The MCAT Chemistry Book - Aryangat A. 2012
Organic Chemistry
Acid Derivatives
A. INTRODUCTION
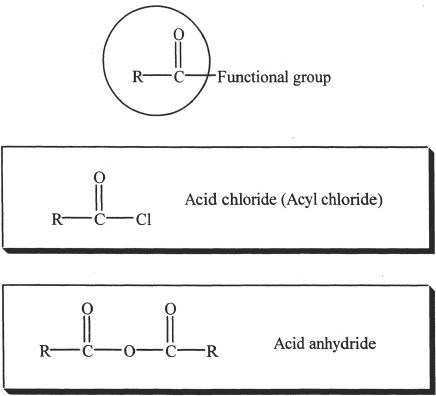
Acid chlorides, anhydrides, amides, esters, and ketoacids are some examples of acid derivatives. An acid derivative has an acyl group which is attached to a functional group. If the functional group attached to the acyl group is a hydroxyl group, then it is a carboxylic acid.
Acid derivative
The acyl group is circled.
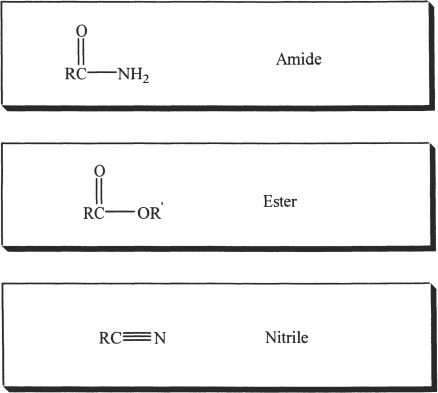
Nitrile is also considered as a carboxylic acid derivative, even though it has no acyl group.
An acid derivative can be converted to the corresponding carboxylic acid by hydrolysis.
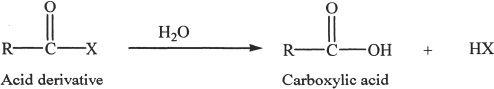
This hydrolysis reaction occurs by nucleophilic substitution.

B. ACID CHLORIDES
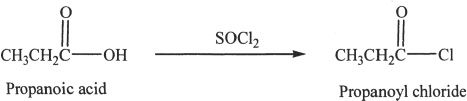
An acid chloride can be prepared by using thionyl chloride and the corresponding carboxylic acid.
Sample reaction 24-1
Reactions of Acid chlorides
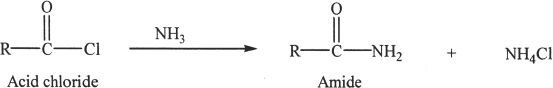
Acid chlorides form amides when reacted with amines or ammonia.
Sample reaction 24-2
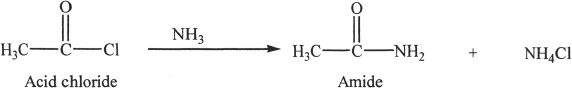
Acid chlorides react with alcohols to form esters.
Sample reaction 24-3
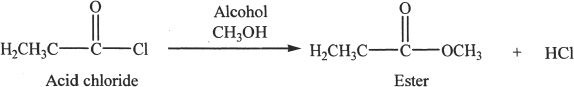
C. ACID ANHYDRIDES
Acid anhydrides have important commercial uses. One of the acid anhydrides of such importance is acetic anhydride.
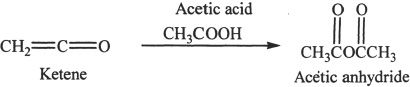
Acetic anhydride can be synthesized by reacting a compound called ketene with acetic acid.
Sample reaction 24-4
Cyclic anhydrides such as succinic anhydride, maleic anhydride, and glutaric anhydride can be prepared by heating the corresponding dicarboxylic acids. The reaction results in intramolecular dehydration and ring formation. Study the following example.
Sample reaction 24-5
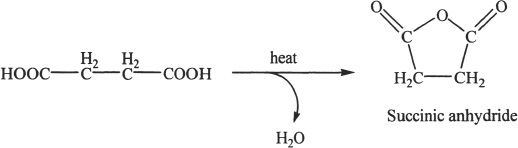
Reaction Involving Acid Anhydrides
Acid anhydrides react with alcohols to form esters and carboxylic acids. A general equation representing this type of reaction is shown in the next sample reaction.
Sample reaction 24-6

D. AMIDES
Amides can be synthesized from acid chlorides by reacting with ammonia.
Sample reaction 24-7
Hydrolysis of Amides
In the hydrolysis reaction of an amide in the presence of acids or bases, the products formed are carboxylic acid and amine. This is a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction.
E. ESTERS
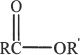
Esters are compounds having the general structure formula shown above. They have moderate dipole moments, resulting in intermolecular attractive forces. For this reason, they have higher boiling points than the corresponding hydrocarbons of comparable weights. But compared to alcohols, esters have lower boiling points, since they cannot form hydrogen bonds among themselves (Reason: No hydroxyl group). Esters can have hydrogen bonds with other hydroxyl containing compounds such as water and carboxylic acids.
Synthesis of Esters
Esters can be synthesized by reacting carboxylic acids with alcohols, in the presence of acid catalysts.
Sample reaction 24-8

F. Reactions of Esters
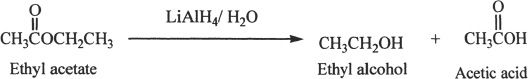
Reduction
Esters can be converted to alcohols by reacting with reducing agents such as lithium aluminum hydride.
Sample reaction 24-9
Esters with Grignard Reagents
Esters can react with Grignard reagents (two equivalents) to form tertiary alcohols. See the following example.
Sample reaction 24-10

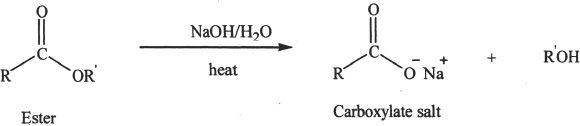
Saponification
The hydrolysis of esters in the presence of bases is called saponification.
Sample reaction 24-11
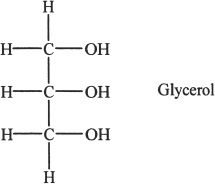
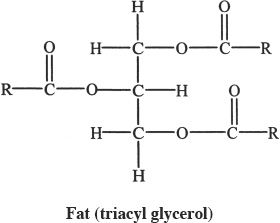
Fats are carboxylic acid esters of glycerol. When these esters are hydrolyzed, carboxylic acids with long hydrocarbon chains called fatty acids are formed, along with the parent alcohol (glycerol).
CHAPTER 24 PRACTICE QUESTIONS
1. Which of the following most readily undergoes hydrolysis among the acid derivatives given below?
A. 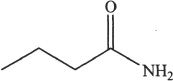
B. 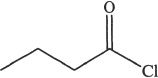
C. 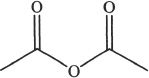
D. 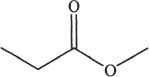
2. Which of the following is the major product of the reaction of an acid chloride with an alcohol?
A. An ester
B. An aldehyde
C. A ketone
D. An alkane
3. The reaction of an ester with Grignard reagent (excess) in the presence of an aqueous acid results in:
A. a primary alcohol.
B. a secondary alcohol.
C. a tertiary alcohol.
D. no reaction at all, because esters are not reactive with Grignard reagents.
4. Name the following compound.
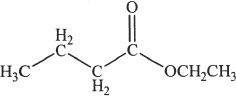
A. Methyl propanoate
B. Ethyl butanoate
C. Propionic anhydride
D. Propyl ethanone
5. Predict the product of the reaction shown below.
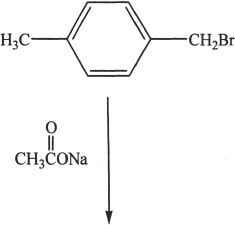
A. Ortho-methylbenzyl acetate
B. Para-methyl benzoic acid
C. Para-methylbenzyl acetate
D. Para-methylethylbenzoate
6. The most likely product of an acyl chloride reaction with ammonia is:
A. a carboxylic acid.
B. an amide.
C. an anhydride.
D. an azide.
7. All the following reactions can be used for the preparation of carboxylic acids, except:
A. ester hydrolysis.
B. nitrile hydrolysis.
C. by the reaction of Grignard reagent with carbon dioxide.
D. by the reduction of aldehydes.