The MCAT Chemistry Book - Aryangat A. 2012
Organic Chemistry
Ethers
A. INTRODUCTION
Ethers are compounds with the general formula ROR’ (e.g., CH3CH2OCH2CH3).
B. PROPERTIES OF ETHERS
Ethers are polar molecules. Compared to alcohols, ethers have very low boiling points mainly because they cannot form hydrogen bonds (intermolecular). The boiling points of ethers are close to alkanes of comparable weights. Ethers are not very reactive.
C. PREPARATION OF ETHERS
Simple ethers can be prepared by acid-catalyzed intermolecular dehydration of alcohols.
Sample reaction 25-1
![]()
An ether can also be prepared by the nucleophilic substitution of an alkyl halide by an alkoxide. The reaction is an example of SN2 reaction. The reaction is called Williamson ether synthesis (Sample reaction 25-2).
Sample reaction 25-2
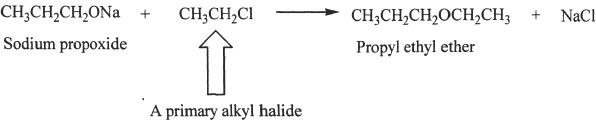
It is best to use primary alkyl halides in this type of reaction. Other halides most likely undergo elimination rather than substitution reaction.
D. CLEAVAGE OF ETHERS BY ACID
Ethers are cleaved when reacted with hydrogen halides to form alkyl halides and water. A sample reaction is shown:
Sample reaction 25-3
![]()
E. THE BASICITY OF ETHERS
Ethers are weakly basic. The basicity is due to the presence of the unshared electrons that are present on the oxygen atom of ethers.
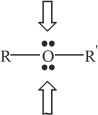
F. EPOXIDES
Epoxides are three-membered cyclic ethers. Epoxides can be synthesized by the oxidation of corresponding alkenes with peroxy acid.
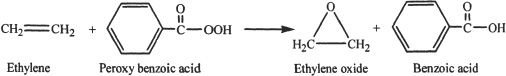
Some Reactions of Epoxides
Epoxides can undergo acid or base-catalyzed ring-opening reactions. If the epoxide used in the reaction is symmetric, the product will be the same under both conditions. But the products will be different, if the epoxide is unsymmetric.
Under Acid-Catalyzed Conditions
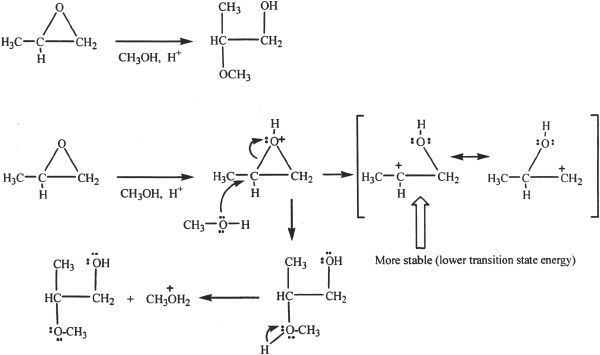
Under acidic conditions, the nucleophilic attack is directed to the protonated epoxide ring. The nucleophile adds to the more highly substituted carbon in the epoxide ring. This is because the in the protonated epoxide, the positive charge is shared by the ring-carbon atoms attached to the oxygen. The positive charge is more stabilized when it is on the more highly substituted carbon (stronger electrophile), and thus the attack of the nucleophile is preferentially on the more substituted carbon under acidic conditions.
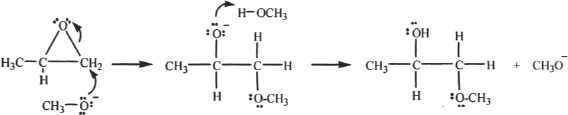
Under Basics Conditions
In a base-catalyzed ring opening of an epoxide, the nucleophilic attack is on the less substituted (less hindered) carbon atom in the epoxide ring. The mechanism is shown below.
CHAPTER 25 PRACTICE QUESTIONS
1. All the reactions described below cannot prepare ethers, except:
A. Williamson synthesis.
B. dehydrogenation of alkenes.
C. decarboxylation of carboxylic acids.
D. Clemmenson reaction.
2. In terms of boiling point, ethers most resemble which of the following types of compounds?
A. alcohols
B. water
C. carboxylic acids
D. alkanes
3. Which of the following regarding ethers is true?
A. They are polar.
B. They are relatively less reactive.
C. They can be used as solvents in reactions.
D. All the above
Questions 4-8 are based on the following passage.
Passage 1
Consider the following synthesis reaction.
Reaction 1
![]()
where R represents an alkyl group
4. Which of the following is true regarding ethers?
I. Ethers are not very reactive.
II. Ethers are extremely reactive.
III. Ethers are flammable.
IV. Ethers have higher boiling points than alcohols.
A. I & III only
B. II & III only
C. II, III, an IV only
D. I & IV only
5. The reaction sequence shown in the passage is most likely to be effective if the reaction runs by SN2 mechanism. Which of the following is the best suited alkyl halide to conduct this reaction most efficiently?
A. ![]()
B. 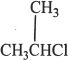
C. 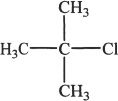
D. 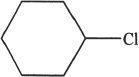
6. All the following alkyl halides can undergo elimination by the reaction represented in Experiment 1, except:
A. 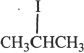
B. ![]()
C. 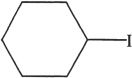
D. 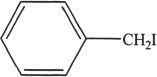
7. Predict the major product (Compound M) of the following reaction.
![]()
A. CH3Br
B. CH3OBr
C. CH3OBrCH3
D. No reaction occurs.
8. Which of the following is not an ether?
A. 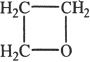
B. ![]()
C. 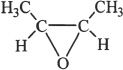
D. ![]()