The MCAT Chemistry Book - Aryangat A. 2012
Organic Chemistry
Carboxylic Acids
A. INTRODUCTION
Carboxylic acids are compounds with the general formula RCOOH.
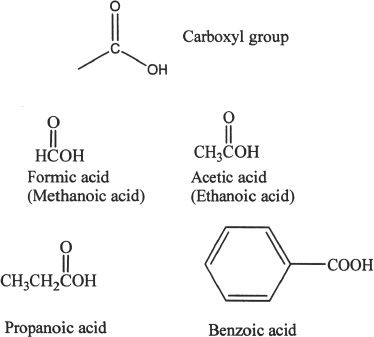
B. PROPERTIES OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
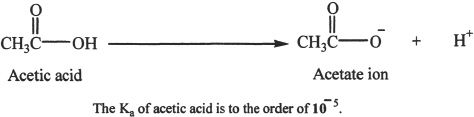
It is clear from the name that carboxylic acids are acidic. The hydrogen of the carboxyl group (-COOH) is acidic. The strength of these acids can be explained in terms of the relative stabilities of their conjugate bases. Weaker the conjugate base is, the stronger the acid. Keep in mind the fact that carboxylic acids are weak acids.
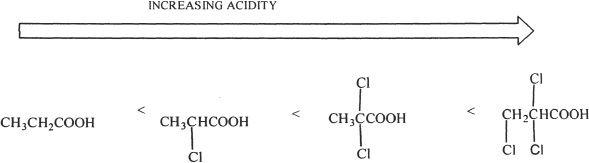
The acidity of a carboxylic acid is influenced by its substituents. Substituents which are very electronegative, especially when they are attached to the a-carbon, increase the acidity of carboxylic acids. As the number of electronegative substituents increases, so does the acidity. This increase in acidity is because of the increased stability of the carboxylate ion formed, as a result of the presence of the electronegative substituent. This effect is due to what is known as inductive effect. Because of the electron withdrawing effect of the substituent, the charge is dispersed and the ion (carboxylate ion) is stabilized. Study the following gradation of increasing acidity to reinforce the point just made.
Carboxylic acids can undergo extensive hydrogen bonding. So they have higher boiling points than alkanes or even alcohols. Carboxylate ions are resonance stabilized (Figure 23-1). The negative charge in the carboxylate anion is shared by both the oxygens.

Figure 23-1
C. SYNTHESIS OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
By Oxidation
Carboxylic acids can be prepared by the oxidation of primary alcohols, and aldehydes. An oxidizing agent such as KMnO4 can accomplish these conversions.
Sample reaction 23-1
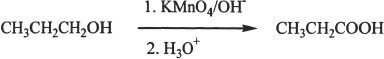
From Grignard Reagents
Another way to synthesize carboxylic acids is to react Grignard reagents with CO2. The Grignard reagent acts as a nucleophile toward the carbon dioxide. In an acidic medium the carboxylate entity formed is converted to carboxylic acid. Grignard reagents can be prepared by reacting alkyl halides with magnesium.
Sample reaction 23-2
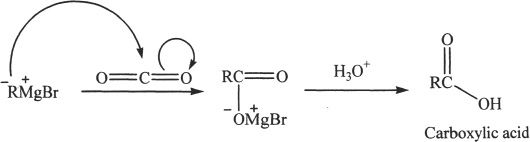
From Alkyl Halides via Nitriles
Primary or secondary alkyl halides can be converted into nitriles (alkyl cyanide) by nucleophilic substitution. The nitriles formed can in turn be converted to carboxylic acids by hydrolysis.
Sample reaction 23-3
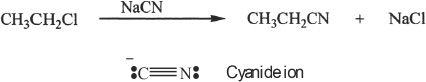
The cyanide ion is negatively charged and the negatively charged carbon atom has nucleophilic character. The reaction usually occurs via SN2 mechanism. The nitrile formed can be hydrolyzed to a carboxylic acid.
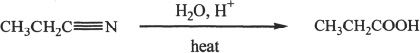
D. REACTIONS OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
Esterification
Carboxylic acids and alcohols can react in the presence of an acid catalyst. The products formed are ester and water.
Sample reaction 23-4

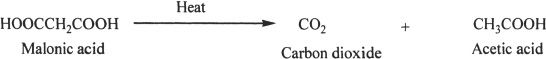
Decarboxylation
In a decarboxylation reaction, the carboxylic acid loses carbon dioxide. The process usually requires heat to progress.
Sample reaction 23-5
CHAPTER 23 PRACTICE QUESTIONS
1. An alkyl magnesium halide is reacted with carbon dioxide under very low pH (acidic conditions). Which of the following are true regarding this reaction?
I) Carbon dioxide acts as the nucleophile in this reaction
II) Carboxylic acid is one of the products
III) Grignard reagent acts as the nucleophile
A. I only
B. II only
C. I & III
D. II & III
2. Predict the major product (compound B) from the series of reactions shown below.
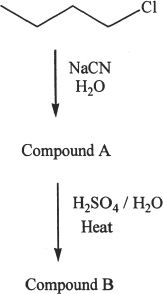
A. A four carbon carboxylic acid
B. A four carbon alkene
C. A five carbon carboxylic acid
D. A five carbon aldehyde
3. Predict the identity of Compound X from the following reaction.
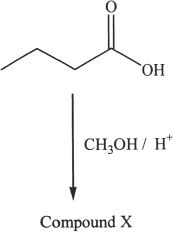
A. Butyl methanoate
B. Butanaldehyde
C. Methyl butanoate
D. Butanol
4. Which of the following has the highest boiling point?
A. Pentanoic acid
B. Pentanol
C. Pentane
D. Pentanone
5. Which of the following is true regarding the acidity of Compounds A & B?
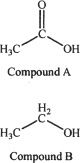
A. Compound B is more acidic, because ethoxide is resonance stabilized.
B. Compound A is less acidic, because acetate is resonance stabilized.
C. Compound B is less acidic, because ethoxide is resonance stabilized.
D. Compound A is more acidic, because acetate is resonance stabilized.
6. Predict the most acidic compound from the choices below?
A. 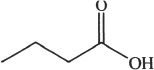
B. 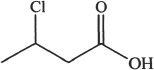
C. 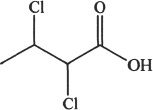
D. 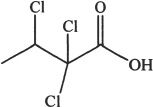
7. The product of the following reaction is:
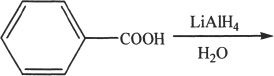
A. toluene.
B. benzene.
C. benzophenone.
D. benzyl alcohol.
8. The general formula indicated below is that of:
RCOOH
A. an alkane.
B. an aldehyde.
C. an ester.
D. a carboxylic acid.
9. Which of the following compounds has the highest boiling point?
A. Propanal
B. Propanoic acid
C. Propanone
D. Propane
10. The name of the structure shown is:
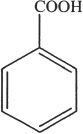
A. benzaldehyde.
B. benzoic acid.
C. phenyl ethanoic acid.
D. heptanoic acid.
Questions 11-16 are based on the following passage.
Passage
The sequence of reactions shown below were done in a lab.
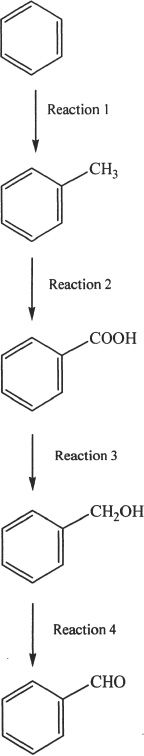
Some of the reactions were done to synthesize compounds that were used to conduct other reactions. The experiments were also used to analyze the efficiency of these reactions.
11. All the statements given below are true, except:
A. CH3COOH can undergo hydrogen bonding.
B. The melting point of carboxylic acids are higher than that of comparable alcohols.
C. The carbonyl group in carboxylic acids are more electrophilic than that of ketones.
D. In carboxylic acids, resonance is possible.
12. Which of the following is true about the conversion involved in Reaction 2?
A. The conversion is an oxidation reaction, and can be accomplished by using LiAlH4.
B. The conversion is a reduction reaction, and can be accomplished by using LiAlH4.
C. The conversion is an oxidation reaction, and can be accomplished by using KMnO4.
D. The conversion is a reduction reaction, and can be accomplished by using KMnO4.
13. If the product of Reaction 2 were converted to an ester, which of the following reagents should be used for this conversion to be done most easily?
A. NaBH4/H2O
B. Alcohol/HCl
C. Thionyl chloride/heat
D. Ether/HCl
14. Formaldehyde can be converted to formic acid. What is the correct hybridization of the carbon atom in the formic acid?
A. sp
B. sp3
C. sp3d
D. sp2
15. Which of the following compounds has the highest pKa value?
A. FCH2CH2COOH
B. F2CHCH2COOH
C. FCH2CH2(CH3)CH2COOH
D. FCH2COOH
16. From the following compounds, choose the compound that is the most acidic?
A. ![]()
B. ![]()
C. 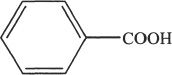
D. ![]()