MCAT General Chemistry Review
Chapter 2: The Periodic Table
Practice Questions
1. Lithium and sodium have similar chemical properties. For example, both can form ionic bonds with chloride. Which of the following best explains this similarity?
1. Both lithium and sodium ions are positively charged.
2. Lithium and sodium are in the same group of the Periodic Table.
3. Lithium and sodium are in the same period of the Periodic Table.
4. Both lithium and sodium have low atomic weights.
2. Carbon and silicon are the basis of biological life and synthetic computing, respectively. While these elements share many chemical properties, which of the following best describes a difference between the two elements?
1. Carbon has a smaller atomic radius than silicon.
2. Silicon has a smaller atomic radius than carbon.
3. Carbon has fewer valence electrons than silicon.
4. Silicon has fewer valence electrons than carbon.
3. What determines the length of an element’s atomic radius?
1. The number of valence electrons
2. The number of electron shells
3. The number of neutrons in the nucleus
1. I only
2. II only
3. I and II only
4. I, II, and III
4. Ionization energy contributes to an atom’s chemical reactivity. Which of the following shows an accurate ranking of ionization energies from lowest to highest?
1. first ionization energy of Be < second ionization energy of Be < first ionization energy of Li
2. first ionization energy of Be < first ionization energy of Li < second ionization energy of Be
3. first ionization energy of Li < first ionization energy of Be < second ionization energy of Be
4. first ionization energy of Li < second ionization energy of Be < first ionization energy of Be
5. Antimony is used in some antiparasitic medications—specifically those targeting Leishmania donovani. What type of element is antimony?
1. Metal
2. Metalloid
3. Halogen
4. Nonmetal
6. The properties of atoms can be predicted, to some extent, by their location within the Periodic Table. Which property or properties increase in the direction of the arrows shown?
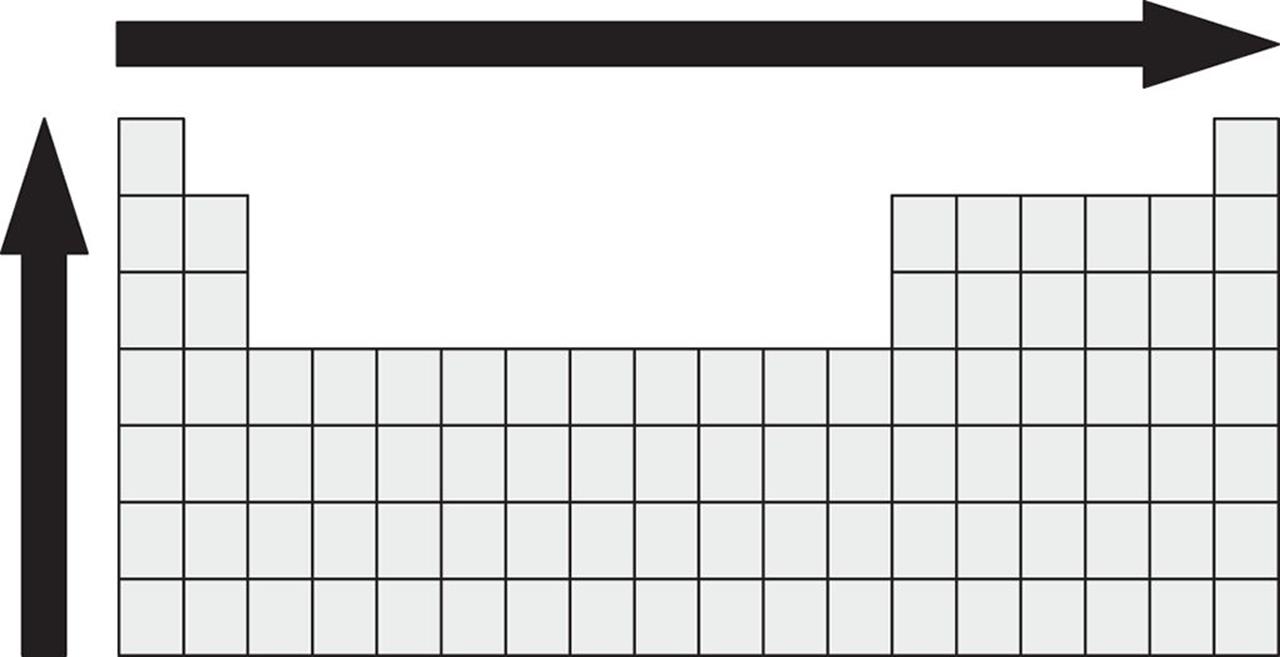
1. Electronegativity
2. Atomic radius
3. First ionization energy
1. I only
2. I and II only
3. I and III only
4. II and III only
7. Metals are often used for making wires that conduct electricity. Which of the following properties of metals explains why?
1. Metals are malleable.
2. Metals have low electronegativities.
3. Metals have valence electrons that can move freely.
4. Metals have high melting points.
8. Which of the following is an important property of the group of elements shaded in the Periodic Table below?
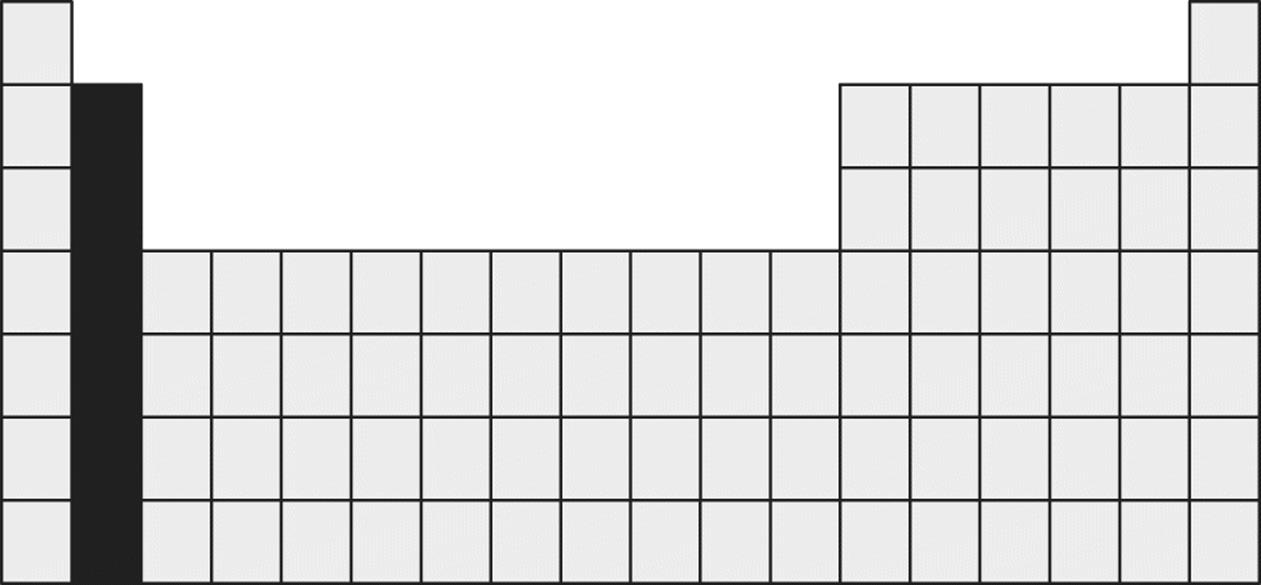
1. These elements are the best electrical conductors in the Periodic Table.
2. These elements form divalent cations.
3. The second ionization energy for these elements is lower than the first ionization energy.
4. The atomic radii of these elements decrease as one moves down the column.
9. When dissolved in water, which of the following ions is most likely to form a complex ion with H2O?
1. Na+
2. Fe2+
3. Cl–
4. S2–
10.How many valence electrons are present in elements in the third period?
1. 2
2. 3
3. The number decreases as the atomic number increases.
4. The number increases as the atomic number increases.
11.Which of the following elements has the highest electronegativity?
1. Mg
2. Cl
3. Zn
4. I
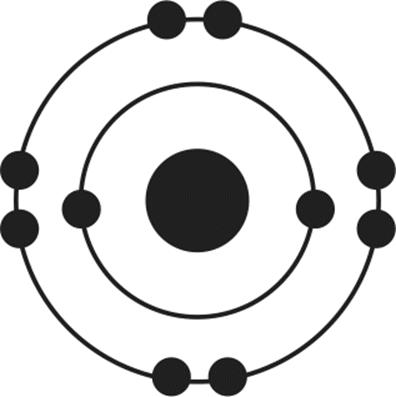
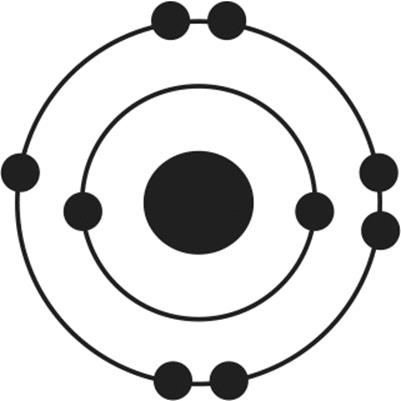
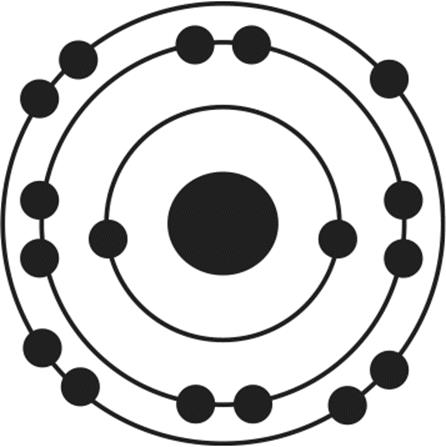
12.Of the four atoms depicted here, which has the highest electron affinity?
1. 
2. 
3. 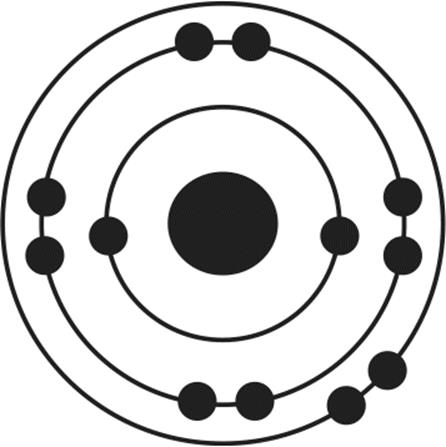
4. 
13.Which of the following atoms or ions has the largest effective nuclear charge?
1. Cl
2. Cl–
3. K
4. K+
14.Why do halogens often form ionic bonds with alkaline earth metals?
1. The alkaline earth metals have much higher electron affinities than the halogens.
2. By sharing electrons equally, the alkaline earth metals and halogens both form full octets.
3. Within the same row, the halogens have smaller atomic radii than the alkaline earth metals.
4. The halogens have much higher electron affinities than the alkaline earth metals.
15.What is the highest-energy orbital of elements with electrons in the n = 3 shell?
1. s-orbital
2. p-orbital
3. d-orbital
4. f-orbital
PRACTICE QUESTIONS