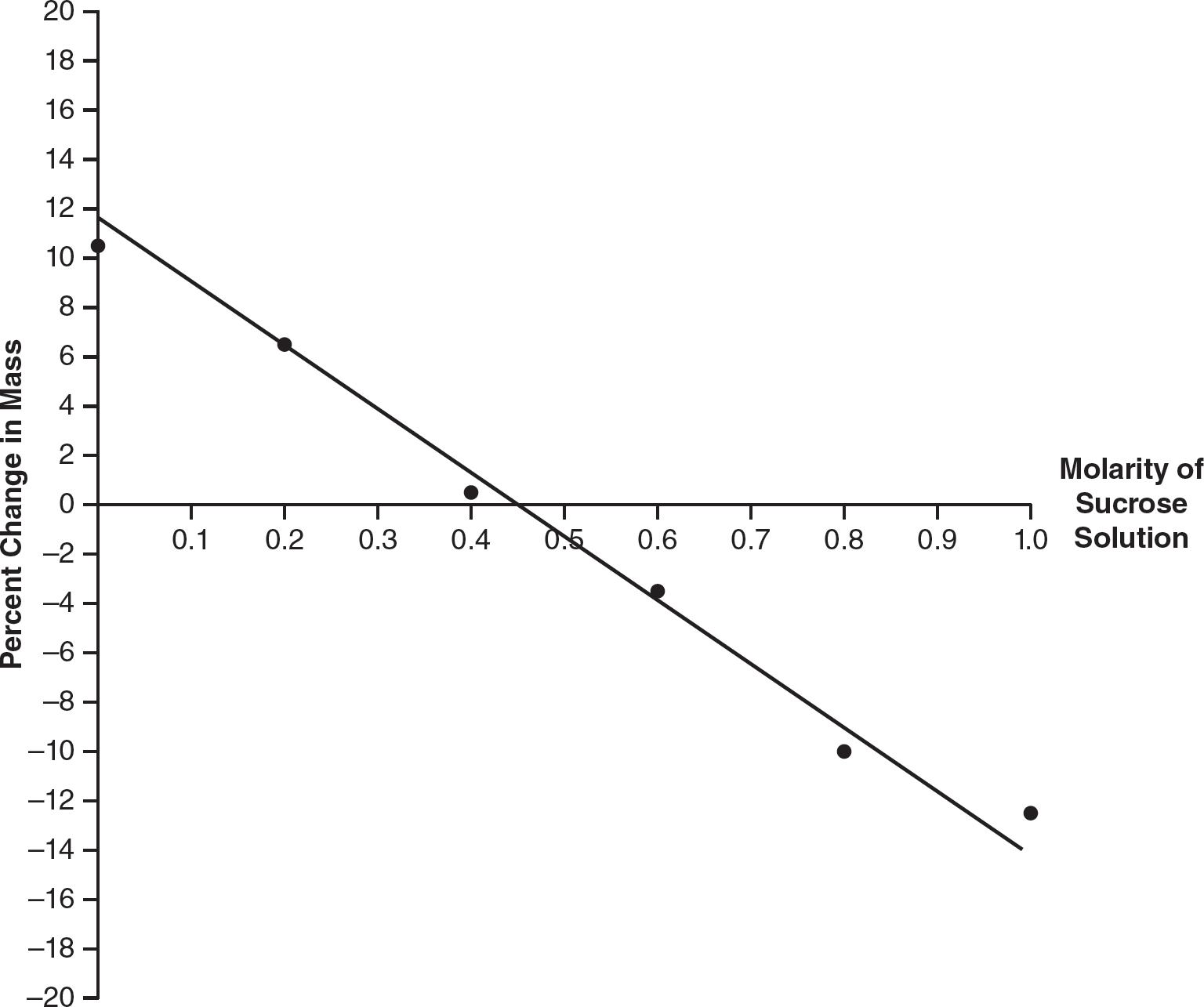
(a)Explain the percent change in mass for each of the cubes tested.
(b)Analyze the graph and predict the molarity of a turnip cell, giving evidence to support your claim.
(c)Calculate the solute potential of a turnip cell.
(d)A new turnip cube is placed in a 0.5 M solution. Predict the percent change in mass of the turnip cube after 24 hours. Justify your prediction.
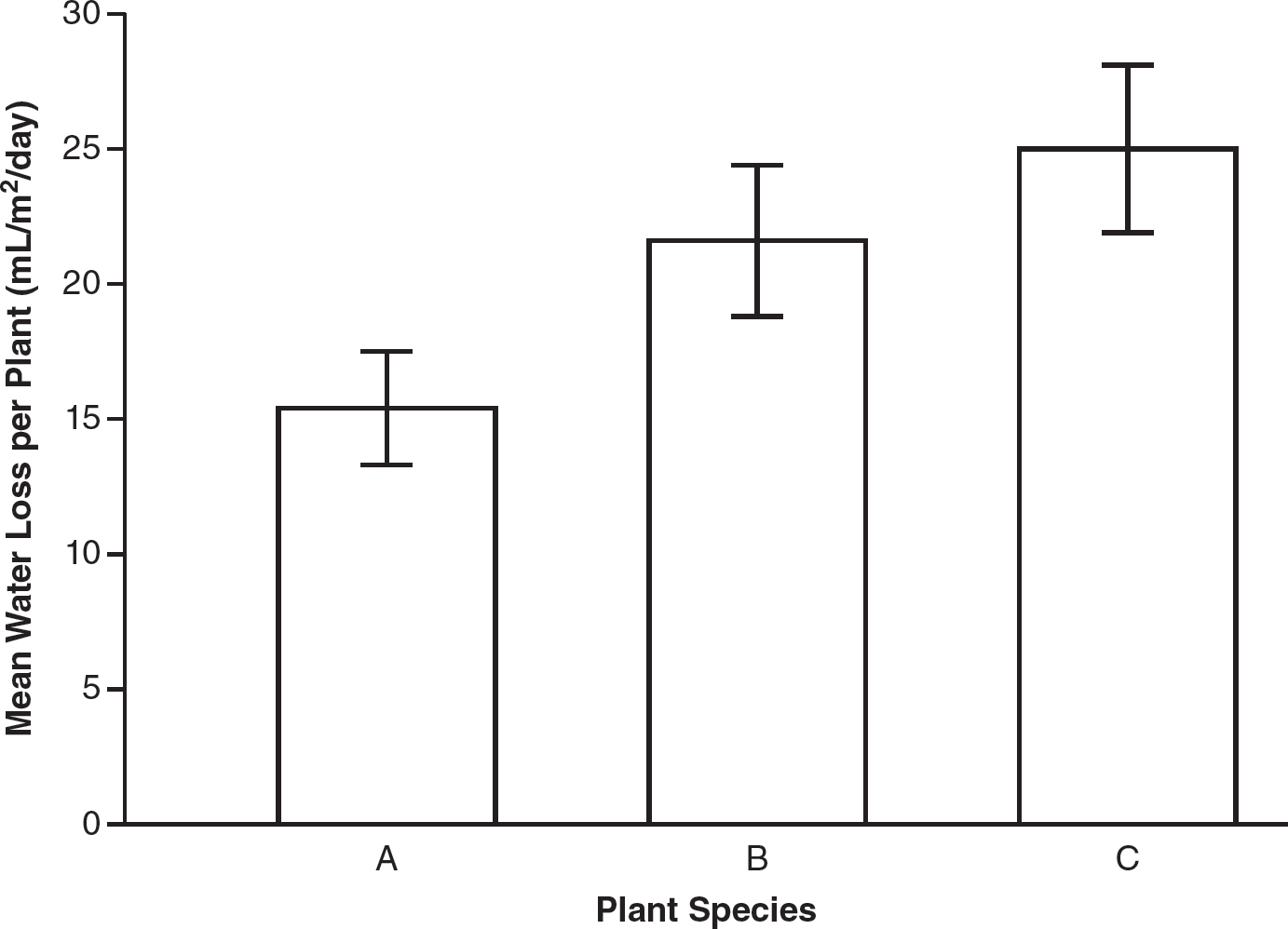
2.Transpiration rate was measured for three different plant species. Ten plants of each species were kept under the same experimental conditions for three days. Total water loss for each plant was measured during the three-day period using a potometer. At the end of the three-day period, the total surface area of the leaves of each plant was measured, and the water loss per square meter of leaf area per day was calculated. Data are shown in the table.
|
Plant Species |
Mean Water Loss per Plant (mL/m2/day) ± 2 SEM* |
A |
15.4 ± 2.1 |
B |
21.6 ± 2.8 |
C |
25.0 ± 3.1 |
*Standard Error of the Mean
(a)Explain the relationship between transpiration and photosynthesis.
(b)On the axes provided, construct a graph of the data using 95% confidence intervals.
(c)Analyze the data to determine which, if any, plant species have a statistically significant difference between the amounts of water loss.
(d)Predict which plant species would be best suited to a dry climate. Justify your prediction using the data from the experiment.
3.A sample of a culture of E. coli is plated onto two LB agar plates: plate 1 containing LB agar and no antibiotic (LB) and plate 2 containing LB agar with 50 micrograms/mL of the antibiotic ampicillin (LB + amp). Both plates are incubated at 37°C for 24 hours. Bacteria from plate 1 are plated onto two more plates: one with LB agar (plate 3) and the other containing LB agar with 50 micrograms/mL of the antibiotic ampicillin (plate 4). Bacteria from plate 2 are placed onto plate 5 (containing LB agar) and plate 6 (containing LB agar with 250 micrograms/mL of the antibiotic ampicillin). This second round of plates are all incubated at 37°C for 24 hours. A diagram of the experiment is shown in the figure.
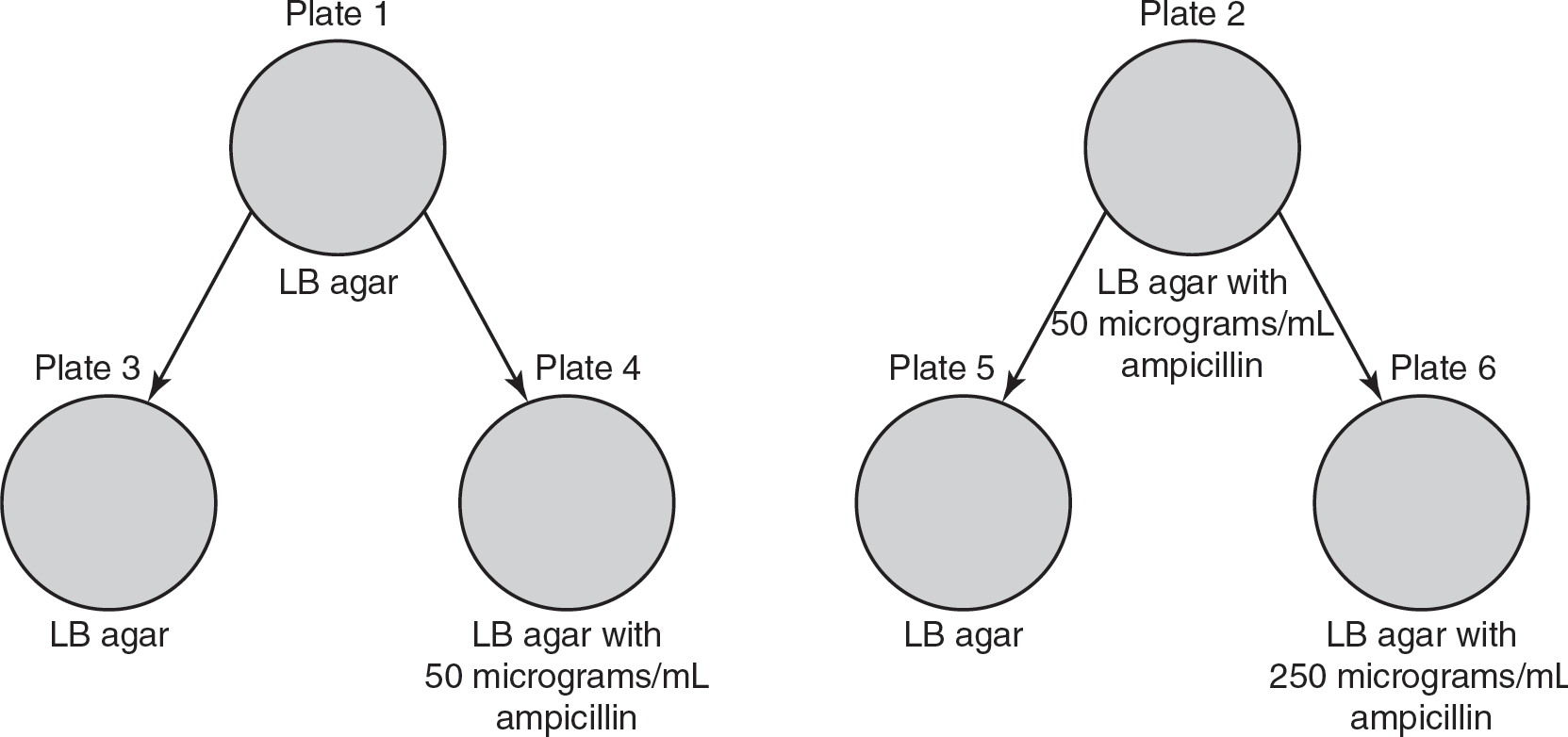
(a)Describe the process of selection used in this experiment.
(b)Make a claim about the presence of bacterial growth on plate 2 and predict the number of colonies compared to plate 1.
(c)Predict which plate will have bacteria that are more resistant to the antibiotic.
(d)Justify your prediction from part (c).
4.The figure shows a food web in an aquatic ecosystem.
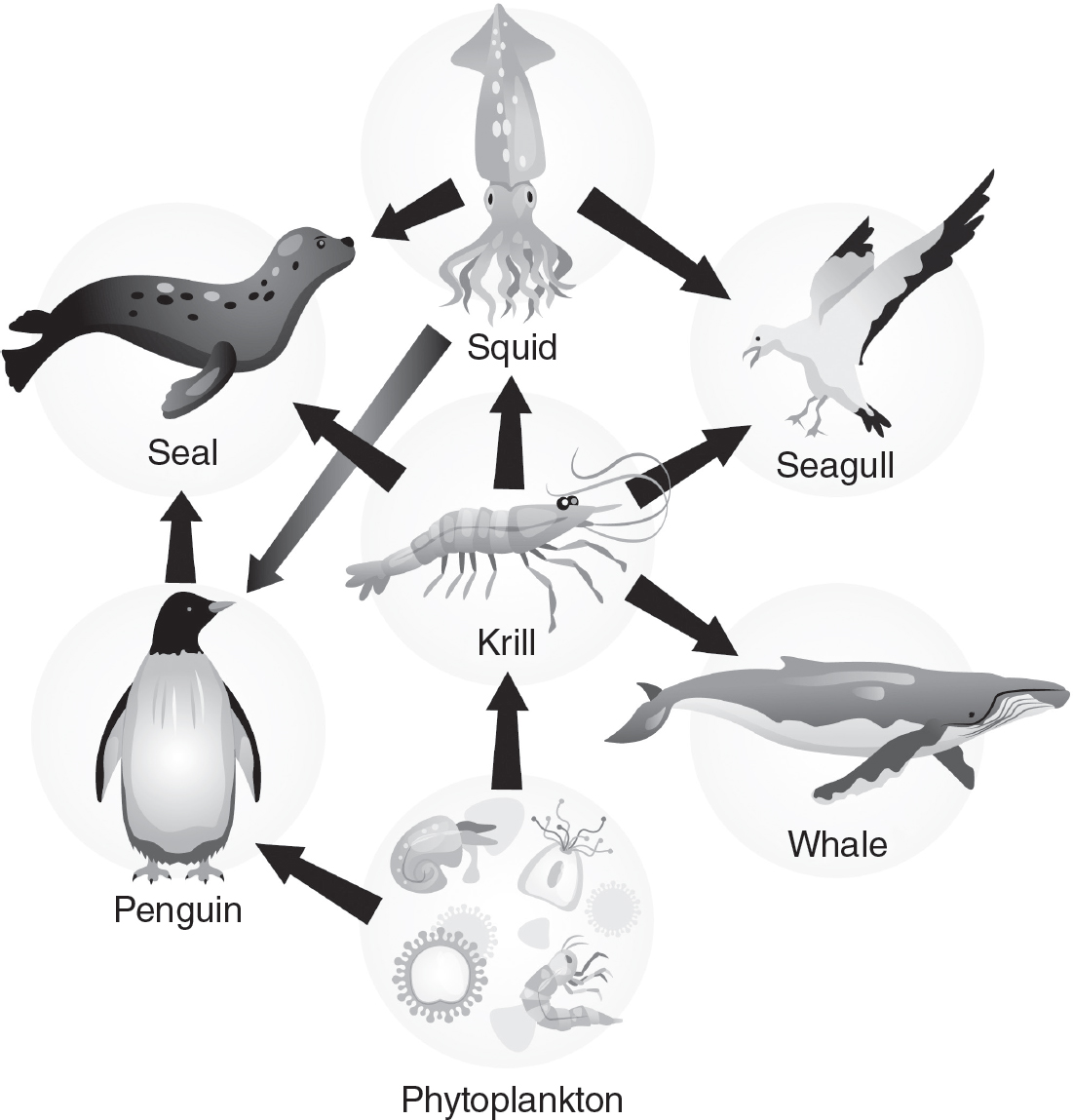
(a)Describe the roles of penguins and seagulls in this food web.
(b)Identify the primary consumer(s) in the food web. Explain your reasoning.
(c)Many species of phytoplankton occur in marine environments, but not all are digestible or desirable to eat. One species of phytoplankton, Coccolithophore, are not a food source. Predict the effect of a Coccolithophore bloom on this aquatic ecosystem.
(d)Justify your prediction from part (c).
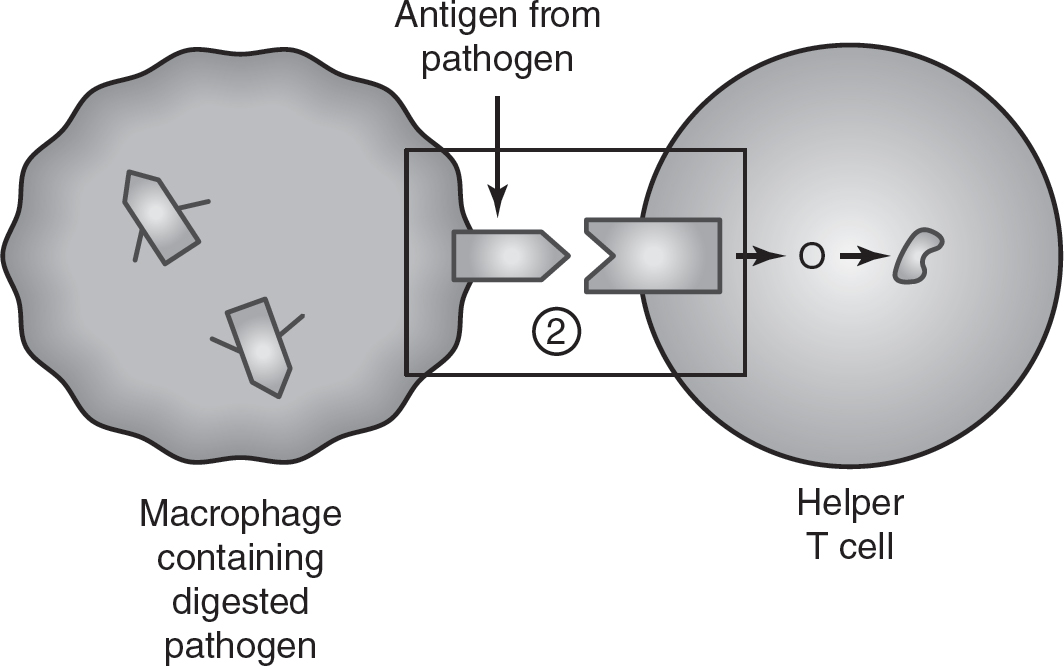
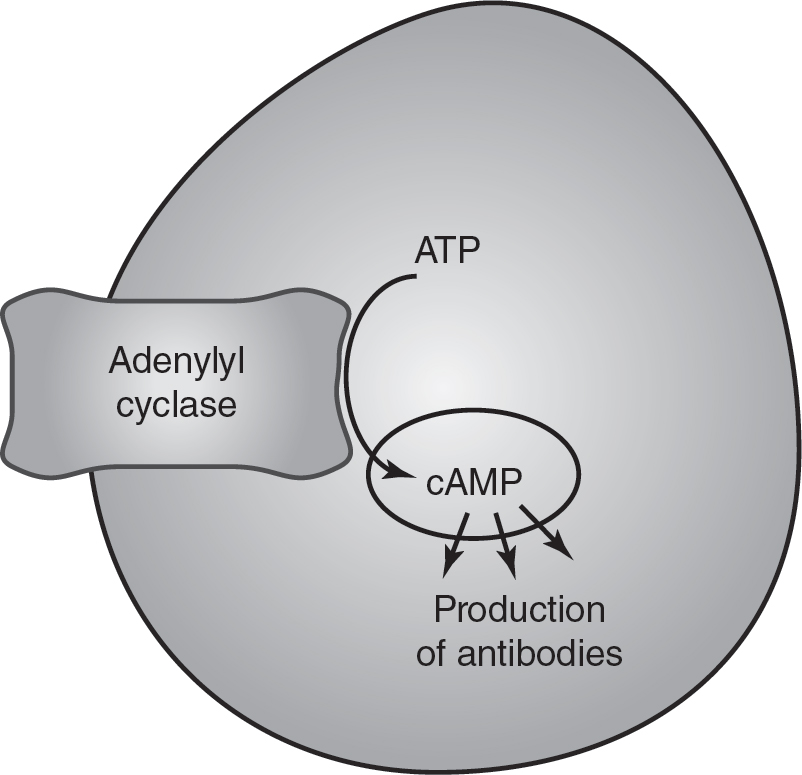
5.A portion of the human immune system response to an invading pathogen is shown in the figure.
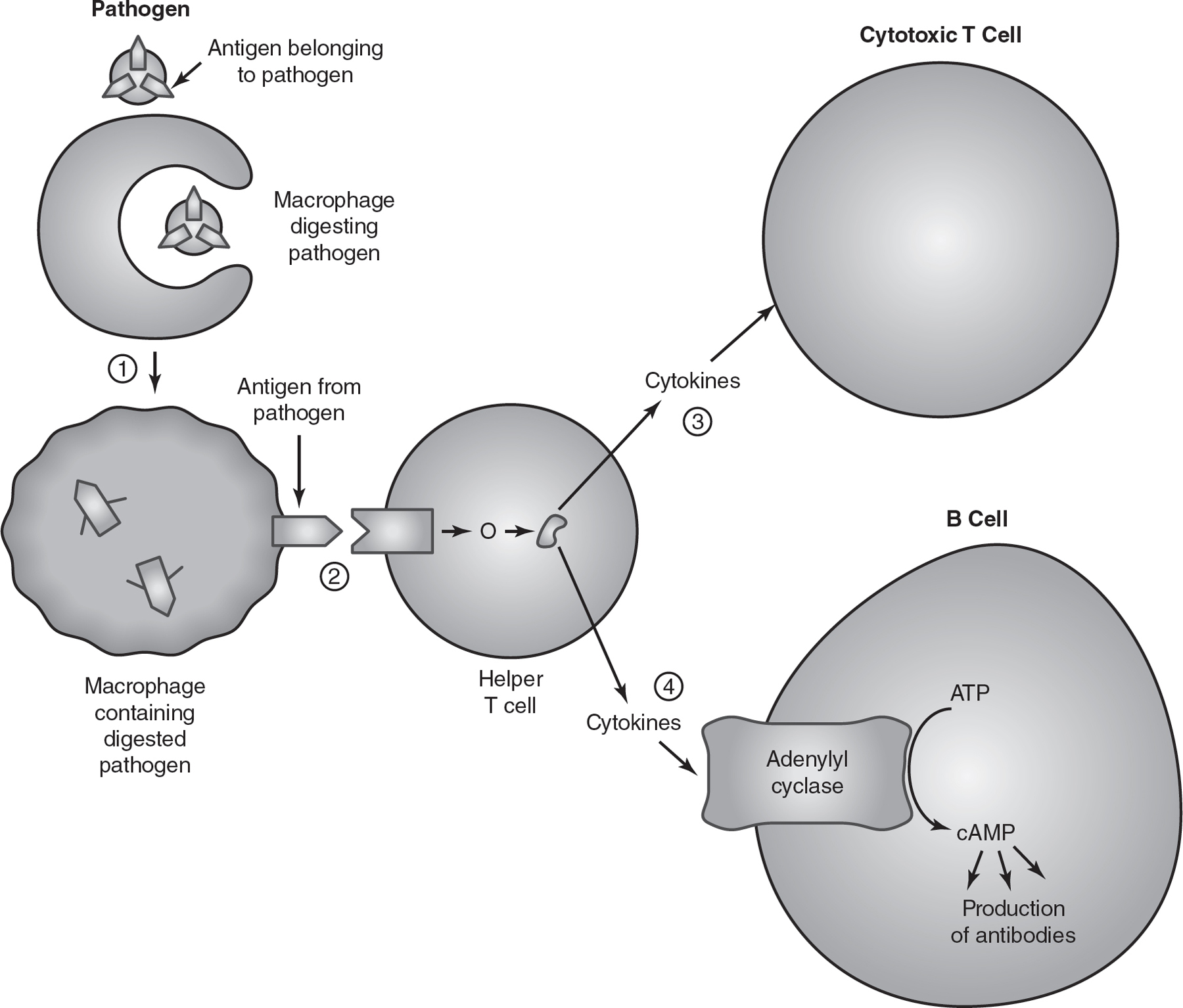
Macrophages are white blood cells that ingest invading pathogens. After digesting the pathogen, macrophages present the antigens from the pathogen to helper T cells in the immune system. These helper T cells then secrete chemical signals called cytokines. The cytokines can travel short distances to activate nearby cytotoxic T cells, which will kill infected cells. Some cytokines will activate the enzyme adenylyl cyclase in nearby B cells to produce cyclic AMP (cAMP). cAMP will then activate the production of antibodies in the B cells.
(a)Describe the characteristics of juxtacrine signaling. Draw a square around the step (1, 2, 3, or 4) in the figure illustrates an example of juxtacrine signaling.
(b)Explain the role cytokines play in the cell signaling process described above.
(c)Circle a molecule that represents a secondary messenger in the figure.
(d)Explain how secondary messengers can amplify a response in a cell.
6.A student investigated the effect of caffeine on the number of cells in mitosis and interphase in onion root tip cells. Onions were planted in sand in two groups. One group of onions received distilled water, and the second group received an aqueous solution of 0.002 M caffeine for two days. The tips of the roots were removed and stained, and the number of cells in mitosis and interphase was counted. The data appear in the table below.
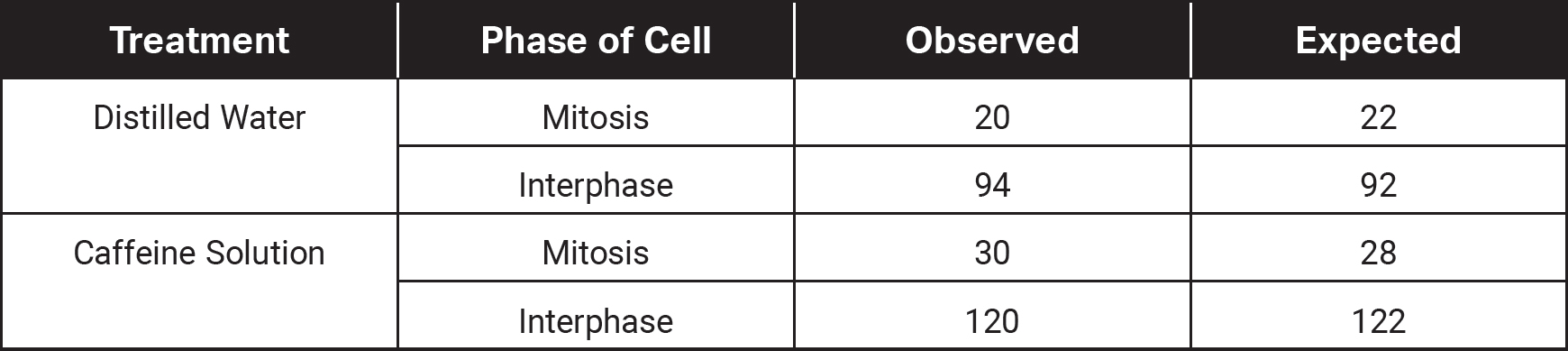
(a)Calculate the percentage of cells in mitosis and interphase observed in each group.
(b)Identify the control group, the independent variable, and the dependent variable in the experiment.
(c)The student makes the following null hypothesis for this experiment: “There is no statistically significant difference between the number of cells in mitosis and in interphase between the onions grown in distilled water and the onions grown in 0.002 M caffeine.” Use the data and the chi-square test to evaluate the student’s hypothesis.
(d)The start of mitosis is triggered in cells by mitosis-promoting factor (MPF). MPF forms when cyclin protein binds to a cyclin-dependent kinase. Explain how a drug that irreversibly binds to the active site of cyclin-dependent kinase would affect the cell cycle.
ANSWER KEY
Practice Test 2
Section I
1.D
2.C
3.D
4.B
5.B
6.B
7.D
8.B
9.B
10.B
11.B
12.D
13.B
14.C
15.D
16.C
17.B
18.C
19.B
20.B
21.D
22.B
23.D
24.A
25.D
26.C
27.C
28.D
29.C
30.D
31.C
32.B
33.D
34.C
35.D
36.B
37.C
38.A
39.B
40.B
41.D
42.D
43.C
44.C
45.D
46.C
47.B
48.C
49.D
50.A
51.A
52.C
53.B
54.A
55.D
56.D
57.B
58.D
59.B
60.B
Section II
See the Answer Explanations section.
Answer Explanations
Section I
1.(D)Birds with crushing beaks would be better equipped to utilize hard-shelled seeds as a food source. The table indicates that birds with crushing beaks eat seeds, while birds with parrot beaks, grasping beaks, and probing beaks do not eat seeds, so choices (A), (B), and (C) are incorrect.
2.(C)The woodpecker finch is a tree finch, so if a hurricane eliminated most trees from the island, it is expected that the number of woodpecker finches would decrease. Cactus finch, warbler finch, and medium ground finch are not tree finches and would be less likely to be affected by the elimination of trees from the island, so choices (A), (B), and (D) are incorrect.
3.(D)Mate choice by females is an example of sexual selection. Choice (A) is incorrect because in artificial selection humans determine which individuals survive and reproduce at a greater rate. Directional selection occurs when one extreme phenotype is favored, which is not the case here, so choice (B) is incorrect. Disruptive selection occurs when both extremes of a phenotype are favored, so choice (C) is also incorrect.
4.(B)During year 4, 30% of the population had the recessive phenotype, so q2 = 0.30 and q = 0.548. p + q = 1 so p = 0.452. The frequency of heterozygotes would be 2pq = 2 × (0.452) × (0.548) = 0.495, or 49.5%.
5.(B)Random mating is a necessary condition for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Choice (A) is incorrect because large (not small) populations are required for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. There needs to be no migration into or out of a population for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, so choice (C) is incorrect. No individuals should have a selective advantage in a Hardy-Weinberg population, so choice (D) is incorrect.
6.(B)The frequency of the recessive phenotype (black body) increased, most likely due to a change in the environment that provided a selective advantage to flies with a black body. Choices (A) and (C) are incorrect because the frequency of the recessive phenotype increased between years 6 and 7, not decreased. Individuals do not evolve; populations evolve. So choice (D) is incorrect.
7.(D)Founder effect occurs when members of a population migrate to a new area and the frequency of one or more alleles in the migrating/founding population is higher than in the original population. Choice (A) is incorrect because there is no evidence that methemoglobinemia has a selective advantage, nor is there evidence that heterozygotes for the trait have a selective advantage, so choice (B) is also incorrect. The bottleneck effect occurs when a population undergoes a rapid and extreme decrease in population size, which is not the case in this example, so choice (C) is incorrect.
8.(B)Species M has all five traits, so it is on the far right of the cladogram. Species L has traits 1, 2, 3, and 4 but not 5, so trait 5 is placed after the branch point for L. Species P has traits 2, 3, and 4, so trait 1 is placed after the branch point for P but before the branch point for L. Species O has traits 2 and 3, so trait 4 is placed after the branch point for O but before the branch point for P. The only trait species N has is trait 2, so trait 3 is placed after the branch point for N but before the branch point for O. Trait 2 is placed before the branch point for N. Choices (A), (C), and (D) are incorrect in their placements of the traits and the species.
9.(B)Species N is the outgroup because it has the least in common with the other species, sharing only trait 2. Choices (A), (C), and (D) are incorrect because every other species shares two or more traits with the others in the cladogram.
10.(B)Sympatric speciation occurs when two species are separated by genetic differences. Choice (A) is incorrect because allopatric speciation requires geographic separation, which is not the case in this example. Polygenic inheritance is when more than one gene contributes to a trait, also not the case here, so choice (C) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because temporal isolation requires that the species breed at different times.
11.(B)Punctuated equilibrium describes long periods of stability during evolution interspersed with periods of rapid change. Choice (A) is incorrect because gradualism describes a slow, constant rate of evolutionary change. Convergent evolution occurs when species share similar traits because of similar environments, not common ancestry, so choice (C) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because coevolution occurs when two species influence each other’s evolution.
12.(D)Natural selection occurs when the natural environment determines which individuals survive and reproduce at a greater rate. Choices (A) and (C) are incorrect because both are examples of artificial selection, when humans breed organisms for desired traits. The darkening of a person’s skin when exposed to the sun is an acquired trait, so choice (B) is also incorrect.
13.(B)Distilled water contains no enzymes, so it would be an appropriate control. Choice (A) is incorrect because changing the size of the paper disk would add another variable. Reducing the temperature of the hydrogen peroxide would not be an appropriate control, so choice (C) is incorrect. Pureeing the potatoes with buffer instead of water would change the conditions of the experiment and would not be a control, so choice (D) is incorrect.
14.(C)The upper limit of the 95% confidence interval for 9% hydrogen peroxide (30 + 2(3.9) = 37.8 sec) overlaps with the lower limit of the 95% confidence interval for 6% hydrogen peroxide (45 — 2(4.3) = 36.4 sec). So it is not likely there is a statistically significant difference between those two concentrations of hydrogen peroxide. The 95% confidence intervals for all of the other pairs of hydrogen peroxide do not overlap and therefore are more likely to have a statistically significant difference between them.
15.(D)At higher concentrations of hydrogen peroxide, more substrate was available to the enzyme so more oxygen was produced and the paper disks floated faster. The amount of heat generated did not change with higher concentrations of hydrogen peroxide, so choice (A) is incorrect. There is no evidence that more concentrated hydrogen peroxide changed the shape of the active site of the enzyme, so choice (B) is incorrect. Oxygen is not an allosteric inhibitor of the enzyme, so choice (C) is also incorrect.
16.(C)Boiling denatures most enzymes, irreversibly changing their shape so they do not function. Choice (A) is incorrect because the enzyme is exposed to the boiling water bath, not the hydrogen peroxide. Boiling will change the time required for the paper disk to float, so choice (B) is incorrect. Not all enzymes are less effective at higher temperatures, so choice (D) is incorrect.
17.(B)Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain in cellular respiration. Oxygen is not required in glycolysis, so choice (A) is incorrect. Oxygen is not required for fermentation nor is it a substrate for enzymes used in fermentation, so choice (C) is incorrect. Pyruvate does not enter the matrix of the mitochondria, so choice (D) is incorrect.
18.(C)During the Krebs cycle, NAD+ is reduced to NADH, so this is a relevant question in understanding the Krebs cycle. The breakdown of glucose into pyruvate occurs during glycolysis, not the Krebs cycle, so choice (A) is incorrect. The proton gradient in the mitochondria is formed during oxidative phosphorylation, not the Krebs cycle, so choice (B) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because the formation of ATP by ATP synthase happens during chemiosmosis, not the Krebs cycle.
19.(B)Both fermentation and the electron transport chain oxidize NADH to NAD+. Choice (A) is incorrect because fermentation does not require oxygen. Fermentation occurs in the cytoplasm, not the mitochondria, so choice (C) is incorrect. One of the end products of the electron transport chain is metabolic water, but fermentation does not form metabolic water. So choice (D) is incorrect.
20.(B)Since a few base pairs are lost each time a linear chromosome is replicated, the repetitive telomere sequences at the ends of linear chromosomes help protect the genetic information in chromosomes from degradation during cell division. Choice (A) is incorrect because telomeres do not function in protein synthesis. Telomeres do not correct mutations in DNA, so choice (C) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because telomeres do not inhibit cell division.
21.(D)Water moves from areas of higher water potential to areas of lower water potential. Celery stalks become stiff after being placed in distilled water for a few hours because water will move from the area of higher water potential in the distilled water to the area of lower water potential in the celery stalks. Celery stalks placed in 1.0 molar sodium chloride will wilt because water will move from the area of higher water potential in the celery to the area of lower water potential in the 1.0 molar sodium chloride solution. Based on the fact that the celery cells became stiff in the distilled water, they must have a lower water potential than that of the distilled water, so choice (A) is incorrect. Since the celery cells wilted in the sodium chloride solution, the water potential in the celery cells must be higher than the water potential in the sodium chloride solution, so choice (B) is incorrect. Celery cells have solutes and therefore cannot have a higher water potential than that of distilled water, so choice (C) is incorrect.
22.(B)Photosynthesis requires light energy, so the vial covered in foil will only perform cellular respiration. Cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide, which forms an acid when dissolved in water and therefore lowers the pH. The vial without foil performs both cellular respiration and photosynthesis. Photosynthesis consumes carbon dioxide, so the vial without foil will not build up as much carbon dioxide and will have a higher pH than the vial covered in foil. Choice (A) is incorrect because the vial without foil will perform both cellular respiration and photosynthesis. The vial covered with foil will not perform photosynthesis, so choices (C) and (D) are incorrect.
23.(D)According to the table, the largest animals have lower cancer rates, so the data do not support the claim that larger animals have greater cancer rates. Choices (A) and (C) are incorrect because larger animals have lower cancer rates. Smaller animals have higher cancer rates than larger animals, so choice (B) is incorrect.
24.(A)Elephants have lower cancer rates than marmosets, Tasmanian devils, and tigers, so elephants are more likely to have more copies of the tumor-suppressing TP53 gene. Choices (B), (C), and (D) are incorrect because marmosets, Tasmanian devils, and tigers all have higher cancer rates than elephants.
25.(D)Since males receive their sole X chromosome from their mother, all the males will have white eyes. All of the females will receive an X chromosome with the dominant red allele from their father, so all of the females will have red eyes. The following figure is a Punnett square that shows the genotypes of the parent flies and the probable offspring from the cross.
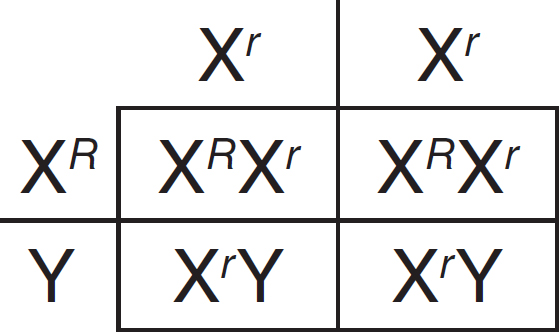
26.(C)Transformation is the uptake of naked foreign DNA by a cell. Choice (A) is incorrect because transcription describes the process of creating a complementary RNA copy of a DNA sequence. Transduction is the introduction of foreign DNA into a cell by a virus, so choice (B) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because translocation describes the exchange of genetic material between nonhomologous chromosomes.
27.(C)A person with sickle cell disease will be homozygous recessive, and a person with the sickle cell trait will be heterozygous. Their offspring will have a 50% likelihood of having sickle cell disease, as shown in the figure.
28.(D)Heterozygote advantage occurs when the individuals with the heterozygous genotype have an advantage over homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive genotypes. In this case, heterozygotes do not have sickle cell disease and are more resistant to malaria. Choice (A) is incorrect because polygenic inheritance describes when more than one gene contributes to a trait. Sexual selection occurs when mate choice determines reproductive success, so choice (B) is incorrect. Choice (C) is incorrect because sex-linked inheritance occurs when the gene for a trait is located on a sex chromosome.
29.(C)A person who does not have sickle cell disease but whose parent had sickle cell disease must be heterozygous. A person with the sickle cell trait is heterozygous, so the child of the two individuals would have a 50% likelihood of having the sickle cell trait, as shown in the figure.
30.(D)Parasitism is a symbiotic relationship where one organism is harmed (the finch nestlings) and the other organism benefits (Philornis downsi). Choice (A) is incorrect because commensalism is a symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits and the other organism neither benefits nor is harmed. Competition is when two species are competing for the same resources, so choice (B) is incorrect. Choice (C) is incorrect because mutualism means both species in the symbiotic relationship benefit.
31.(C)Seagrass will absorb carbon dioxide as it performs photosynthesis. Choice (A) is incorrect because there is no evidence that planting seagrass would reduce habitats for invasive species. Photosynthesis adds oxygen to the atmosphere; it does not remove oxygen, so choice (B) is incorrect. There is no evidence that seagrass plantings would increase soil erosion, so choice (D) is incorrect.
32.(B)More drops of water can be placed on the penny than the other liquids, demonstrating that water has stronger cohesive properties than the other liquids, and therefore water forms more hydrogen bonds than the other liquids. Choice (A) is incorrect because vegetable oil is a nonpolar compound and does not form hydrogen bonds. Ions are attracted to metals, not repelled, so choice (C) is incorrect. Ethanol is a larger molecule than water, but it does not form more hydrogen bonds than water. So choice (D) is incorrect.
33.(D)Starch molecules are too large to pass through the semipermeable membrane, but water and iodine can pass through the membrane. Iodine will move down its concentration gradient from side A to side B and react with the starch molecules, which will turn dark blue. Since the starch molecules cannot move down their concentration gradient and will remain on side B, the water potential on side B will be lower than the water potential on side A. Water will move from the area of higher water potential on side A to the area of lower water potential on side B, raising the water level on side B of the U-tube apparatus.
34.(C)Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site of an enzyme, preventing the substrate from binding to the active site, so adding a competitive inhibitor would be an effective way to slow the rate of cell division in cells containing the BCR-ABL kinase. Cofactors and coenzymes increase the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, so choices (A) and (B) are incorrect. Transcription factors increase the rate of transcription of RNA from DNA, so choice (D) is incorrect.
35.(D)Water moves from areas of higher water potential to areas of lower water potential, and distilled water has a higher water potential than the inside of a red blood cell (due to the solutes in the red blood cell). So water would move into the red blood cell, and the cell would eventually burst. Choices (A) and (B) are incorrect because red blood cells have a lower water potential than distilled water. Choice (C) is incorrect because water moving into the red blood cells would cause them to swell and lyse, not shrivel.
36.(B)The presence of wildebeests has a disproportionally large effect on many other species in the ecosystem, so it is a keystone species. Choice (A) is incorrect because an apex predator consumes other organisms and has no predators itself, but the wildebeest is a primary consumer because it eats grass. Producers (such as grass) perform photosynthesis, so choice (C) is incorrect. Secondary consumers eat primary consumers, not producers. So the wildebeest is not a secondary consumer, and choice (D) is incorrect.
37.(C)Bacteria do not have nuclei but do have cell membranes and cell walls. Choice (A) is incorrect because bacteria do not have nuclei, mitochondria, or chloroplasts. Bacteria do not have nuclei or mitochondria, so choices (B) and (D) are incorrect.
38.(A)Plants depend on pollinators for reproduction, and plants have chloroplasts. Choices (B), (C), and (D) are incorrect because they do not have chloroplasts.
39.(B)Human muscle tissue would have nuclei and mitochondria but not chloroplasts or cell walls. Choice (A) is incorrect because human cells do not contain chloroplasts. Choice (C) is incorrect because human cells have nuclei, and choice (D) is incorrect because human cells do not have cell walls.
40.(B)Hydrolysis uses water to break down polymers into monomers, and dehydration synthesis combines monomers into polymers while removing a water molecule. Choice (A) is incorrect because hydrolysis does not build monomers nor does dehydration synthesis break down monomers. Hydrolysis reactions consume, not release, water, so choice (C) is incorrect. All macromolecules, not just carbohydrates and proteins, can be broken down by hydrolysis reactions, so choice (D) is incorrect.
41.(D)Water has a high specific heat because hydrogen bonds form between the oxygen atom on one water molecule and the hydrogen atom on another water molecule. Choices (A) and (C) are incorrect because the high specific heat of water is directly due to hydrogen bonds between water molecules, not covalent bonds between water molecules. Hydrogen bonds do not form between oxygen atoms, so choice (B) is incorrect.
42.(D)Alpha helixes and beta sheets are forms of secondary structure and are formed by hydrogen bonds. Choices (A) and (B) are incorrect because alpha helixes and beta sheets are not forms of primary structure. Secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds, not peptide bonds, so choice (C) is incorrect.
43.(C)Nucleic acids contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Choice (A) is incorrect because carbohydrates do not usually contain nitrogen or phosphorus. Lipids usually do not contain nitrogen, so choice (B) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because proteins usually do not contain phosphorus.
44.(C)The R-group (also known as the side chain) of an amino acid is unique to that amino acid and determines whether the amino acid is hydrophobic or hydrophilic. Therefore, it influences how the amino acid would interact with the aqueous environment of the cell. All amino acids contain a carboxyl group. An amino group and a hydrogen atom are attached to the central carbon but are less likely to affect the interaction of an amino acid with the aqueous environment of the cell. For those reasons, choices (A), (B), and (D) are incorrect.
45.(D)Signal amplification involves one signaling molecule (also known as a ligand) triggering multiple chemical reactions, magnifying the effect of the chemical signal. Choices (A), (B), and (C) are incorrect because they each involve one reaction triggering just one event.
46.(C)DNA replication occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle. Choices (A), (B), and (D) are incorrect because DNA replication does not occur during those phases.
47.(B)Positive feedback occurs when the stimulus increases the response and moves the condition further away from homeostasis. Choice (A) is incorrect because it is an example of the formation of a secondary messenger. Excess tryptophan shutting down the operon that produces tryptophan is an example of negative feedback, so choice (C) is incorrect. The release of insulin lowers blood sugar, returning blood sugar levels to normal levels, so choice (D) is also incorrect.
48.(C)Mutations in a splice site could result in errors in intron splicing and the loss of exons. Choice (A) is incorrect because a nonsense mutation (which would form a stop codon) would result in a truncated protein, not the deletion of two exons at different locations in the gene. Translocations would most likely form a completely different protein, so choice (B) is incorrect. A point mutation would not result in the deletion of two different exons, so choice (D) is incorrect.
49.(D)The F508del mutation results in a misfolded protein, so a treatment that helps the CFTR protein fold correctly would be an effective treatment for the result of this mutation. Activation of transcription of the CFTR gene with the F508del mutation would not be effective. It would just produce more of the misfolded protein, so choice (A) is incorrect. Choice (B) is incorrect because repression of the number of ribosomes would result in less production of all proteins in the cell. The F508del mutation does not code for a premature stop codon, so choice (C) is incorrect.
50.(A)Since there would be fewer copies of the CFTR protein, a drug that causes the CFTR channel to stay open and function longer might help alleviate the symptoms of the disease. Choice (B) is incorrect because suppression of the expression of the CFTR gene would make the symptoms worse, not better. Similarly, decreasing the number of chloride ions exiting the cell would also make the symptoms worse, so choice (C) is incorrect. Stimulating the Na+/K+ pump would not help with the migration of chloride ions, so choice (D) is incorrect.
51.(A)Since cystic fibrosis is a recessive disorder, an individual would have to inherit a copy of the cystic fibrosis allele from both parents. If one of the parents did not have the cystic fibrosis allele, a child with a person who did have cystic fibrosis would have no chance of inheriting the disease, though their child would be a heterozygous carrier of the allele, as shown in the figure.
52.(C)The product formed by the enzymes of a repressible operon acts as a corepressor to help the repressor shut off the operon when an excess of the product is present. Choice (A) is incorrect because arginine would not induce the operon to turn on nor would arginine stimulate transcription, so choice (B) is also incorrect. Arginine does not stimulate the production of cyclic AMP, so choice (D) is incorrect.
53.(B)Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used to make multiple copies of a specific DNA sequence. Choice (A) is incorrect because gel electrophoresis is used to separate DNA fragments by size and charge. CRISPR-Cas9 is used in gene editing, so choice (C) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because DNA sequencing is the process of reading the sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA.
54.(A)Horizontal gene transfer is the transfer of genetic information between organisms in the same generation; conjugation, transformation, and transduction are all forms of horizontal gene transfer. Choice (B) is incorrect because having the incorrect number of chromosomes is an aneuploidy. Horizontal gene transfer can occur in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, so choice (C) is incorrect. Horizontal gene transfer does not reduce genetic diversity, so choice (D) is incorrect.
55.(D)If the birth rate exceeds the death rate in a population, the population size will increase. Choice (A) is incorrect because a population’s size could increase if the birth rate was less than 1.0 and if the death rate was less than the birth rate. If the death rate is greater than 0 but the birth rate is greater than the death rate, the population size will increase, so choice (B) is incorrect. There is no evidence there is an unlimited food source, so choice (C) is incorrect.
56.(D)A natural disaster is a density-independent factor. Choices (A), (B), and (C) are all density-dependent factors and are therefore incorrect.
57.(B)Both species are competing for the same food source (nutrient-rich sap from the host plant), so this is an example of interspecies competition. Choice (A) is incorrect because intraspecies competition is when members of the same species compete for a resource. Mutualism is when both species benefit. F. formicaria is harmed by the presence of F. geoica, so choice (C) is incorrect. Both Fordinae species are parasites of the host plants but not of each other, so choice (D) is incorrect.
58.(D)Both Fordinae species are parasites on the host plant because they obtain nutrition from the host plant but provide no benefit to the host plant. Choices (A), (B), and (C) are incorrect, as explained in the answer explanation to Question 57.
59.(B)Catfish declined by over 90% after the introduction of the carp. Bass decreased by about 50%, so choice (A) is incorrect. Steelheads decreased by about 65%, so choice (C) is incorrect. Choice (D) is incorrect because trout decreased by about 33%.
60.(B)The Simpson’s Diversity Index of the population in 1985 (0.7145) was greater than the Simpson’s Diversity Index of the population in 1991 (0.6575). So the 1985 population would be more resilient and more able to recover from an ecological disturbance. Choice (A) is incorrect because even though the population size was the same both years, the population was much less diverse in 1991 than in 1985. Choice (C) is incorrect because a higher Simpson’s Diversity Index makes a population more likely to recover from an ecological disturbance. Choice (D) is incorrect because even though there was one more species present in 1991 than in 1985, there was less diversity in 1991 than in 1985.
Self-Analysis Chart for Section I
Use this chart to help identify areas where you need to focus your review. After scoring the multiple-choice section, circle the questions in this chart that you answered incorrectly. Note the units that you scored well in as well as the units that might require further study. Be sure to also review the answer explanations for Section II as all of those questions cover a wide variety of units and topics.
|
Unit |
Questions |
Unit 1: Chemistry of Life |
32, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44 |
Unit 2: Cell Structure and Function |
21, 33, 35, 37, 38, 39 |
Unit 3: Cellular Energetics |
13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 22, 34 |
Unit 4: Cell Communication and Cell Cycle |
23, 24, 45, 46, 47 |
Unit 5: Heredity |
20, 25, 27, 28, 29, 51 |
Unit 6: Gene Expression and Regulation |
26, 48, 49, 50, 52, 53, 54 |
Unit 7: Natural Selection |
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 |
Unit 8: Ecology |
30, 31, 36, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60 |
Section II
1.(a)Turnips placed in solutions with a higher water potential than the turnip cells would have a positive percent change in mass because water flows from an area of higher water potential to an area of lower water potential. Water would flow into the turnip cells, and the turnips would gain mass. Turnips placed in solutions with a lower water potential than the turnip cells would have a negative percent change in mass because water would flow out of the turnip cells into the surrounding solution and the turnips would lose mass.
TIP
Remember to always use temperatures in Kelvin when calculating water potential!
(b)The molarity of the turnip cell would be about 0.45 molar. The line of best fit crosses the x-axis at the coordinates (0.45 molar, 0%), which indicates a 0.45 solution that would be isotonic to a turnip cell and in which a turnip cell would have 0% change in mass.
(c)The line of best fit crosses the x-axis at approximately 0.45 molar, so that would be the best estimate of the concentration of solutes in a turnip cell. Since the turnip is open to the atmosphere, the pressure potential is 0. The water potential of the turnip cell would then depend solely on the solute potential, which is calculated as follows:
![]()
i = 1 (because sucrose is a covalent compound and does not form ions)
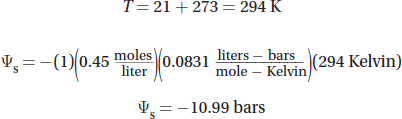
(d)The turnip in the 0.5 molar pickling solution would probably have a negative percent change in mass because the line of best fit is below 0% change in mass for a molarity of 0.5.
2.(a)A plant needs to open its stomata to take in the carbon dioxide it needs for photosynthesis. However, each time a plant opens its stomata, it can lose water to the atmosphere. The plant needs to balance its needs for carbon dioxide and water, and this is called the photosynthesis-transpiration compromise.
(b)
(c)There is a statistically significant difference between plant species A and the other two plant species because the 95% confidence interval for species A does not overlap with the 95% confidence interval for either species B or species C. However, the 95% confidence intervals for species B and species C do overlap, so we cannot say there is a statistically significant difference between species B and species C.
(d)Species A would be best suited for a dry climate because its rate of water loss due to transpiration is lower than that of species B and species C.
3.(a)This is an example of artificial selection because a person is selecting for a particular trait (antibiotic resistance).
(b)Since plate 2 contains the antibiotic, only bacteria with resistance to the antibiotic will grow on plate 2. Plate 1 does not contain antibiotic, so bacteria with and without resistance to the antibiotic will grow on plate 1. There will be fewer bacteria on plate 2 than on plate 1.
(c)Plate 6 will have bacteria with the greatest resistance to the antibiotic.
(d)Plate 6 has the greatest concentration of ampicillin, so the bacteria that survive on that plate will have the greatest resistance to ampicillin.
4.(a)Seagulls have no predators in this ecosystem. Penguins are prey for seals. Penguins are primary consumers (because they eat plankton) and tertiary consumers (because they eat squid, squid eat krill, krill eat plankton). Seagulls are secondary consumers (because they eat krill, krill eat producers) and tertiary consumers (because they eat squid, squid eat krill, krill eat plankton).
(b)Penguins and krill are primary consumers because they both eat producers (plankton).
(c)The number of krill would decrease.
(d)A bloom of a phytoplankton Coccolithophore (which krill cannot eat) would outcompete the phytoplankton that krill can eat, depleting the food supply for the krill. So krill would die.
5.(a)Juxtacrine signaling involves direct contact between cells.
(b)Cytokines function as signaling molecules or ligands.
(c)
(d)Secondary messengers amplify a response in a cell by triggering multiple chemical reactions through the process of signal amplification.
6.(a)In the distilled water group, ![]() of the cells are in mitosis, and
of the cells are in mitosis, and ![]() of the cells are in interphase. In the caffeine group,
of the cells are in interphase. In the caffeine group, ![]() of the cells are in mitosis, and
of the cells are in mitosis, and ![]() of the cells are in interphase.
of the cells are in interphase.
(b)The onions grown in distilled water are the control group, the independent variable is the presence or absence of 2 millimolars of caffeine in the growth medium, and the dependent variable is the number of cells in mitosis and interphase in each group.
(c)Using the formula for chi-square:
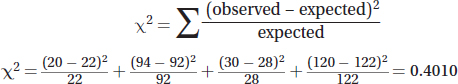
There are four possible outcomes in the experiment, so the number of degrees of freedom is 4 — 1 = 3. Using a p-value of 0.05 and the chi-square table, the critical value is 7.81. Since the calculated chi-square value (0.4010) is less than the critical value in the chi-square table, the null hypothesis is supported (or we can say we fail to reject the null hypothesis).
(d)A drug that binds irreversibly to the active site of the cyclin-dependent kinase would prevent the binding of cyclin to the cyclin-dependent kinase and therefore prevent the formation of mitosis-promoting factor. The cell cycle would be arrested at the end of interphase and would not enter mitosis.