The MCAT Chemistry Book - Aryangat A. 2012
Organic Chemistry
Amines
A. INTRODUCTION
Amines are derivatives of ammonia. The alkyl derivatives of ammonia are called alkyl amines, and the aryl (aromatic) derivatives of ammonia are called aryl amines. These nitrogen-containing compounds are unique for their basicity.
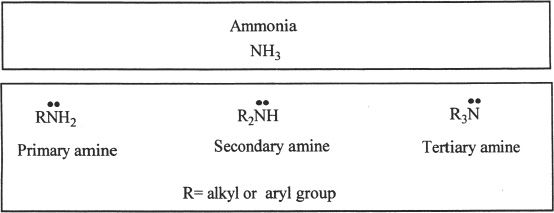
B. STRUCTURE OF AMINES
The carbon to which the nitrogen is attached in an alkyl amine is sp3 hybridized, and in aryl amines it is sp2 hybridized. The nitrogen in the amines is sp3 hybridized. As you have probably noticed, the nitrogen present in an amine has an unshared electron pair. In alkyl amines, the substituents attached to the nitrogen atom are arranged in a pyramidal manner around the nitrogen. In aryl amines, this pyramidal mode is more flat compared to alkyl amines. Moreover, the unshared pair of electrons in aryl amines has the advantage of delocalization into the pi electrons in the aromatic ring.
C. PROPERTIES OF AMINES
Amines are somewhat polar. But the polarity is not as high as that of alcohols. As Figure 27-1 indicates, the amines have intermediate boiling points.
Keep in mind that we are comparing the boiling points of amines with comparable alkanes and alcohols. Among amines only primary and secondary amines can form hydrogen bonds. Lower amines are soluble in water.
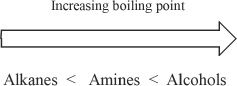
Figure 27-1
D. PREPARATION OF AMINES
Alkylation Method
Amines can be prepared by the alkylation of ammonia. In this array of reactions (Figure 27-2), the amines nucleophilically attack the alkyl halides. As shown below, the first reaction yields a primary amine. Primary amines yield secondary amines which in turn yield tertiary amines, and tertiary amines yield quaternary ammonium salts.
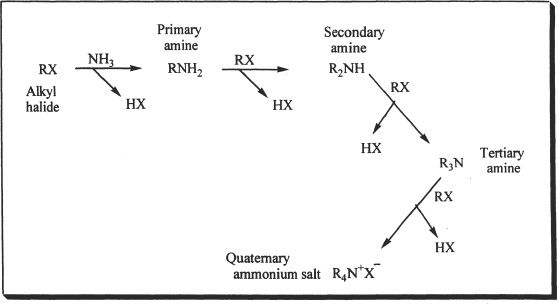
Figure 27-2
E. REACTIONS OF AMINES
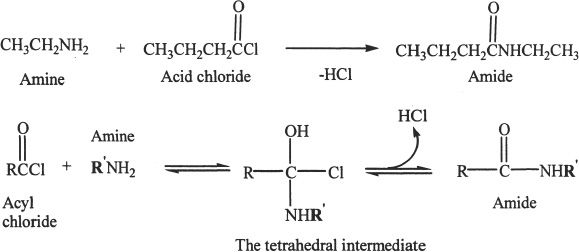
Formation of Amides
Amines can react with acid chlorides to form amides. A representative reaction (Sample reaction 27-1 is shown. The reaction proceeds by nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl group by the amine.
Sample reaction 27-1
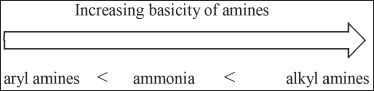
F. BASICITY OF AMINES
Amines are weakly basic compounds. Alkyl amines are more basic than ammonia, and aryl amines are less basic than ammonia.
CHAPTER 27 PRACTICE QUESTIONS
1. Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of boiling points?
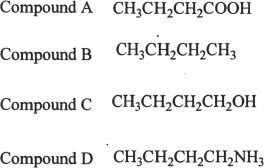
A. A<b<c<d< p=""></b<c<d<>
B. B<d<c<a< p=""></d<c<a<>
C. B<c<d<a< p=""></c<d<a<>
D. B<d<a<c< p=""></d<a<c<>
2. Which of the following compounds has the highest basicity?
A. ![]()
B. ![]()
C. 
D. ![]()
3. All the following are nitrogen-containing compounds, except:
A. aniline.
B. quaternary ammonium salt.
C. oxime.
D. ester.
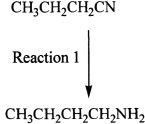
4. The conversion involved in Reaction 1 can be best characterized as:
A. oxidation.
B. dehydrogenation.
C. isomerization.
D. reduction.
Questions 5-10 are based on the following passage.
Passage 1
Amines range from simple structures to very complex structures. Some simple amines and their Kb values are given below.
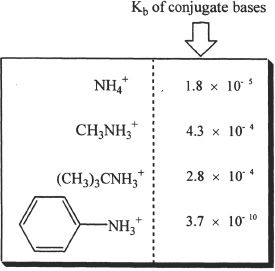
There are a wide variety of naturally occurring amines. Amines include caffeine, morphine, cocaine, quinine, and amphetamines, just to name a few. Amines are also biologically important. Some of the biologically important amines include thiamine, adrenaline, acetyl choline, and riboflavin.
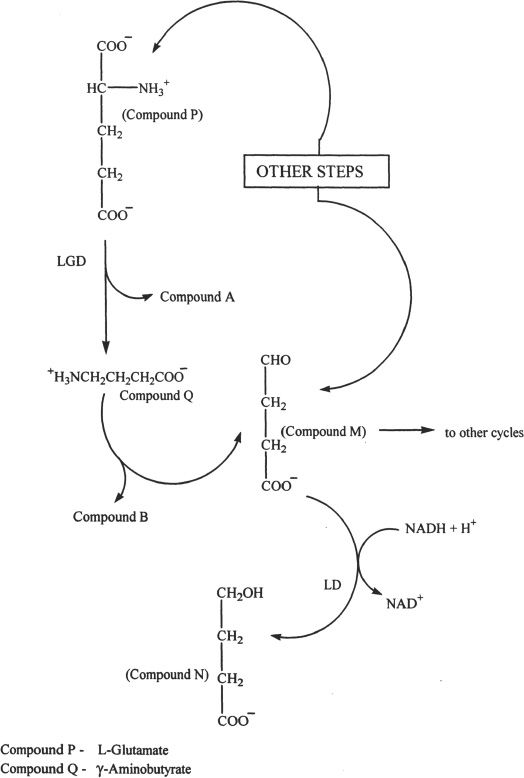
Gamma-aminobutyrate is an amine and a neurotransmitter. It has mainly an inhibitory function and is extensively found as a neurotransmitter in the Purkinje cells of the central nervous system.
5. Which of the following is the most acidic?
A. CH3NH2
B. CH3CH2NH2
C. (CH3)2NH
D. CH3OH
6. All the following can undergo hydrogen bonding themselves, except:
A. aniline.
B. triethylamine.
C. ammonia.
D. methylamine.
7. The conjugate acid of which of the following is the most acidic?
A. Methylamine.
B. Ammonia.
C. tert-Butylamine.
D. Aniline.
8. The conversion of glutamate to aminobutyrate is best described as:
A. a neutralization reaction.
B. a decarboxylation reaction.
C. a deamination reaction.
D. an amination reaction.
9. The conversion of Compound M to Compound N is done by the process of:
A. oxidation.
B. transamination.
C. inversion of configuration.
D. reduction.
10. γ-Aminobutyrate can be best described as a:
A. primary amine.
B. secondary amine.
C. tertiary amine.
D. peptide.