Organic Chemistry: Concepts and Applications - Headley Allan D. 2020
Free Radical Substitution Reactions Involving Alkanes
14.1 Introduction
Saturated hydrocarbons, also called alkanes, are fairly unreactive, but they do undergo some reaction types mentioned in Chapter 6. We have seen that most alkanes readily undergo oxidation under specific reaction conditions to liberate heat, along with water and carbon dioxide. In this chapter, we will examine another reaction type that alkanes undergo, and that is substitution reactions. Substitution reactions involving different types of alkanes with chlorine or bromine in the presence of energy in the form of heat or light to form much more reactive compounds, alkyl halides will be examined. Alkyl halides are used frequently for the synthesis of larger and other useful compounds, which will be covered in this chapter. We have already covered some of the reactions of alky halides, which include elimination reactions. Alkyl halides are alkanes in which one or more of the hydrogens of the alkanes has been substituted for one or more halogens. The usual representation of alkyl halides is R-X, where R represents the alkyl group, and X represents the halogen. Some alkyl halides are used as solvents in organic and industrial labs. Such halogenated solvents are immiscible with water and are denser than water (Figure 14.1).
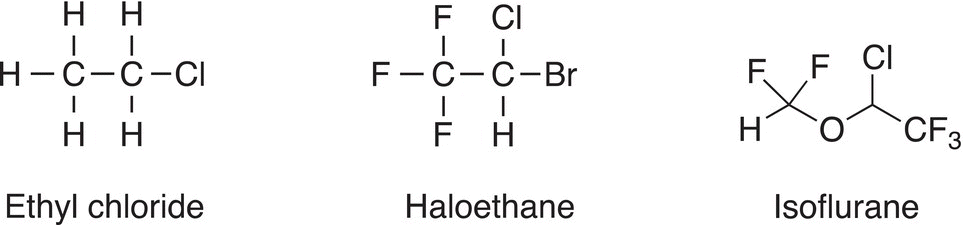
Chloroform was one of the first compounds discovered to induce general anesthesia. The use of this compound opened the possibility to perform surgery on patients who became unconscious when vapors of chloroform were inhaled. It was later discovered that chloroform is toxic and carcinogenic, so its use for this purpose was stopped. Several compounds, such as N2O and BrClCHCF3, have been used instead. Over the years, less toxic alkyl halides, such as ethyl chloride haloethane and isoflurane, were used.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are very volatile compounds, and they were used as the propellant for aerosols in deodorants, paints, hair spray, and other spray products. They are also called Freon and are used as refrigerants in air conditioners, refrigerators, and freezers. Since these CFCs are inert compounds, they were considered ideal volatile propellants until in the 1970s, it was discovered that they ultimately find their way to the stratosphere where they deplete the ozone (O3) layer. Even though CFCs are fairly inert, they deplete the ozone layer by reacting with ozone in the presence of ultraviolet radiation. The ozone layer helps to shield us from harmful ultraviolet radiation. The ozone hole, a term used to describe this depletion, is constantly getting larger over time. It is only recently that it was reported that the depletion of the ozone hole is not as severe as earlier years.
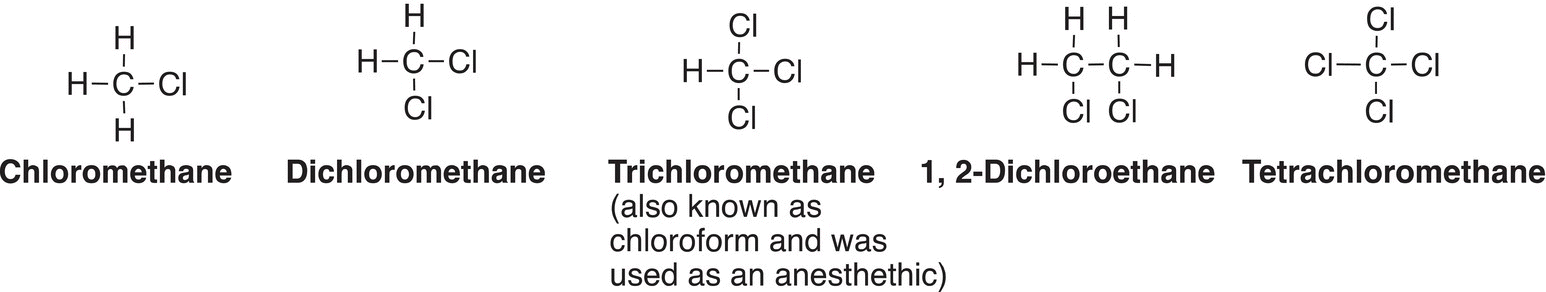
Figure 14.1 Common alkyl halides that are used as common organic solvents.

Alkyl chlorides have been used also as insecticides, three examples are shown below.
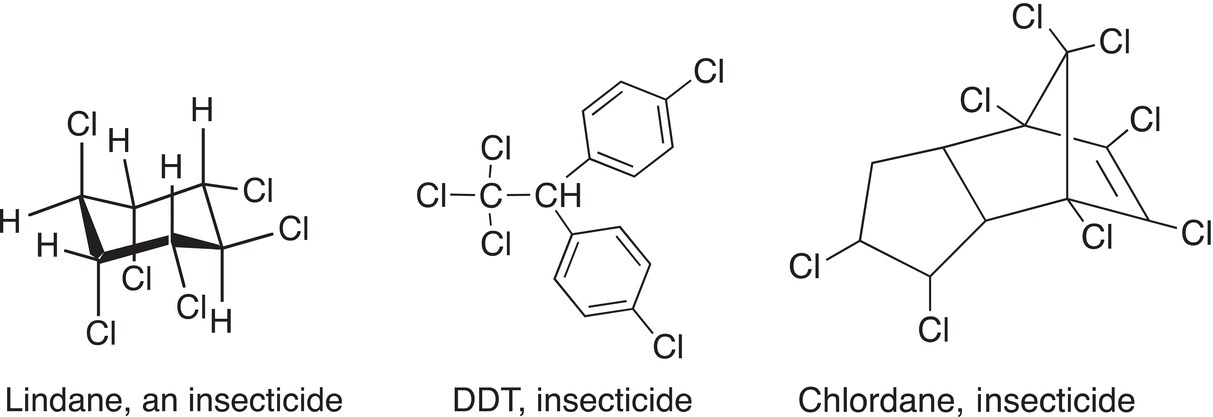
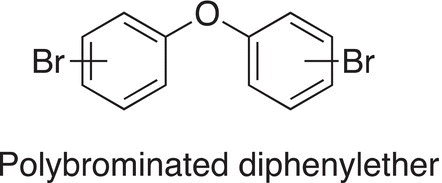
Lindane is an insecticide and is also used for the pharmaceutical treatment of scabies and lice. DDT was also used in World War II to control various diseases, including malaria, typhus, and bubonic plague. DDT was a very common pesticide, but its use was banned in the early 1970s due to negative environmental consequences associated with its use. Chlordane was used widely in the United States as a pesticide for a wide variety of agricultural products, but due to environmental concerns and health risks to humans, its use was banned in the early 1980s. Polybrominated diphenylethers are used as flame retardants; they have been used in the production of various other products, including plastics, foams, and textiles.
A very important use of alkyl halides, however, is that they are the starting materials for the synthesis of a lot of other useful organic compounds, including various polymers. In this chapter, we will learn how to synthesize alkyl halides from saturated hydrocarbons, and in other chapters, we will examine additional reactions that alkyl halides undergo.